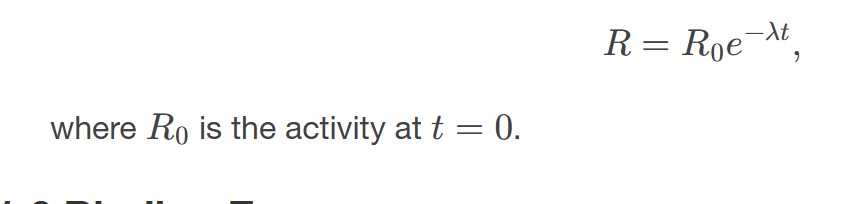Chapter 31: Radioactivity and Nuclear Physics
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
activity
the rate of decay for radioactive nuclides
alpha decay
type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle
alpha rays
one of the types of rays emitted from the nucleus of an atom
antielectron
another term for positron
antimatter
composed of antiparticles
atomic mass
the total mass of the protons, neutrons, and electrons in a single atom
atomic number
number of protons in a nucleus
barrier penetration
quantum mechanical effect whereby a particle has a nonzero probability to cross through a potential energy barrier despite not having sufficient energy to pass over the barrier; also called quantum mechanical tunneling
becquerel
SI unit for rate of decay of a radioactive material
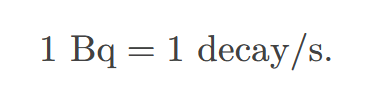
beta decay
type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle
beta rays
one of the types of rays emitted from the nucleus of an atom
binding energy
the energy needed to separate nucleus into individual protons and neutrons

binding energy per nucleon
the binding energy calculated per nucleon; it reveals the details of the nuclear force—larger the BE/𝐴, the more stable the nucleus
carbon-14 dating
a radioactive dating technique based on the radioactivity of carbon-14
chart of the nuclides
a table comprising stable and unstable nuclei
curie
the activity of 1g of 226Ra, equal to 3.70×1010Bq
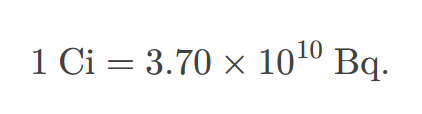
daughter
the nucleus obtained when parent nucleus decays and produces another nucleus following the rules and the conservation laws
decay
the process by which an atomic nucleus of an unstable atom loses mass and energy by emitting ionizing particles
decay constant
quantity that is inversely proportional to the half-life and that is used in equation for number of nuclei as a function of time
decay equation
the equation to find out how much of a radioactive material is left after a given period of time
decay series
process whereby subsequent nuclides decay until a stable nuclide is produced
electron capture
the process in which a proton-rich nuclide absorbs an inner atomic electron and simultaneously emits a neutrino
electron capture equation
equation representing the electron capture
electron’s antineutrino
antiparticle of electron’s neutrino
electron’s neutrino
a subatomic elementary particle which has no net electric charge
gamma decay
type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a gamma particle
gamma rays
one of the types of rays emitted from the nucleus of an atom
Geiger tube
a very common radiation detector that usually gives an audio output
half-life
the time in which there is a 50% chance that a nucleus will decay
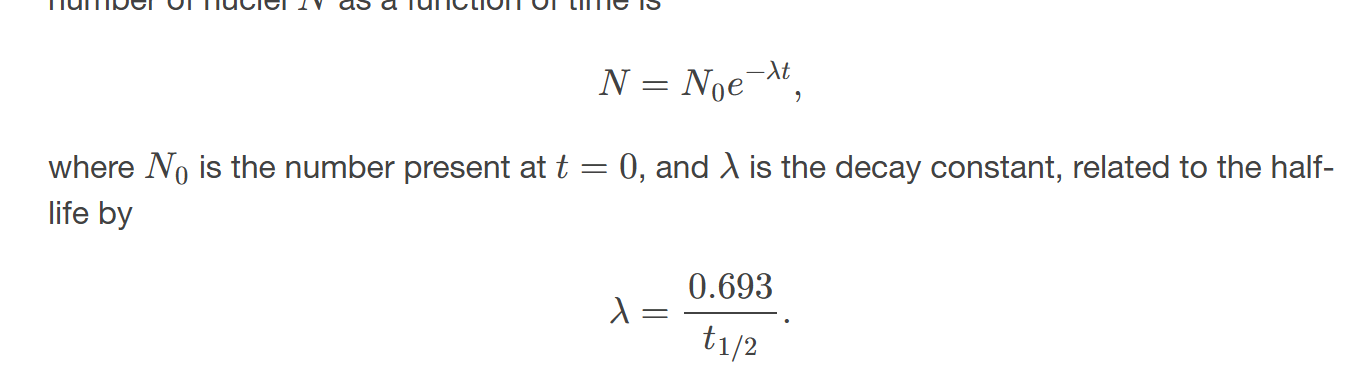
ionizing radiation
radiation (whether nuclear in origin or not) that produces ionization whether nuclear in origin or not
isotopes
nuclei having the same 𝑍 and different 𝑁s
magic numbers
a number that indicates a shell structure for the nucleus in which closed shells are more stable
mass number
number of nucleons in a nucleus
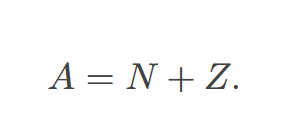
neutrino
an electrically neutral, weakly interacting elementary subatomic particle
neutron
a neutral particle that is found in a nucleus
nuclear radiation
rays that originate in the nuclei of atoms, the first examples of which were discovered by Becquerel
nuclear reaction energy
the energy created in a nuclear reaction
nucleons
the particles found inside nuclei
nucleus
a region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom
nuclide
a type of atom whose nucleus has specific numbers of protons and neutrons
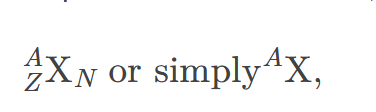
parent
the original state of nucleus before decay
photomultiplier
a device that converts light into electrical signals
positron
the particle that results from positive beta decay; also known as an antielectron
positron decay
type of beta decay in which a proton is converted to a neutron, releasing a positron and a neutrino
protons
the positively charged nucleons found in a nucleus
quantum mechanical tunneling
quantum mechanical effect whereby a particle has a nonzero probability to cross through a potential energy barrier despite not having sufficient energy to pass over the barrier; also called barrier penetration
radiation detector
a device that is used to detect and track the radiation from a radioactive reaction
radioactive
a substance or object that emits nuclear radiation
radioactive dating
an application of radioactive decay in which the age of a material is determined by the amount of radioactivity of a particular type that occurs
radioactivity
the emission of rays from the nuclei of atoms
radius of a nucleus
the radius of a nucleus is 𝑟=𝑟0𝐴1/3

range of radiation
the distance that the radiation can travel through a material
rate of decay
the number of radioactive events per unit time
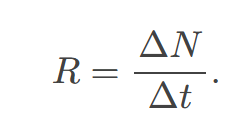
scintillators
a radiation detection method that records light produced when radiation interacts with materials
solid-state radiation detectors
semiconductors fabricated to directly convert incident radiation into electrical current
tunneling
a quantum mechanical process of potential energy barrier penetration
A mass unit convenient to atomic and nuclear processes is the unified atomic mass unit (u), defined to be
1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
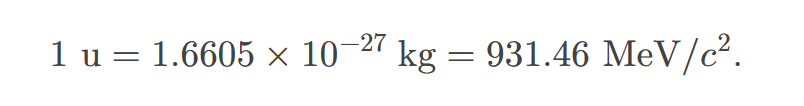
alpha nuclear decay equation
The equation representing the process in which an alpha particle is emitted from a nucleus, typically written as A\rightarrow A-4+X.
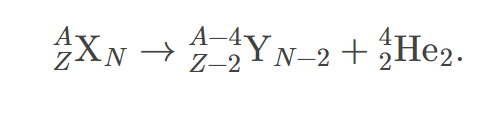
Nuclear decay releases an amount of energy 𝐸 related to the mass destroyed Δ𝑚 by
the equation E=Δ𝑚c², where c is the speed of light.
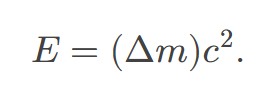
Beta decay equations
describe the transformation of a neutron into a proton and an electron, emitting a beta particle in the process.

𝛾 decay equation
describes the process of gamma radiation emission from an excited nucleus, which transitions to a lower energy state without a change in the number of protons or neutrons.
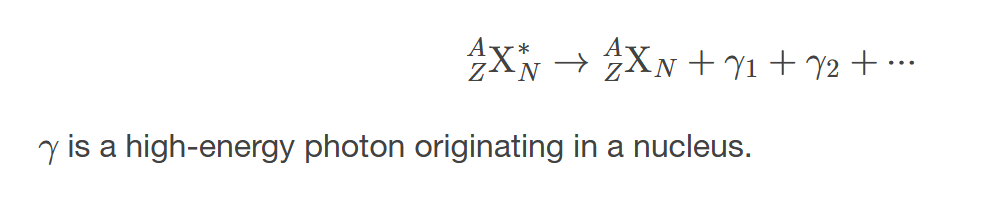
The activity 𝑅 of a source is related to 𝑁 and 𝑡1/2 by
the equation R = λN, where λ is the decay constant.
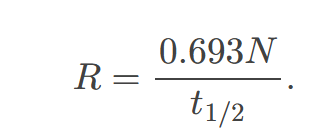
Since 𝑁 has an exponential behavior as in the equation 𝑁=𝑁0𝑒−𝜆𝑡, the activity also has an exponential behavior, given by