Global Systems and Governance
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Globalisation definition
the process of becoming more globally interconnected + interdependent on a variety of scales. Its the movement of people, ideas, knowledge goods money ect across national borders, leading to a "borderless world"
Types of globalistaion:
economic, political, cultural, social

Economic globalisation:
= The intensification and stretching of economic interrelations around the world
- TNCs use outsourcing and offshoring to lower costs
- Industries moving to developing countries to lower costs
- Trading blocs create economic integration
- sources of income from international companies

political globalisation
= the intensification and expansion of political interrelations around the world
- Governments form trade connections through trade deals and trading blocs
- Deregulations allow markets to grow
- Western democracies have influence on political ideologies worldwide e.g UN

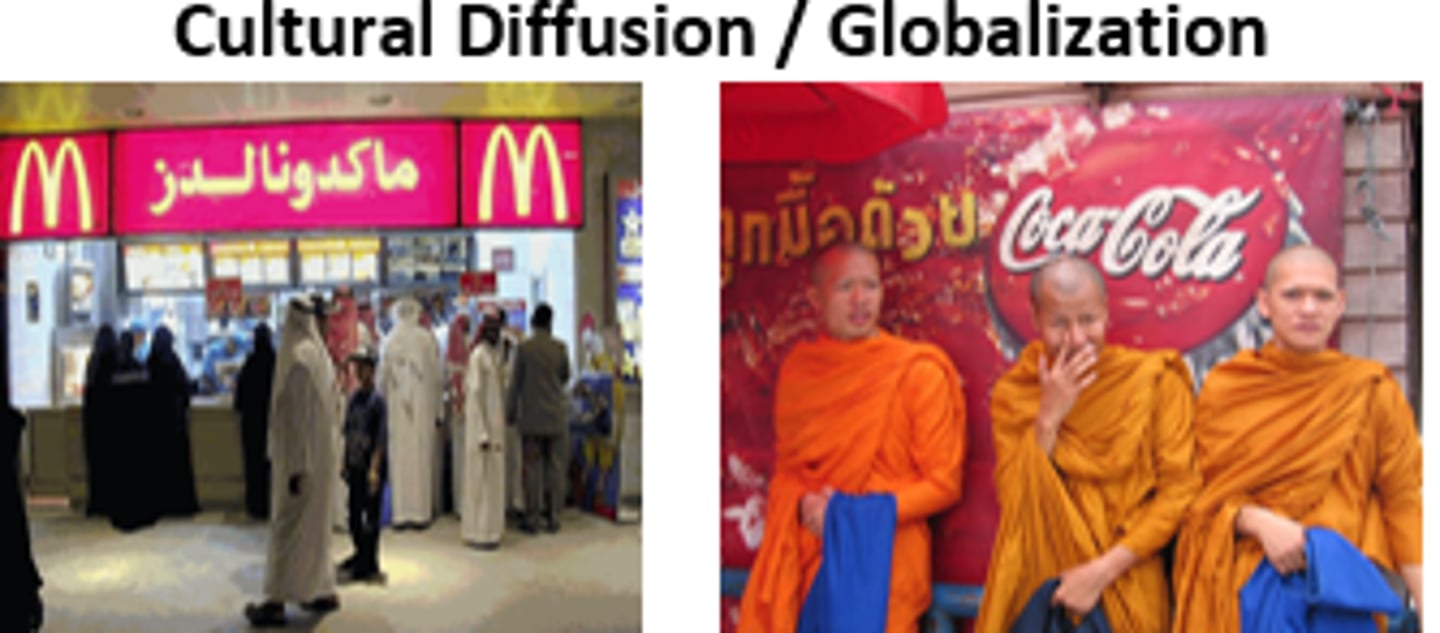
Cultural Globalization
= The intensification and expansion of cultural flows across the globe
-The interconnected nature of culture through meetings and the influence of cultures on one another
- media sources allow people to understand other cultures
- travelling internationally lets people experience cultures
-westernisation is the domination of western cultural traits in non-western areas e.g starbuck

Social Globalisation
- International immigration is causing multicultural societies
- Social networks have allowed for instant communication between people across the globe
- NGOs and Charities involved in global improvements of education and health (world health organisation)
Environmental globalization
the world's ecosystems are connected and all countries must protect the environment together.- pollutants from one country can affect the climate of another
Dimensions of Globalisation:
The dimensions of globalization are the flows in globalization:
- Capital Flows
- Labour Flows
- Product Flows
- Service Flows
- Information Flows
- Global Marketing
Flow definition
when countries share things with one another. the movement of people, ideas, goods, or services from one place to another
Flows of capital
The movement of money for the purpose of investment, trade or business production.
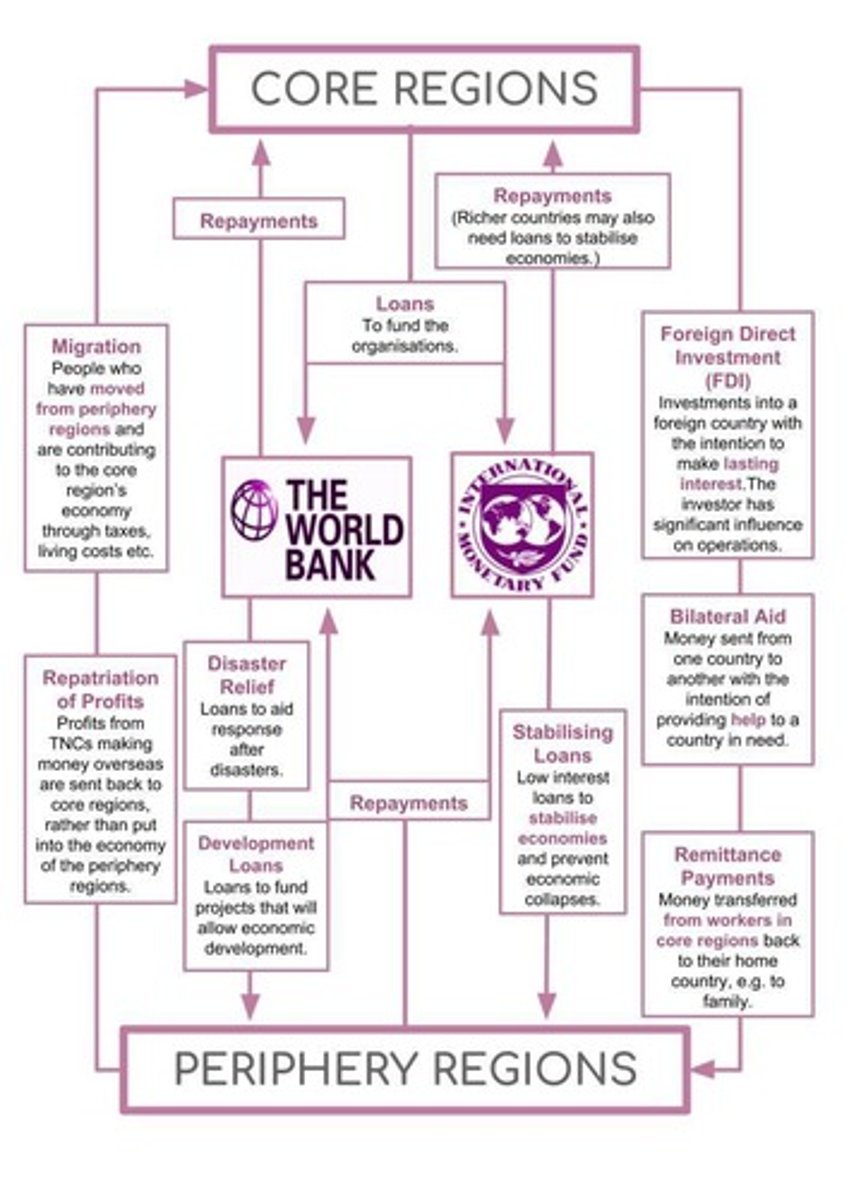
Where do the major flows of capitol occur between?
Core regions- wealthier developed countries
Periphery regions- less wealthy developing countries
The international monetary Fundy- international corporation that aims to "secure financial security + facilitate international trade"
The world Bank: a group of global institutions that give out loans for development or relief e.g disaster relief
- Money flows electronically between heds which invest into leds to take advanatge of lower labour costs
Flows of labour
Movement of migrants mainly seeking better employment opportunities. E.g. movement from developing countries in South Asia, Africa and Latin America to the richer areas of North America and Europe. 3-4% of the world's population are international immigrants .
- High skilled workers are ususally highly trained and want to move to high income countries as wages are higher for the same job than in lower income countries.
- Unskilled workers are those unqualified and do not posess expert knowledge in their employment. They too move to high income countries in the hope of getting higher paid jobs. This can lead to overpopulation however and exploitation, end up working in the informal economy
Flows of products
The international movement of products which is facilitated by the reduction in costs of trade..
- Products used to be mainly produced in HICS
- now internationally traded due to transport links + TECHNOLOGICAL advatmencts
-production has relocated internationally especially in low income countries.
Flows of services
- This flow concerns economic activities that are traded without the involvement / production of material goods. E.g financial or insurance services. (tertiary sector)
- These can be divided into High level services and Low level services.
- services flow as they can be produced in a diff country to where they are received e.g call centers
High level services - Flows of Services
- This is the term for services for business such as advertising, investment and finance. They are of higher skill level
Low level services - Flows of Services
services that require less training
Flows of information
any type of info can move from one place to another via the internet and phone calls ect.. Example of how it flows= fast broadband, social media, real time data, data bases, researching employment oppurtunities
Global Marketing
A marketing strategy that consciously addresses customers, markets, and competition throughout the world and globalization has allowed this.
Global marketing strategies:
awarness of the brand: creating a trademark
keeping the same strategy:
Patterns of production
the distribution of places where goods and services are made with each product having its own centres of production and areas where production does not happen eg most clothing is now made in SE Asia, electronic goods are mostly made in Korea/China/Japan and in HICS dveleopeed makets dominate
patterns of consumption
the distribution of places where goods and services are mostly bought or areas where they are not purchased eg most high value electronic goods are bought in Europe and USA whilst fewer are bought in sub-Saharan Africa (HICS AND LICS)
Factors affecting Globalisation
-Financial= systems technologies and systems
-Transport= technologies systems and relationships
- Security= technologies and systems
-Communication= technologies
-Management and Information systems
- Trade agreements
Financial systems: (factor of globalisation)
Financial system= the relationship between those who borrow money and those who invest money, and the institutions that hold, give out and take in money e.g a bank

How do banks work?
- the bank pays the person interest for the amount of money deposited
- the bank gives people wanting loans your money that was put in the bank
- the bank charges people who take out loans more interest, so they end up getting a profit
Financial technologies (globalization factor)
- has made info and money easily accessible for people across the world.
-global communication technology improve decisions about investment and e.g stock market trends.
- ability to transfer money thanks to the internet has revolutionized global finance e.g cryptocurrency

transport (globalization factor)
Transporting Goods:
-innovation in transport has made it easier to transport goods faster and in larger quantities. e.g high speed rail + faster and bigger planes and boats (cargo aircraft)
-Containerisation= freight (products transported in bulk) can be transported internationally, is also a lot cheaper
Transporting People:
- increases flow in labour, e.g through high speed rail
- air travel through faster and chepaer flights.

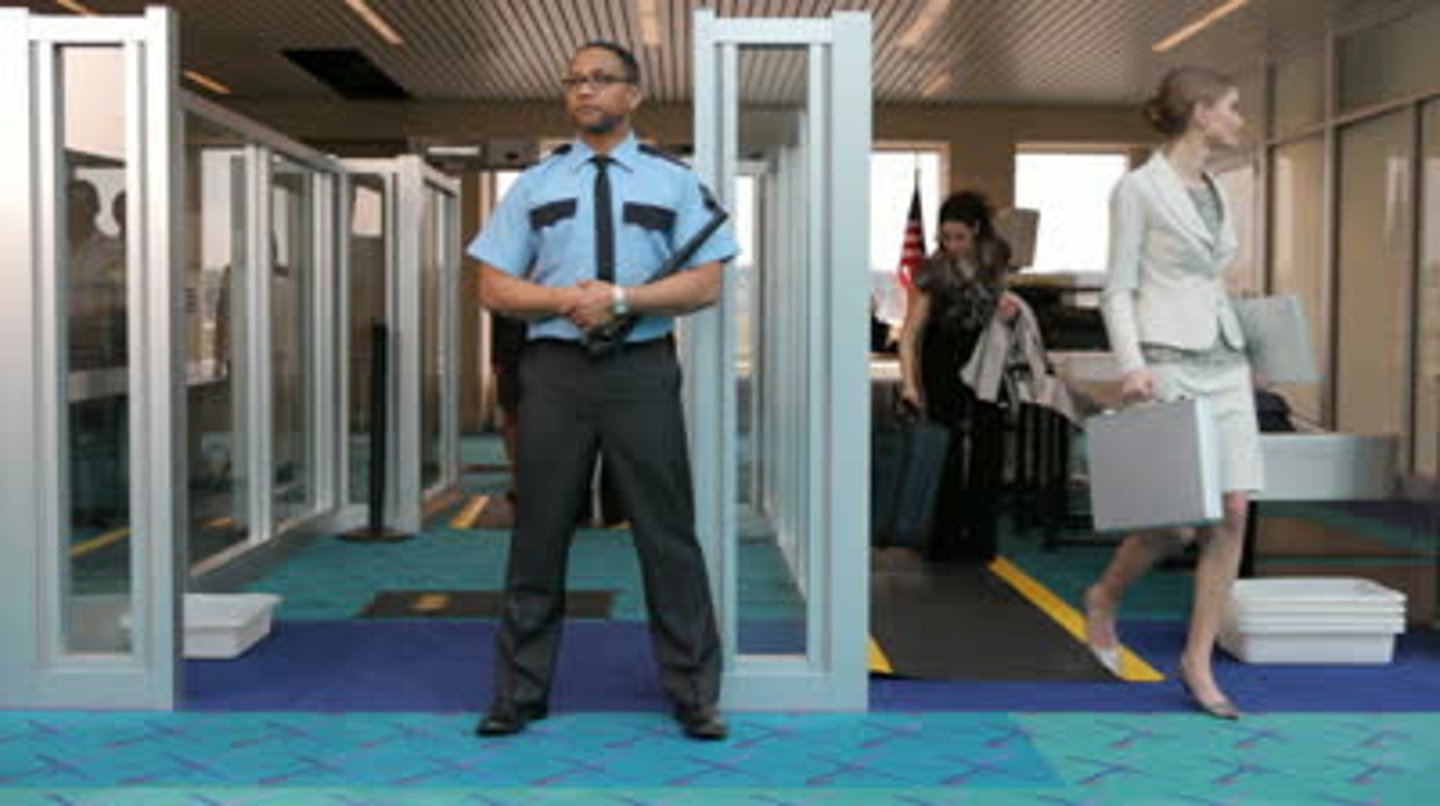
security (globalization factor)
due to globalization, countries face threats from other countries- as such security systems have been developed using technology
-strict regulations have been put in place
-international customs control the flow of people and goods through x ray technology.
-cybersecurity is a global concern, as such technologies are being developed to counter these attacks.

communication (globalization factor)
communication technologies: allowed flows of information, services and capital. e.g
-satellites have enabled internet
-services can be accessed through the internet
-enhanced flows of labout

Management (globalization factors)
Management plays a crucial role in accelerating globalization by optimizing the flow of labor, products, services, information, and capital. Companies enhance efficiency through economies of scale, reducing production costs by bulk purchasing, mass production, and large-scale shipping. Global supply chains allow different stages of production to be spread across multiple countries, cutting costs and improving specialization. Outsourcing enables firms to delegate essential tasks, such as customer service or advertising, to third parties, often in lower-income countries, reducing labor costs. Similarly, offshoring relocates business operations abroad to take advantage of cheaper labor, lower taxes, and resource availability. These management strategies drive globalization by making businesses more cost-effective and interconnected.

Trade Agreements (globalization factors)
Trade agreements have significantly accelerated globalization by reducing the costs and complexities of international trade. Countries impose trade restrictions such as tariffs, quotas, and outright bans, making imports and exports expensive. To facilitate trade, nations enter trade agreements, where restrictions are lowered or removed in exchange for mutual benefits. These agreements, overseen by the World Trade Organization (WTO), promote fair trade and economic integration. An example is NAFTA, which reduced tariffs between the USA, Canada, and Mexico, though its effectiveness has been debated. By making trade easier and more cost-effective, trade agreements deepen global economic interconnection.

what is interdependence?
is the theory that nations depend on each other economically + politically + socially + environmentally

what are the diff forms of interdependence?
- economic
-political
-social
-environmental
what is economic interdependence?
-countries rely on each other to buy/sell the the goods that they need and produce
-dependence on flows of labour to provide work force
what is political interdependence?
Countries need to work together to tackle global
issues
Political unrest
Conflict
what is social interdependence?
1. diaspora =When people leave their home country and live spread out in other countries, but still keep connections to their culture and homeland
2.Media= films and tv is increasingly consumed all around the world not just from one country
what is environmental interdependence?
Every country in the world is dependent on the rest of the world to look after the environment + deal w global threats:
-e.g climate change + loss of biodiversity

How does unequal flows + interdependence relate?
-Unequal flows of people+money+ideas+technology can cause problems for countries that depend on others.
-Some countries give more than they receive, which can lead to unfairness.
-While unequal flows can bring economic and social benefits, they can also create inequality, injustice, and even conflict.
what are the 5 unequal flows?
(powerful minds influence the planet)
p= people
m=money
i=ideas
t= technology
p= power
Describe why there is an unequal flow of people globally:
- migration occurs from low income--> high income countries due to promise of better oppurtunities, so flow of people= unequal globally.

What are the benefits for the country an unequal flow of people are flowing into:
-Migrants become intertwined in work forces and often do unwanted + lowest paid jobs (e.g cleaner) in these high income countries.
- states that are home to large diaspora populations often have strong ties to teh diasporas country of origin --> creating a sense of community.
what are the problems for the country that the unequal flows are flowing into?
-Host countries become dependent on the migrant workers, which causes issues if there is a change in circumstance.
-unequal flows can cause overpopulation. Many countries experiencing large flows of people believe they suffer due to pressure on services such as health care and migrants "taking" jobs.

what are the benefits of the country unequal flows are flowing away from?
-workers send remittances back to their home country, helping their economy grow.
-those fleeing from conflict or poor quality of life may have a better life in countries they move to.
what are the problems for the country unequal flows are flowing away from?
-country that migrants originate from become dependent on remittances so a change in circumstance may damage the economy.
-large amounts of leaving causes unemployemnt, economic deteriation and brain drain, as areas become underpopulated. Skilled workers leave to work in high incoem countries, meaning unskilled people are left to run the economy.
-as many migrants are desperate for work that nationals, theyre vulnerabel to exploiatation such as poor wages/ conditions
describe why there is an unequal flow of money globally?
- majority of flows are into lower income countries through fdi, ais, remittnaces
- money into high income countries are majorly profit sent back to home countries through tncs
what are the benefits of unequal flow of money?
1. the country receiving the fdi can improve quality of life + create a multiplier affect.
2. ais + remittances also help improve quality of life, e.g rebuilding after a disaster.
3. schemes such as help for home schemes, which help rebuild stronger homes.
4. those sending money can take advantage of lower labour costs , maximising their profits.
what are the problems of unequal flows of money?
1. workers used to low incomes depend on higher wages given e.g tncs meaning they subject themselves to harsh conditions and low wages.
2. foreigh aid can reduce incentive for the governemnt of that country to help its own country as it overly relie son foreighn aid.
3. Tncs can force govenrments to relax their regualtions and enviornemntal laws in the promise of investing
4. Tncs take most of the profit, the host country doenst recieve a lot of it.
describe why there is an unequal flow of ideas globally?
High-Income Countries (HICs) often influence global trade and governance ideas.
This is because they have more money and power than Low-Income Countries (LICs).
These ideas (like deregulation and free trade) are spread to LICs and NEEs (Newly Emerging Economies).
what are the benefits of unequal flows of ideas by HICS?
-Deregulation can lower prices and improve services through competition.
-Free trade boosts global markets and reduces chances of conflict.
-FDI growth supports business expansion.
-HICs can share successful strategies with LICs to promote growth and reduce inequality.
what are the problems of unequal flows of ideas led by HICS?
LICs may struggle to keep up with fast deregulation.
Big companies may profit more than LIC economies through privatisation.
LICs may feel pressured to adopt HIC policies, even if they don’t fit their needs.
Deregulation can lead to weaker social & environmental protection.
National identity may feel threatened by global interdependence and multiculturalism.
describe the unequal flows of technology globally?
Technology flows between HICs and LICs/NEEs, but not equally.
HICs invest manufacturing tech in LICs to make a profit.
LICs often manufacture consumer tech that is exported to HICs.
LICs rarely invest in HICs due to lower benefits and higher costs.
what are the benefits of unequal flows of technology?
LIC economies grow through tech investment (factories, jobs).
Trade links improve between HICs and LICs.
HICs benefit from cheaper exports and advanced tech innovations.
Consumers get better quality products from global production.
Companies can increase profits via cheaper overseas production.
what are the problems of unequal flows of technology?
LICs can’t afford tech to improve their own development.
Widening tech gap keeps LICs behind HICs.
Workers in LICs are underpaid and face poor conditions.
HIC workers lose jobs as companies move manufacturing abroad.
Profit is unequal—TNCs earn most, workers gain little.
describe unequal flows of power relations?
-->HDE countries have more control over global systems bringing benefits: greater wealth, better access to technology and increased economic and political power
-->LDE countries have limited power and struggle to respond to global challenges such as climate change and
organisations that enhance this:
The International Monetary Fund (imf) and World Bank are examples of global financial institutions which reinforce unequal power relations
How do IMF and world bank enhance unequal power relations.
-- decisions are heavily done by the USA
-- they promote neoliberalism (the idea that the economy works best when businesses are free from government control)
--loans tend to have conditions attached to it reducing the sovereignty (a countries ability to make its own decisions due to it having to follow lenders rules) of borrowing countries.
What is a case study to show the influence of the internet to control global information?
China's "great firewall"--> blocks acess to certain foreighn websites.
what is a case study to show a single product economy?
= Nigeria and OIl
-80% of nigerias income comes from oil and gas
- it has many natural resources and should have benefited from globalisation due to trade.
key takeaways:
Nigeria's oil wealth has fuelled economic growth, but unequal flows of profits and resources have left the country dependent on foreign companies.
Globalisation & OPEC membership have boosted trade but worsened inequalities and reliance on imports.
The Dutch disease effect has weakened Nigeria's manufacturing sector, making it less competitive internationally
what are the consequences of nigeria being a single economy of oil?
Unequal Flow of Profits:
Foreign TNCs dominate Nigeria’s oil industry, extracting resources while sending profits abroad, leaving little wealth for local communities.
Rural-Urban Migration:
Loss of traditional jobs has driven people to cities like Lagos & Abuja, causing overcrowding & rural poverty.
Foreign Exploitation:
Oil reserves were developed by major global companies since Nigeria lacked technology & skills.
These companies have been criticised for environmental damage & exploitation of local workers.
Dutch Disease & Deindustrialisation:
High oil revenue overvalues Nigeria’s currency, making imports cheaper and domestic goods uncompetitive.
Manufacturing declines, forcing more people into the low-paid oil sector, worsening inequality.
what is international trade:
The exchange of goods and services and money between countries
describe the global patterns of international trade?
-Global trade and investment patterns are shifting, with emerging (EME) and less developed economies (LDE) playing a bigger role.
-China is now the top exporter and second-largest importer, after the USA. While high-developed economies (HDEs) still lead in FDI outflows, investment from EMEs and LDEs is rising, especially via China's Belt and Road Initiative. EMEs now receive over 50% of global FDI, with China as the third-largest recipient.
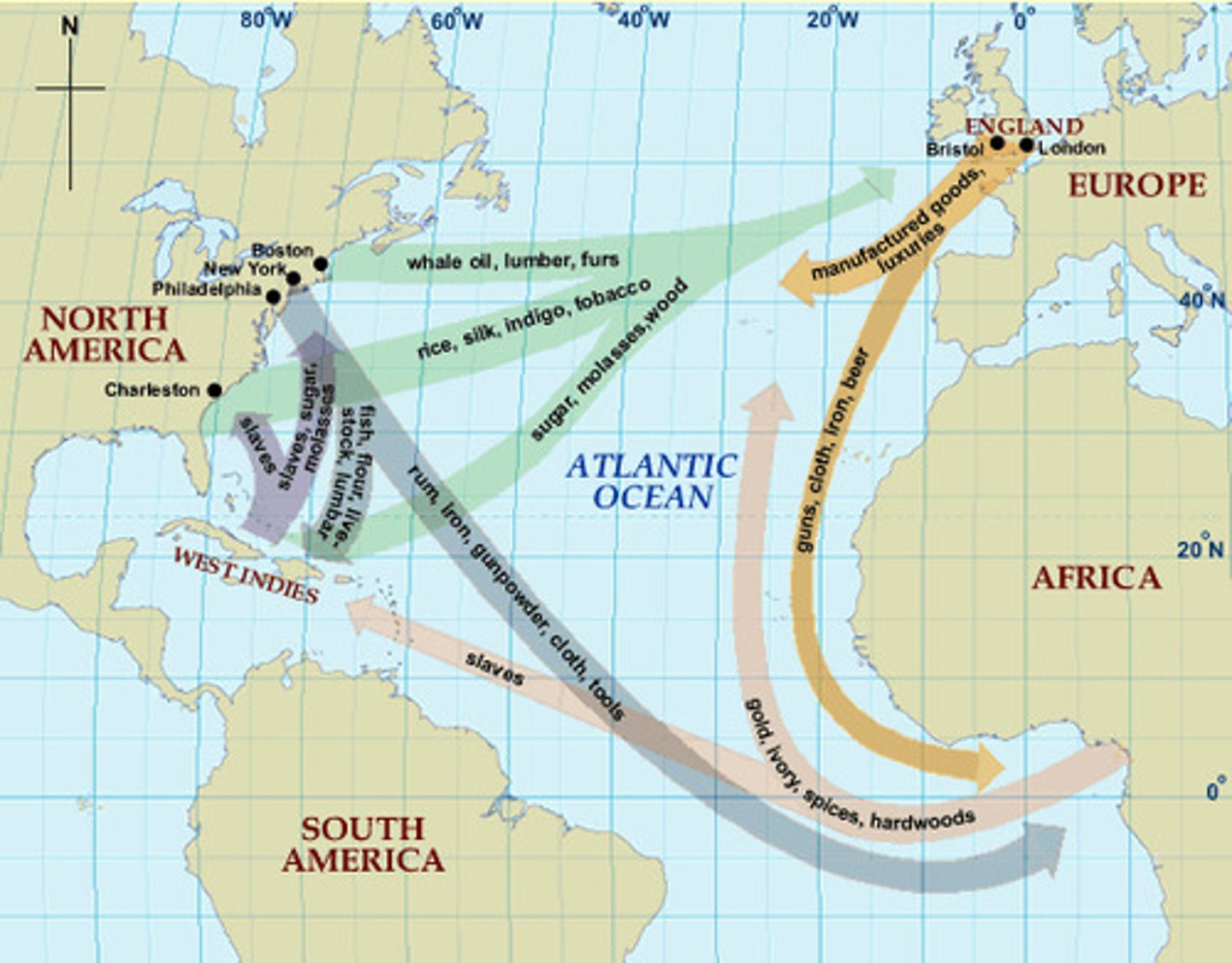
the advantages of trade=

disadvantages of trade=

A case study that shows specialization:
Songxia & the Global Umbrella Industry
China makes 70% of the world’s umbrellas, with Songxia (Shaoxing) producing over 500 million annually across 1,200+ factories. A single worker can make up to 300 umbrellas a day.
Why Songxia Leads:
Specialisation: Wide variety—rain, golf, mini, kids, wedding, fashion, etc.
Low Costs: Cheap labour (40,000 workers) and long hours.
Market Access: Strong transport links for exports.
Government Support: Tax breaks, supply chain help, and the Songxia Umbrella Industrial Park.
Impact on Trade:High output, low costs, and export readiness make Songxia a key player in global umbrella trade, boosting China’s role in international markets.
What are FDI's
an investment in a business by a foreign entity. investment in a country from outside that county. this is mainly through TNCs but can also be directly by governments. e.g. Nike factory in china

Why does most global trade occur between HDE countries?
Specialise in high-tech goods
Wealthier = more consumer spending
Strong trade agreements
Advanced infrastructure
Why are EME countries becoming more important in global trade?
Low labour costs → attract FDI
Rapid economic growth
Large and growing populations = bigger markets
How has China's trade position changed?
Now the largest exporter and second-largest importer of goods globally
Why do LDE countries participate less in global trade?
Poor infrastructure
Low GDP = less investment & spending
Political instability deters FDI
Who do LDE countries mainly trade with?
Mostly with EME and HDE countries
Trade growth is slower than EMEs
What do different country types export?
LDEs: Primary commodities (e.g., raw materials)
HDEs & EMEs: Secondary commodities (e.g., manufactured goods)
What are Special Economic Zones (SEZs)?
Areas with relaxed trade rules, lower tariffs/taxes
Attract investment and increase international trade
What has the global shift in metal trade caused?
Moved extraction from HDEs to EMEs/LDEs (esp. Africa)
Brought jobs & investment, but also labour rights and environmental issues
What is China's role in steel dumping?
China sold surplus steel below cost (dumping)
Harmed UK, EU & US industries – job losses & factory closures
EU responded with tariffs in 2015
How does China influence copper trade?
Imports 40% of global copper
Sourced from Chile, Peru, Mexico
Heavy investment in African mining, esp. Zambia
Case Study: Zambia-China Collum Coal Mine Dispute – What happened?
Chinese-owned mine faced labour disputes, unsafe conditions, violent clashes
Zambian gov’t seized it over safety & tax violations
What are the key issues in global metal trade?
HDEs: Job losses due to steel dumping
LDEs: Gain investment but face poor conditions and raw export dependency
Trade often unfair, favouring HDEs
Tata Steel, UK – What was the impact of Chinese steel?
Cheap Chinese steel caused UK plant closures
UK gov’t avoided direct intervention
What actions did the EU take against steel dumping?
Imposed tariffs on China & Taiwan in 2015
Brexit complicated ongoing trade protection efforts
What is a trade bloc?
a group of countries that work together to promote trade with one another + boost economic growth - (Tpe of trade agreement)
how do trade blocs work?
All countries within the bloc can trade freely with each other, which means that no tariffs are put in place. This makes goods and services cheaper, however they can charge tariffs on many goods and services imported from outside the bloc.
negative affects of trade blocs?
🚫 Restricted Trade: Countries in trade agreements may face limitations on trading with non-member nations (e.g., UK leaving the EU partly due to trade restrictions).
💰 Disadvantages for Non-Members:
LICs face tariffs, making it harder to compete in global markets.
Kenya & South Africa struggle to sell agricultural products to the EU due to high tariffs protecting EU farmers.
🌍 Unequal Benefits:
Core regions (HICs) gain the most from trade blocs, while periphery regions (LICs) struggle to access markets.
--> TEH SCHENEGN AGREEMENT MEANS no movement withthin eu + uk
🔴 Social
Illegal migration: Open borders make it harder to control movement.
Labour restrictions: Laws may limit working hours.
🔴 Economic
Loss of global trade: Focus on internal trade weakens global free trade.
Protectionism: Inefficient producers (e.g., EU farmers) shielded from competition.
Trade wars: Disputes arise (e.g., EU vs. NAFTA on beef).
Exclusion of non-members: Countries outside the bloc face trade barriers.
High costs: Running blocs (e.g., EU £960B budget) requires heavy taxation.
Loss of financial control: Central banks (e.g., European Central Bank) dictate policies.
🔴 Environmental
More food miles: Cheapest products travel long distances, increasing emissions.
Resource-sharing issues: Some industries (e.g., UK fishing) are negatively impacted.
🔴 Political
Undemocratic structures: Wealthy nations dominate institutions (e.g., IMF voting power).
Bureaucracy: Extra government layers make decisions costly and slow.
Loss of sovereignty: Local decisions overridden by higher authorities (e.g., EU courts).
Separatism: Centralisation fuels independence movements (e.g., Scottish referendum).
advantages of trade blocs
Social
Freedom of movement: People can live/work in any member country (e.g., EU).
Higher living standards: Prosperous trade boosts incomes.
Economic
Trade protection: Member economies shielded from external competition.
Free trade & specialisation: Boosts efficiency and lowers costs.
Economies of scale: Bulk production lowers prices.
Job creation: More trade = more employment (e.g., 3M EU jobs in 2011).
Support for weaker regions: Stronger areas help less developed ones.
Environmental
Stronger regulations: Unions enforce green policies (e.g., EU carbon rules).
Political
Less conflict: Trade fosters peace and cooperation.
Greater influence: Unified voice in global affairs (e.g., EU voting power).
Democracy boost: Citizens can vote in union-wide decisions (e.g., EU Parliament).
EU trade bloc facts:

USMCA trade bloc facts:

How does the WTO help enhance international trade?

What does the world bank do?
The World Bank provides financial and technical support to developing countries, funding projects that aim to reduce poverty and promote long-term economic development, such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare initiatives
What does the IMF and OECED DO?
International Monetary Fund (IMF): The IMF monitors the global financial system, offering short-term loans to countries facing economic crises. It promotes monetary stability, exchange rate cooperation, and economic growth by advising governments on financial policies.
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD): The OECD works to promote policies that improve economic and social well-being globally. It provides research and policy recommendations to help governments foster sustainable economic growth and development.
What is a TNC (Transnational Corporation)?
A large company that operates in several countries with its headquarters, production, and sales spread across different regions.
TNCs- drivers of globalisation
how much of global trade does TNC's take up?
80%
what is the global supply chain of TNC's
TNCs have hierarchical structures, with headquarters in HDEs and production spread across EMEs and LDEs.
Global Supply Chain Breakdown
Headquarters (HQ) & R&D - Located in HDEs (e.g., USA, UK, Germany) where high-skilled workers and strong infrastructure exist.
Raw Material Sourcing - Happens globally, often in LDEs where labour is cheap and environmental restrictions are weaker.
Manufacturing - Mainly in EMEs (e.g., China, India, Mexico), taking advantage of low wages and tax incentives.
Retail & Marketing - Located worldwide, often in major consumer markets like the EU, USA, and China.
what is vertical and horizontal integration?
Horizontal Integration: When a company buys or merges with another company at the same stage of production to reduce competition and increase market share. Example: A fast-food chain buying another fast-food chain.
Vertical Integration: When a company controls multiple stages of the supply chain (from raw materials to sales) to cut costs and increase efficiency. Example: A clothing brand owning cotton farms, factories, and retail stores.
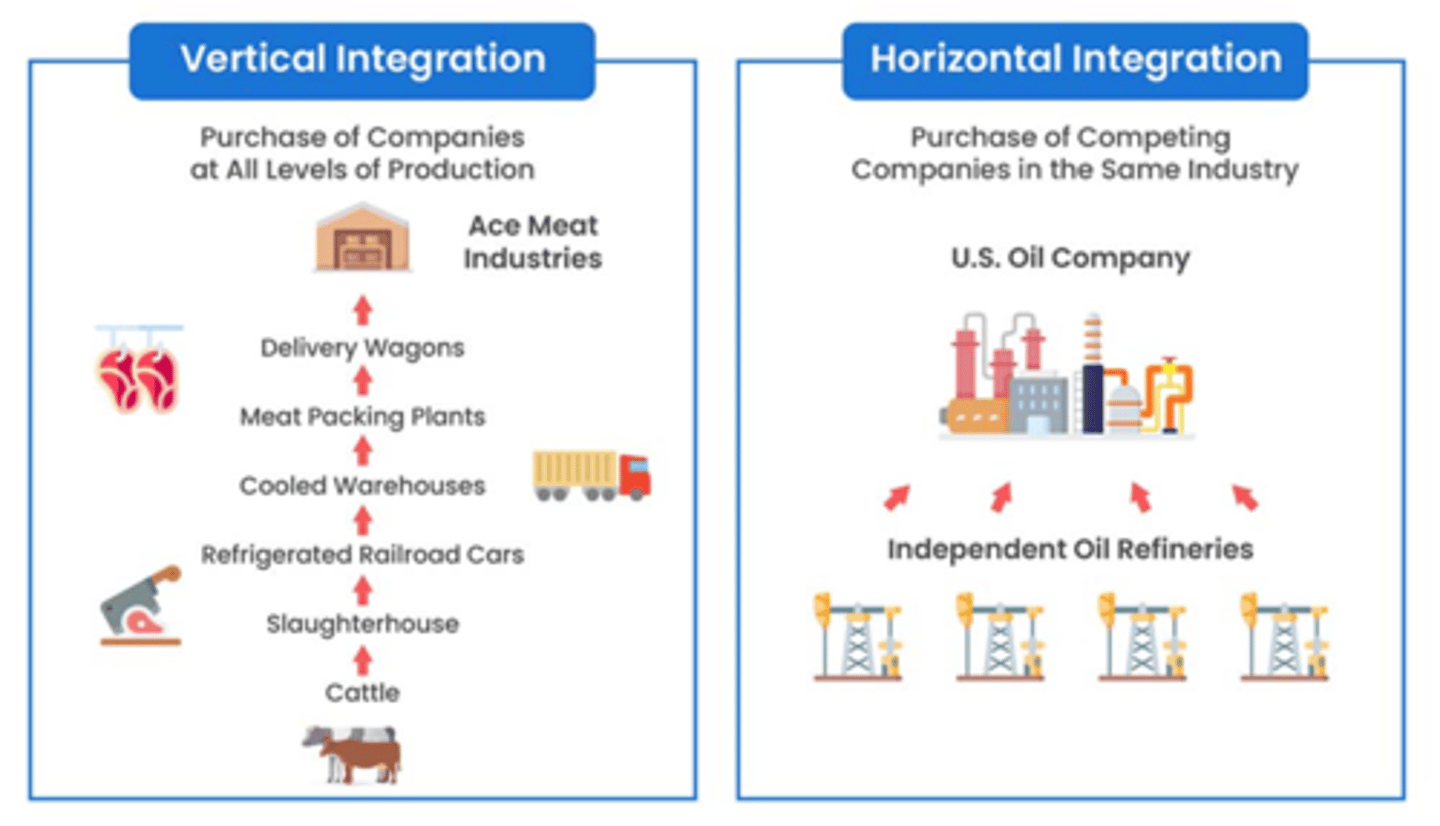
Why do TNCs grow?
Cheap Labour - Lower wages in LDEs and unemployed workers in HDEs.
Mergers & Acquisitions - Large companies buy out smaller ones (e.g., ExxonMobil merger).
Technological
Advancements - Improved transport (e.g., containerisation) and communication allow global operations.
Fewer Environmental Restrictions - TNCs exploit weaker environmental laws (e.g., oil drilling in the Niger Delta).
Government Incentives - Tax breaks and subsidies encourage TNCs to invest in certain locations (e.g., Toyota in the UK to access the EU market).
What are the positives and negatives of TNC;s in the host country:
Favourable (Positive Effects)
✅ Employment & Living Standards - TNCs create jobs, improving income and quality of life.✅ Skill & Technology Transfer - Advanced skills, expertise, and new technologies benefit local workers.✅ Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) - TNCs bring infrastructure, better facilities, and development.✅ Socio-Economic Multiplier Effect - Higher wages lead to increased consumer spending, boosting local businesses.✅ Improved Trade & Balance of Payments - Foreign currency inflows strengthen the economy.
Negatives of tnc's in host country:
Unfavourable (Negative Effects)
❌ Low-Skilled Jobs - Many roles in LEDCs are low-paid with little opportunity for progression.❌ Limited Local Management Development - Senior positions are often given to foreign workers.❌ Profit Repatriation - The majority of profits return to the home country, reducing local benefits.❌ Environmental Damage - Resource exploitation, pollution, and deforestation.❌ Labour Exploitation - Poor working conditions, long hours, and low wages due to weak labour laws.❌ Negative Multiplier Effects - Economic power allows TNCs to influence policies, sometimes at the cost of environmental and labour protections.
positives of tnc's in headquarters
Favourable (Positive Effects)
✅ Technology & Innovation Growth - Research & development (R&D) and high-tech jobs increase.✅ Higher-Order Jobs - Managerial and professional roles expand, boosting the economy.✅ Overseas Investment Increases National Income - Profits from foreign operations flow back into the home country.✅ Wider Share Ownership - TNCs attract investors, boosting stock markets and business expansion.
Negatievs of tnc in origin countries:
Unfavourable (Negative Effects)
❌ Job Relocation & Outsourcing - Manufacturing jobs move abroad, increasing domestic unemployment.❌ Short-Term Investment Risks - TNCs may suddenly withdraw from foreign markets, affecting economic stability.❌ Tax Avoidance & Loopholes - Some TNCs avoid paying full corporate taxes, reducing government revenue.❌ Speculative Investment Risks - Stock market volatility tied to TNCs can contribute to financial crises, such as the 2008 global downturn.
hwo do tnc influenec gloabl trade?
TNCs influence global trade by controlling supply chains, production, and distribution.
Steel Dumping - China flooded markets with cheap steel, harming industries in the UK, USA, and EU.
Trade Tariffs - The EU imposed tariffs on Chinese steel in 2015 to protect local businesses.
Global Marketing - TNCs promote universal branding while adapting products for local markets (glocalisation).
Glocalisation Examples
Cadbury makes its chocolate sweeter in China.
McDonald's India serves the McAloo Tikki instead of beef burgers.
How do TNC'S + sport relate?
Tncs sponsor--> sport teams to boost brand visibility. HOWEVER, sponsorphips often conglict w sport values
e.g fats food chains sponsor the olympics
What are the two major case studies for TNC'S?
Shell + COCACOLA
What is the 5th most traded fruit globally?
bannanas
What are the positive impacts of banana trade?
- nutritional benefits- especially for leds
-employment oppurtunities- 300000 people in philipine sin banana industry
-export earning of bananas support major countries such as ecuador
-development of infrastructure to transport the bananas.