BIOL 1410 Digestive system
1/170
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LECTURE 15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
What is the Gastrointestinal (GI) tract?
Tube from mouth to anus
What are the accessory organs in the mouth?
Teeth, tongue, salivary glands
What are the (3) main accessory organs?
Pancreas, liver, gall bladder
What are the (4) digestive processes (beginning with ingestion)?
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, defecation
Define ingestion
Food into the oral cavity
Define digestion
Large molecules broken into smaller molecules
What are the two types of digestion?
Mechanical + chemical
Define absorption
End products of digestion enter blood or lymph
Define defecation
Elimination of undigested material
What are the 4 initial structures of the digestive system?
Oral cavity, salivary glands, dentition (teeth), oropharynx/laryngopharynx
What 3 things are included in the oral cavity?
Lips, cheeks, palate
Which palate is posterior to the other (hard/soft)?
Soft: posterior to hard
What type of muscle is the soft palate made of?
Skeletal muscle
What material is the hard palate made of?
2 maxillae + 2 palatine bones
What is the posterior projection of the soft palate called?
Uvula
When does the uvula rise to close what?
To close nasopharynx when swallowing
What bone is the tongue attached to?
Hyoid bone
What type of muscle is the tongue made of?
Skeletal muscle
What are papillae on the tongue?
Projections of mucosa (taste buds)?
What are the 3 pairs of salivary glands?
Parotid, submandibular, sublingual

Which pair of salivary glands are inferior + anterior to the ears?
Parotid gland(s)
What are mumps?
Inflammation of 1 or both parotids
Which pair of salivary glands is found in the floor of the mouth?
Submandibular gland(s)
What is the composition of saliva?
99.5% water, 0.5% solutes
What are the two types of dentition?
Child/primary dentition, adult/secondary dentition
How many premolars do children vs. adults have (in each quadrant)?
Child (0), adult (2)
How many molars do children vs. adults have (in each quadrant)?
Child (2), adult (3)
How many total teeth do children vs. adults have?
Child (20), adult (32)
What are the 5 components of tooth structure?
Crown, root, neck, periodontal ligaments, root canal (→ pulp cavity)
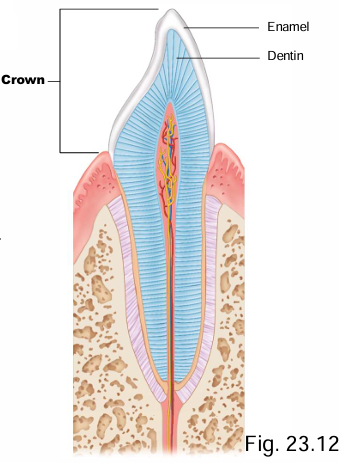
What 2 tissues are found at the crown of the tooth above the gum?
Dentin + enamel
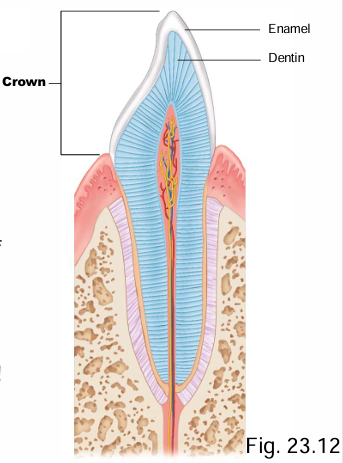
Which tissue covers the majority of the tooth?
Dentin
Which tissue is the overlay of the crown of the tooth?
Enamel
What are the (3) important key features of enamel?
Acellular, highly calcified, hard
What tissues overlay the root of the tooth?
Dentin + cementum
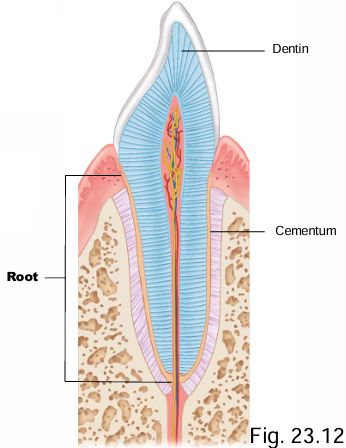
Dentin, enamel and cementum are similar to bone, but have what difference?
Avascular (while bone is highly vascular)
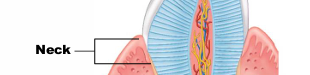
What 2 tissues (specific to dentition) is the neck of the tooth composed of + where is the neck of the tooth located?
Composed of enamel + cementum, boundary at the gums between the crown and root
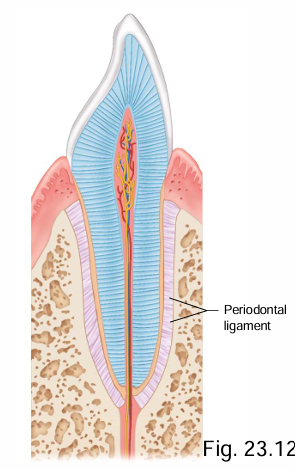
What do the periodontal ligaments do?
Attach root to bones
What is contained in the root canal (extending into the pulp cavity)
CT, blood/lymph vessels, nerves
What 2 tissue types is the oropharynx and laryngopharynx made of?
Muscularis externa (skeletal muscle) + stratified squamous epithelium
What are the 4 basic layers of the GI Tract (inner → outer)?
Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
What are the 3 sublayers of the mucosa (inner → outer)?
Epithelium, lamina propria (areolar CT), muscularis mucosa
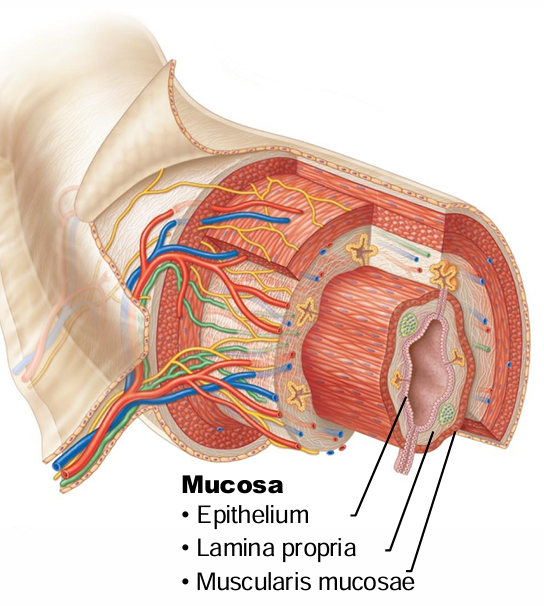
What type of glandular cells are concentrated in the epithelial layer of the mucosa?
Goblet cells
What two subtypes of epithelial tissue are found in the GI Tract?
Stratified squamous + simple columnar
The GI Tract is very long, and the epithelial tissue differs depending on the location you are observing. In what 2 places is the stratified squamous epithelium?
Esophagus + anal canal
The GI Tract is very long, and the epithelial tissue differs depending on the location you are observing. In what ~4 places is the simple columnar epithelium?
stomach, small/large intestines, rectum
Reminder: What is lamina propria?
Loose areolar CT
What is contained in the lamina propria layer of the mucosa?
Blood, lymph vessels, lymph nodules/tissues (immune)
What does the muscularis mucosa (smooth muscle layer of mucosa of the GI Tract) allow for?
Movement of mucosa
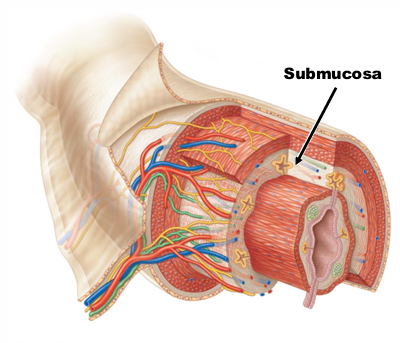
What major/subtype tissue is the submucosa layer of the GI Tract composed of?
Loose areolar CT

What is contained in the submucosa layer of the GI Tract?
Blood, lymphatic vessels, network of nerve cells
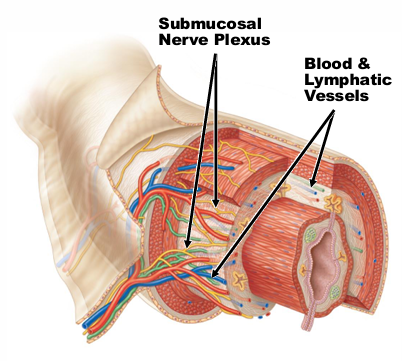
Muscularis externa of the GI tract is _ layers of smooth muscle, separated by what?
“2,” Separated by 2nd network of nerve cells (2nd after previously mentioned submucosa)
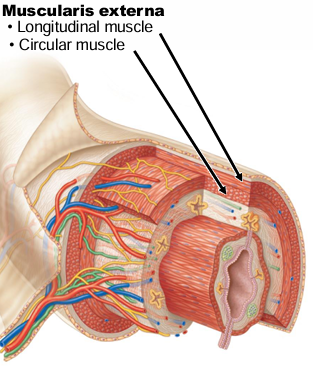
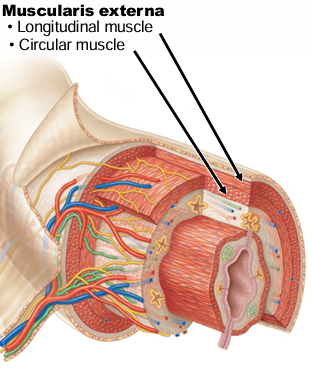
The inner circular layer of muscularis externa constricts the lumen by __________
“contraction”
The outer longitudinal layer of the muscularis externa contracts, which shortens ___ ______
“gut length”
Overall, the contraction of the muscularis externa causes what?
Motility (mixing + movement)
The outer layer (farthest from lumen) of the GI Tract is serosa/adventitia. What is a key defining feature of its membrane?
It has a double-walled membrane
The cavity of the GI Tract where substances pass through is called?
Lumen
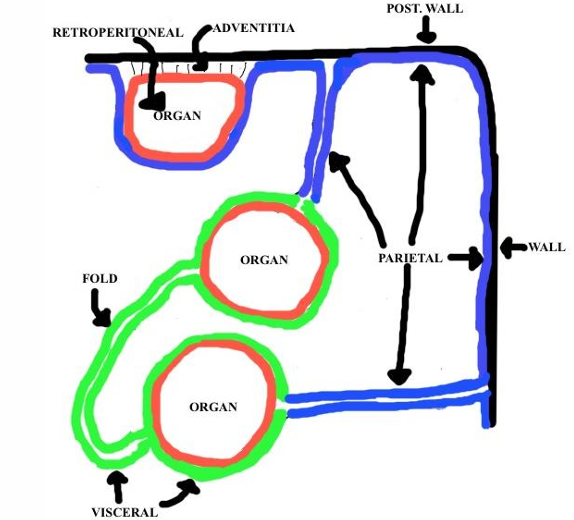
What is the peritoneum?
The serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity + most of the abdominal organs
What are the 2 layers of the peritoneum?
Parietal and visceral
Which peritoneum layer is against the organ wall, and which is against the abdominal cavity wall?
Visceral (organ wall), parietal (abdominal cavity wall)
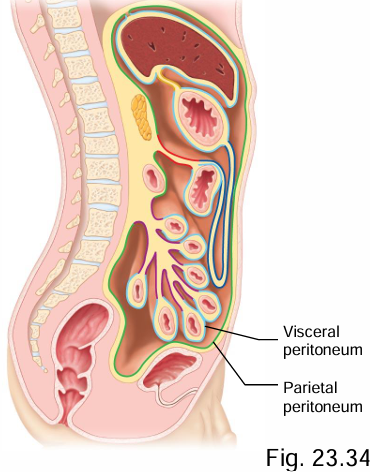
What is the peritoneal cavity of the peritoneum?
Space between peritoneum layers (visceral/parietal)
What fluid is contained within the peritoneal cavity?
Serous fluid
What are the 2 specializations (folds of serosa) of the peritoneum?
Omenta, mesentery
The omenta is folds of serosa between what structures?
Organs
The omenta is a sheet of 2 fused layers of _______ peritoneum
“visceral”
What does the omenta contain?
Blood/lymph vessels + nerves
The omenta is subdivided into what 2 sections?
The greater and lesser omentum
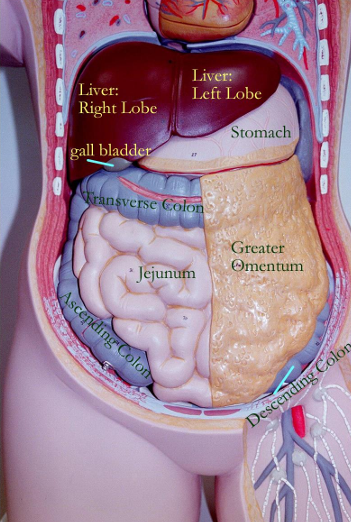
Which omentum (greater/lesser) is the “fatty apron”?
Greater omentum
What structures does the greater omentum connect?
Stomach → transverse colon
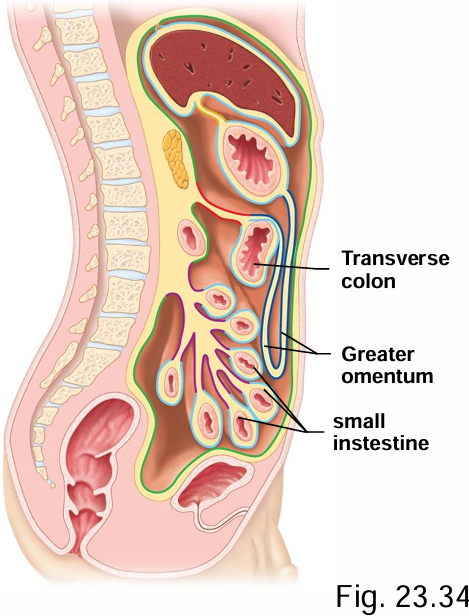
The greater omentum forms a large fold that hands down over what 2 structures?
Transverse colon + small intestine
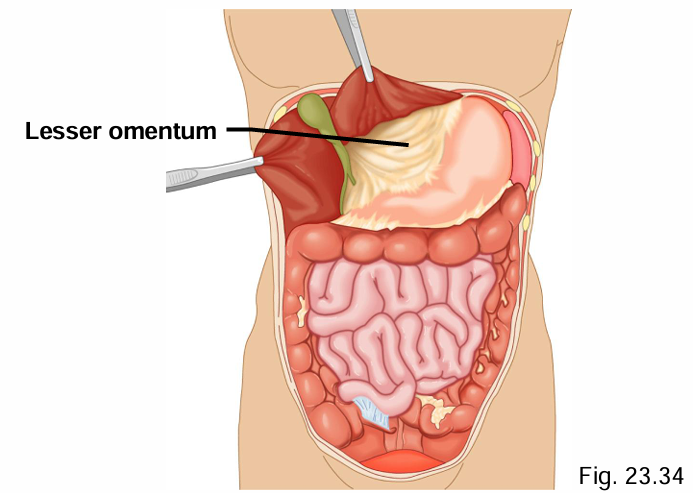
What structures does the lesser omentum connect?
Liver → stomach
The mesentery is folds of serosa between what specific structures?
Posterior abdominal cavity wall + small/large intestines

The mesentery is a sheet of 2 fused layers of _______ peritoneum
“parietal”
The mesentery is an entry/exit point for what structures?
Blood vessels, nerves, lymphatic vessels (that specifically supply digestive organs)
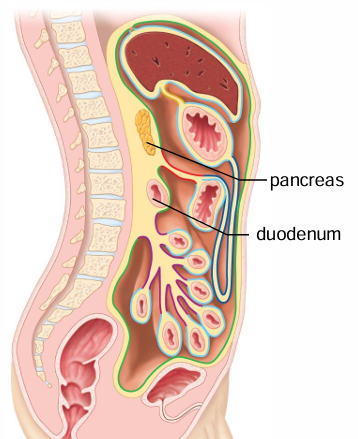
Where are the retroperitoneal organs located?
Posterior to the parietal peritoneum
The peritoneum only lines the _______ side of retroperitoneal organs
“anterior”
What is an example or two of a retroperitoneal organ?
E.g. pancreas, duodenum
What is the posterior side of a retroperitoneal organ lined by?
CT (adventitia)
Which is posterior to the other; esophagus or trachea?
Esophagus is posterior to trachea
The esophagus passes through the diaphragm to the _________ cavity
“abdominal”
What are the 2 components of the histology of the esophagus (superior → inferior)?
Muscularis externa, adventitia/serosa
The muscularis externa of the esophagus is divided into 3 sections based on the type of muscle it contains. From the upper 1/3 to the lower 1/3, list the muscle type(s) of these layers.
Upper 1/3 (skeletal), middle 1/3 (skeletal/smooth), lower 1/3 (smooth)
Of the adventitia/serosa layer of the esophagus, which is the outer layer?
Adventitia
Of the adventitia/serosa layer of the esophagus, one is within the thoracic cavity and one is within the abdominal cavity. Which is which?
Adventitia (thoracic), serosa (abdominal)
The stomach stores, partially digests, and regulates the emptying of what substance?
Chyme (food + gastric juice)
Chyme moves from the stomach to what structure?
The small intestine
What are the 4 regions of the stomach?
Cardiac region (cardia), fundus, body, pyloric region (pylorus)
Which stomach region is attached to the inferior esophagus?
Cardiac region (cardia)

Which stomach region is superior to the esophageal entrance?
Fundus
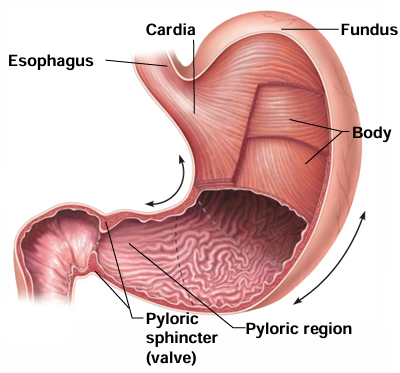
Which stomach region is the middle portion?
Body
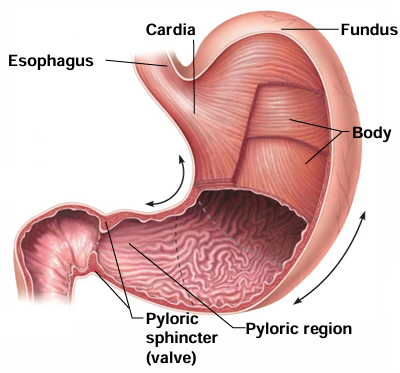
Which stomach region is the inferior portion?
Pyloric region (pylorus)
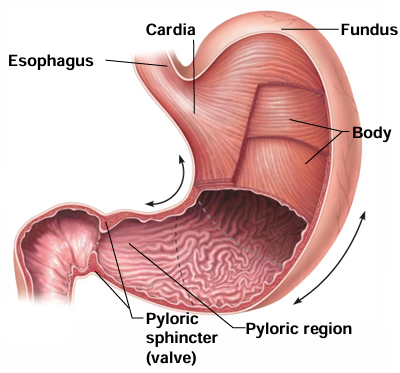
What does the pyloric sphincter (within the pyloric region) regulate?
Regulates release of stomach contents into small intestine
What are the 3 components of the histology of the stomach?
Mucosal surface, rugae, muscularis externa
The mucosal surface of the stomach is exclusively formed by what cells?
Mucous cells
What does the mucosal surface have millions of?
Gastric pits
What are gastric pits?
Invaginations (surface folding inward to form a pocket) of epithelium
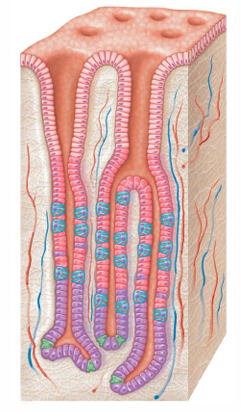
What are gastric pits of the stomach connected to?
Underlying gastric glands
What are gastric glands (exocrine or endocrine/secretion)?
Exocrine glands, secrete gastric juice into gastric pits (then enters stomach lumen)
What 4 types of cells are contained in gastric glands?
Goblet cells, chief cells, parietal cells, G (enteroendocrine) cells
Chief cells secrete enzymes for digestion of specifically what 2 macromolecules?
Protein + fat
What do parietal cells secrete to lower stomach pH?
Secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl)