AP bio Unit 7
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Evolution
Change in the genetic makeup of a population overtime
Natural Selection
Process by which organisms better suited to an environment have a higher chance of survival to reproduce
Variation
Genetic differences among organisms in a population
Adaptation
Factors that provides advantages in an environment
How do we measure evolutionary fitness?
By reproductive success
Fitness
The ability of an organism to survive and produce fertile offspring
Reproductive success
Production of offspring
Heritability
The ability to pass on traits
How does environmental stability affect evolution?
More stable environments have populations that are less likely to evolve
The more unstable an environment is, the quicker the evolution is
Why is genetic/phenotypic variation important to a population?
Genetic variation increases the probability a population will survive in a changing environment
Genetic variation can result in varying phenotypes →higher chance of one being better suited
Genetic variation
Genotypic and Phenotypic differences between individuals in a population
Selective pressure
Any biotic or abiotic factors influencing survivability
How do phenotypes affect fitness?
Phenotypes that increase an individuals chances of survival will increase fitness
Artificial selection
The process by which humans select desirable traits in organisms and selectively breed those traits.
What can artificial selection result in?
Phenotypes that wouldn’t exist in nature otherwise
More OR less genetic diversity
Convergent evolution
The process by which similar environmental conditions select for similar traits in different populations/species overtime
Analagous structures
Similar traits observed in distantly related or unrelated species
Genetic drift
random change in frequency of a particular allele within a population
nonselective, generally in small populations
Bottleneck
Large, diverse population suddenly reduced
natural disasters
Founder effect
random, reduces genetic variation in a small population due to separation from a larger population
migration/geological events
Gene flow
movement of individuals causes allele exchange between populations
introduction of new genes →increased genetic variation
Continued migration →decreases diversity
Hardy Weinberg model
a model describing and predicting allele frequencies in a non-evolving population
What conditions must be met for the Weinberg model?
Large population →no genetic drift
No migration → no gene flow
No net mutation →No modified, deleted, or duplicated genes
Random mating → no sexual selection
Absence of selection → no natural selection
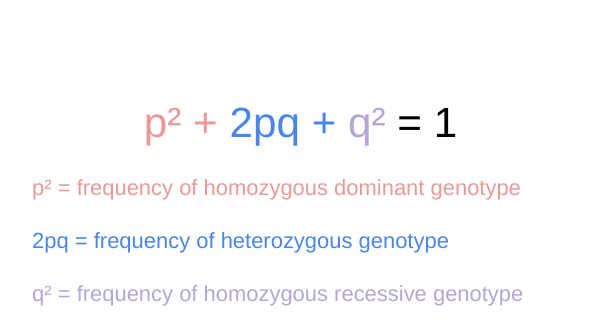
What is the equation for calculating genotype/phenotypes frequencies and what do the variables represent?
What is the equation for calculating the frequency of a particular allele and what do the variables represent?

Evidence supporting evolution
Geographical - evidence based on characteristics of a habitat or land
Geological - evidence based on features of the earth OVER TIME
fossils document patterns of evolution and changes in environment
Physical - evidence based on phenotypes
Biochemical - evidence based on chemical composition
comparison of biomolecules like DNA and proteins
Mathematical - evidence based on models/simulations that provide statistics
How can fossils be dated?
age of surrounding rocks
The decay of isotopes like carbon-14
Geographical data
What do morphological homologies represent?
Features shared by common ancestry →modified traits shared by different species
Homologous structures
Variation in a structure that was present in a common ancestor (Divergent evolution)
Vestigial structures
Reduced or obsolete features that serve little to no purpose
Analagous structures
Structures that evolved independent of each other but in similar environments/selective pressures (white coats of animals in snowy environments) →convergent evolution
What evidence supports common ancestry for all eukaryotes?
membrane bound organelles
linear chromosomes
Genes that contain introns
What are the similarities between mitochondria and chloroplasts?
double membrane
circular genomes
ribosomes
endosymbiotic theory - descirbe the processes and evidence supporting these similarities
What are chromosomal similarities between eukaryotic organisms?
linear
large genome
capped with telomeres
inside the nucleus
What does it mean when a pathogen is chemically compatible with the host?
co-evolve with the host
presence of pathogens can change phenotypes selected for and against
Phylogenetic tree
branched diagram showing the evolutionary relationship between species
can show changes over time
Cladogram
a diagram used to show evolutionary relationships between species
a clade is any group on a cladogram sharing a common ancestor
How is the out-group useful?
Provides a frame of reference.
Node
where 2 lines meet
represents the most recent common ancestor
Root
represent the most common ancestor of all the species on the diagram
Derived characteristic
a trait in a recent species that evolved from an ancestor
Monophyletic
Diagram that includes an ancestor and ALL of its descendants
Paraphyletic
Diagram that includes an ancestor and SOME of its descendants
Polyphyletic
Diagram that includes descendants but no common ancestor
When does speciation occur?
When populations are reproductively isolated from each other.
Species
Group capable of interbreeding and exchanging genetic information to produce viable, fertile offspring.
Speciation
The creation of a new species
Prezygotic barriers
Prevent the formation of a fertilized egg
habitat isolation: species occupy different habitats and rarely come into contact
Temporal isolation: species breed at different times of the day, year, season
Behavioral isolation: different courtship behaviors or preferences
Mechanical isolation: structural differences in reproductive organs
Gamete isolation: sperm and egg meet but do not produce a zygote
Postzygotic barriers
Prevent a zygote from developing into a viable, fertile offspring
hybrid inviabilty: mating results in a zygote but incompatibility may prevent the development
Hybrid sterility: an offspring is produced but is sterile
Hybrid breakdown: hybrids are viable and sterile but resulting generations are feeble or sterile (decreasing fitness)
Allopathic speciation
Speciation due to a movement from one geographical region to another
no gene flow
Can expose populations to different selective pressures
Sympatric speciation
Speciation due to being reproductive isolated from a surviving ancestral population
no geographical barrier
Can result from genetic mutations
Can result from habitat differences
Can result from sexual selection
Punctuated equilibrium
Evolution occurs rapidly after a long period of stasis
changing ecological conditions are the stimulus for evolution
Gradualism
Evolution occurs slowly
ecological conditions change slowly
Adaptive radiation
The evolution of a new species that allows empty ecological roles/niches to be filled
Extinction
Disappearance of a species, such that no future generations will naturally populate the earth
What factors lead to extinction
Catastrophic changes to an ecosystem
How do environmental changes increase risk of extinction?
By changing conditions too rapidly for an organism to adapt.
How do speciation and extinction rates impact species diversity?
High speciation and low extinction rates can suit in high biodiversity. The opposite can result in low biodiversity.
How does extinction create new niches?
When a species goes extinct, the role that it played is open for another species to occupy.
can lead to repod soeciation and adaptive radiation
How does genetic diversity of a species or population affect its ability to withstand environmental pressures?
Due to the diverse amount of adaptations, Higher genetic diversity results in an increased ability withstand environmental pressures and lower genetic diversity does the opposite.
Variation
Different combination of alleles and phenotypes in a population
What makes genetically diverse populations resilient?
Because of the diverse amount of adaptations in a genetically diverse populations, they are more likely to contain individuals that can withstand new environmental pressures.
Deleterious
Traits that reduce chance of survival
What determines if an allele is deleterious or adaptive?
The selective pressures of an environment
What scientific evidence provides support for models of the origin of life on earth?
Geological evidence
earth formed apx 4.6 billion years ago
The environment was too hostel for life until 3.9 billion years ago
The earliest fossil evidence for life dates to 3.5 billion years ago
What did primitive earth provide
Inorganic precursors from which organic molecules could have been synthesized.
What was there a presence and absence of in primitive earth
Presence of free energy and an absence of significant quantity of atmospheric oxygen
What is RNA world hypothesis
Proposes that RNA could have been the earliest genetic molecule