5.4 Non-Mendelian Genetics, 5.5 Environmental Effects on Phenotype
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Non-Mendelian Genetics
varying degrees of dominance
many traits are produced through multiple genes acting together
some traits are determined by genes on the sex chromosomes
some genes are adjacent or close to one another on the same chromosome and will segregate as a unit
some traits are the result of non-nuclear inheritance (ex. chloroplasts and mitochondria)
Degrees of Dominance
alleles can show varying degrees of dominance
mendel worked with traits that showed complete dominance
-homozygous dominant and heterozygous individuals are phenotypically(appear) the same in complete dominance
includes incomplete dominance, codominance, and multiple alleles
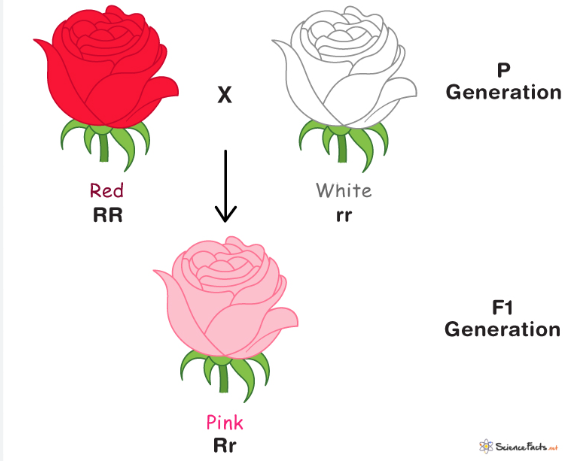
Incomplete dominance
neither allele is fully dominant
F1 generation has a phenotype that is a mix of those of the parent generation
ex. red flowers crossed with white flowers produce pink offspring
Codominance
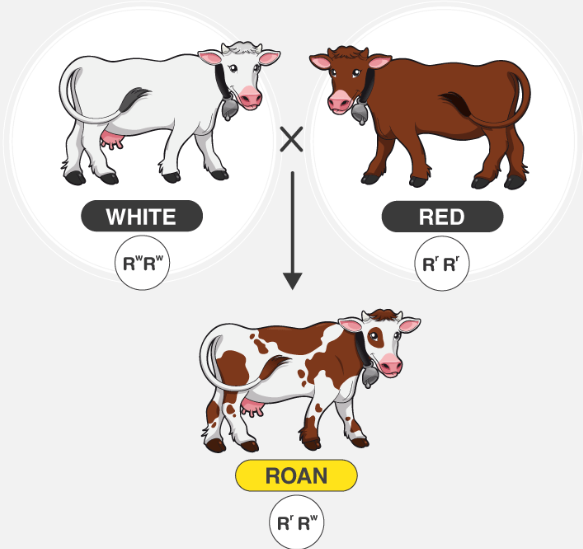
2 alleles that affect phenotype are both expressed
ex. human blood
-AB blood: A & B are both expressed
ex. cows can have red (RR) and white (WW) hair(RW)
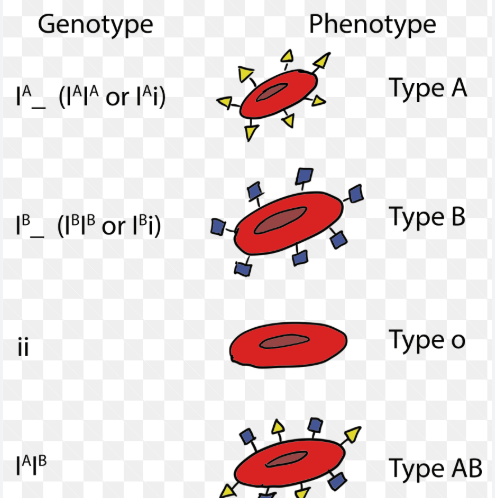
Multiple Alleles
genes that exist in forms with more than 2 alleles
ex. human blood groups
-alleles are I^A,I^B,i
Multiple Genes
in many cases, 2 or more genes are responsible in determining phenotypes
includes epistasis and polygenic inheritance
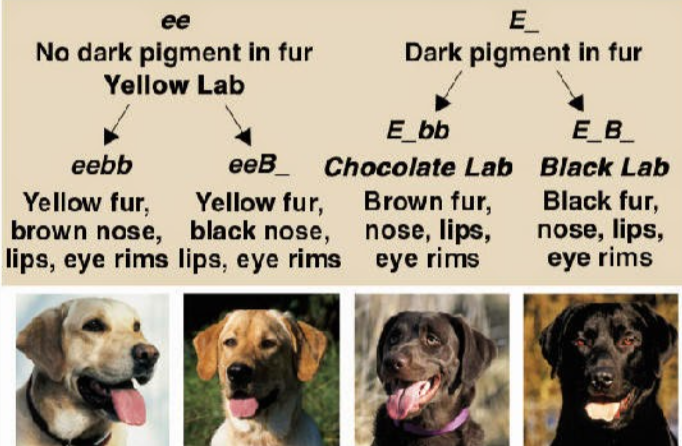
Epistasis
the phenotypic expression of a gene at one locus affects a gene at another locus
ex. coat color in labs and some mice
one gene codes for pigment and a second gene determines whether or not that pigment will be expressed in the hair
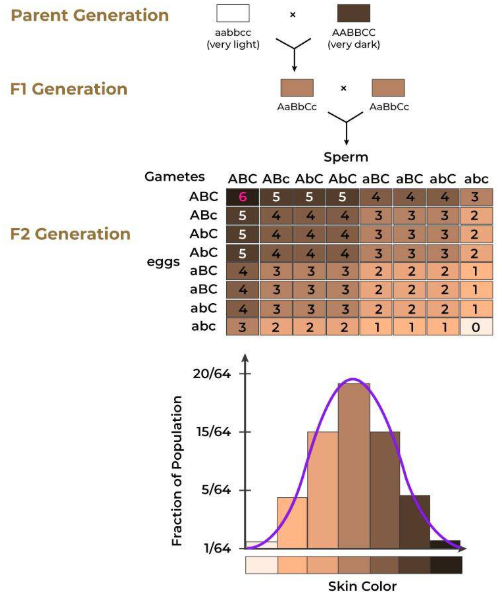
Polygenic inheritance
the effect of two or more genes acting on a single phenotype
ex. height, human skin color
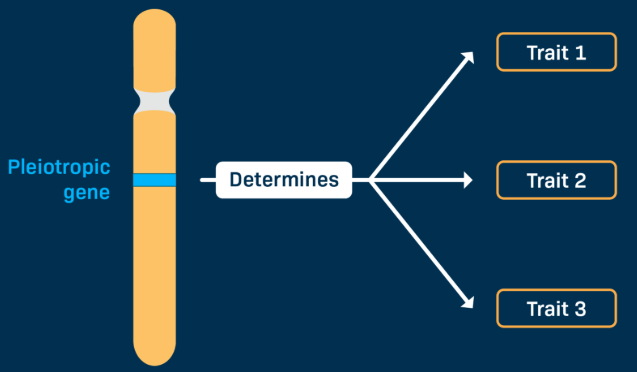
Pleiotropy
when a single gene controls multiple traits
typically in multiple body systems
since these traits are determined by the same gene, they will NOT segregate independently
ex. Marfan Syndrome
-an autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder caused by a mutation in the FBN1 gene(codes for proteins that make strong fibers that add strength to the body’s connective tissues)
Sex-linked Genes
Y-linked gene- genes specifically found on the Y chromosome
-very few Y-linked genes, so very few disorders
X-linked genes- genes found on the X chromosome
Inheritance of X-linked genes
fathers can pass X-linked alleles to all of their daughters, but none of their sons
mothers can pass X-linked alleles to both daughters and sons
if an X-linked trait is due to a recessive allele
-females will only express the trait if they are homozygous
-males only have 1 X chromosome, so they will express the trait if they inherit it from their mother(they are called hemizygous, since the term heterozygous does not apply)
due to this, males are much more likely to have an X-linked disorder
X-linked disorders
duchenne muscular dystrophy- progressive weakening of muscles
hemophilia- inability to properly clot blood
color blindness- inability to correctly see colors
X-inactivation
females inherit 2 X chromosomes
during development, most of the X chromosomes in each cell becomes inactive
-the inactive X in each cell of a female condenses into a Barr body(helps to regulate gene dosage/hormones in females)
Linked Genes
genes on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together
crossing over still occurs, but the genes do not assort independently
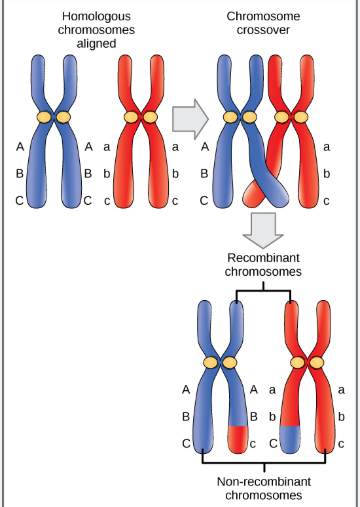
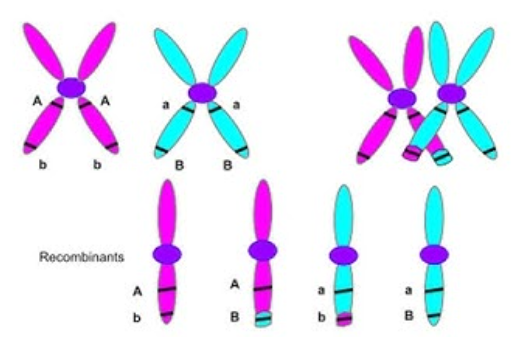
Genetic Recombination
production of offspring with a new combination of alleles from parents
parental types- offspring with the parental allele combination of alleles from parents
recombinants- offspring with new allele combinations from the parents
due to independent assortment, 50% recombination is the max: indicates that genes are unlinked, or on different chromosomes
Linked genes: crossing over
linked genes show parental types in offspring at higher than 50%
during crossing over homologous chromosomes exchange corresponding segments, but crossovers BETWEEN two genes that are close together are not common
the further apart two genes are on the same chromosome, the higher the probability that crossing over event will occur between them and the higher the combination frequency (50% being the max)
Mapping Distance
experiments performed by Sturtevant allowed scientists to map genes and their locations on chromosomes
linkage map- genetic map that is based on recombination frequencies
the distance between genes are map units
-1 map units is equivalent to 1% recombination frequency (this is an estimate of physical distance)
-express the relative distances along chromosomes
-50% recombination means that the genes are far apart on the same chromosome or on 2 different chromosomes
note: chromosomes may be longer than 50 map units, BUT 50% recombination is still the max we can measure (so to determine the distance between genes further than this we must look at the recombination frequencies of multiple genes to construct a linkage map)

Non-Nuclear DNA
some traits are located on DNA found in the mitochondria or chloroplasts
both chloroplasts and mitochondria are randomly assorted to gametes and daughter cells
in animals, mitochondria are transmitted by the egg, NOT the sperm, which means all mitochondrial DNA is maternally inherited
in plants, mitochondria and chloroplasts are transmitted in the ovule, NOT the pollen, which means both mitochondrial and chloroplast determined traits are maternally inherited
Environmental Effects on Phenotype
various environmental factors can influence gene expression and lead to phenotype plasticity
Phenotype plasticity
individuals with the same genotype exhibit different phenotypes in different environments
ex. temperature can change coat color in rabbits and Siamese cats, like fox white in snow brown in forest
soil pH can affect flower color
UV exposure can increase melanin production in the skin
