Topic 7 - Magnetism and Electromagnetism
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Describe a magnet?
A magnet is an object that produces a magnetic field, attracting magnetic materials such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
Magnets have two poles, north and south, where the magnetic force is strongest. If two poles of a magnet are put near each other they will exert a force on eachother.
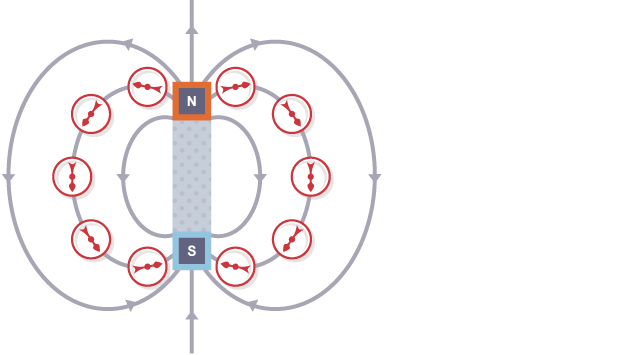
How can you create a Magnetic Field Diagram?
Place a magnet in the centre of a piece of paper
Draw 8 dots around the north pole of the magnet
Place a compass on your first point
Place a dot at the end of the compass where the arrow is pointing
Repeat this for the next few points until your line reaches the other pole
Connect the points together
Repeat the whole process for the next 7 points around the pole
What are the two types of magnets?
Permanent Magnets - They produce their own magnetic field
Induced Magnets - They become magnetized in the presence of an external magnetic field and lose their magnetism when removed from the field
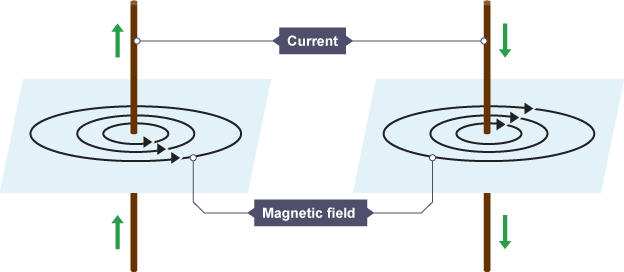
How does a wire create a magnetic field?
When an electric current flows through a wire, it generates a magnetic field around it. This field forms concentric circles around the wire, with the strength of the field depending on the current's intensity.
The direction of the magnetic field can be determined using the right-hand rule.
The right-hand rule states that if you point your thumb in the direction of the current, the curled fingers show the direction of the magnetic field.
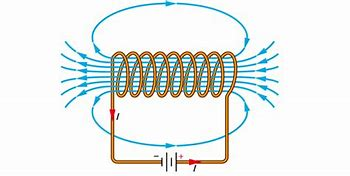
What is a Solenoid?
A solenoid is a coil of wire that generates a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it. This magnetic field is similar to that of a bar magnet and can be controlled by varying the current.
Inside the solenoid, the strength is very high as there are lots of field line pointing in the same direction due to the coils.
You can increase the field strength with an iron core, creating an electromagnet.
What can Electromagnets be used for?
Electromagnets can be used in various applications such as electric motors, generators, magnetic locks and loudspeakers.
What is the Motor effect?
When a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field experiences a force that causes it to move.
What is the formula for Force?
Force (N) = Magnetic Field Strength (T) × Current (A) × Length (m)
F=BIL
What is Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule?
A rule used to determine the direction of force experienced by a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
The thumb represents the direction of the motion, the index finger represents magnetic field direction, and the middle finger represents current direction.
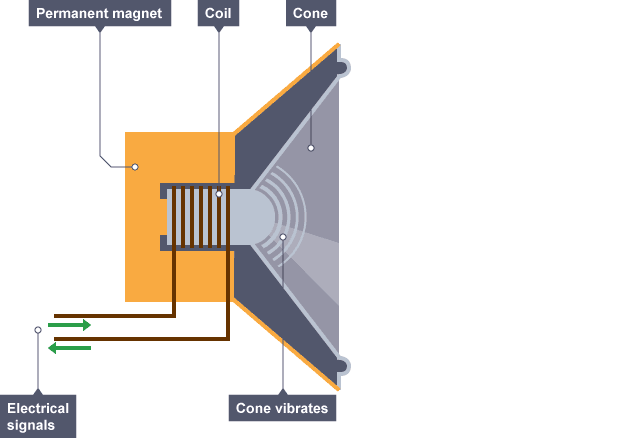
How do Loudspeakers work?
An alternating current is sent through a coil of wire creating a electromagnetic field
The field interacts with the permanent magnet, generating a force that pushes the cone outwards
When the current reverses, the force acts in the opposite direction
This causes the cone to vibrate and produce sound waves
By controlling the frequency of the ac you can alter the sound wave produced
What is the Generator Effect?
The induction of a potential difference in a wire which is moving relative to a magnetic field, or experiencing a change in magnetic field.
This effect occurs when a magnet is moved near a coil of wire or when the coil is moved within a magnetic field, resulting in the generation of electrical energy.
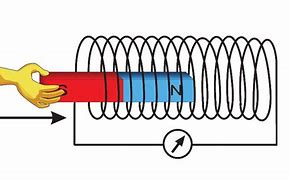
Why does the induced current oppose the change made?
The direction of induced current will be such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. This is a consequence of the conservation of energy.
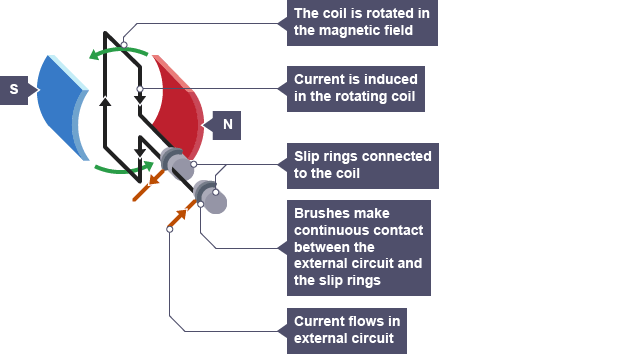
What are Alternators?
A device which generates an ac supply using the generator effect.
As the coil spins, a current is induced in the coil. This current changes direction every half turn.
Ac generators have slip rings and brushes so the contacts don’t swap every half turn.
This produces an alternating potential difference.
What are Dynamos?
A device which generates a dc supply using the generator effect.
They work in the same way as alternators except they have a split ring commutator instead of slip rings.
This swaps the connection every half turn to keep the current flowing in the same direction.
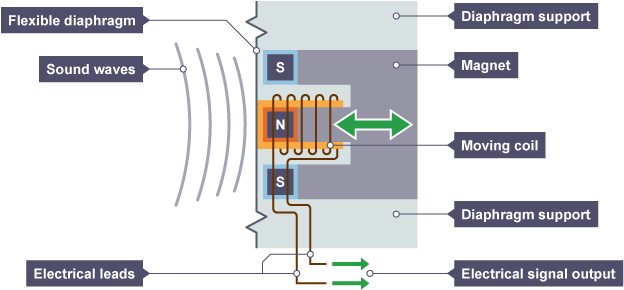
How do Microphones work?
Sound waves enter a flexible diaphragm that is attached to a coil of wire wrapped around a magnet
This causes the coil of wire to move in the magnetic field creating a current
The movement of the coil depends on the sound wave's pressure variations, converting sound into an electrical signal
What do Transformers do?
They change the size of the potential difference of an alternating current.
Transformers consist of two coils of wire, known as the primary and secondary coils, which are wound around a core.
When an alternating current passes through the primary coil, the iron core magnetises and demagnetises quickly. This changing magnetic field induces an alternating pd in the secondary coil.
If the second coil is part of a complete circuit, this causes a current to be induced.
The ration between the primary and secondary pds is the same as the number of coils.

What is the Transformer Equation
Input PD / Output PD = Primary coils / Secondary coils