Lab 4- Cranial Nerves & the Eye, pt. 1: Cranial Nerves
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
olfactory nerve foramina
Cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
what CN controls the special sense of smell?
CN I- Olfactory
What cranial nerve controls the special sense of vision?
CN II- Optic
Optic nerve foramina
optic foramina (optic canal)
Damage to what structure causes loss of temporal vision in both eyes, resulting in tunnel vision (loss of peripheral vision)?
loss of info from medial (nasal) retina of both eyes.
**medial (nasal) retina carries info from temporal (peripheral) visual field, therefore only nasal part of visual field of both eyes is retained.
optic chiasm
damage to what structure causes loss of vision in the eye on the same side that this is damaged? (ipsilateral)
This structure attached directly to the eye
optic nerve
damage to what structure causes loss of vision in the eye on the opposite side of the damage? (contralateral)
optic tract
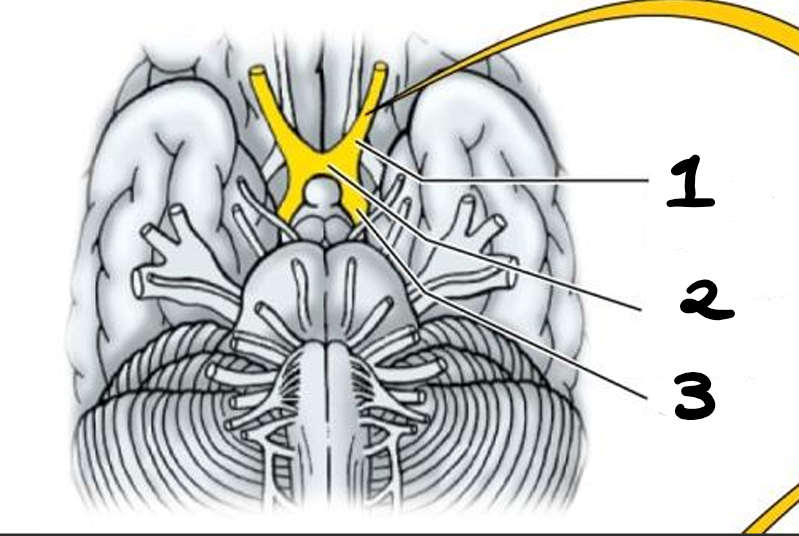
optic nerve (CN II)
optic chiasm
optic tract
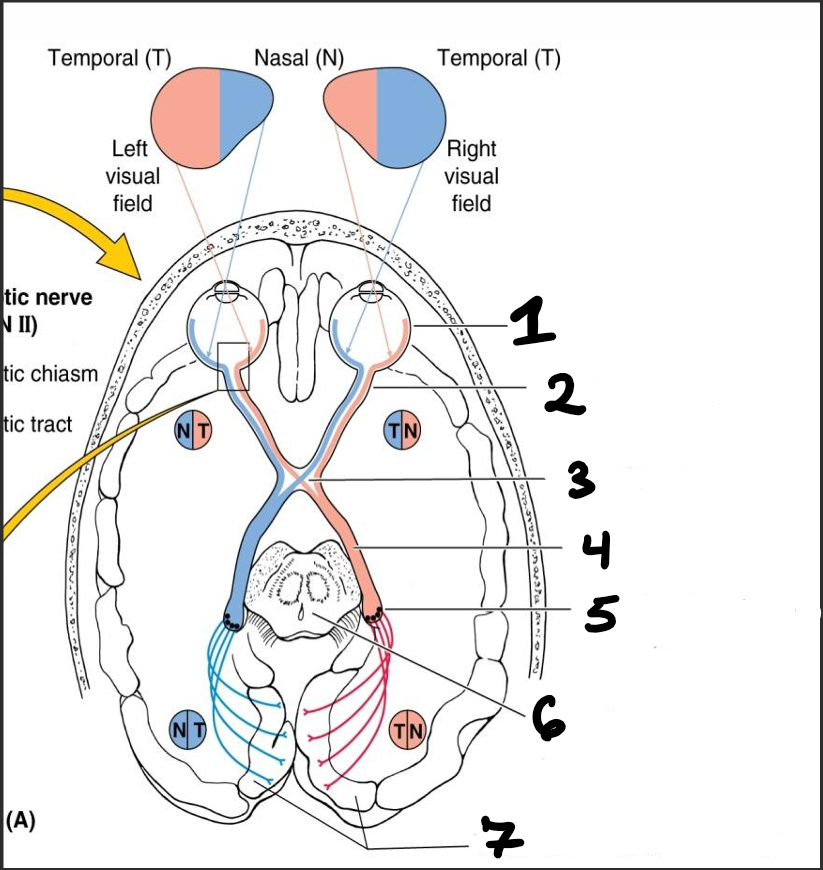
retina
optic nerve (CN II)
optic chiasm
right optic tract
diencephalon
midbrain
visual cortices of occipital lobes
what cranial nerve has motor function that moves the eye & eyelid by controlling 4/6 extraocular muscles,
has the parasympathetic function of accommodation & light reflex (constrict pupil by contracting sphincter pupillary muscles)
CN III- Oculomotor
what is the visual pathway?
light hits eye (retina)
CN II
optic foramina (optic canal)
optic chiasm
optic tract
thalamus
visual cortex in occipital lobe
what are the 4 extraocular muscles controlled by the oculomotor nerve?
superior rectus
medial rectus
inferior rectus
inferior oblique
What is the process whereby the ciliary muscles contract, causing the zonular fibers to slacken, then the lens becomes rounded/thickened?
Accommodation for near vision
What is the process whereby the ciliary muscles relax, causing the zonular fibers to stretch/lengthen, then the lens becomes flattened for near vision?
Accommodation for distant vision
what is the pathway of the light reflex & what CN controls this?
high amount of light enters eye
pupils constrict
sphincter pupillary muscles contract
squinting
controlled by CN III- oculomotor (parasympathetic)
foramina of oculomotor nerve
superior orbital fissure
what CN has motor function that moves the eye downward & laterally by controlling 1/6 extraocular muscles (superior oblique)?
CN IV- Trochlear “pulley”
what extraocular muscle does the trochlear nerve control and how does it move the eye?
superior oblique- downward & lateral eye movement
foramina of trochlear nerve
superior orbital fissure
what cranial nerve has motor function that abducts the eye (outward gaze)
CN VI- Abducens
foramina of abducens nerve
superior orbital fissure
what muscle does the abducens CN control?
lateral rectus muscle
What CN has sensory function of face, eyes, nasal cavity, & general sensation (NOT TASTE) of anterior 2/3 of tongue?
It also has motor function of mastication by controlling masseter muscle
CN V- Trigeminal
(think “tri” = 3 senses controlled)/3 branches
branch of trigeminal nerve that controls sensory info from forehead (superior orbital notch), eye, upper eyelid, & parts of the nose?
ex) pain sensation when cornea is poked → this branch of CN V
V1- Ophthalmic branch
foramina of ophthalmic branch (V1) of trigeminal nerve
superior orbital fissure
branch of trigeminal nerve that controls sensory info from upper jaw, cheek & face (infraorbital foramen), upper lip, nasal cavity, oral cavity, & upper teeth?
V2- Maxillary branch
foramina of maxillary (V2) branch of trigeminal nerve
foramen rotundum
branch of trigeminal nerve that controls sensory info from ear, lower jaw, lower face, lower lip, lower teeth, nasal cavity, oral cavity, & anterior 2/3 tongue general senses NOT taste?
Also has motor function of mastication
V3- Mandibular branch
foramina of mandibular (V3) branch of trigeminal nerve
foramen ovale
what muscle elevates the mandible & closes the jaws and what CN controls it?
masseter
CN V- trigeminal (V3- Mandibular branch)
what CN has motor function of facial expression muscles, sensory function of taste of anterior 2/3 tongue, and parasympathetic function of gland secretions (tears & saliva)?
ex) eat spicy food = saliva, tears, & expressions
CN VII- Facial
foramina of facial nerve
internal acoustic meatus & stylomastoid foramen
what CN has sensory function of balance via semicircular canals & hearing via cochlea?
CN VIII- Vestibulocochlear
foramina of vestibulocochlear nerve
internal acoustic meatus
damage to what CN could cause vertigo?
vestibulocochlear
what CN has sensory function of posterior 1/3 tongue taste & general sensation, upper throat, carotid sinus (pressure) & body (oxygen levels), involved in gag reflex
motor function = stylopharyngeus muscle
parasympathetic function = innervates parotid gland for saliva production
CN IX- Glossopharyngeal
what muscle controls swallowing
stylopharyngeus (controlled by glossopharyngeal)
foramina of glossopharyngeal nerve
jugular foramen
What CN has sensory function of inferior pharynx & larynx (lower throat) and thoracic& abdominal organs,
motor function of soft palate (closes nasal opening while swallowing), pharynx, and larynx (speech aka voice box), and involved gag reflex).
parasympathetic function of digestion via thoracic & abdominal viscera → heart rate, breathing rate, bowel movements (secretes bile, prevents constipation, promotes proper digestion
CN X- Vagus
what is Vagus nerve also known as
wanderer
what two cranial nerves are involved in the gag reflex & what are their roles?
CN IX (glossopharyngeal)- sensation in upper throat
CN X (vagus)- gag via pharyngeal muscles motor function
foramen of vagus nerve
jugular foramen
what cranial nerve has motor function of sternocleidomastoid muscle (rotate head) & trapezius muscle (shrug shoulders)?
CN XI- Accessory
foramina of accessory nerve
foramen magnum & exits thru jugular foramen to muscle
what CN has motor function of extrinsic (shape for speech) & intrinsic (swallow) tongue muscles?
movement of tongue
CN XII- Hypoglossal
foramina of hypoglossal nerve
hypoglossal canal
what is the lower jaw bone called?
mandible
what nerve is responsible for sticking out your tongue?
hypoglossal
what type of damage would occur if the jugular foramen was injured?
glossopharyngeal, vagus, & accessory nerves all pass through
Injury results:
Glossopharyngeal → lose gag reflex(no upper throat sensation) & lose taste/general sensation of posterior 1/3 tongue
Vagus → lose gag reflex (no pharyngeal muscle movement), voice changes, difficulty swallowing
Accessory → unable/weak head turning & shoulder shrugging/droop
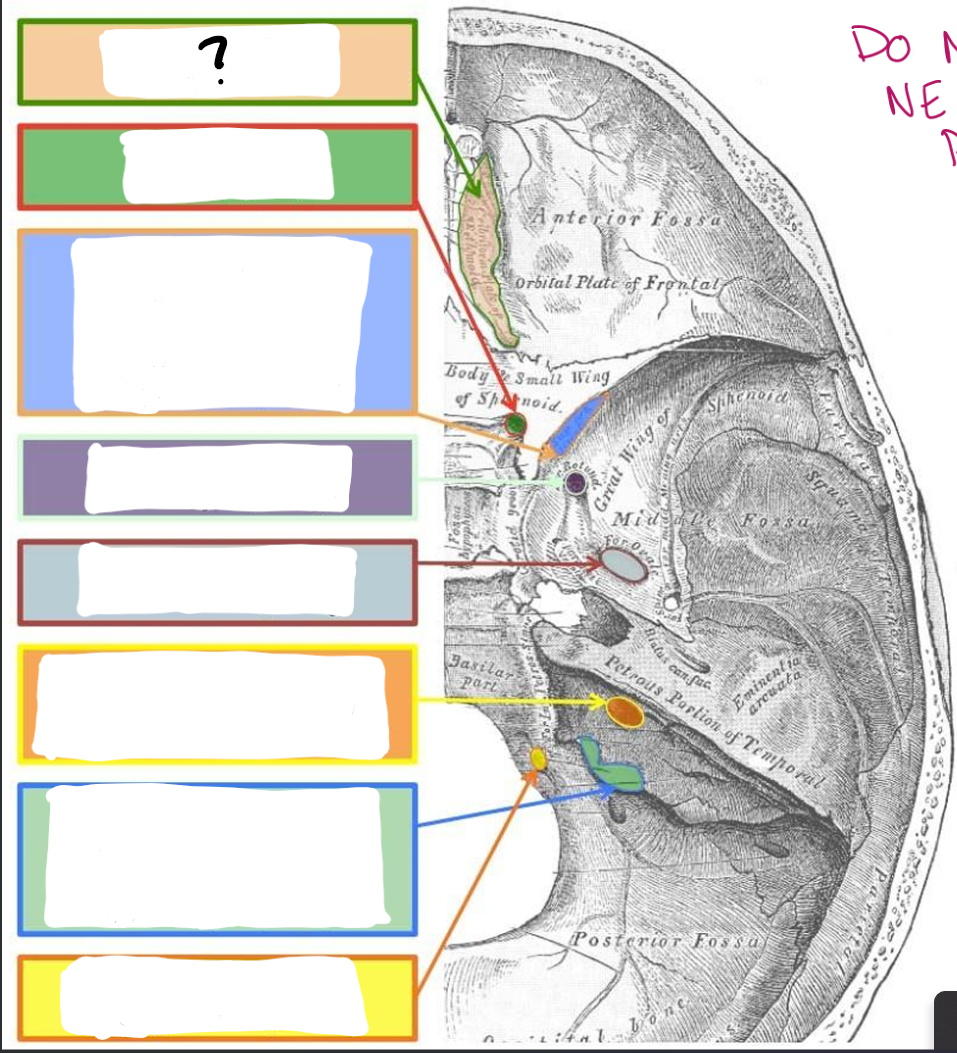
Cribriform Plate:
CN I- Olfactory
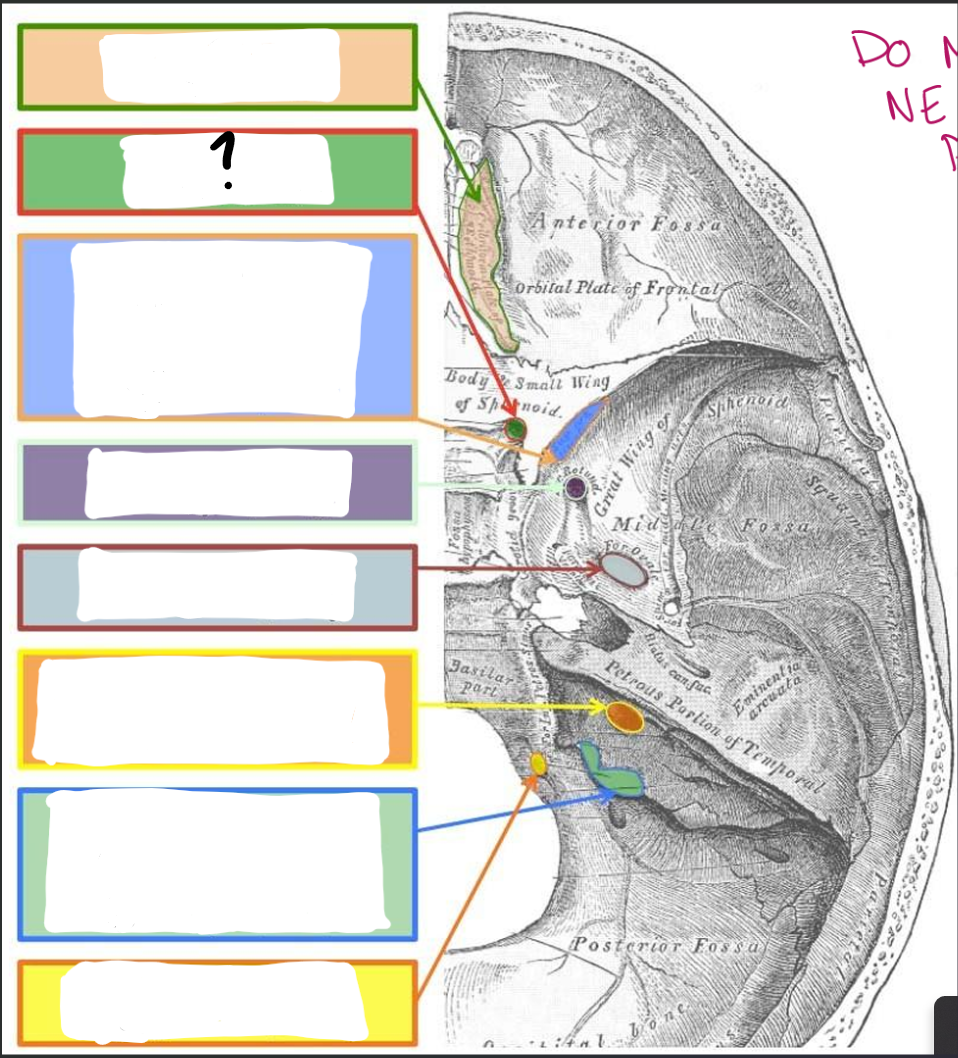
Optic Canal/Foramina:
CN II- Optic
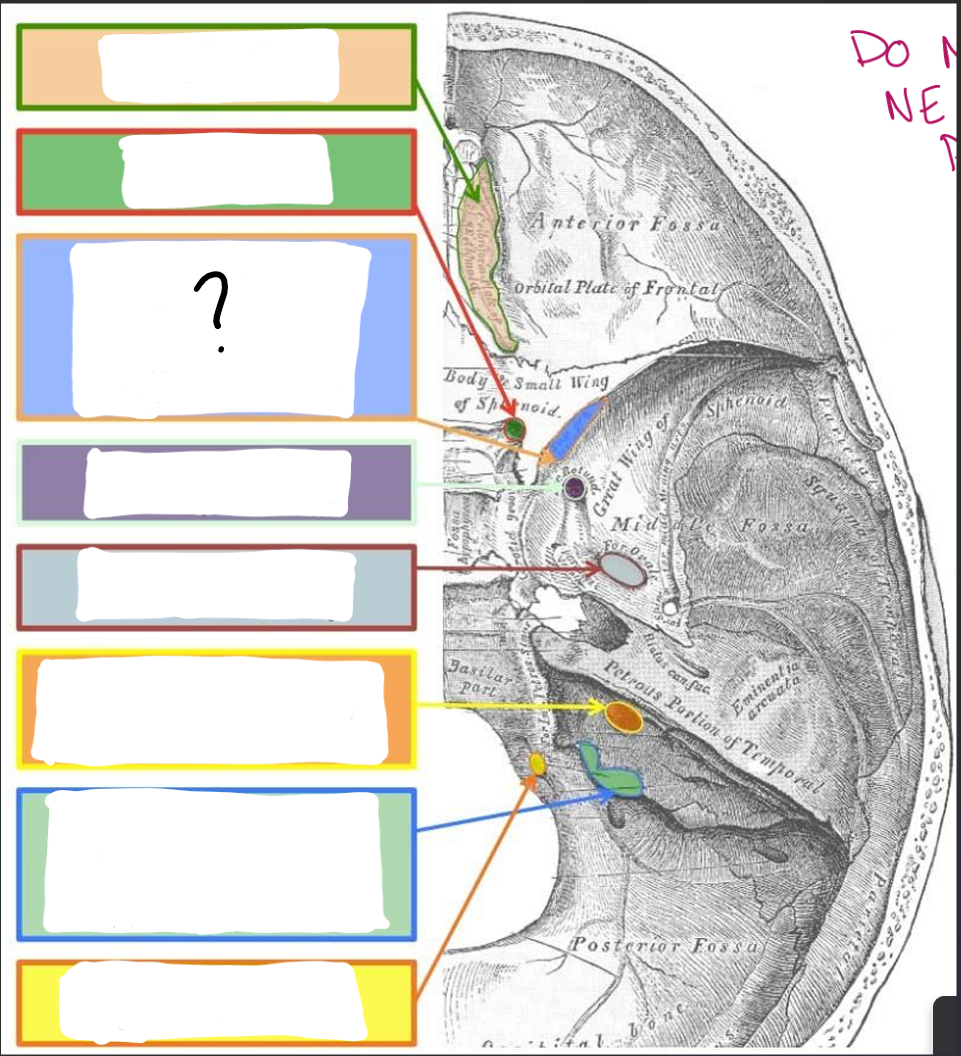
Superior orbital Fissure:
CN III- Oculomotor
CN IV- Trochlear
V1- Ophthalmic branch of trigeminal
CN VI- Abducens
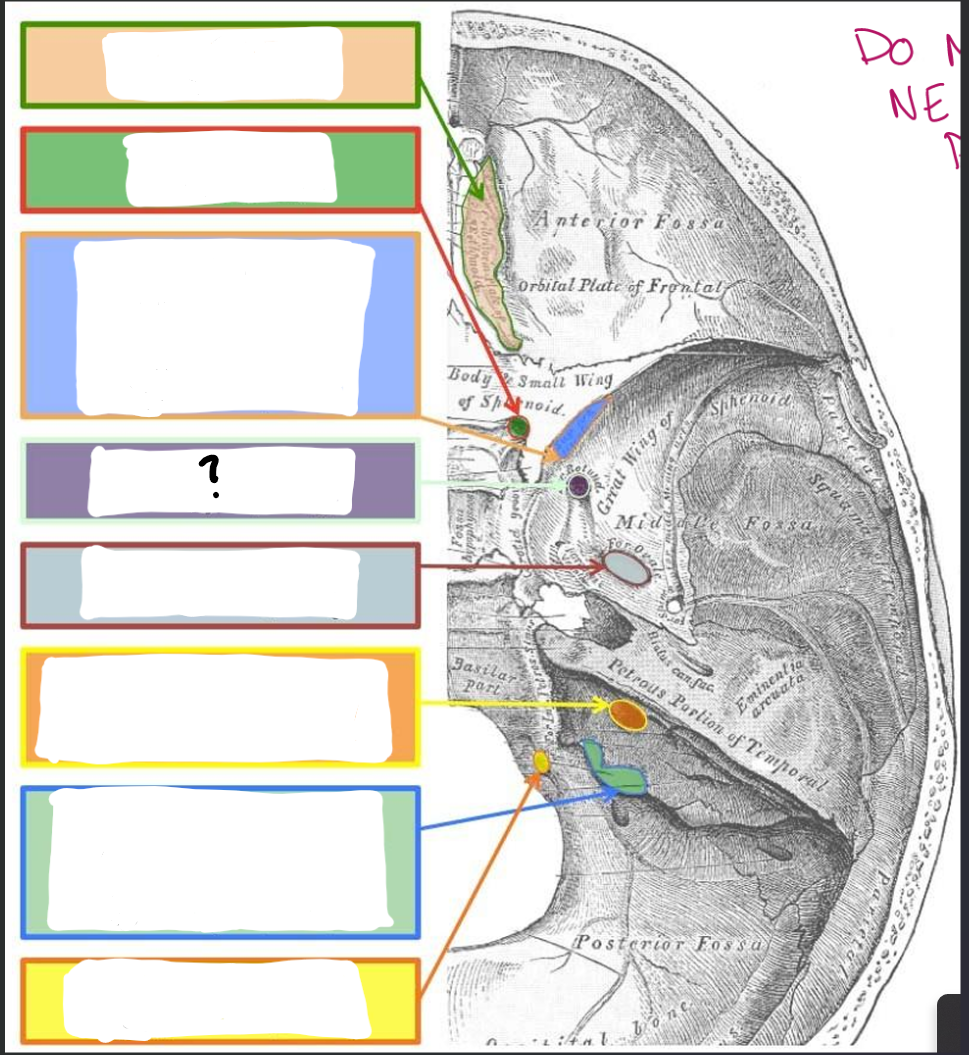
Foramen rotundum:
V2- Maxillary branch of trigeminal
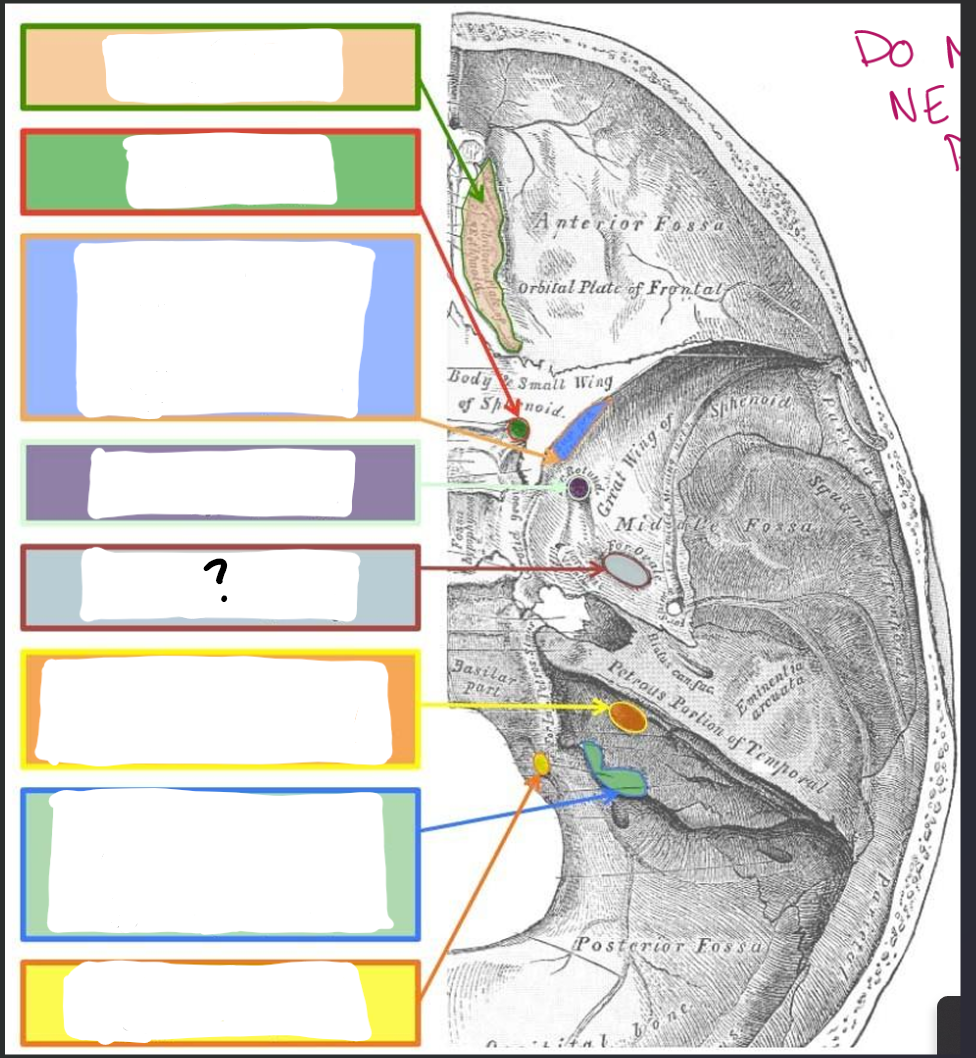
Foramen ovale:
V3- Mandibular branch of trigeminal
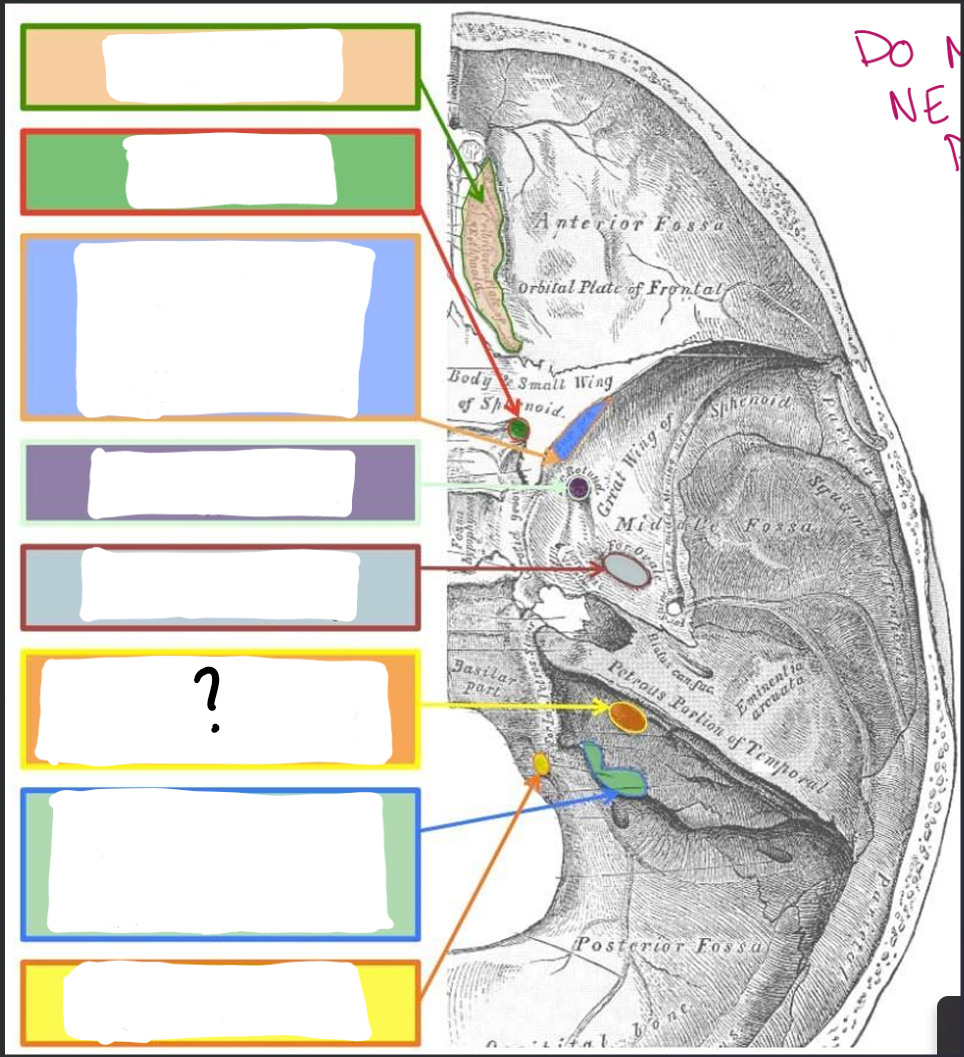
Internal Acoustic Meatus:
CN VII- Facial
CN VIII- Vestibulocochlear
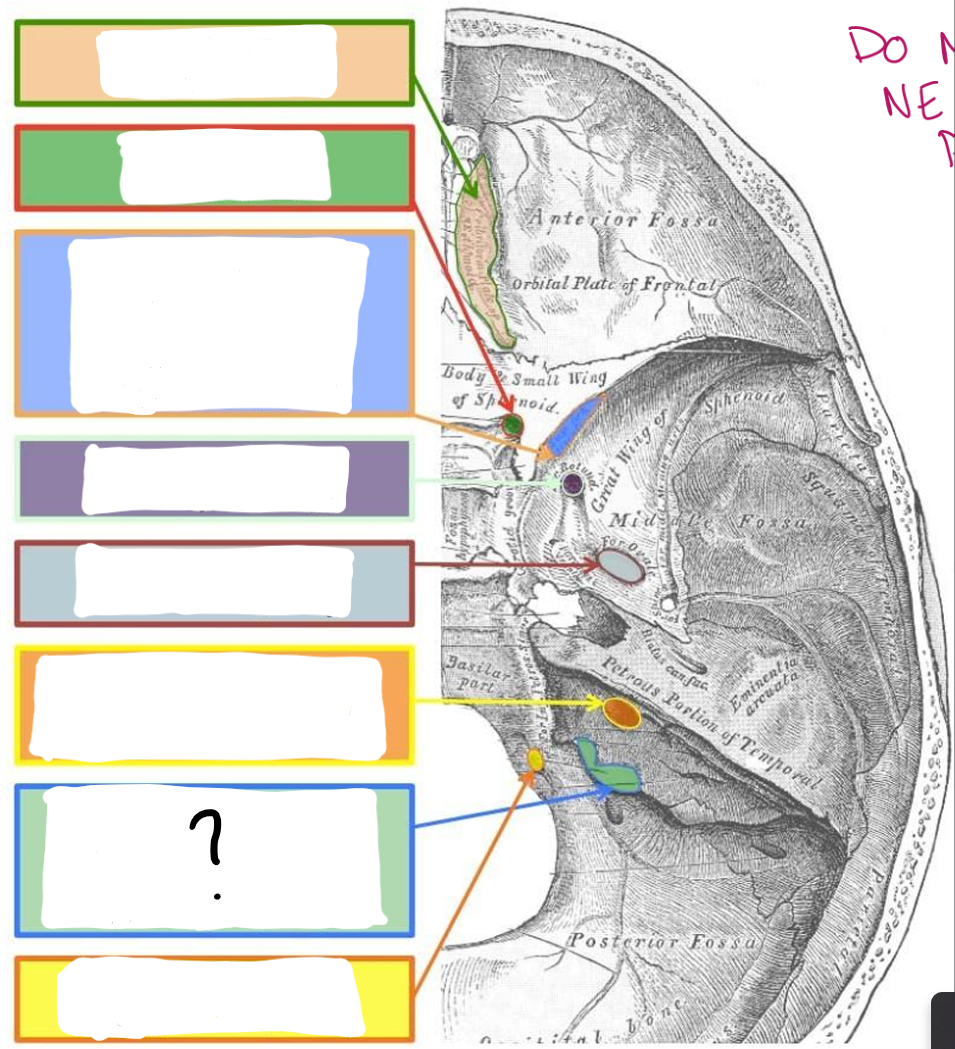
Jugular Foramen:
CN IX- Glossopharyngeal
CN X- Vagus
CN XI- Accessory
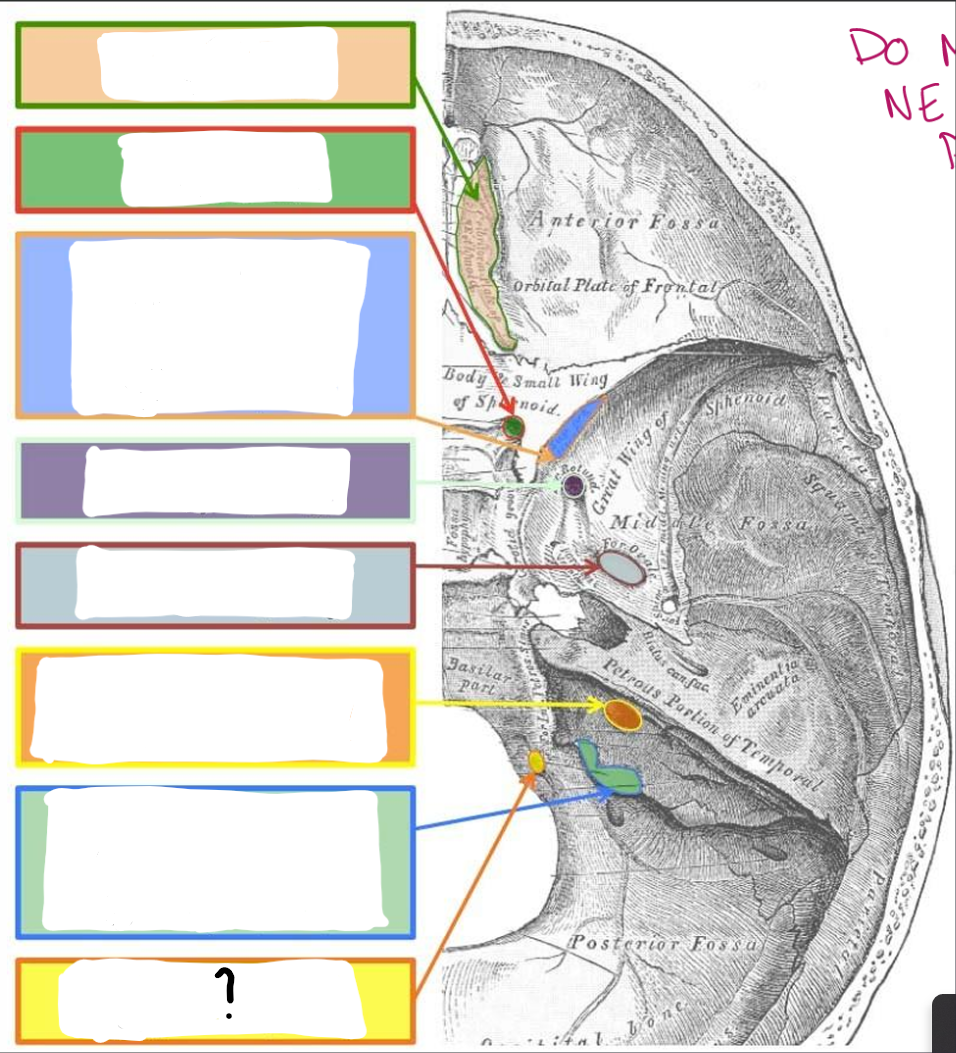
Hypoglossal Canal:
CN XII- Hypoglossal