OPT 313 Inherited Disorders
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
What is ERG?
CL on the front of the eye measures the mass electrical response of the retina to photopic stimulation
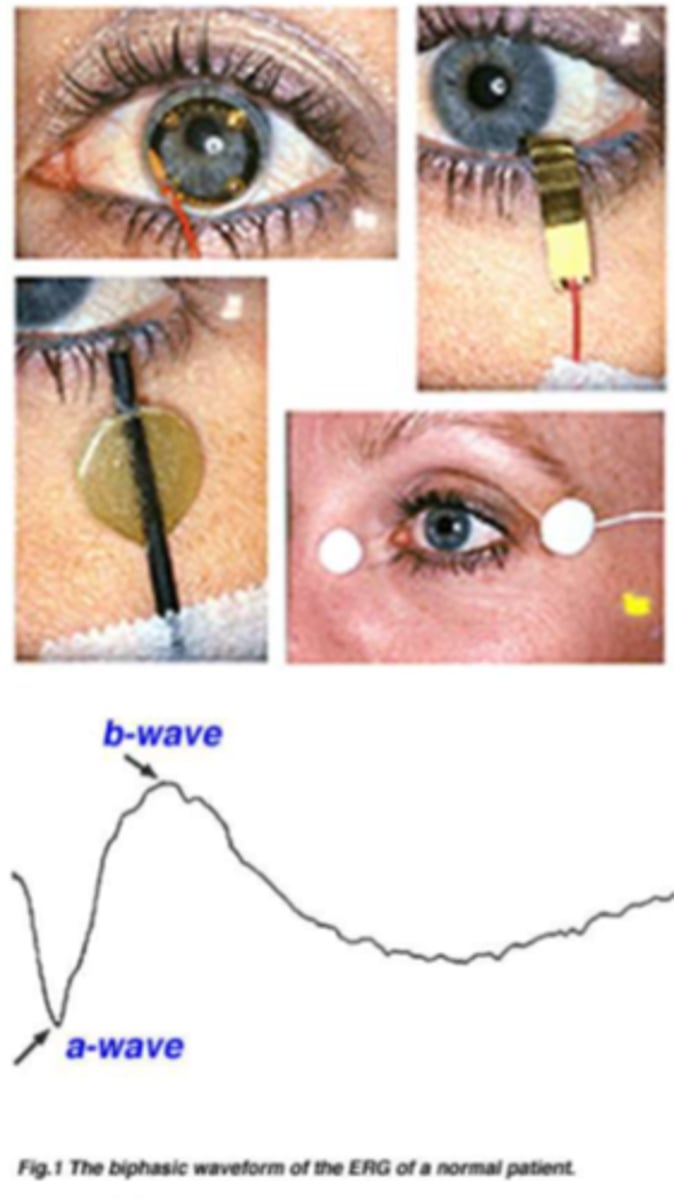
What do the a and b wave show on ERG?
a wave = first negative component = photoreceptors
b wave = bottom of a wave to peak = bipolar and Muller cells

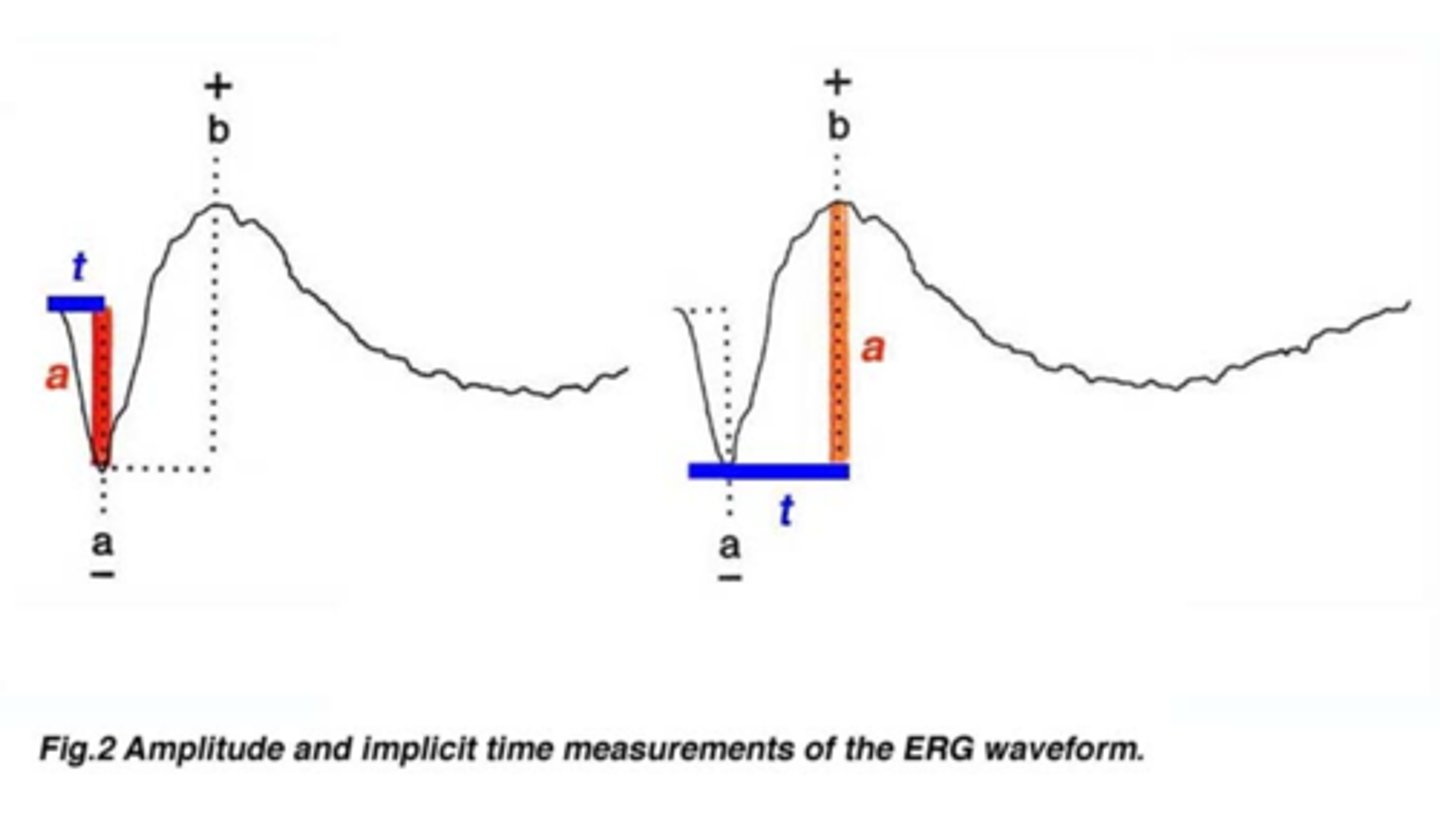
What are the 2 measures we look at on ERG?
amplitude of a and b wave = often reduced in disease
implicit time from flash to wave onset = often increased in disease
What is the purpose of white flash on ERG?
results in a mostly rod response
What is the purpose of colour stimuli on ERG?
cone response
What is the purpose of rapid flicker on ERG?
cone only response since rods cannot follow a fast flicker
What is the purpose of dark-adapted with bright flash on ERG?
mostly a rod response
What is the purpose of light-adapted on ERG?
mostly a cone response
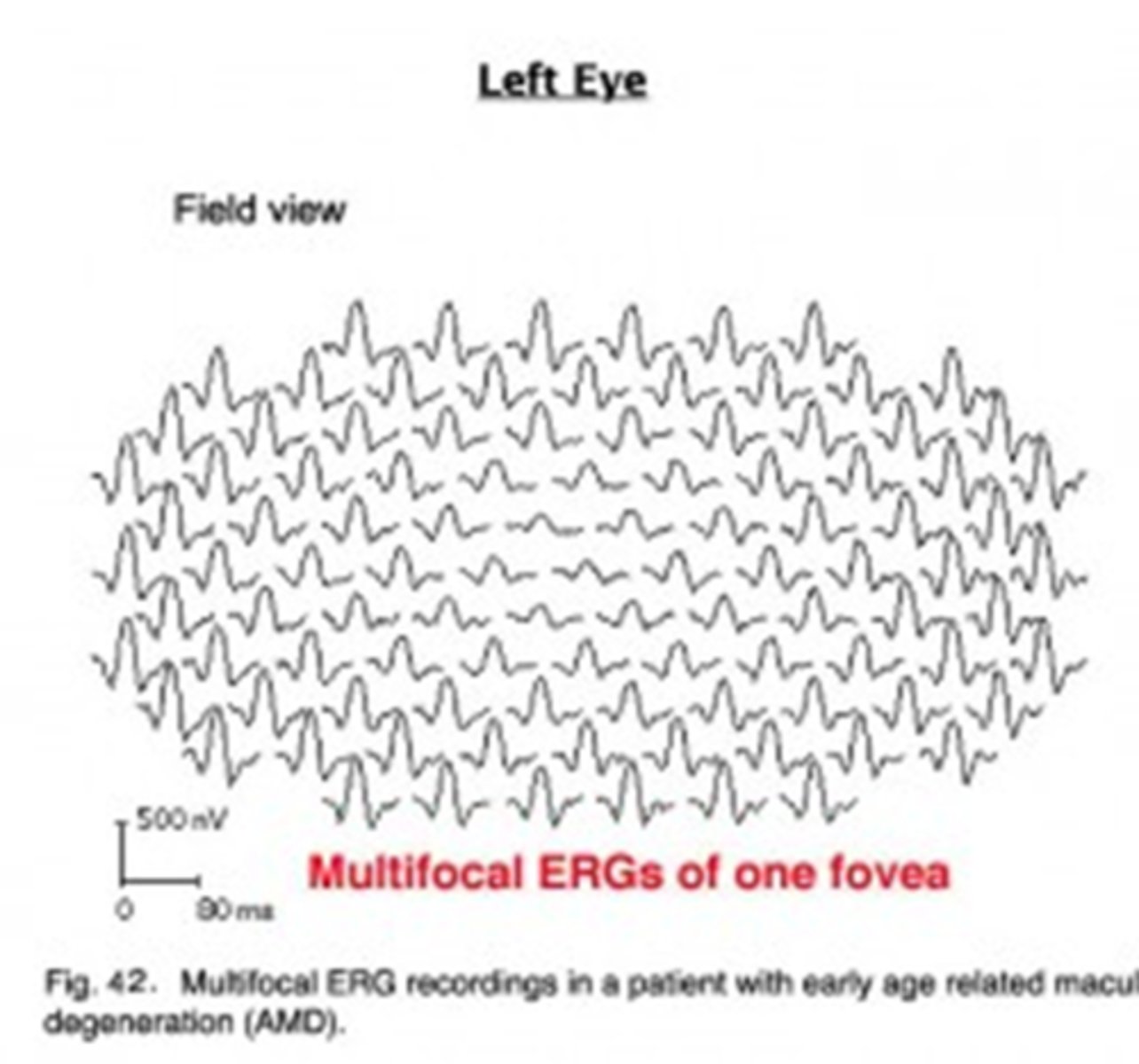
What is the purpose of multifocal testing on ERG?
assesses retinal activity in small areas of retina
What is the purpose of pattern testing on ERG?
assesses ganglion cell activity
What is an EOG?
measures the potential between cornea and Bruch's, specifically at the RPE and mid-retina
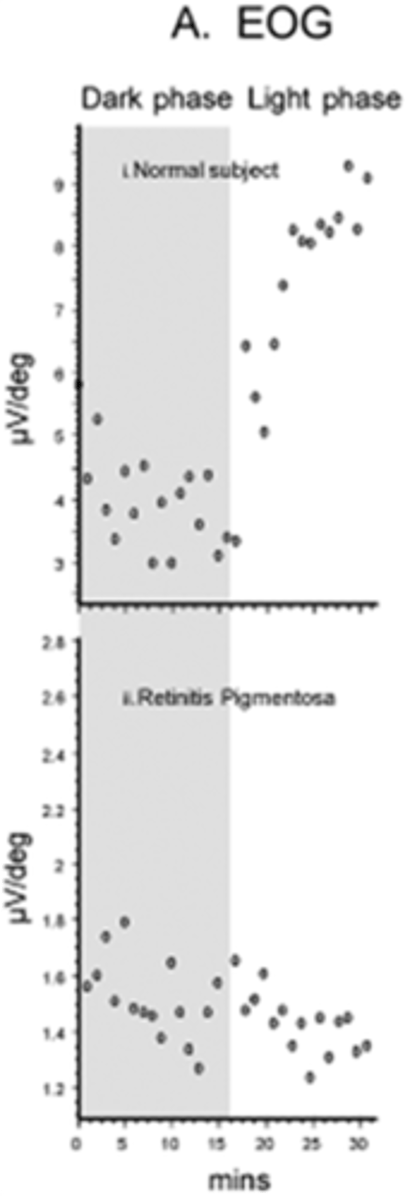
Does abnormal ERG and EOG typically occur together in retinal disease?
yes
in Best's disease where there is diffuse RPE atrophy, the ERG may be normal but the EOG is abnormal
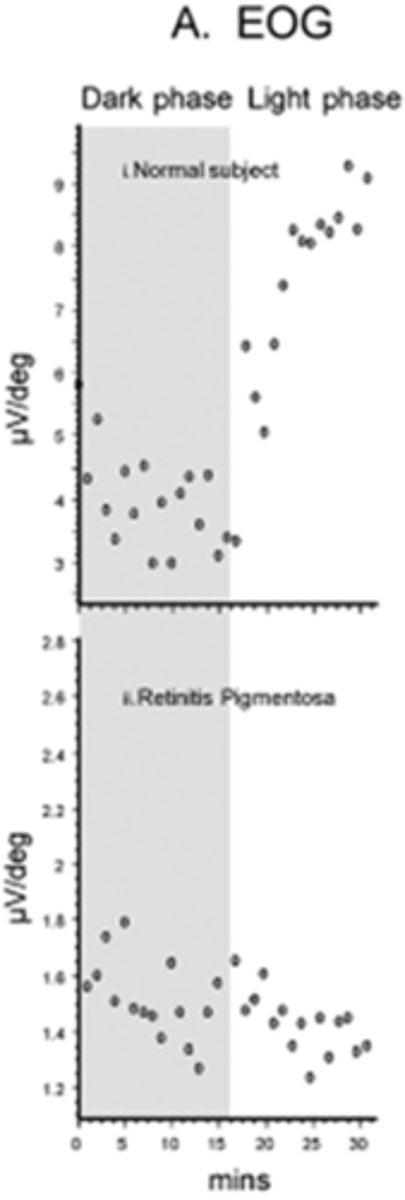
What is the dark trough vs light peak seen in EOG?
dark trough = 15min in darkness = depends on integrity of RPE, cornea, lens, CB
light peak = 25min in light = depol of basal RPE membrane

How do we calculate the Arden ratio in EOG?
= light peak / dark trough
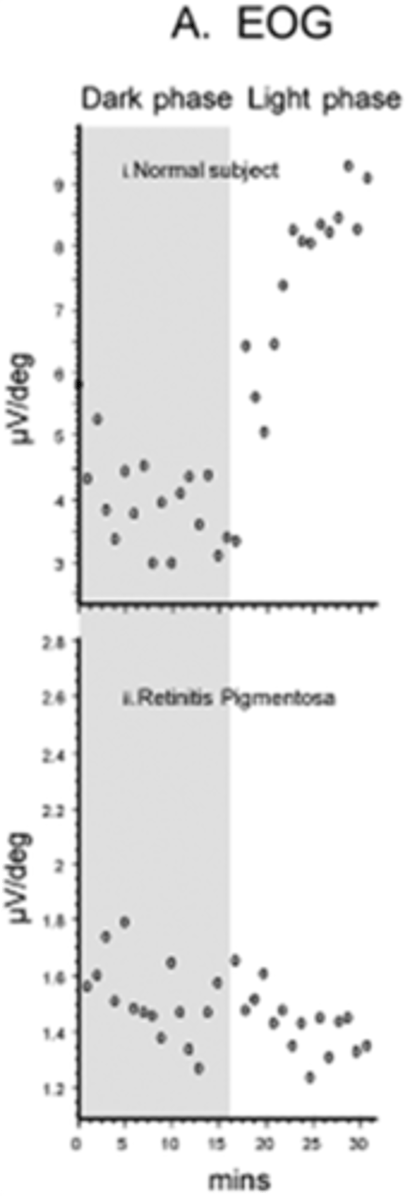
What is the lower limit for Arden ratio in normal subjects?
lower limit of 1.8 roughly (below 1.65 is significantly abnormal)
When do we perform genetic testing? 2 situations.
suspected IRD that genes have been identified for
predictive/carrier testing for those who are asymptomatic but have an affected family member (but caution if there is no tx)
What are the 3 reasons we may do genetic testing?
confirm Dx or distinguish between different diseases
improve management with better prognosis, less other testing, more therapies
genetic counseling by identifying inheritance patterns
What are 2 cautions against genetic testing?
do not use to R/O an IRD since not all genes for all diseases are on every panel
discourage testing of adult-onset conditions for minors if there is no available therapy, may worry parents unnecessarily
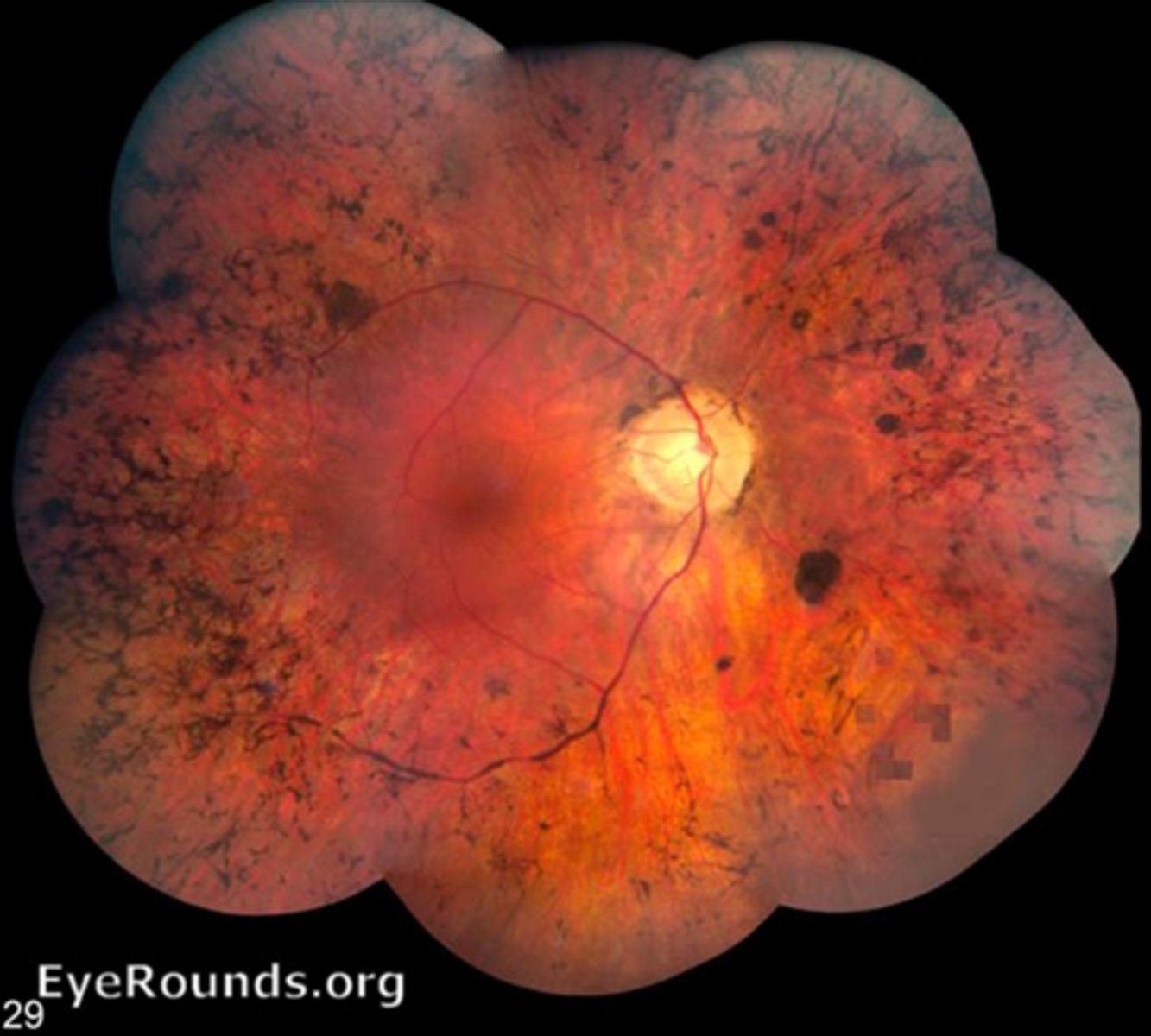
What is retinitis pigmentosa (RP)?
group of inherited disorders with diffuse progressive bilateral dysfunction of rods, then cones and RPE later (due to PR apoptosis and loss of OS)
What are the main 3 genetic inheritance patterns of RP?
AR in 50-60%
AD in 30-40%
X-linked in 5-15%
NOTE: >100 different genes may cause RP
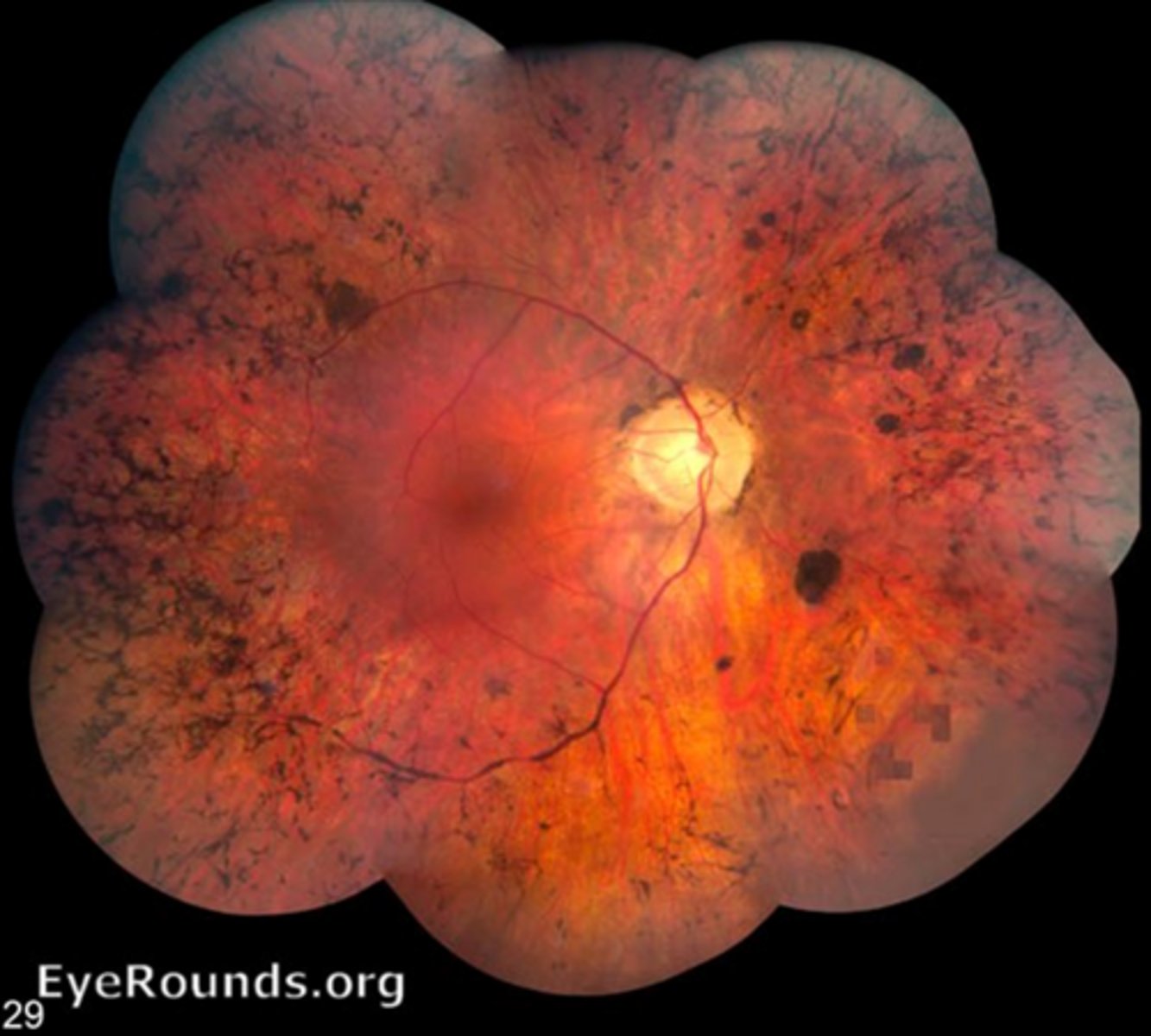
What is the clinical triad of RP?
artery attenuation due to reduced O2 demand in the retina
bone spicule pigment due to RPE cell migration
waxy ONH pallor
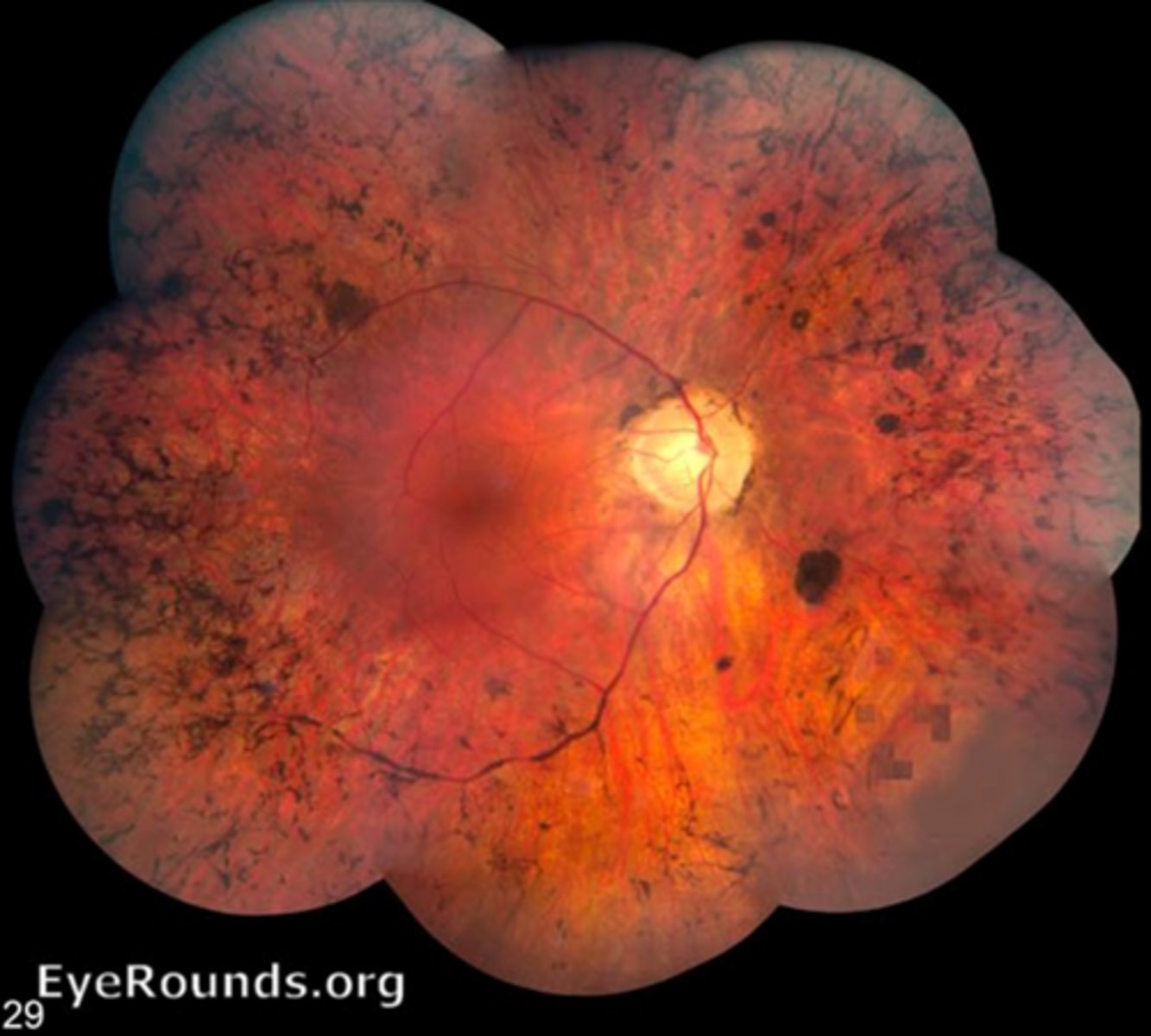
What are some other signs of RP?
vitreous cells
RPE depigmentation/atrophy
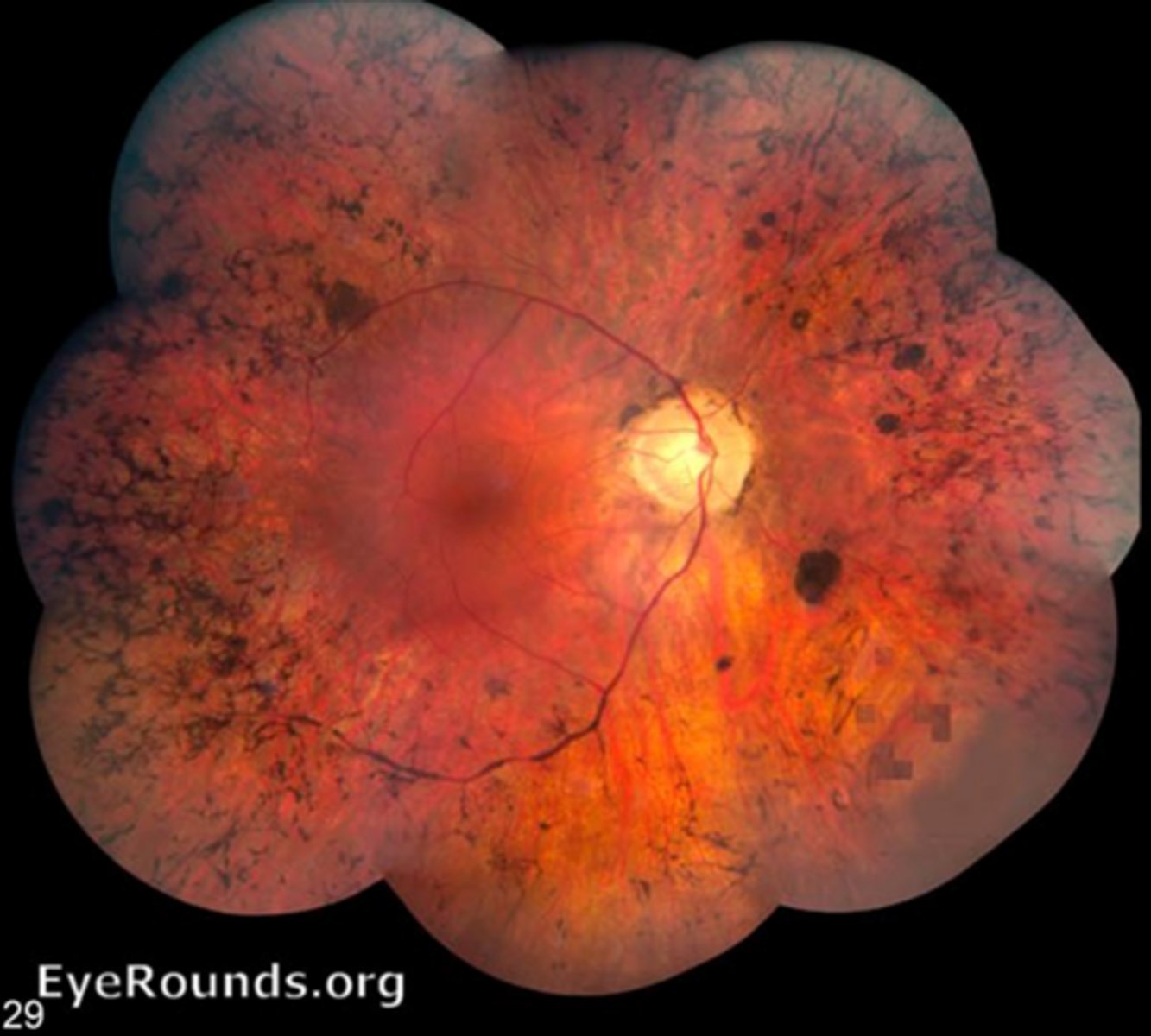
What are some symptoms of RP?
night blindeness from rod loss
progressive VF loss from midperiphery to far (ring scotoma!)
reduced contrast
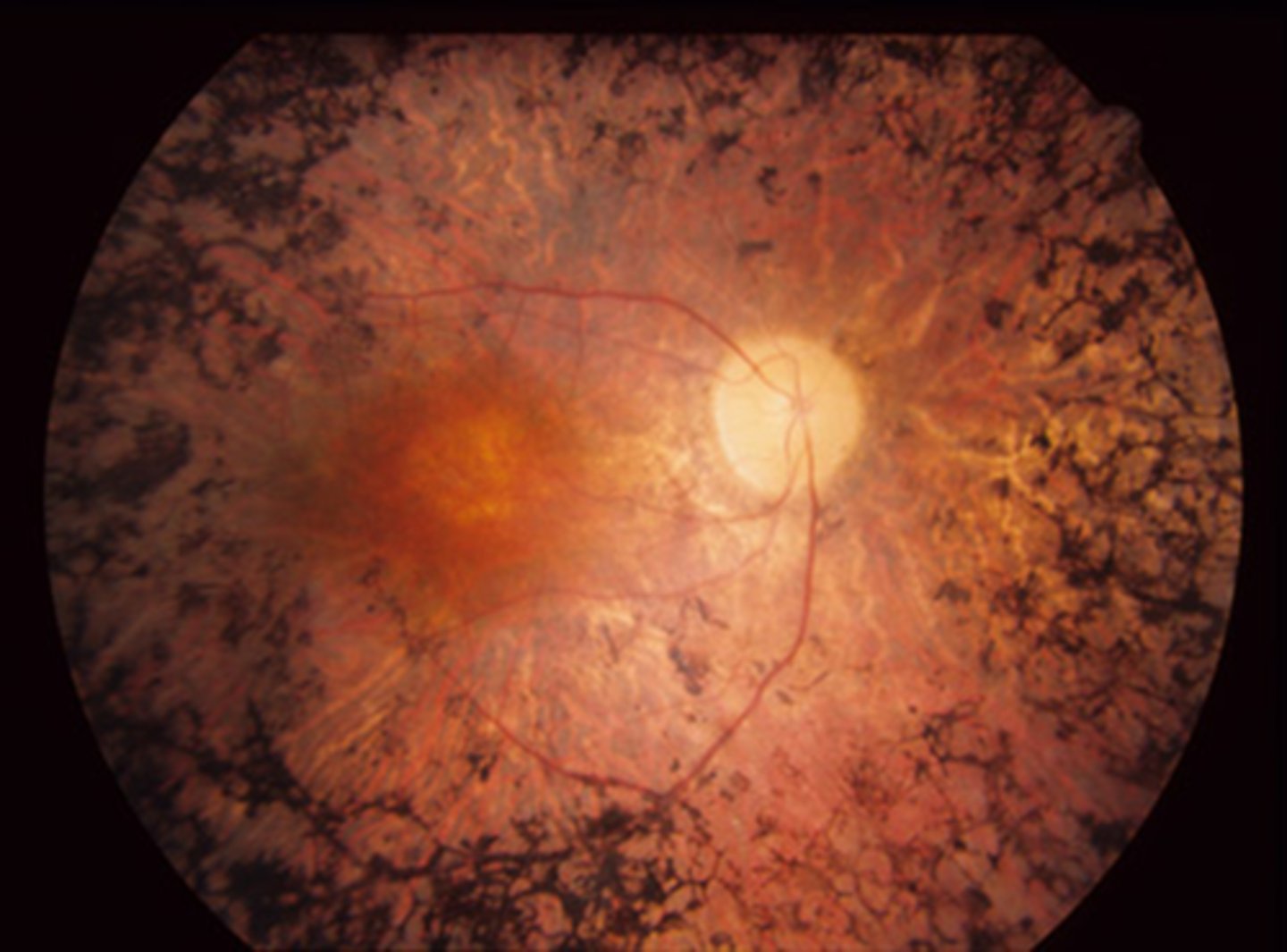
Describe the evolution of RP.
onset based on inheritance pattern = PR loss, then RPE changes = mid-peripheral followed by far-peripheral = central vision affected at end-stage disease
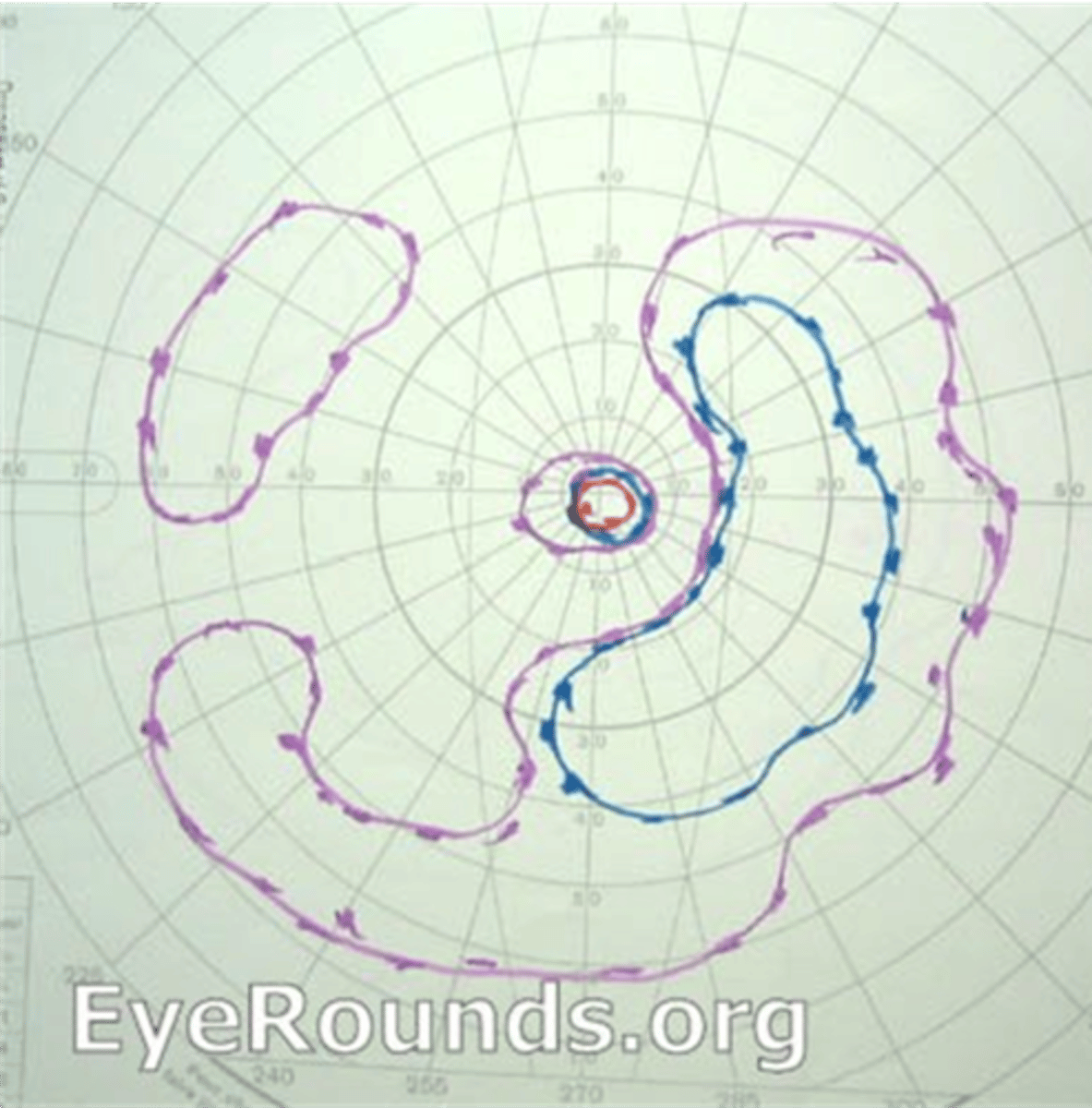
How does RP appear on VF?
isolated scotomas around 20deg from fixation = coalesce into a ring scotoma in midperiphery = expands quickly into far periphery, slowly into central fixation

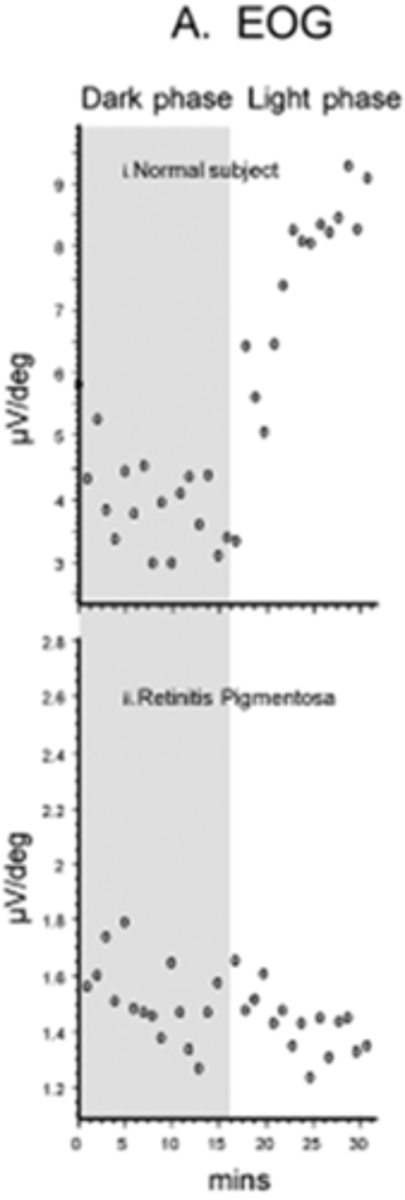
How does RP appear on EOG?
abnormal BUT note that ERG is typically better test bc more sensitive

How does RP appear on OCT?
cystic macular lesions, ERM, VMT in some RP pt's with reduced central VA - may have outer>inner retinal layer thinning
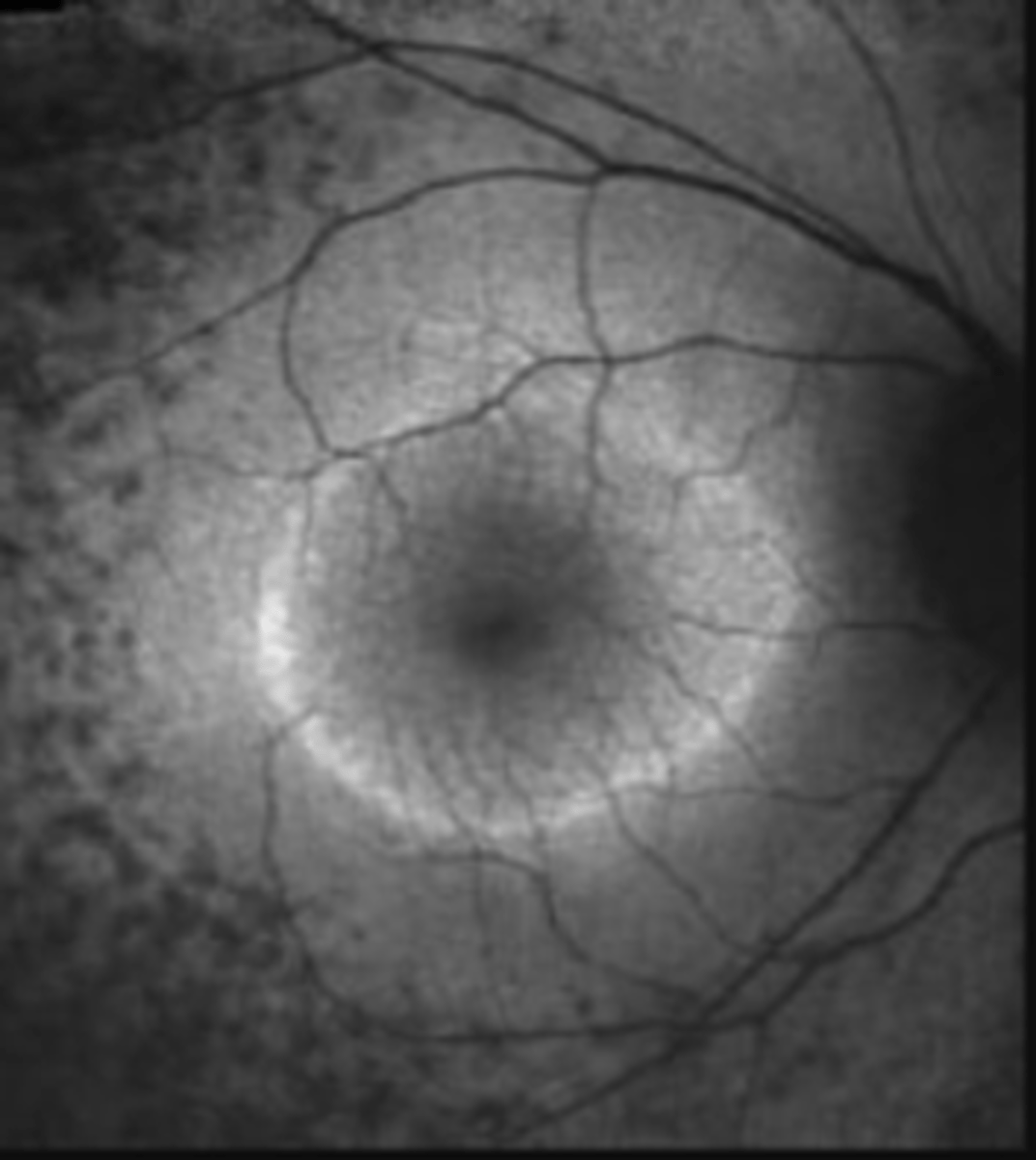
How does RP appear on FAF?
ring of hyperAF encircles fovea due to increased lipofuscin in RPE (PR degeneration)
hypoAF in periphery due to RPE atrophy
How does RP appear on genetic testing?
RPE65 gene variant (mostly seen in Leber's but some RP also has it)
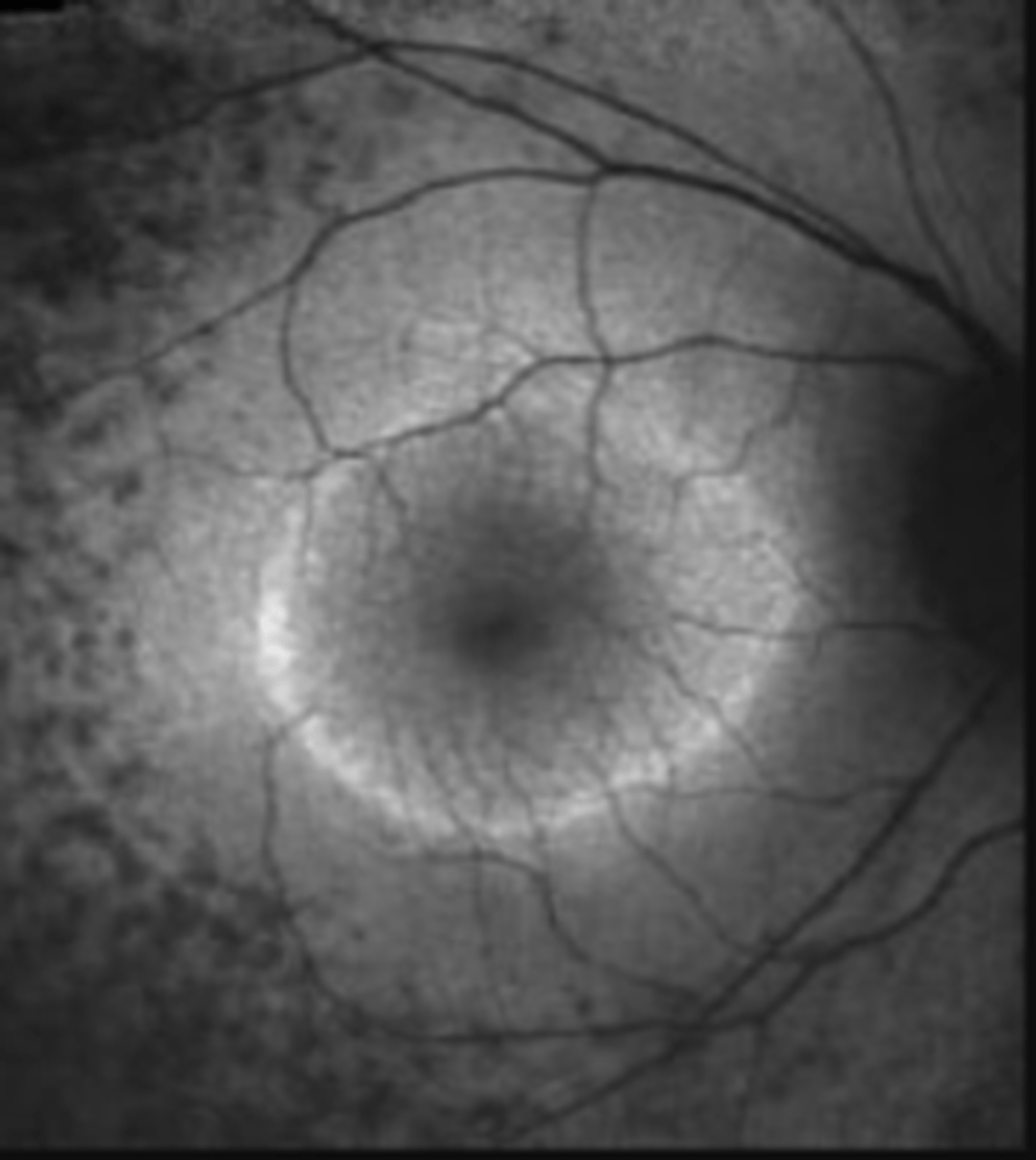
How does RP appear on ERG?
reduced a and b wave
normal or prolonged implicit time
NOTE: may be undetectable in advanced disease
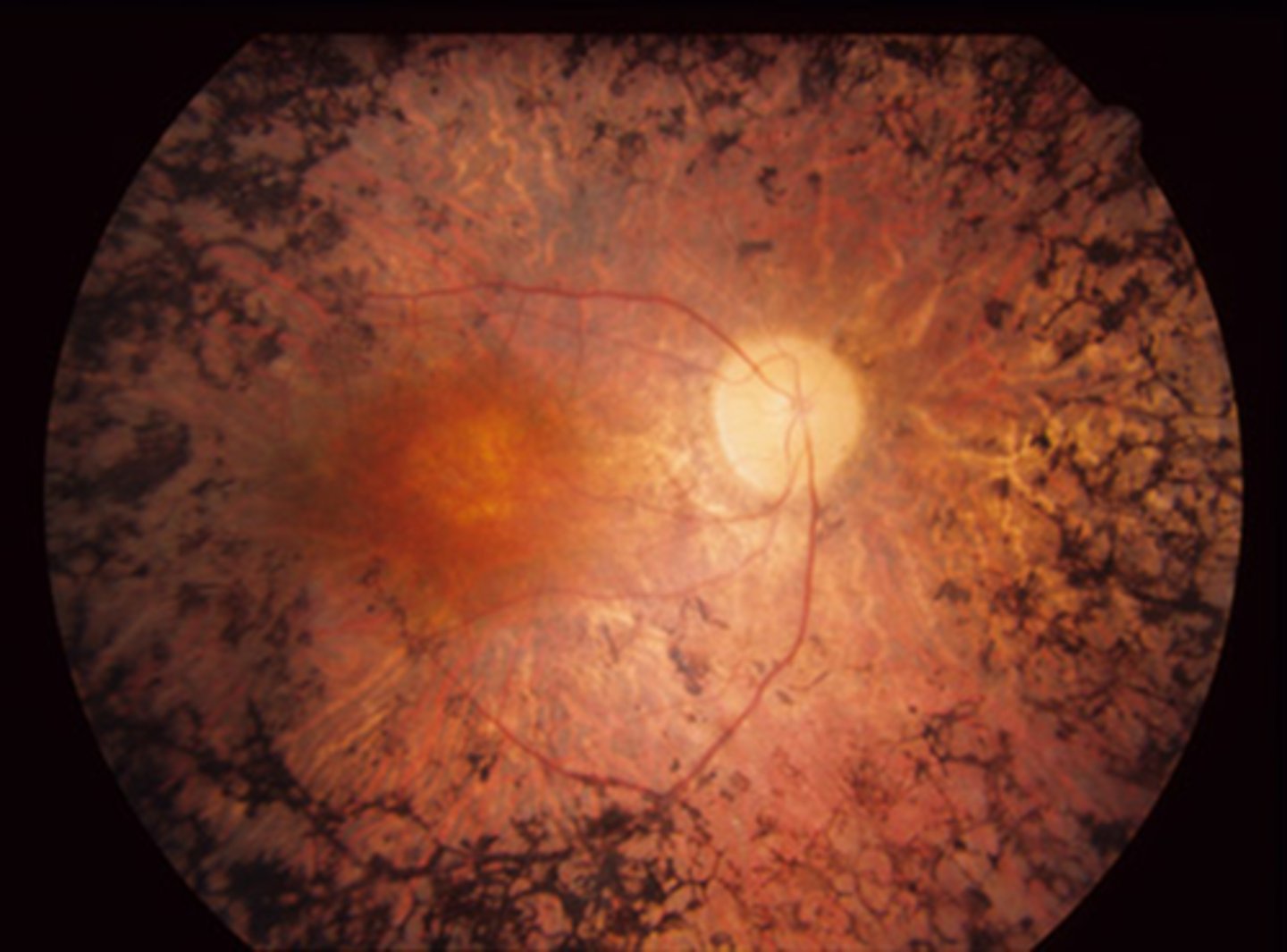
What are 2 possible complications of RP?
CME
PSC
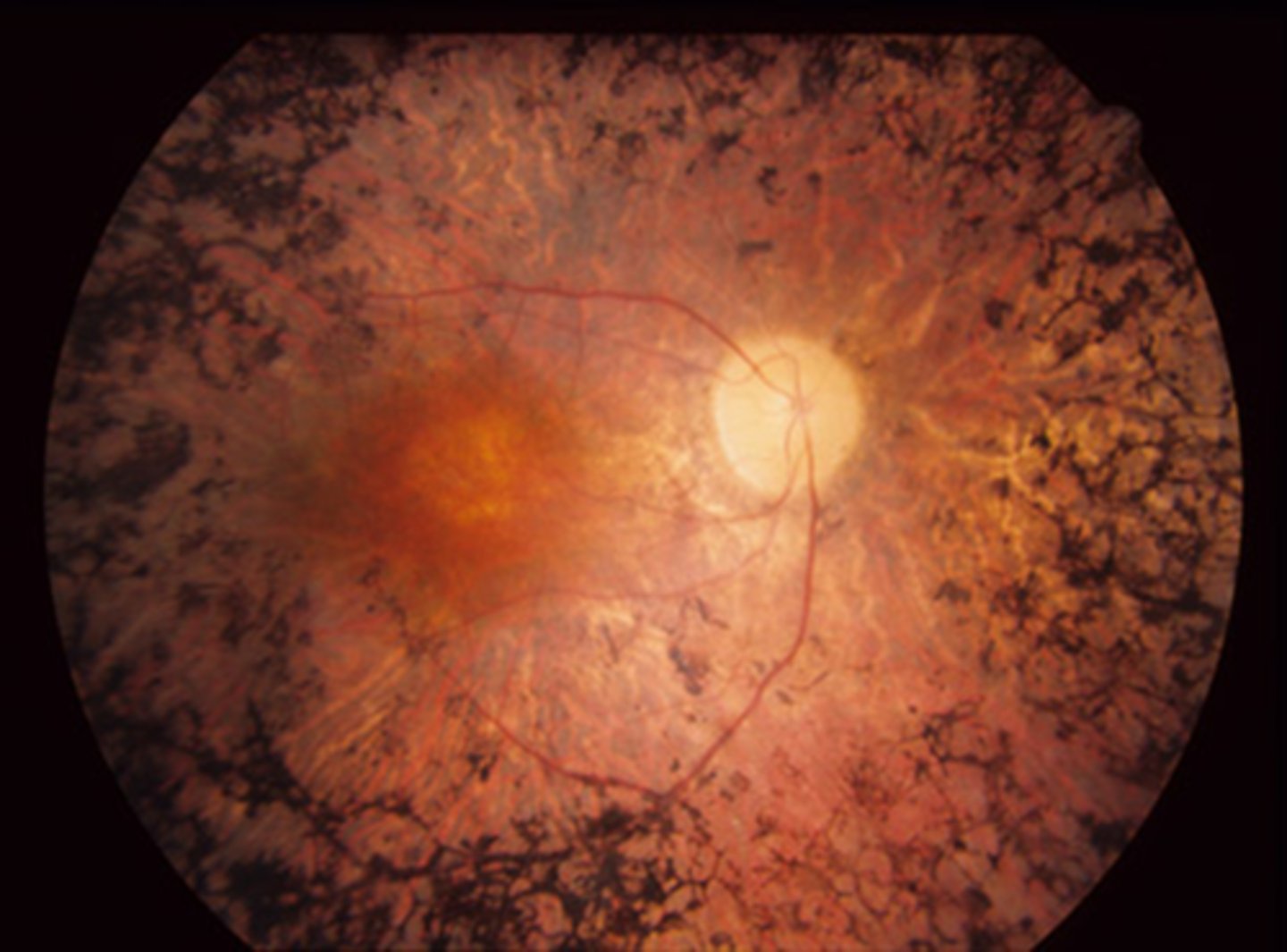
Which gene specifically is important to note for RP as there is genetic therapy available (esp for young pt's)?
RPE65
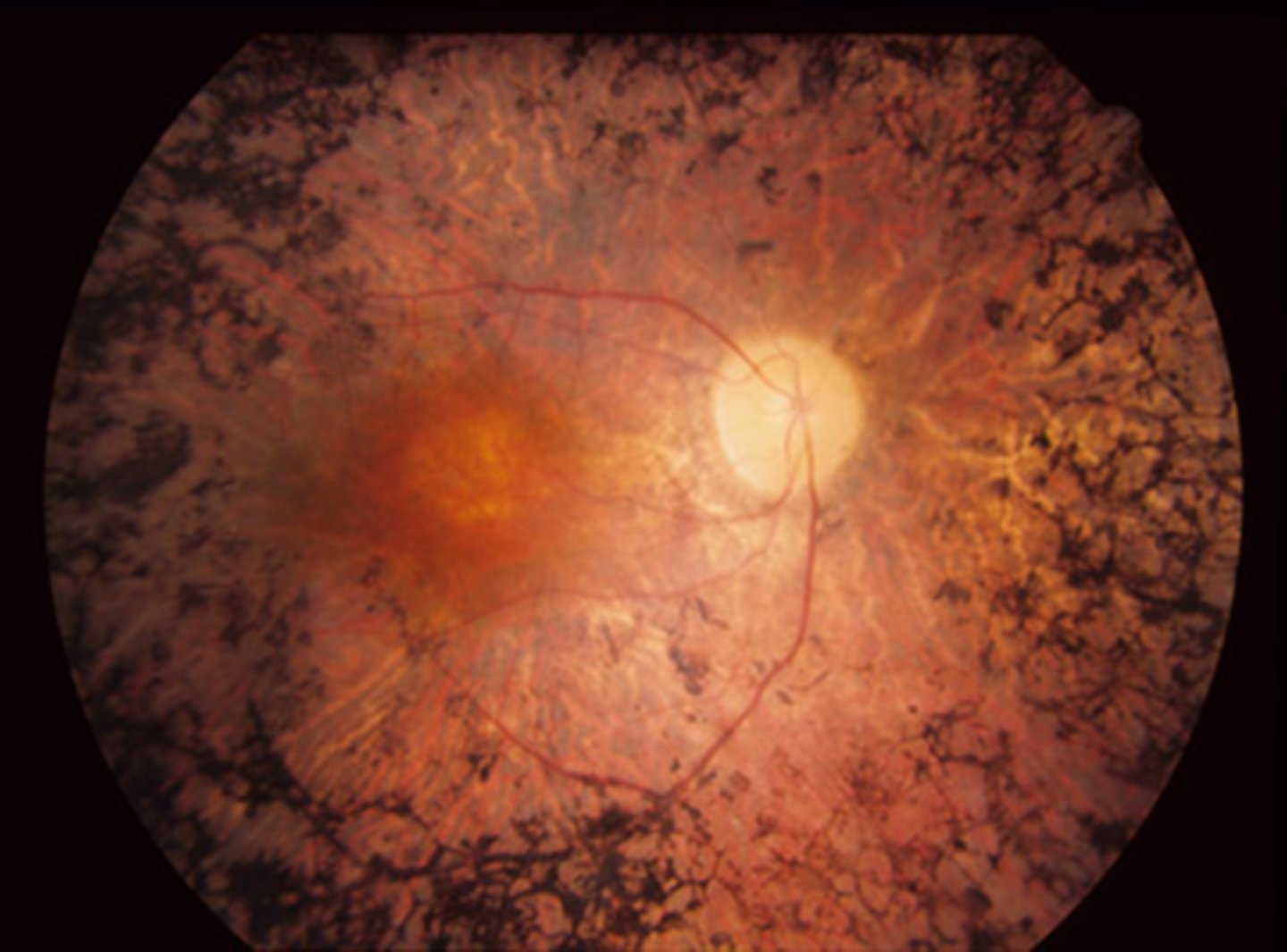
What is the tx for RP?
Luxturna gene therapy for RPE65
CAIs for CME - topical or oral
Vit A palmitate in high dosage of 15,000 IU (marginal benefts of 2% slowed progression, lots of risks like liver damage)
retinal prosthesis
LV referral
CAT Sx if PSC develop
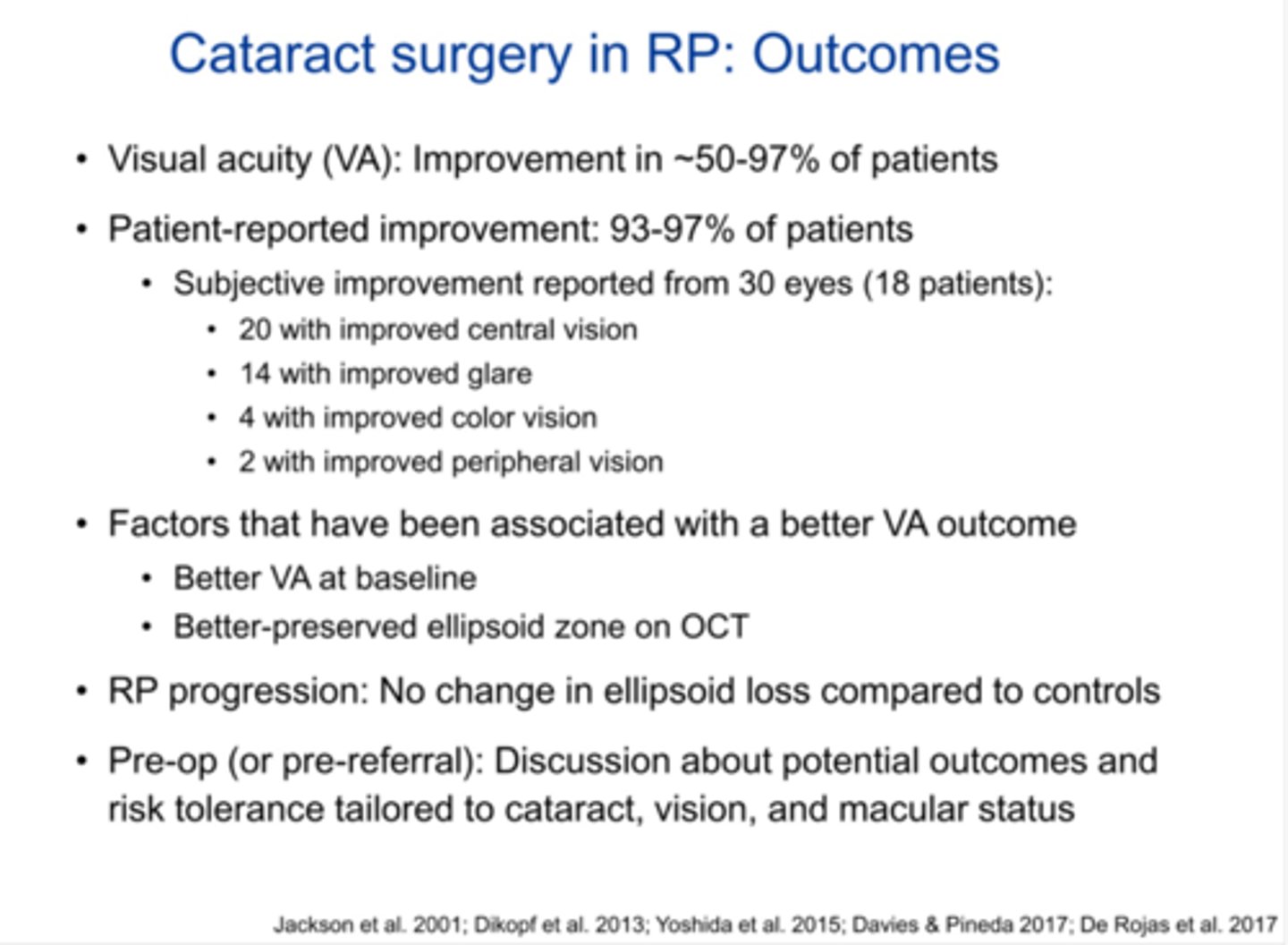
What are some benefits of performing CAT Sx in pt's with RP?
visual improvements can include VA, glare, color vision, peripheral vision
better outcomes if better starting VA, more preserved ellipsoid zone on OCT
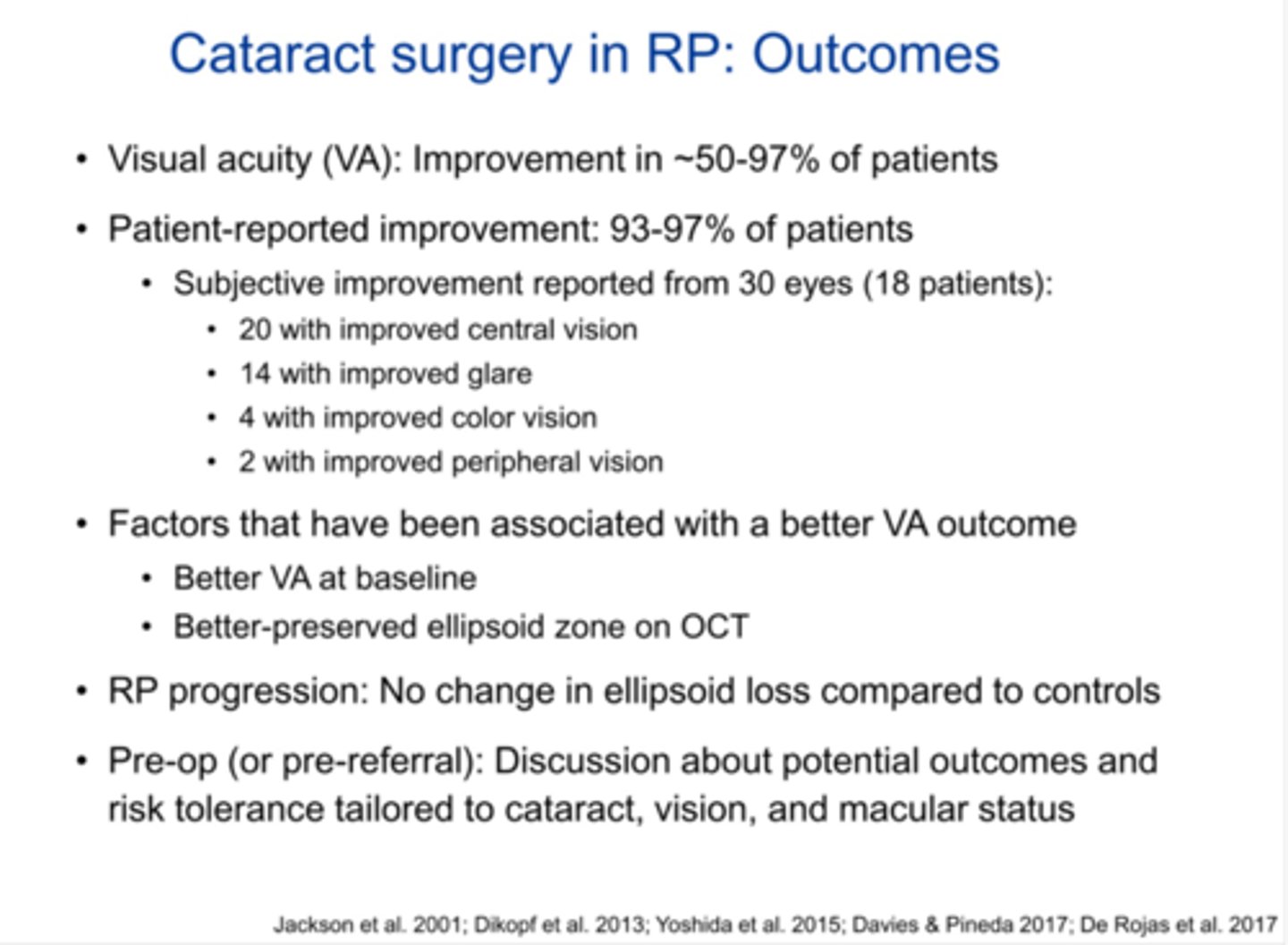
What are 4 complications of performing CAT Sx in pt's with RP?
zonular weakness in 10-20% of patients
light toxicity = need to decrease to 60% light intensity and cover light when not needed
post-op CME in 10-15% of patients = may need prolonged NSAID, steroid, CAI
PCO in 60-84% of patients = may need YAG
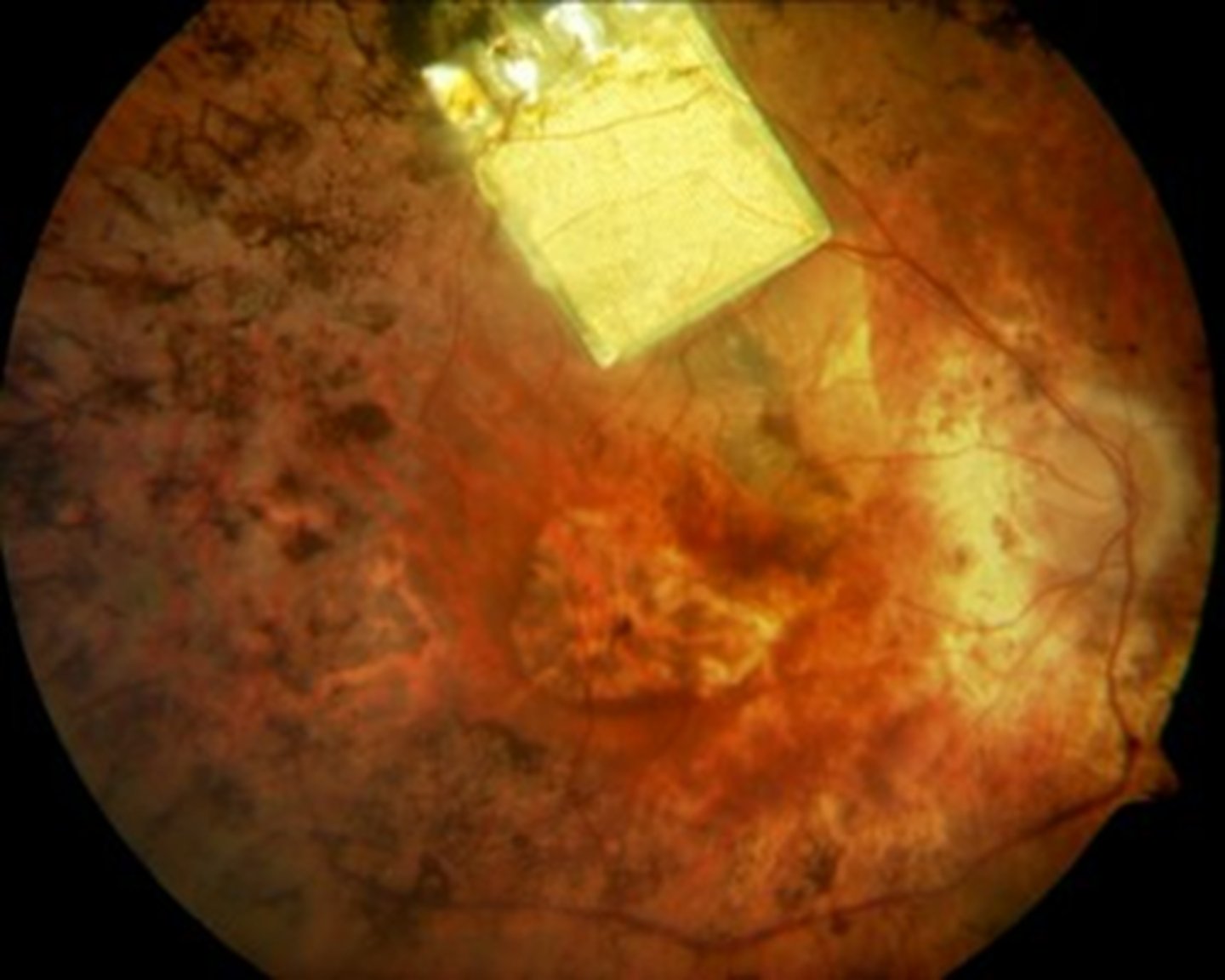
What is RP sine pigmento?
variant of RP = absence of bone-spicule-like pigmentary changes, but still have artery attenuation and atrophy of RPE
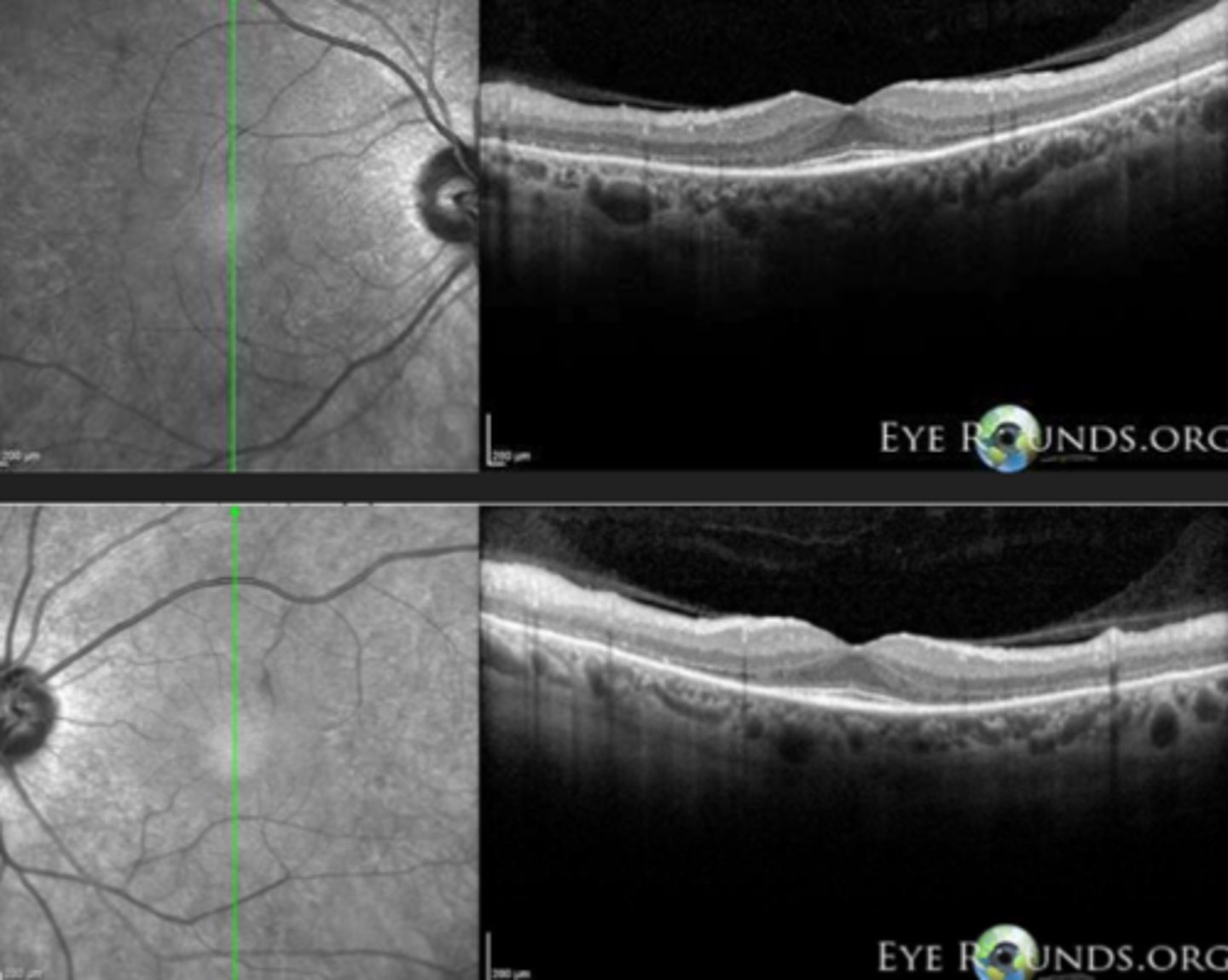
What feature of RP sine pigmento is seen here?
perifoveal loss of PR's and RPE on OCT = ring scotoma very close to fixation seen on HVF
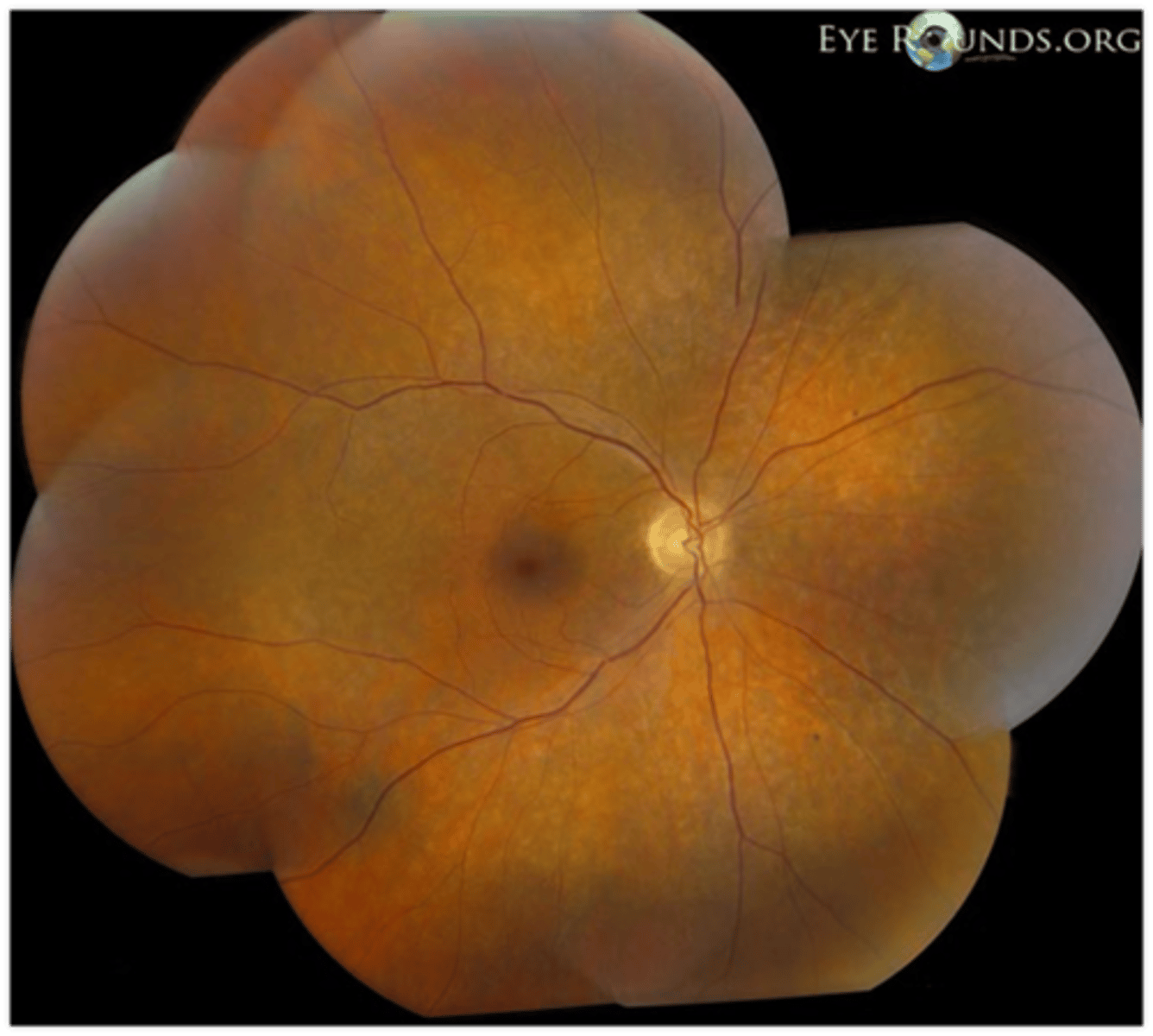
What is sectoral RP?
variant of RP = only certain regions show degeneration, but is still symmetrical between eyes
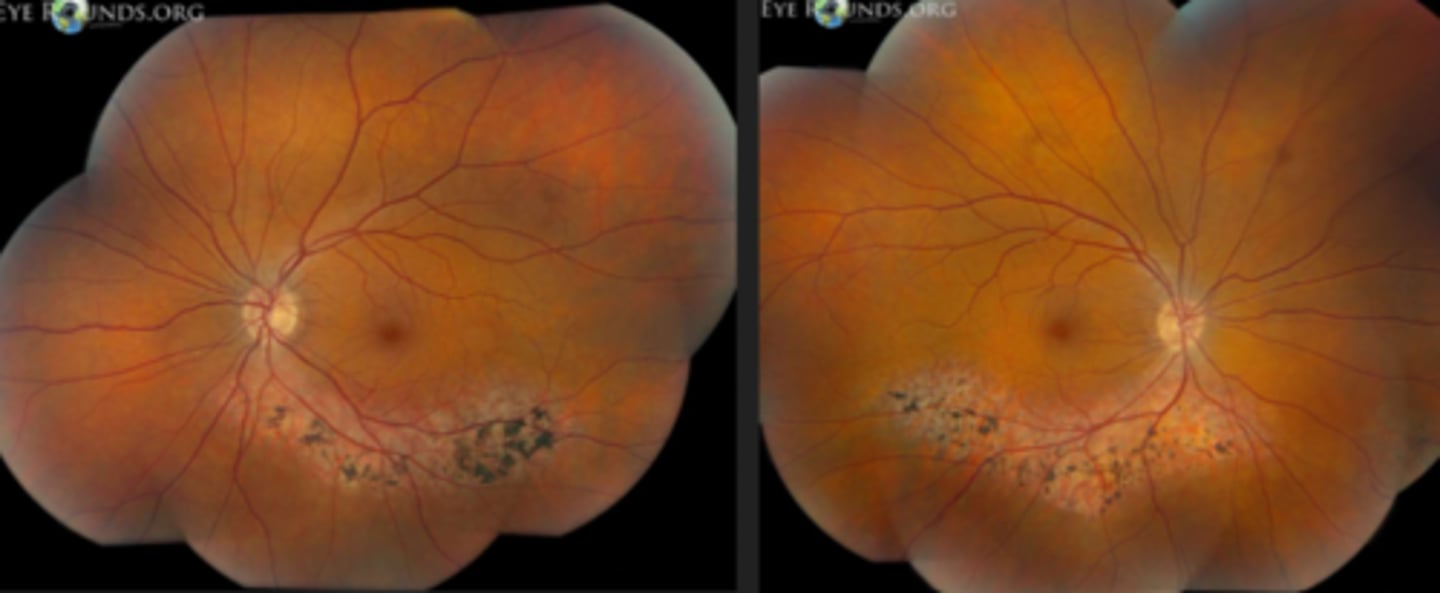
What feature of sectoral RP is seen here?
still has PIL loss and RPE thinning on OCT

What are the 8 main systemic associations seen with RP?
Usher syndrome
Alport syndrome
Kearns-Sayre syndrome
Bardet-Biedl syndrome
Refsum disease
Abetalipoproteinemia
Alstrom disease
Cockayne syndrome
What is Usher syndrome sometimes seen with RP?
AR genetic condition resulting in RP and deafness

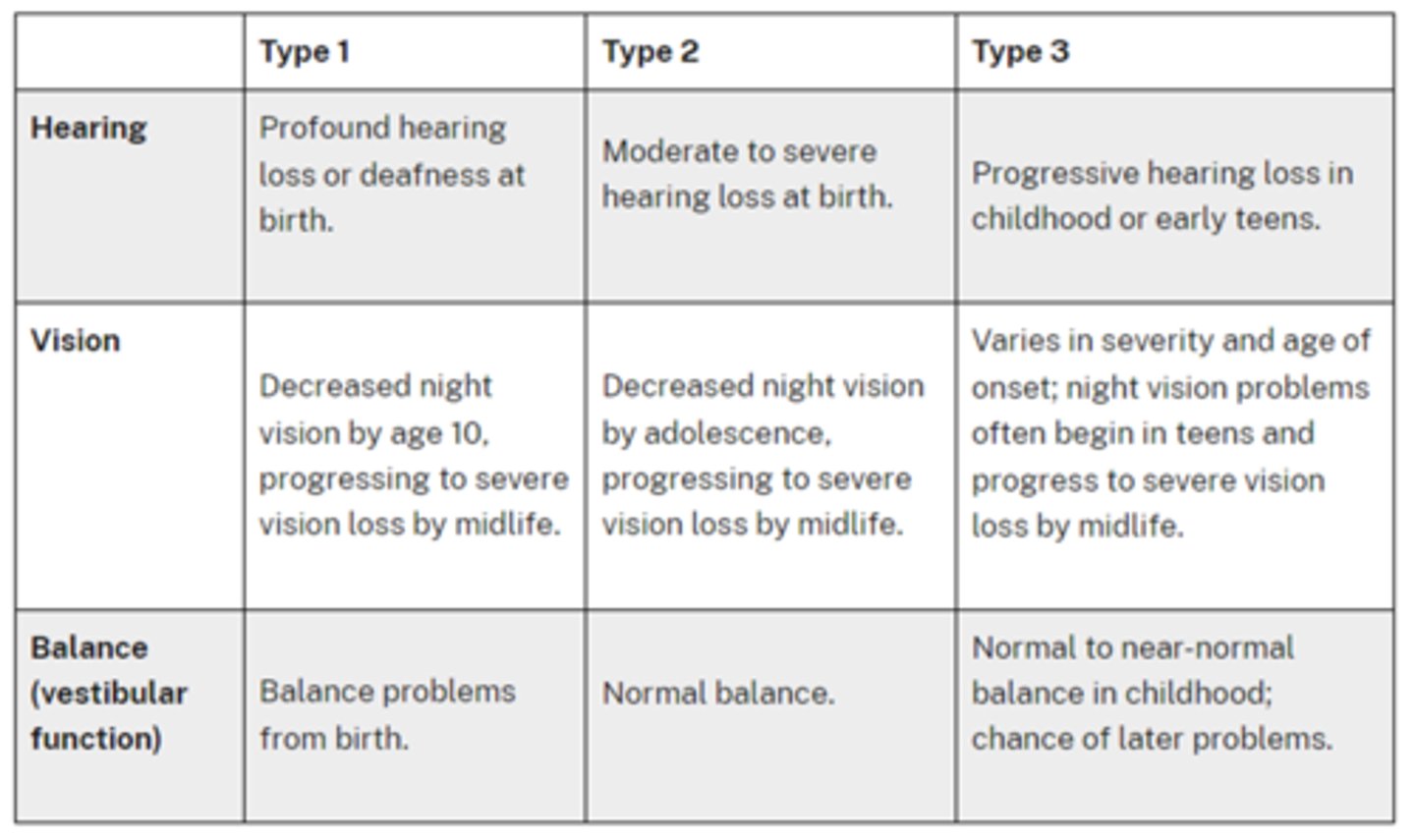
What are the 3 main types of Usher syndrome associated with RP?
type 1 = severe hearing & balance loss at birth, nyctalopia by age 10, vision loss later in life
type 2 = hearing loss at birth, nyctalopia by adolescence, vision loss later in life, NORMAL balance
type 3 = progressive hearing loss in childhood, nyctalopia by adolescence, vision loss later in life, NORMAL balance
What is Alport syndrome sometimes seen with RP?
X-linked, AR, or AD genetic condition that affects type IV collagen in early childhood = deafness, RP, kidney disease
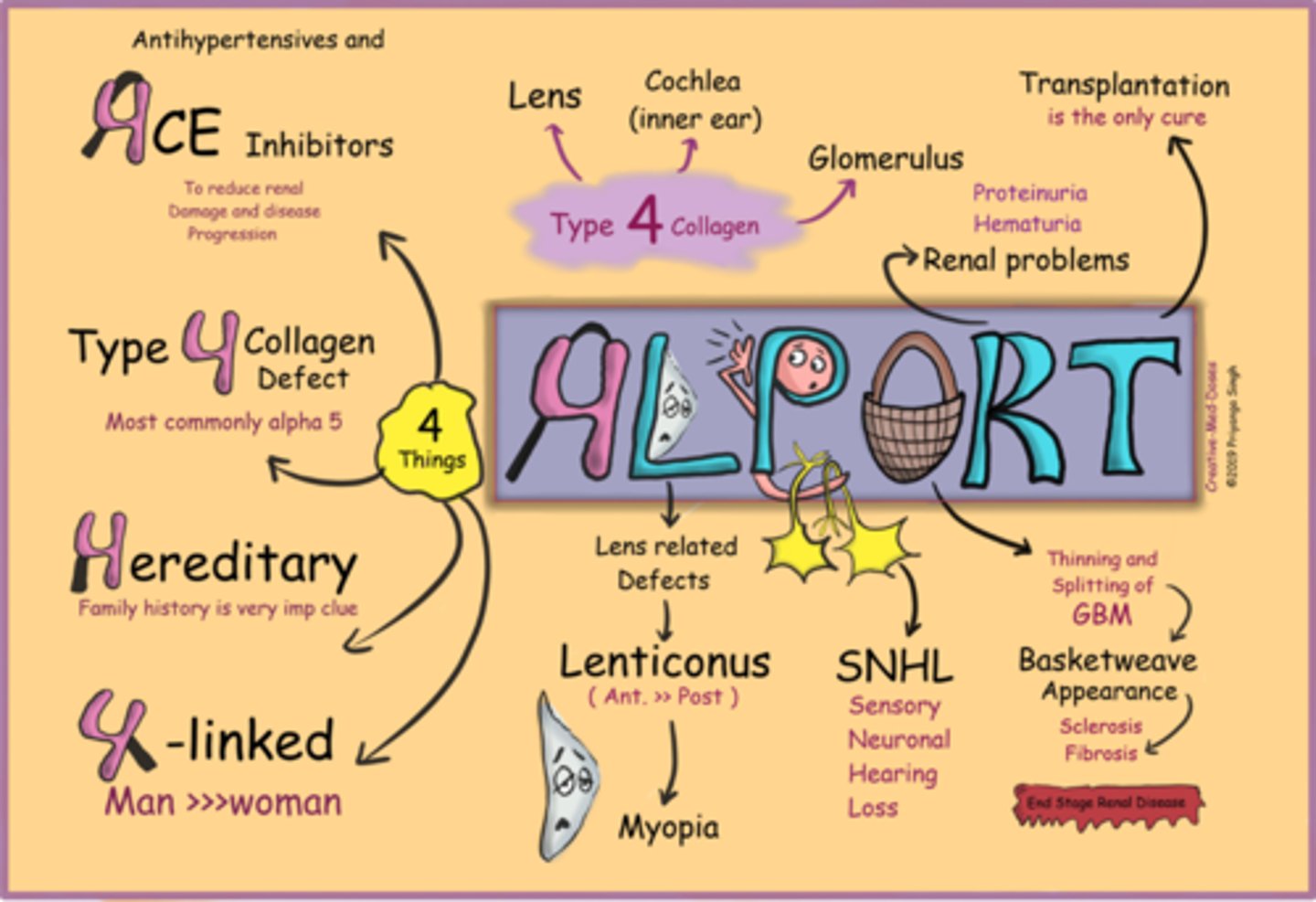
Aside from genetic testing, how can we dx Alport syndrome?
kidney biopsy
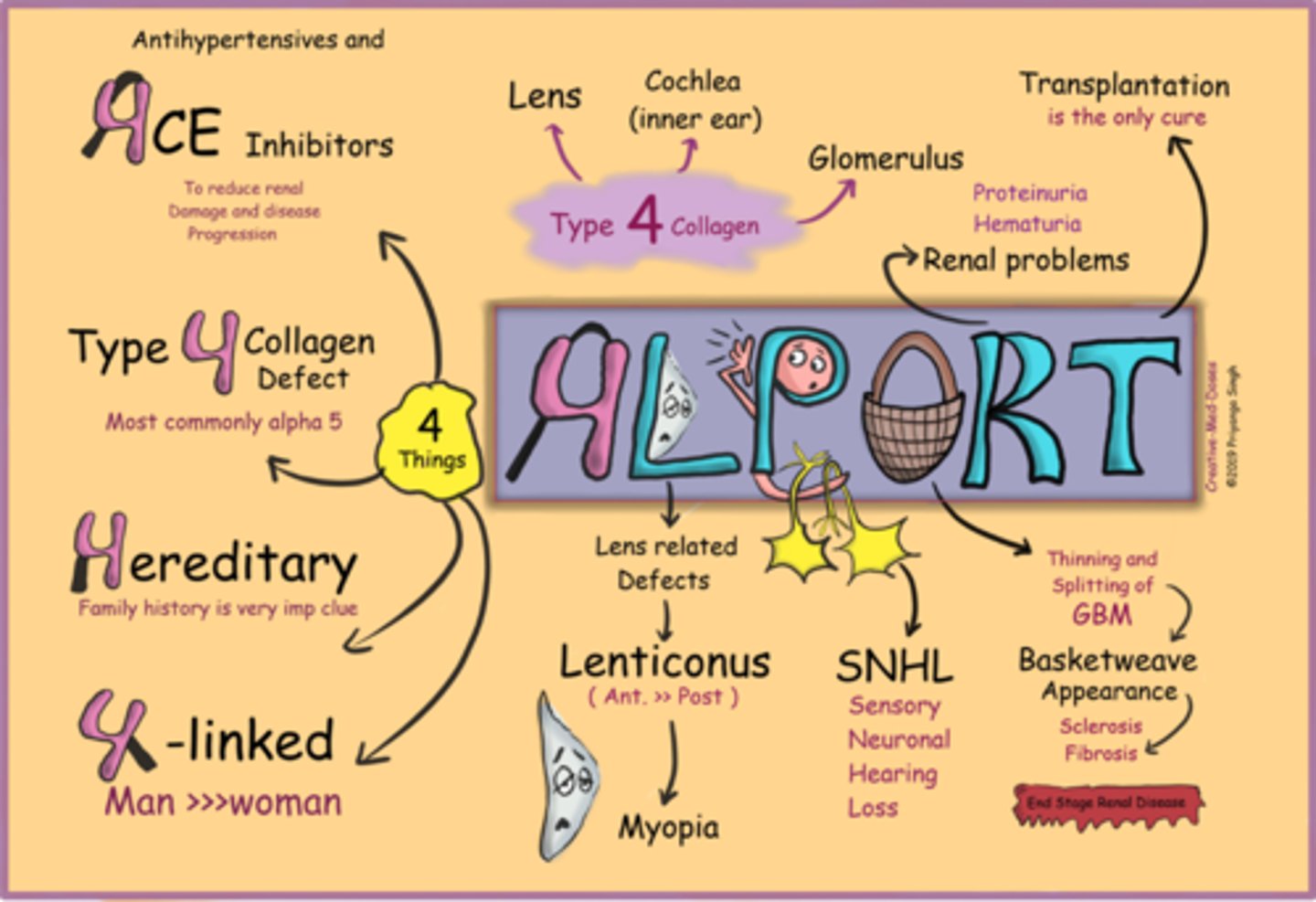
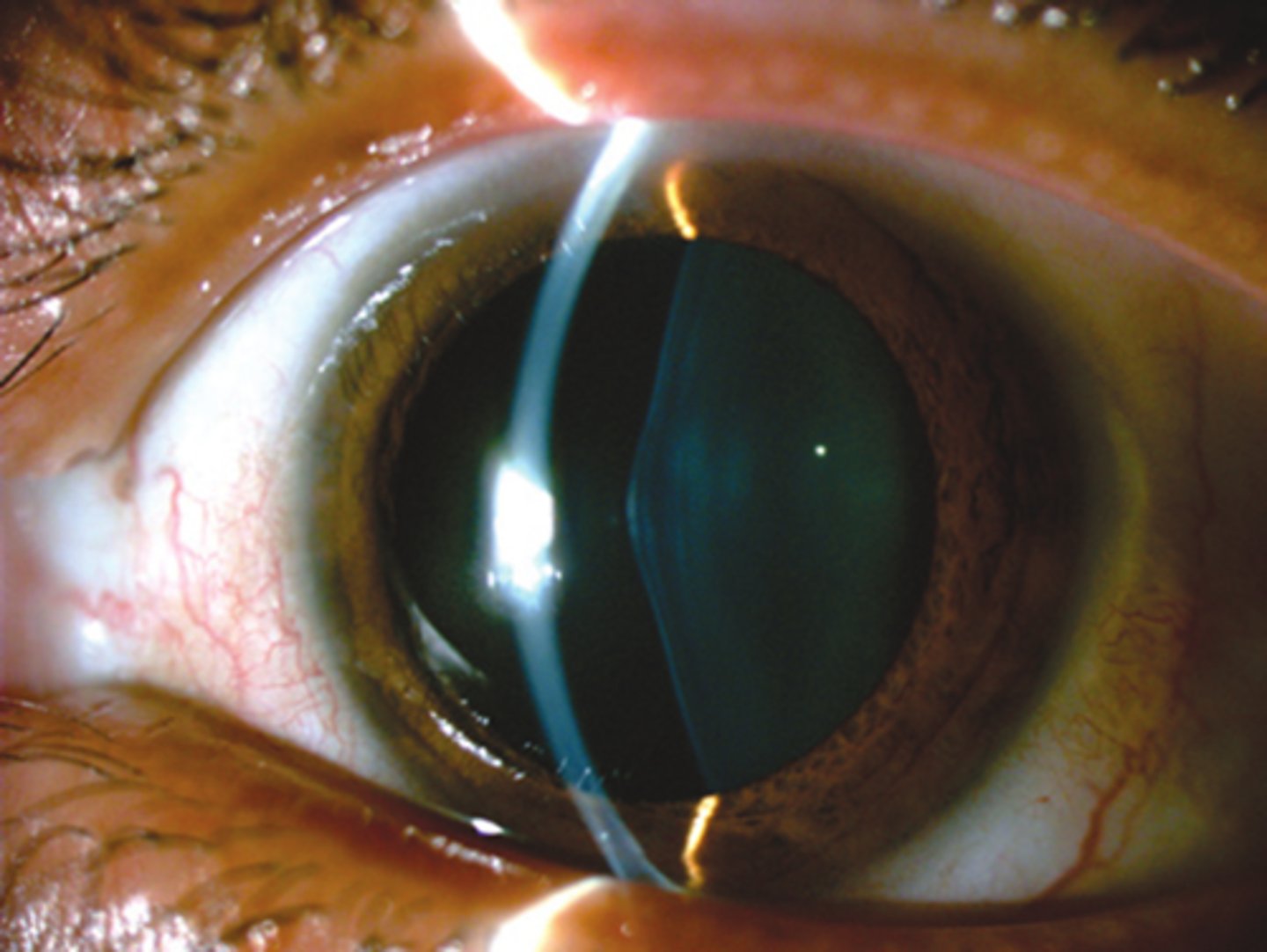
Aside from deafness, RP, and kidney disease, what other finding of Alport syndrome is seen here?
anterior lenticonus
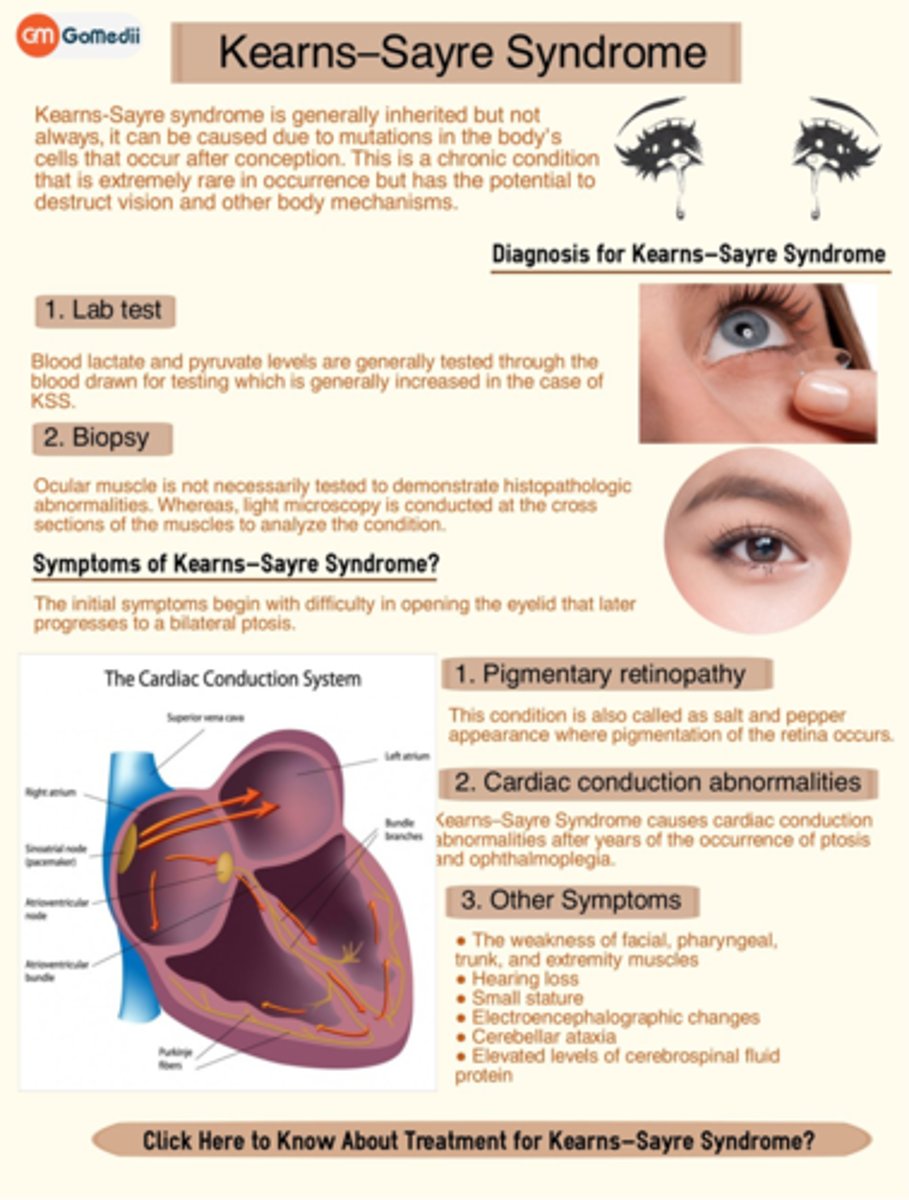
What is Kearns-Sayre syndrome sometimes seen with RP?
spontaneous or inherited mutation causing impaired ATP production in mitochondria = NM dysfunction by age 20 onset
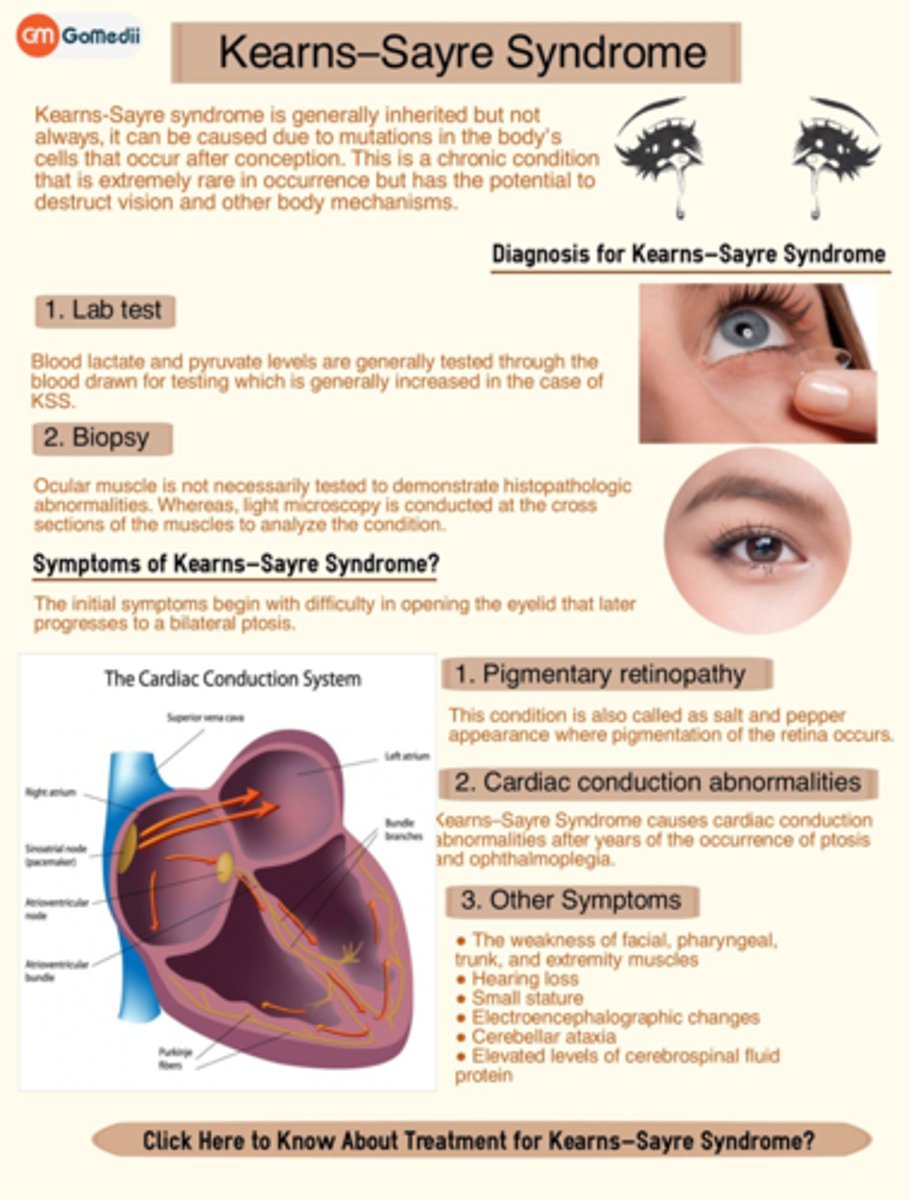
Aside from genetic testing, how can we dx Kearns-Sayre syndrome?
skeletal mm biopsy will show ragged red fibers due to abnormal mitochondria
CSF test will show protein >1mg/mL, lactate & pyruvate elevated in CSF and blood
What are the 3 main S/S seen in Kearns-Sayre syndrome?
RP or salt-and-pepper fundus
chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) = progressive paralysis of all EOMs
cardiac abnormalities from conduction deficits
ataxia
dementia
hearing loss
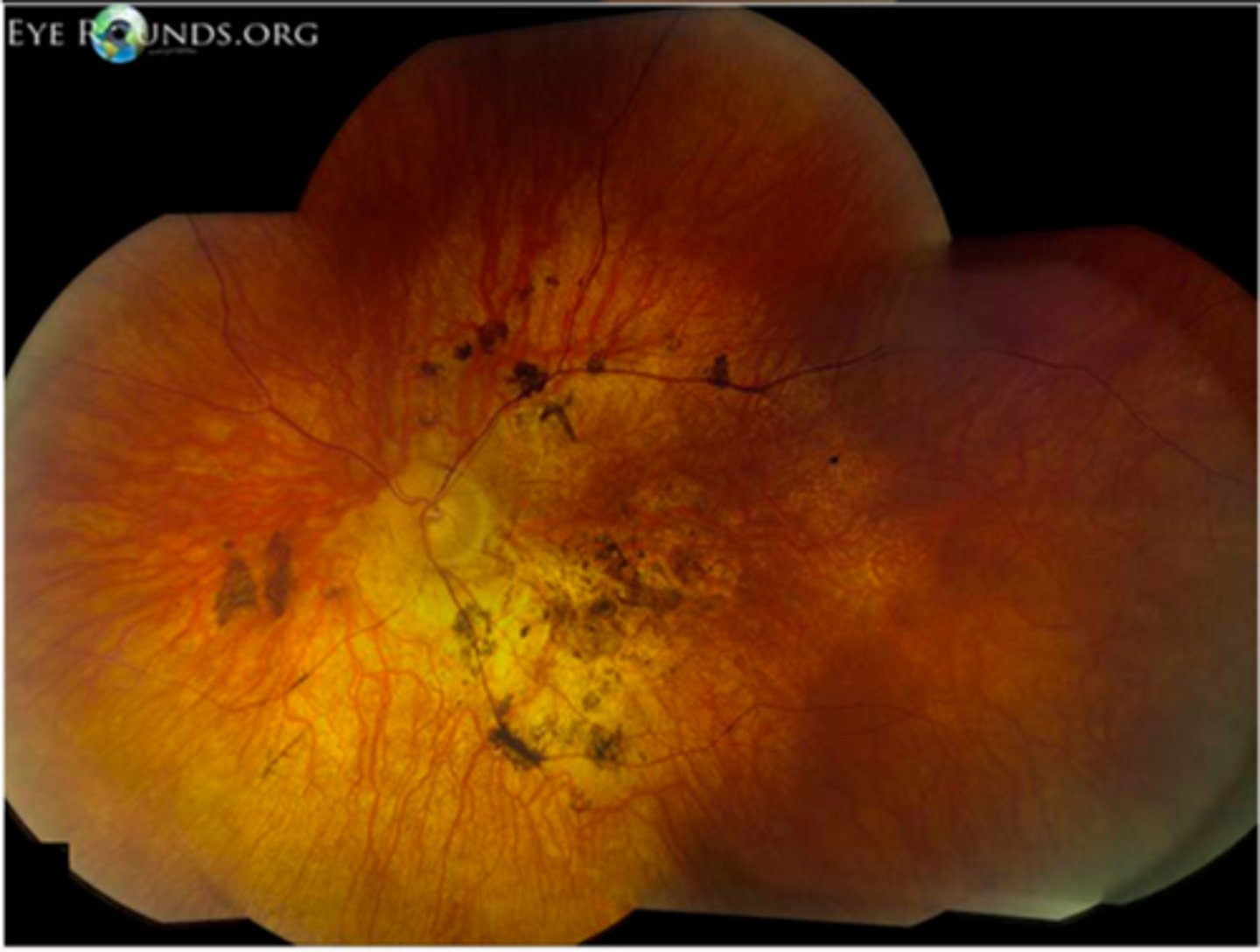
What is Bardet-Biedl syndrome sometimes seen in RP?
AR genetic condition causing ciliopathy throughout the body with juvenile onset
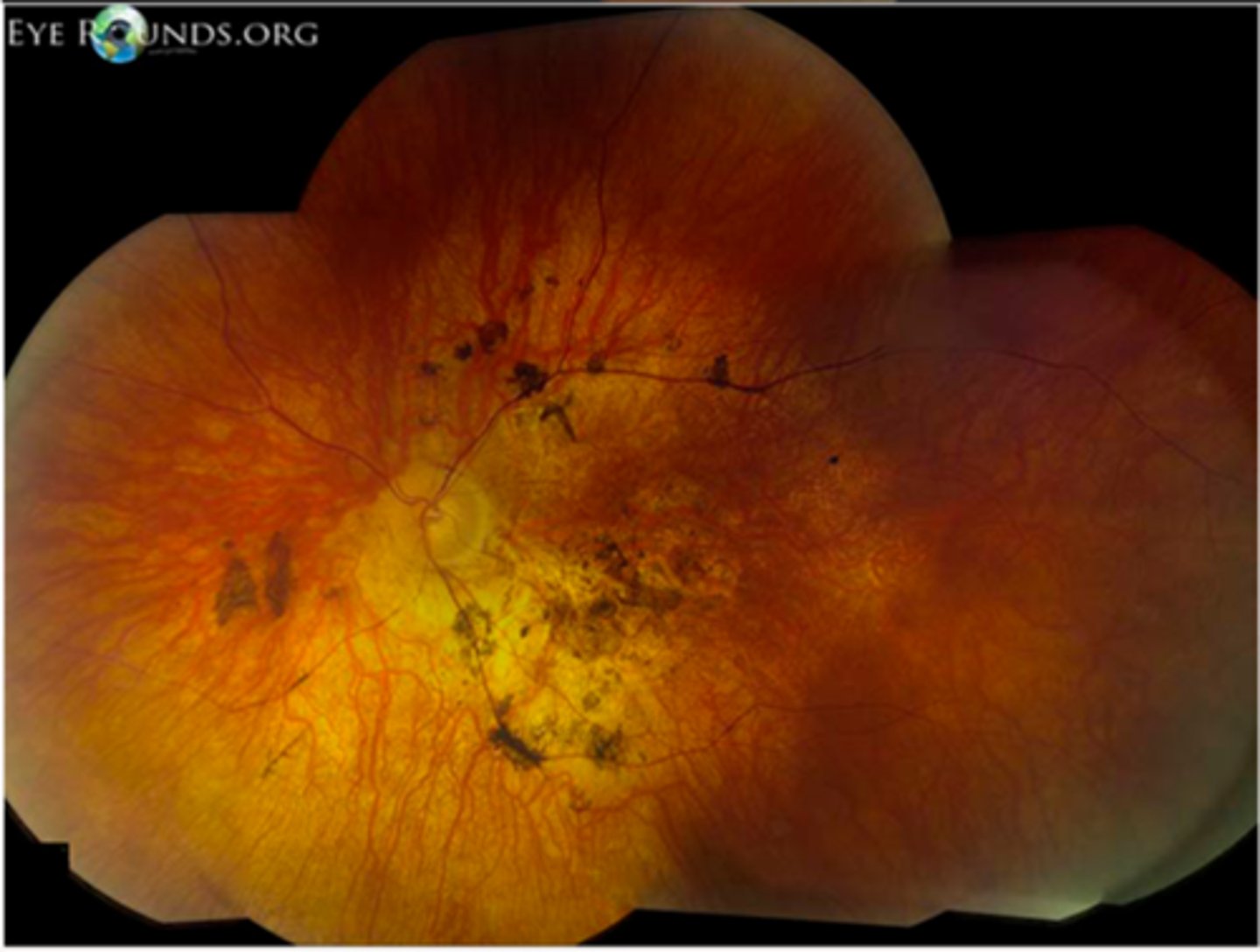
What are some features of Bardet-Biedl syndrome?
rod/cone dystrophy or cone/rod or RP
strabismus
obesity
T2DM
HTN
high Cholesterol
hypogonadism in males
polydactyly
renal anomalies
mental handicap
What is Refsum disease sometimes seen in RP?
AR genetic condition that causes RP vision loss and anosmia
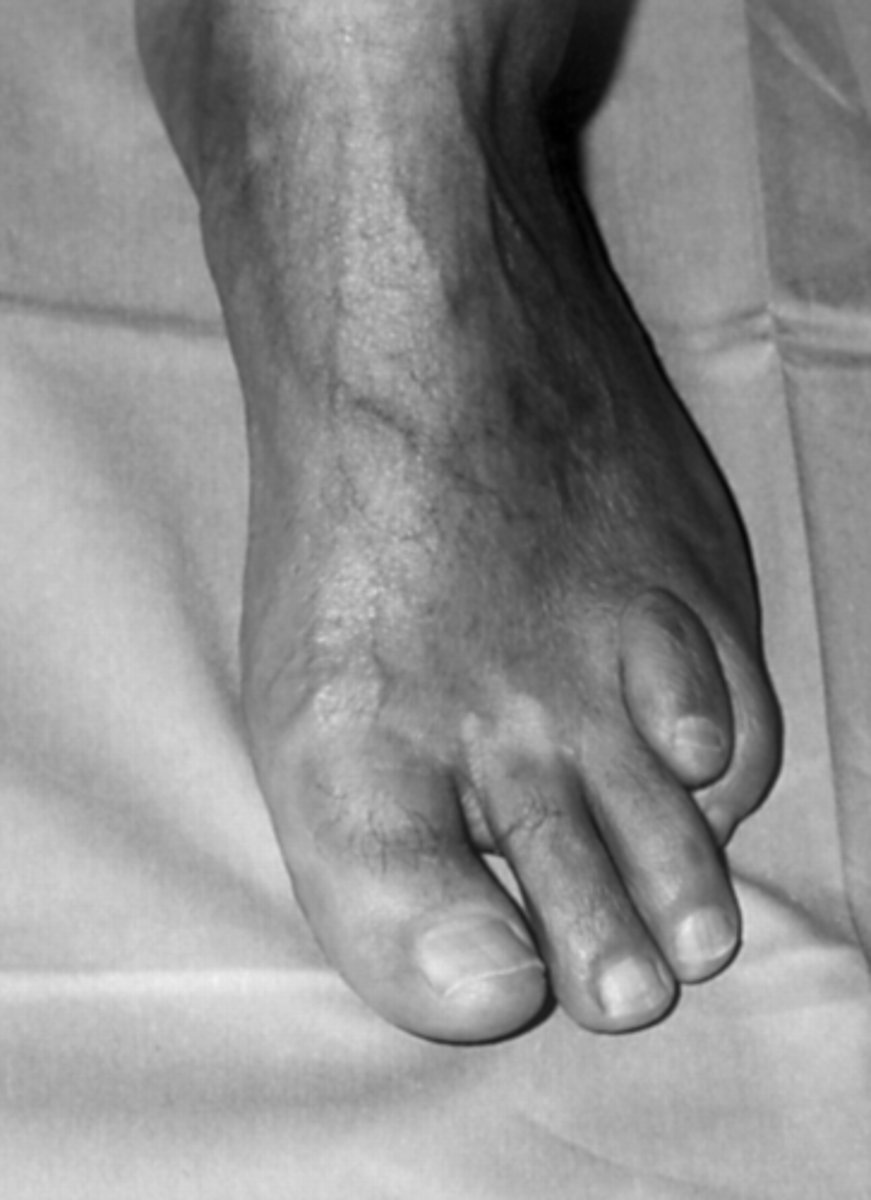
What are some features of Refsum syndrome?
RP vision loss
anosmia = loss of sense of smell
bone abnormalities in hands/feet
progressive mm wasting
poor balance/coordination
hearing loss
dry, scaly skin
cardiac arrhythmias
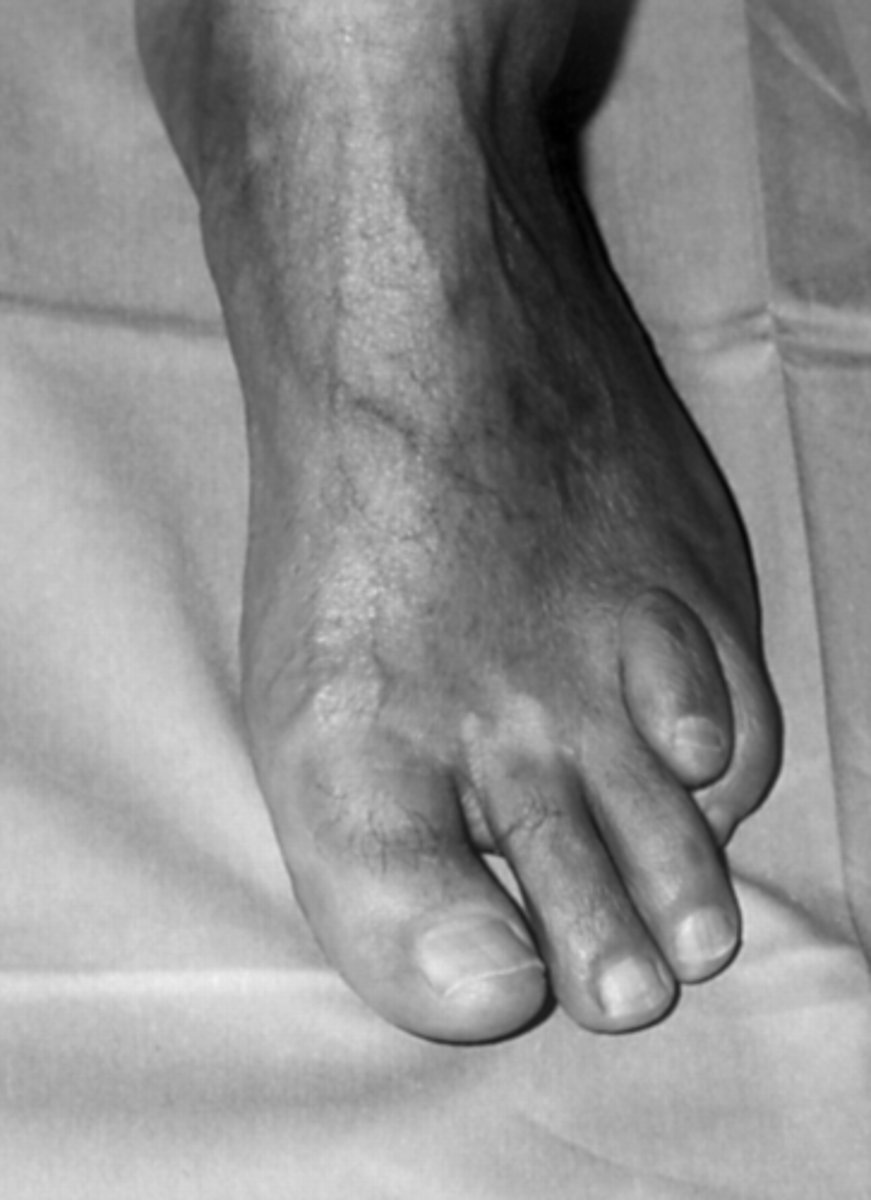
What is Abetalipoproteinemia sometimes seen in RP?
AR genetic condition that affects fat absorption (intestine) and mobilization (liver) = nutrient deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins like KADE

Aside from genetic testing, how else can we dx Abetalipoproteinemia?
blood work for cholesterol/TAGs/fat-soluble vitamins, acanthocytes
What are some S/S of Abetalipoproteinemia?
progressive neuro deterioration
mm weakness
difficulty walking
liver dysfunction
anemia
cardiac arrhythmia
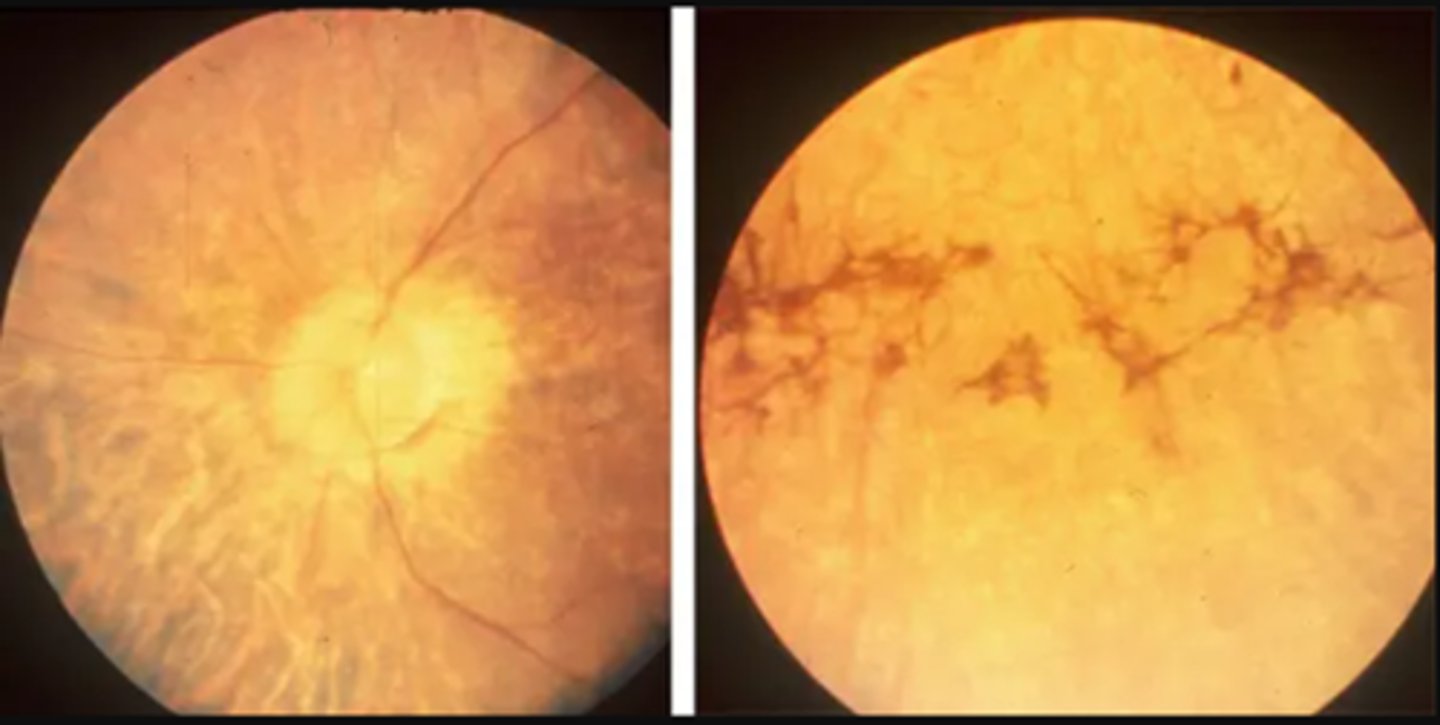
What is Alstrom syndrome sometimes seen in RP?
AR genetic condition causing ciliopathy throughout the body with onset witihn first 18mos of life
What are the main features of Alstrom syndrome?
cone/rod dystrophy or RP
strabismus
progressive hearing loss
dilated cardiomyopathy
hyperphagia
T2DM
short stature
liver steatosis
kidney failure
acanthosis nigrans
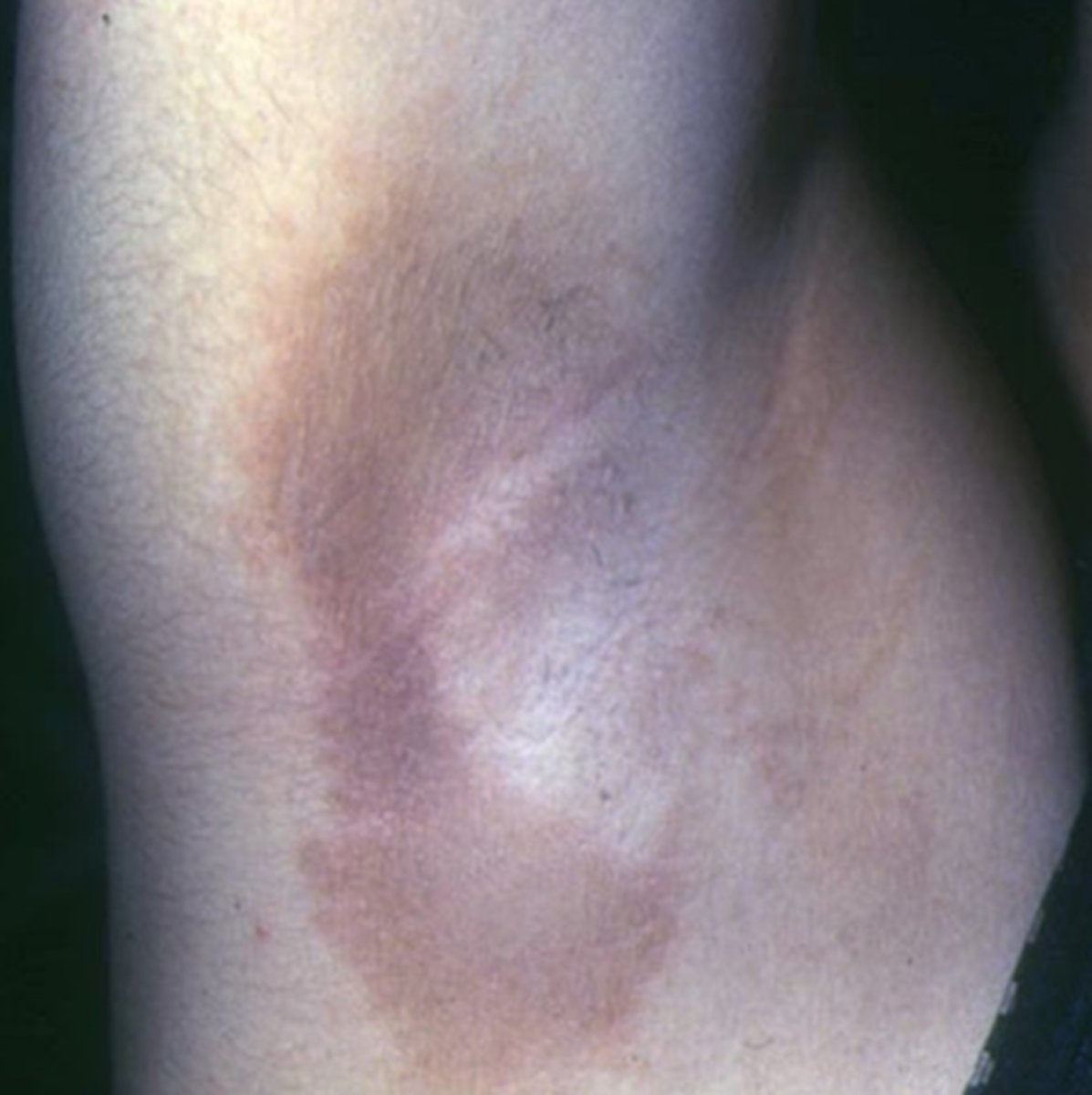
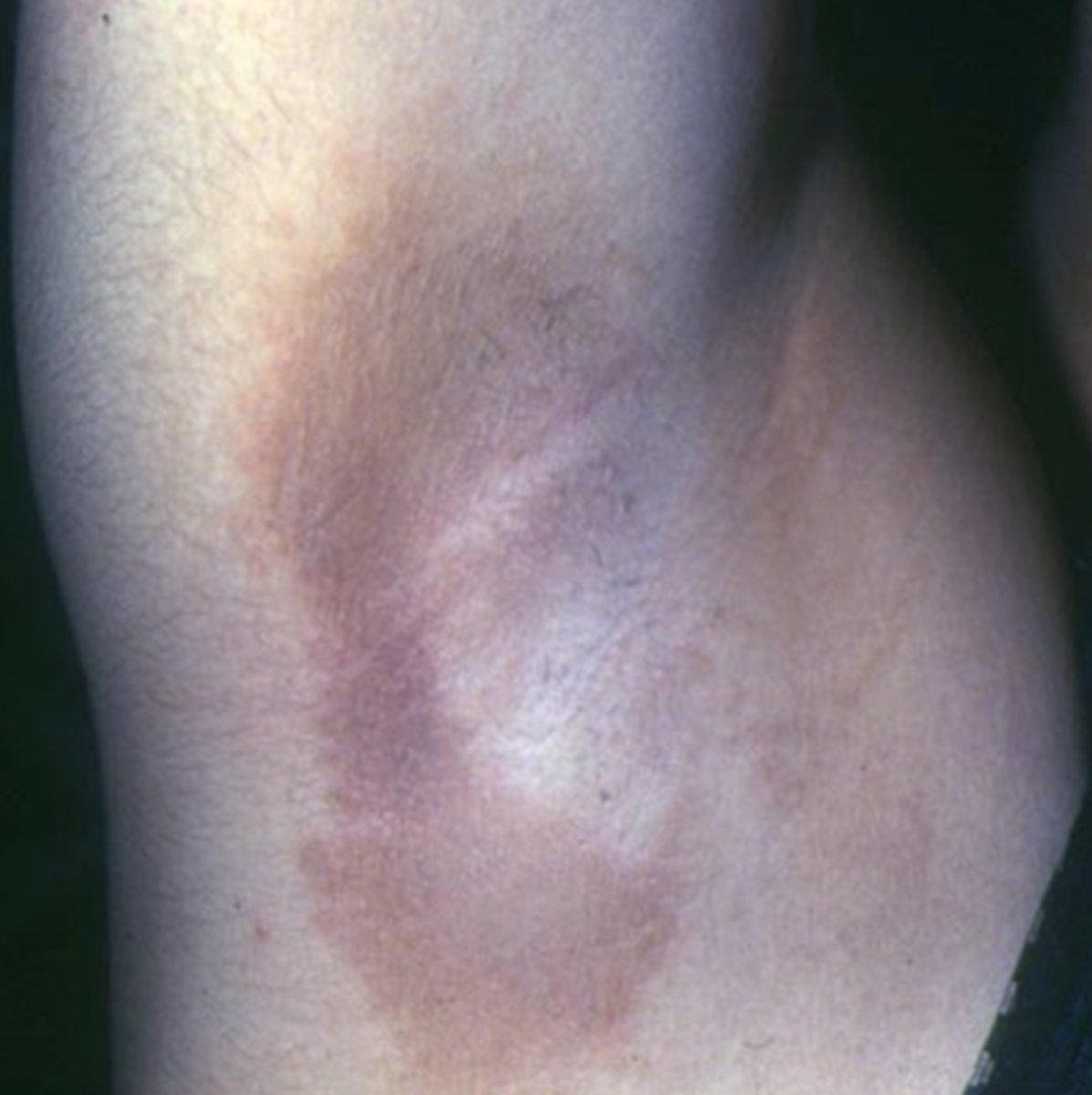
What is Cockayne syndrome sometimes seen in RP?
AR genetic condition that affects genes responsible for DNA repair after UV damage
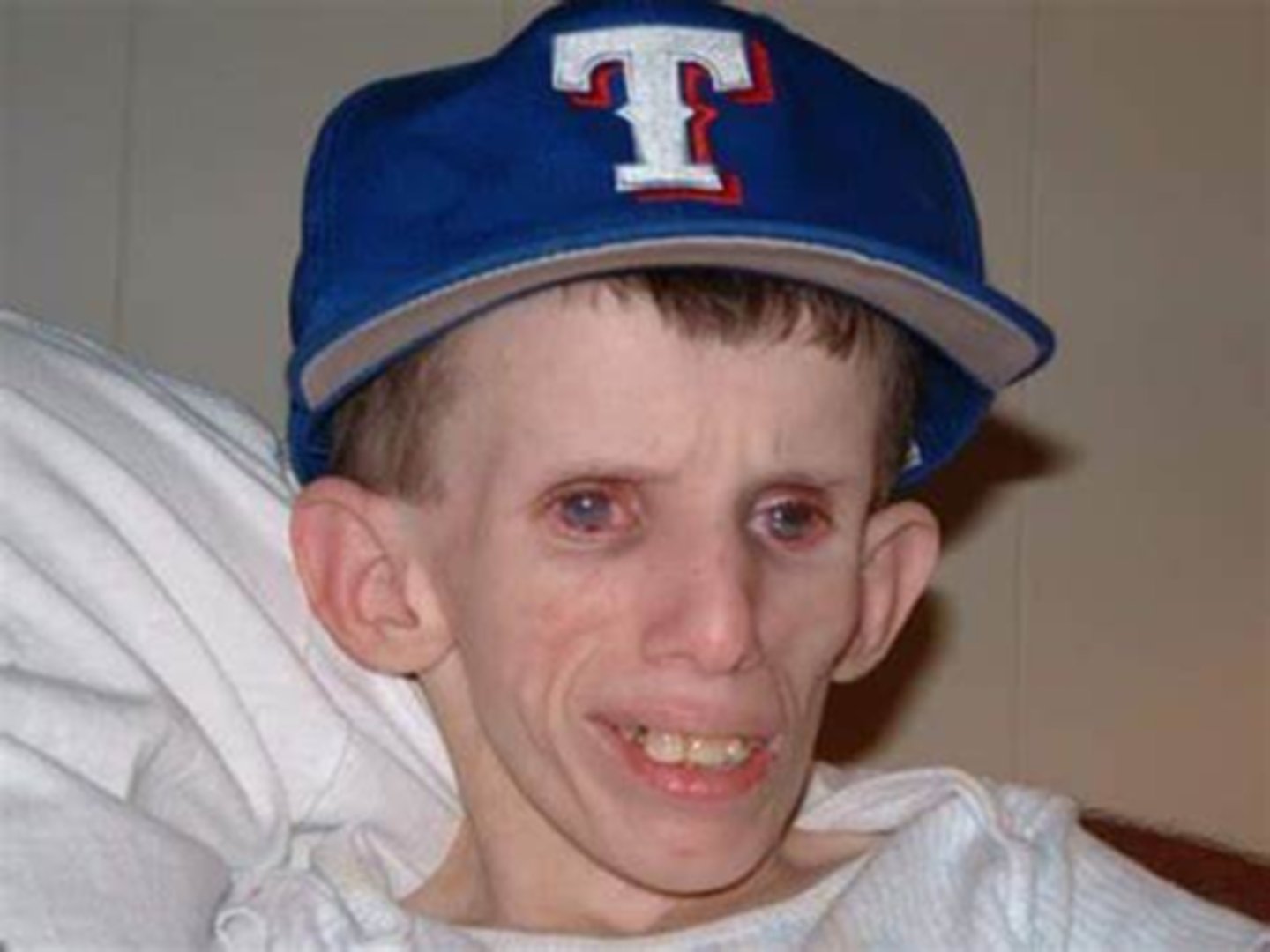
What are the main features of Cockayne syndrome?
RP-like pigmentary degeneration
skin photosensitivity = burn easily with no increased cancer risk
microcephaly
tooth decay
bone abnormalities
failure to gain weight/grow at expected rate
hearing loss
What is Leber's Congenital Amaurosis?
AR or AD genetic condition inhibits phototransduction
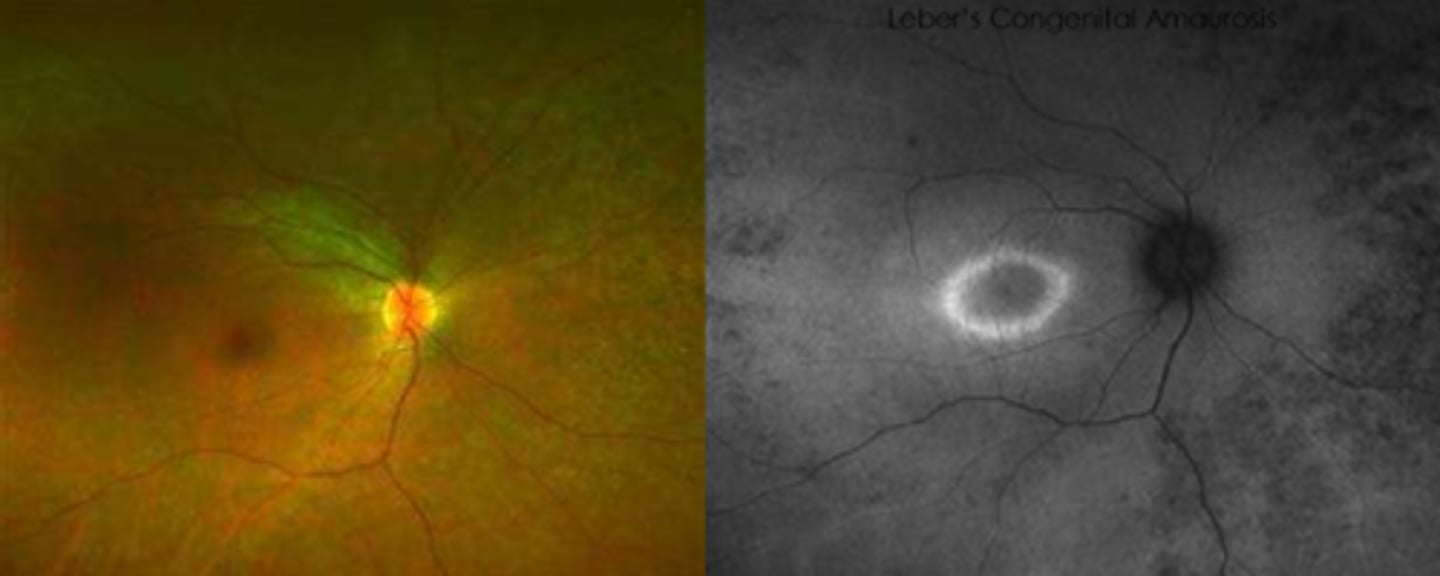
Aside from genetic testing, how can we dx Leber's Congenital Amaurosis?
abnormal ERG (light or dark adapted) = may even be undetectable
What are some ocular signs of Leber's Congenital Amaurosis?
abnormal pupil response
nystagmus
retinal changes may include normal early on, chorioretinal degeneration and atrophy centered around fovea, “bone-spicule" like pigmentation, subretinal flecks, "marbled" fundus, pigmented nummular lesions at RPE level, optic disc abnormalities, “Coats like” reaction
What gene is implicated in some cases of Leber's Congenital Amaurosis?
RPE65
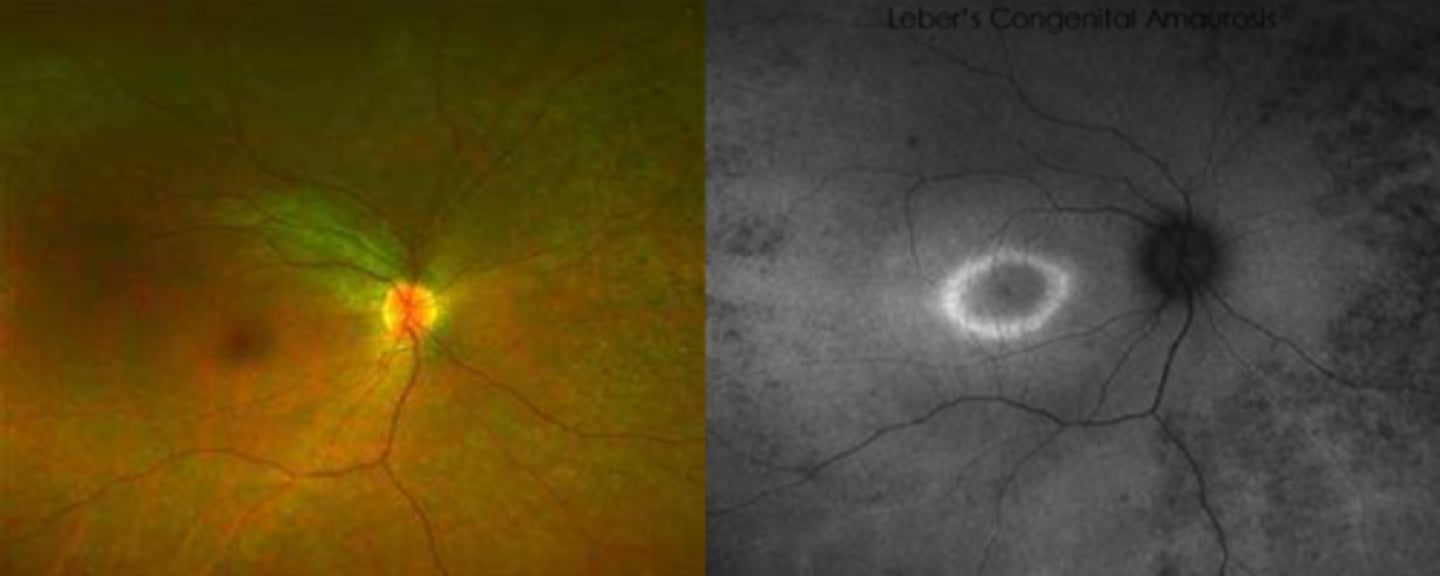
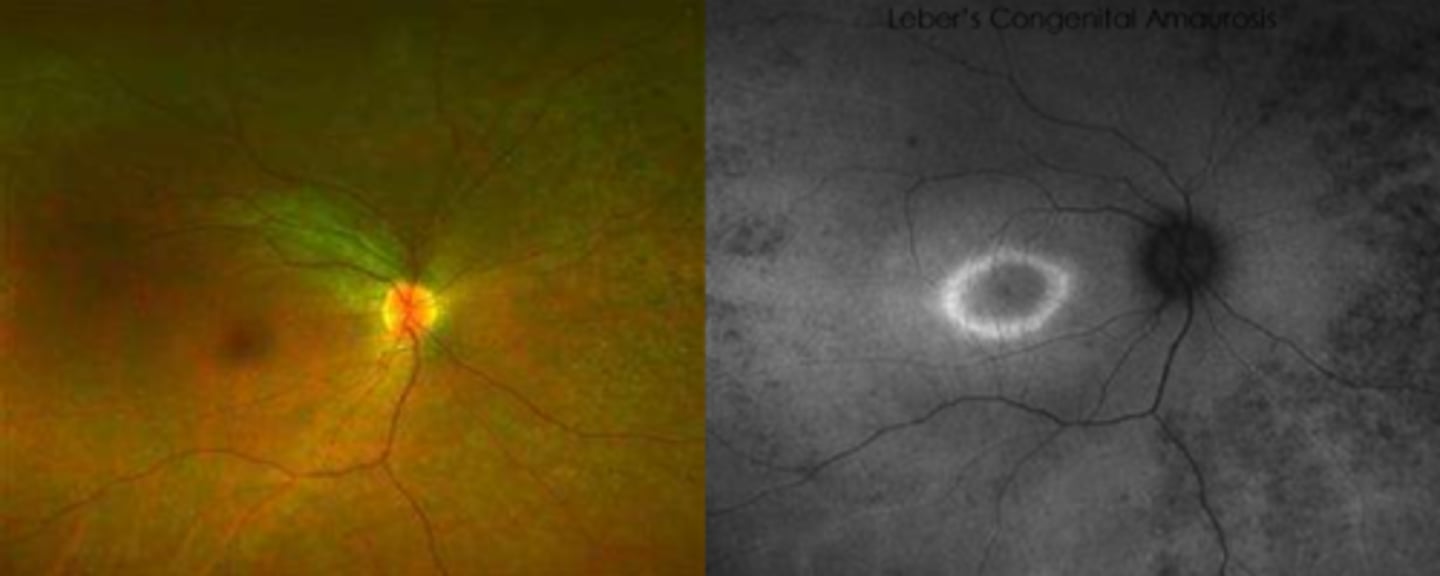
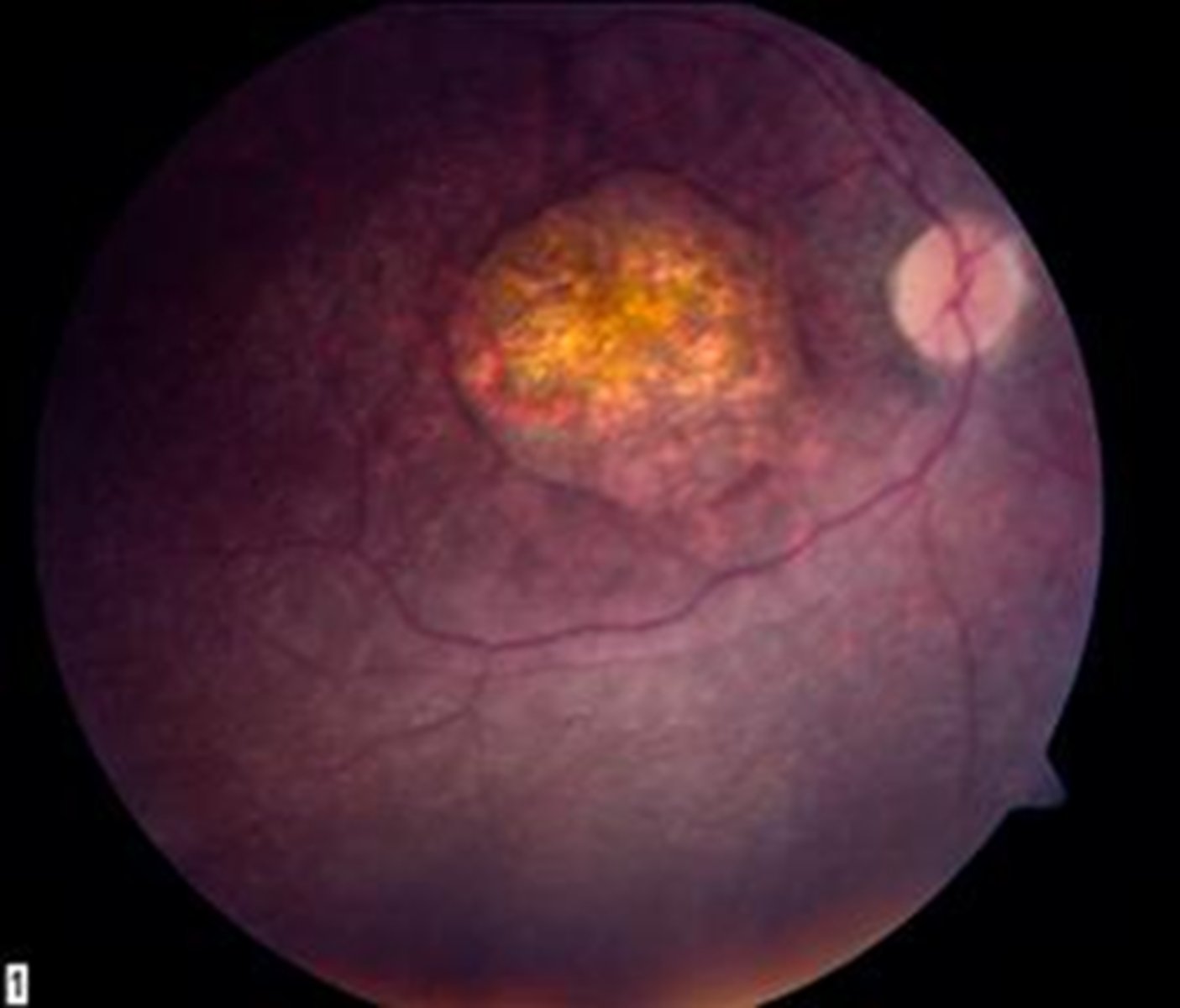
What findings of Leber's Congenital Amaurosis are seen here?
attenuated BV
peripheral pigmentary changes
FAF = peripheral hypopigmented spots and a ring of hyperfluorescence surrounding the fovea
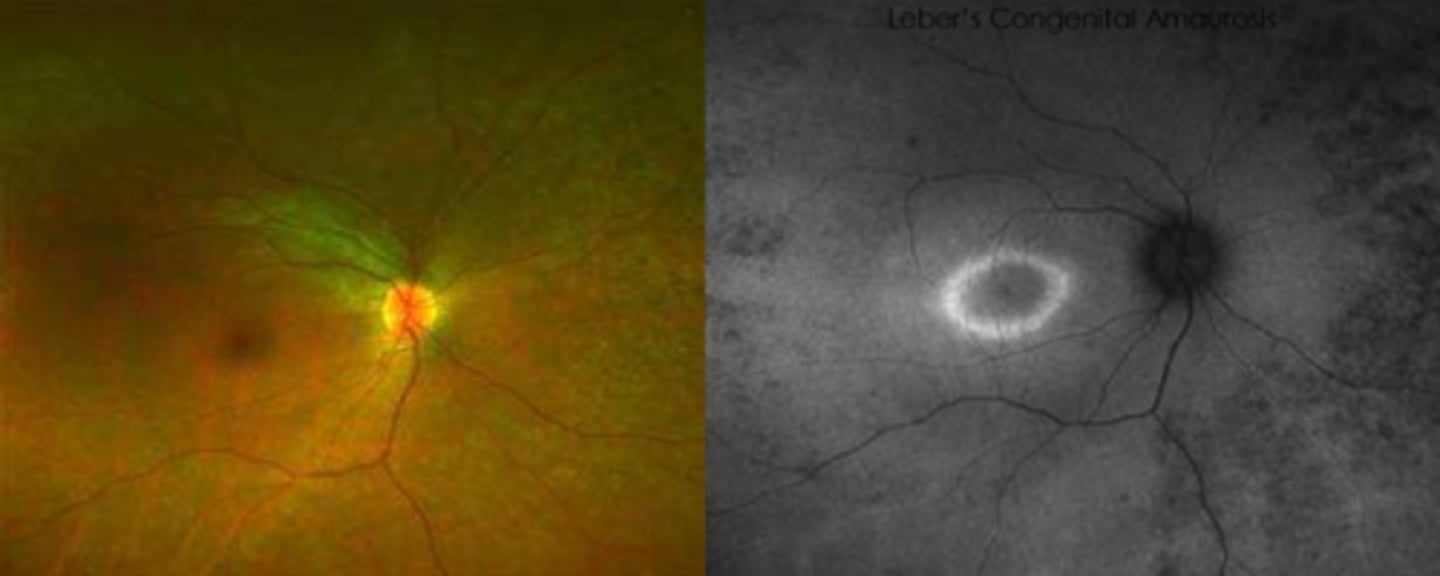
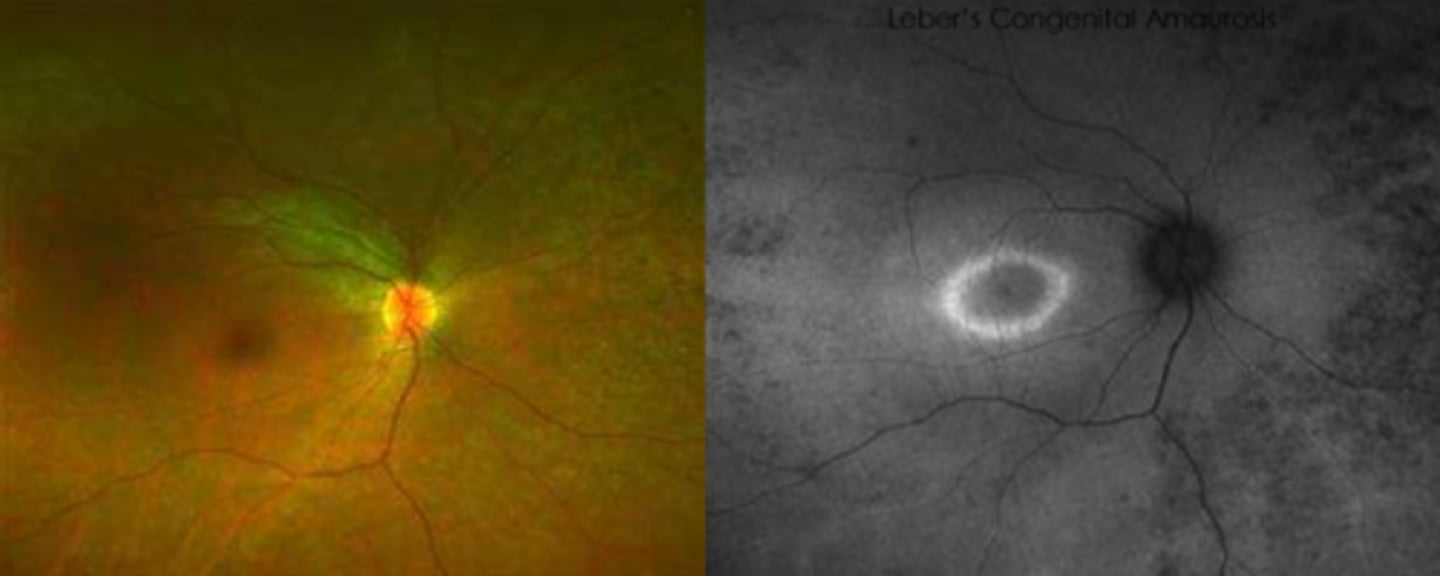
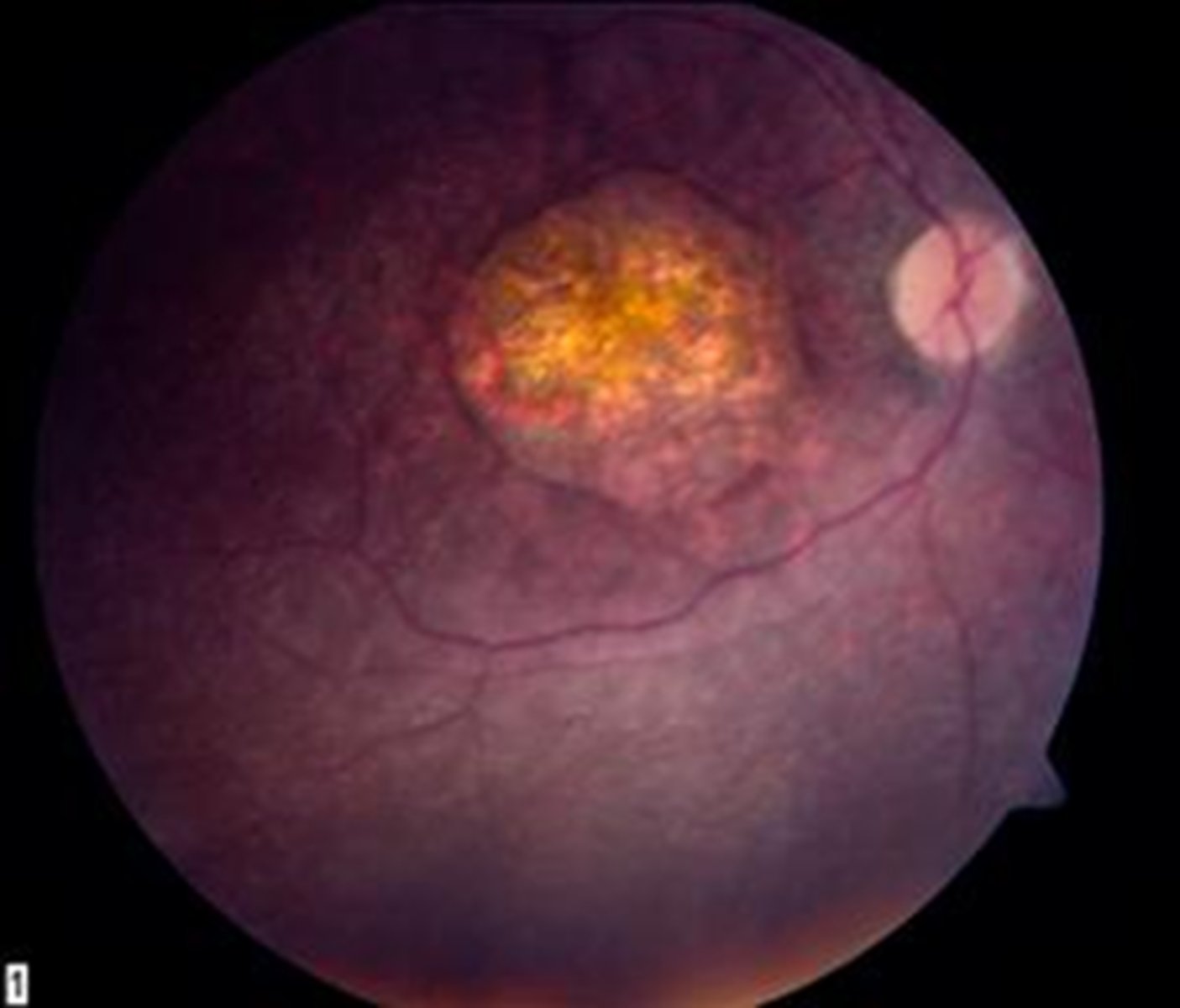
What findings of Leber's Congenital Amaurosis are seen here?
macular atrophic lesion
attenuated BV
peripheral pigmentary changes
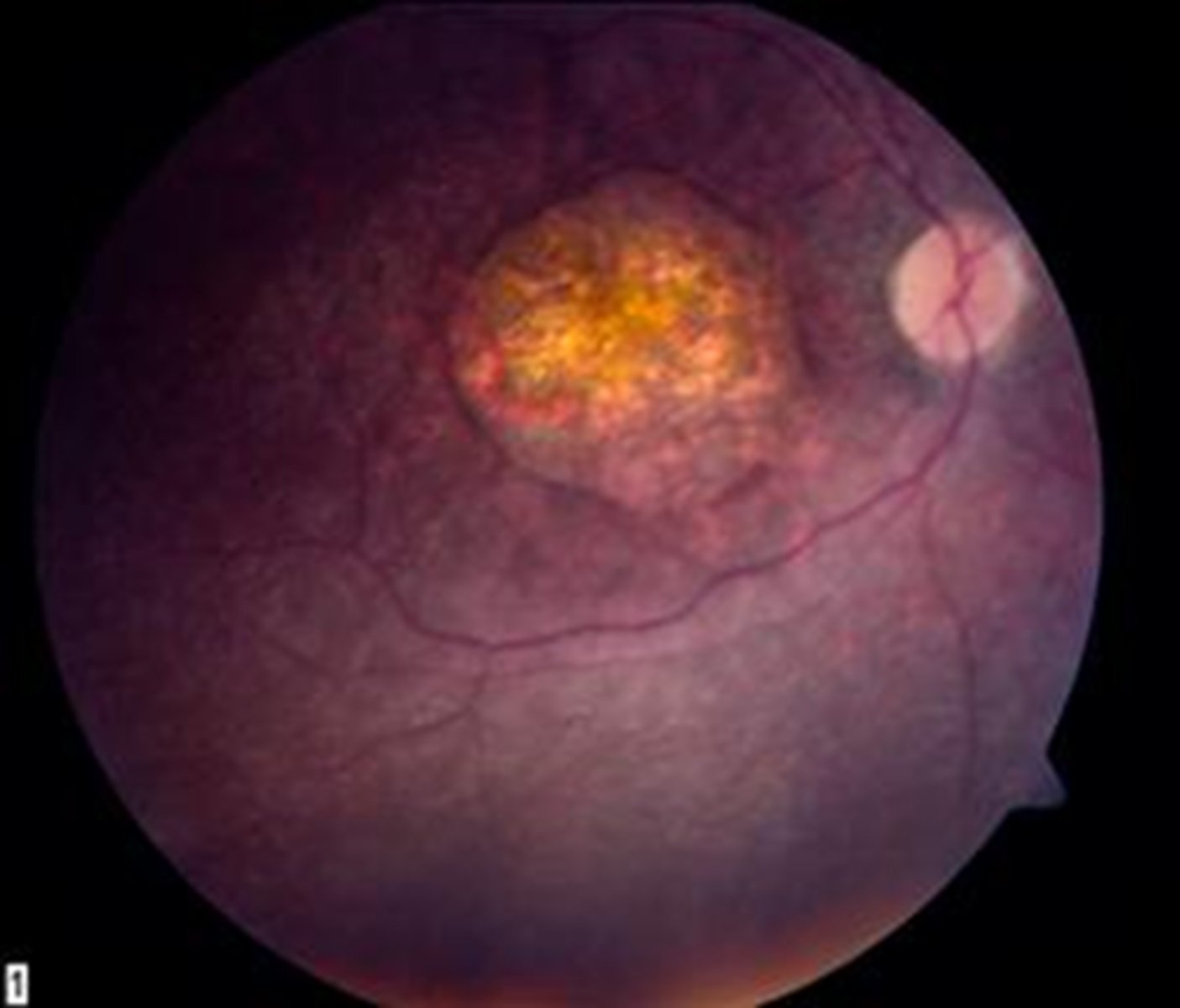
What are some symptoms of Leber's Congenital Amaurosis?
photophobia
nyctalopia
profound vision loss 20/200 to NLP even from birth (can progress slowly then stabilize)
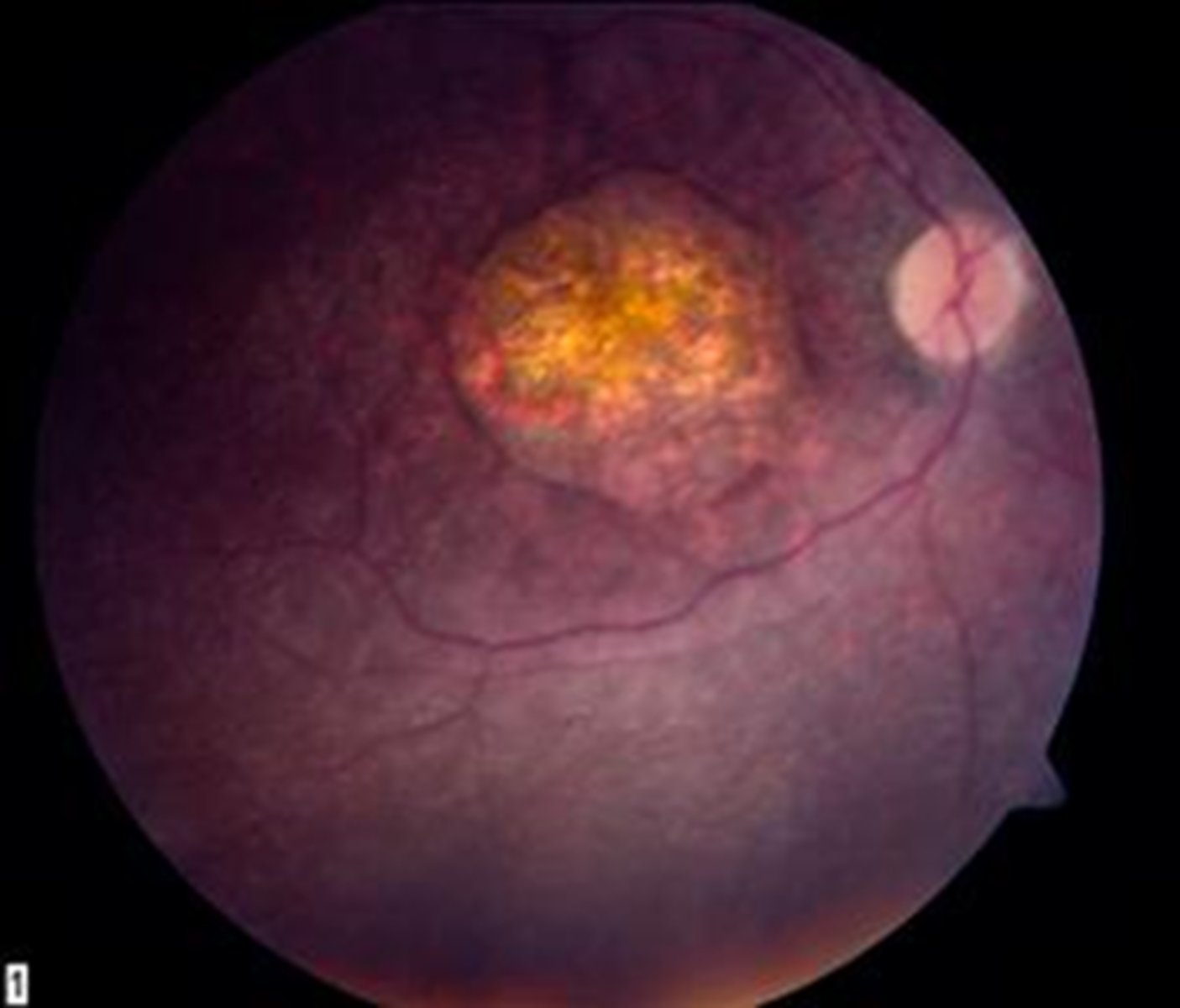
What are some signs of Leber's Congenital Amaurosis?
eye rubbing = oculo-digital reflex creates phosphene BUT increased risk for KCN
poor fixation
nystagmus
What is the tx for Leber's Congenital Amaurosis?
Luxturna gene therapy if RPE65
correct Rx
LV referral
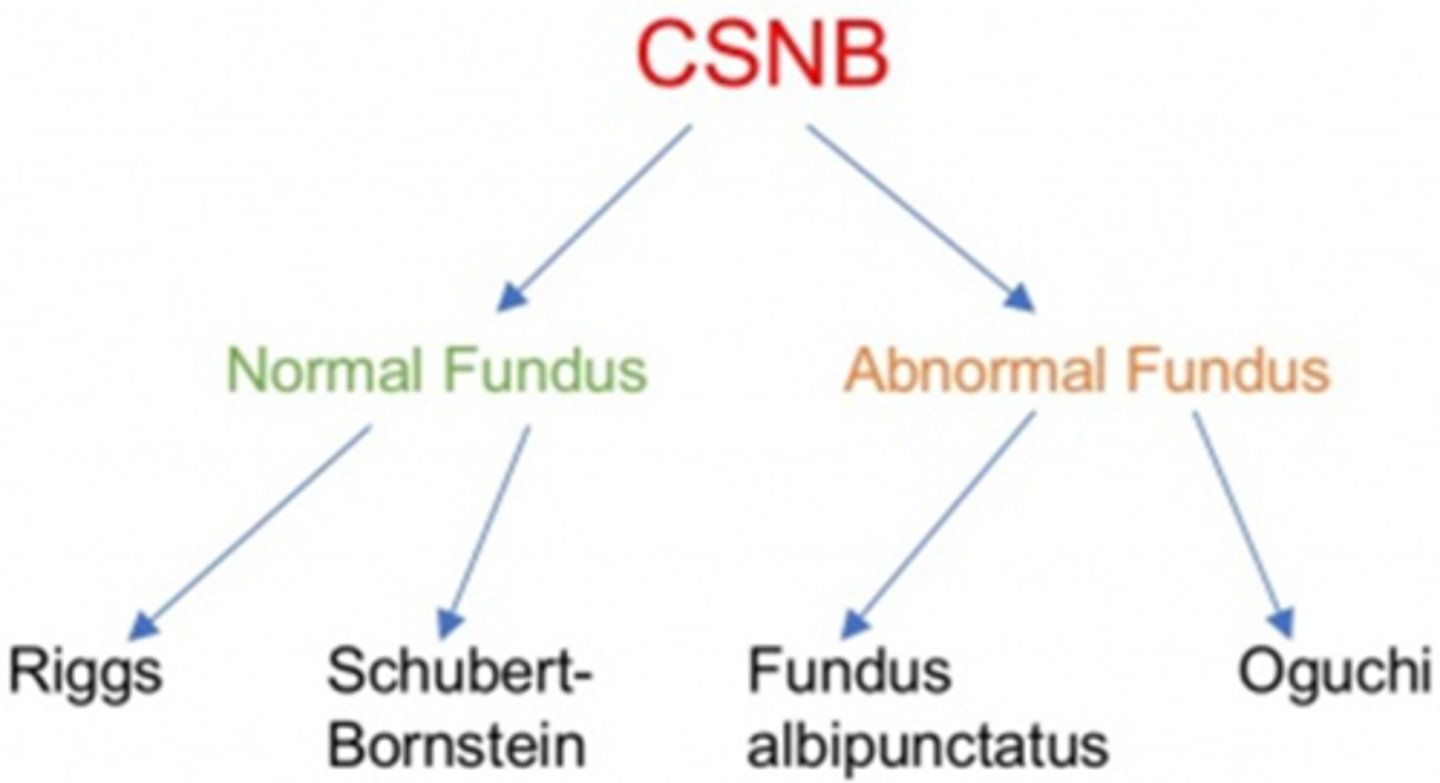
What is congenital stationary night blindness?
non-progressive nyctalopia starting from birth
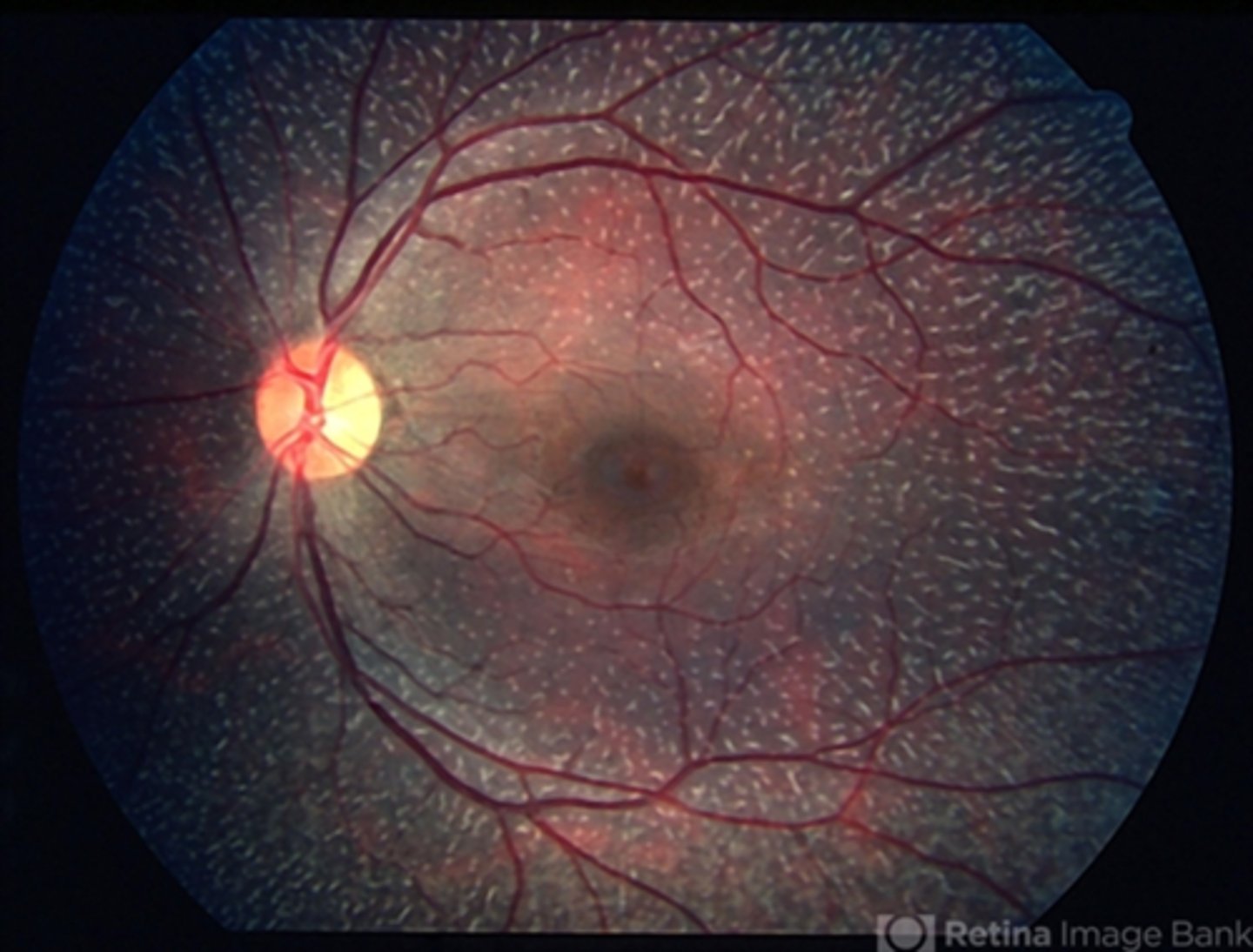
What is the fundus albipunctatus appearance of congenital stationary night blindness?
scattered yellow-white dots in the posterior pole (sparing the macula) that extend to the mid-periphery = dots typically stable, may disappear over time
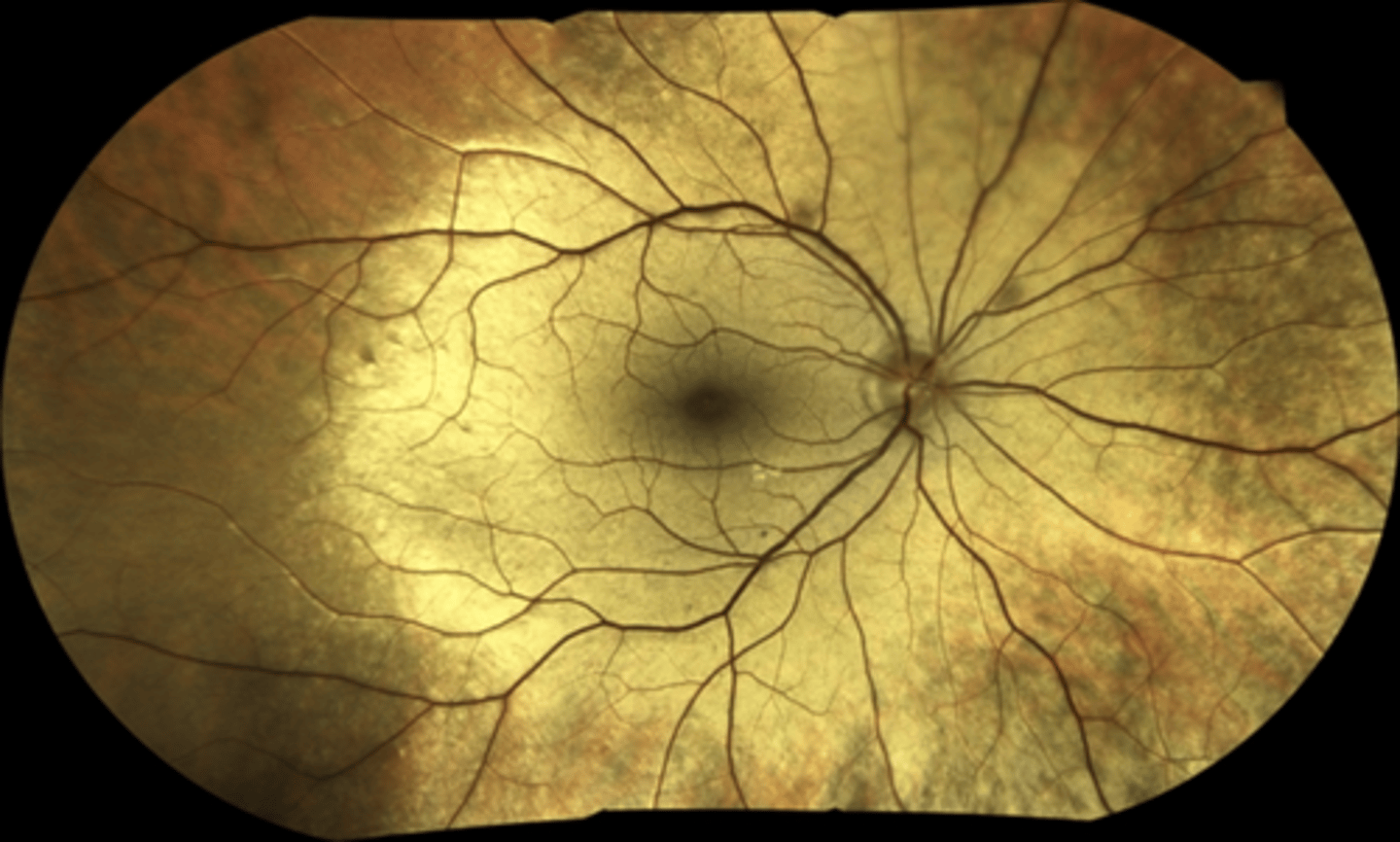
What is the Oguchi appearance of congenital stationary night blindness?
Mizuo-Nakamura phenomenon = fundus is unremarkable in the dark-adapted state, but has a yellow iridescent (golden) sheen after light exposure
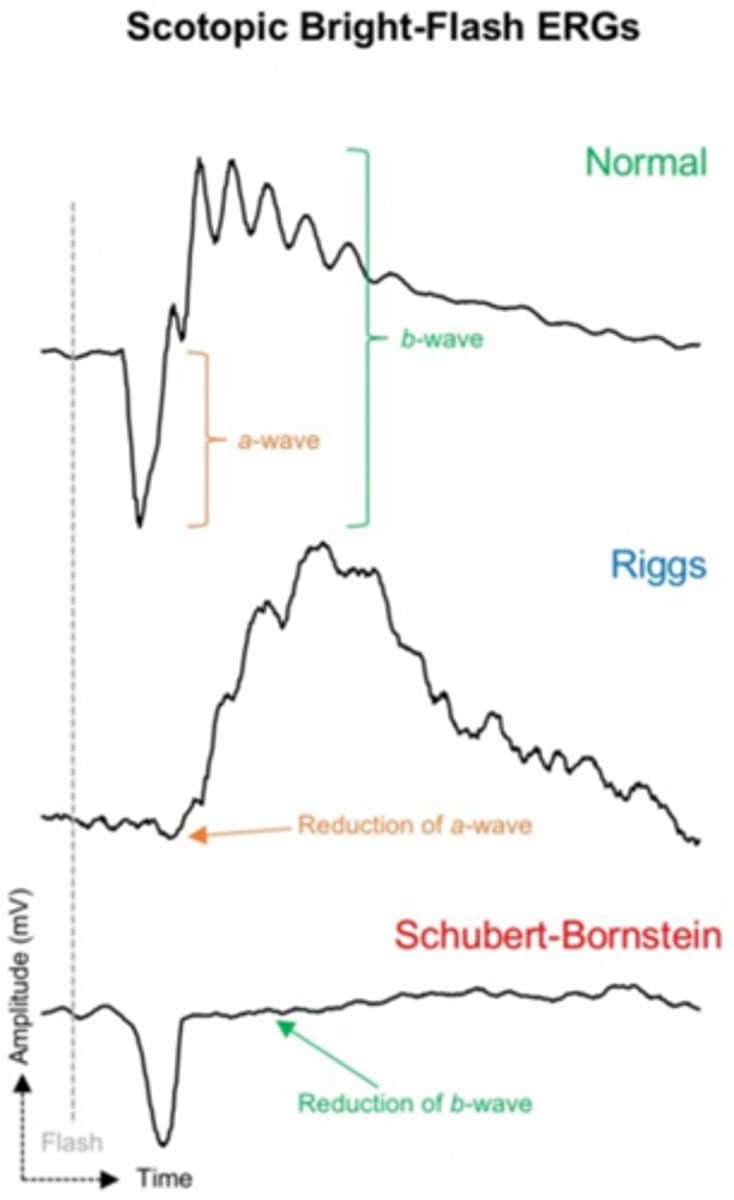
What is the diagnostic testing for congenital stationary night blindness?
scotopic ERG will be abnormal
Aside from the nyctalopia, what are some other ocular findings of congenital stationary night blindness?
reduced VA (20/40 to 20/60)
photophobia
myopia
strabismus
nystagmus
What is the tx for congenital stationary night blindness?
LV referral
high dose 9-cis-beta-carotene may possibly improve VF and ERG results
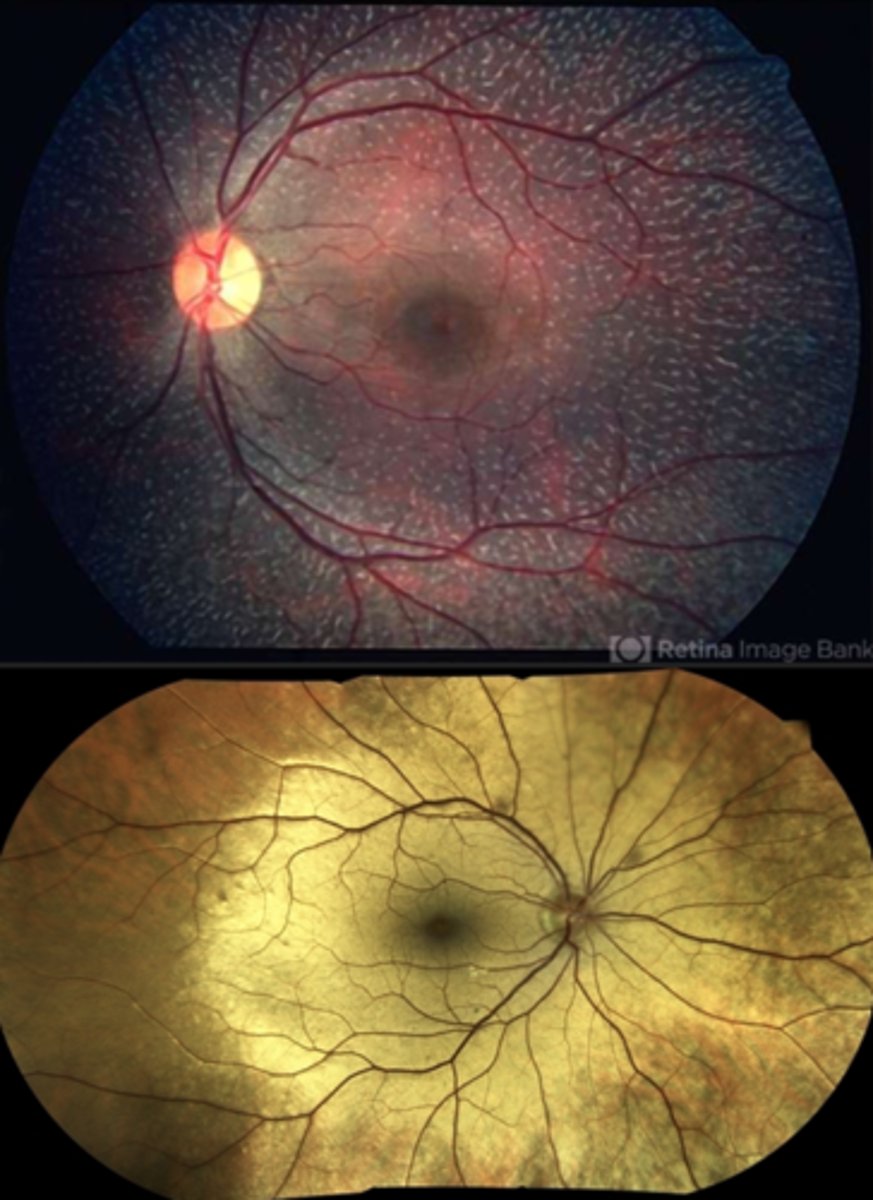
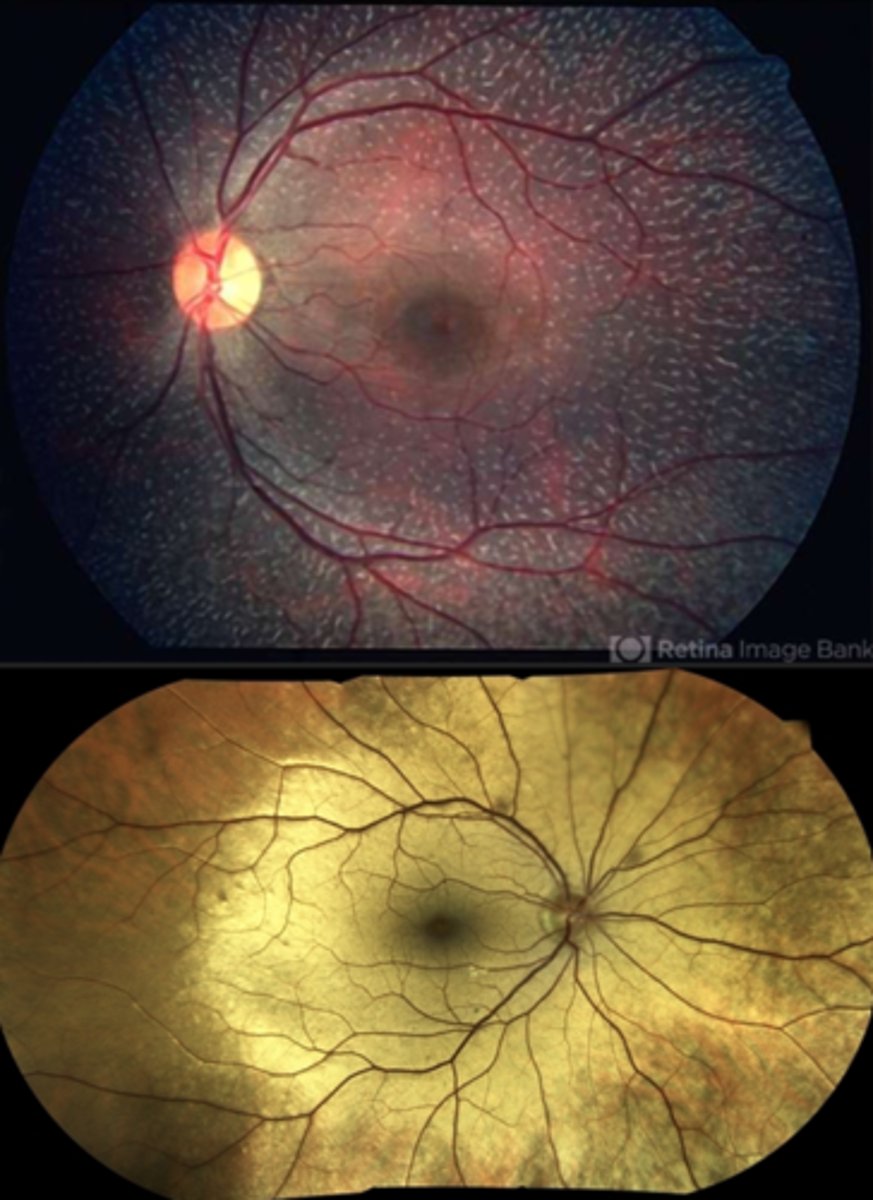
What is choroideremia?
X-linked dystrophy resulting in progressive degeneration of the RPE, PR's, choriocapillaris = underlying white sclera exposed

What are some features of the appearance of choroidemia?
pigment clumping at the level of the RPE
well-defined atrophy = visible sclera and large choroidal BV remain = mostly in the postequatorial region just outside the arcades; advance centripetally
island of foveal tissue may persist until later stages
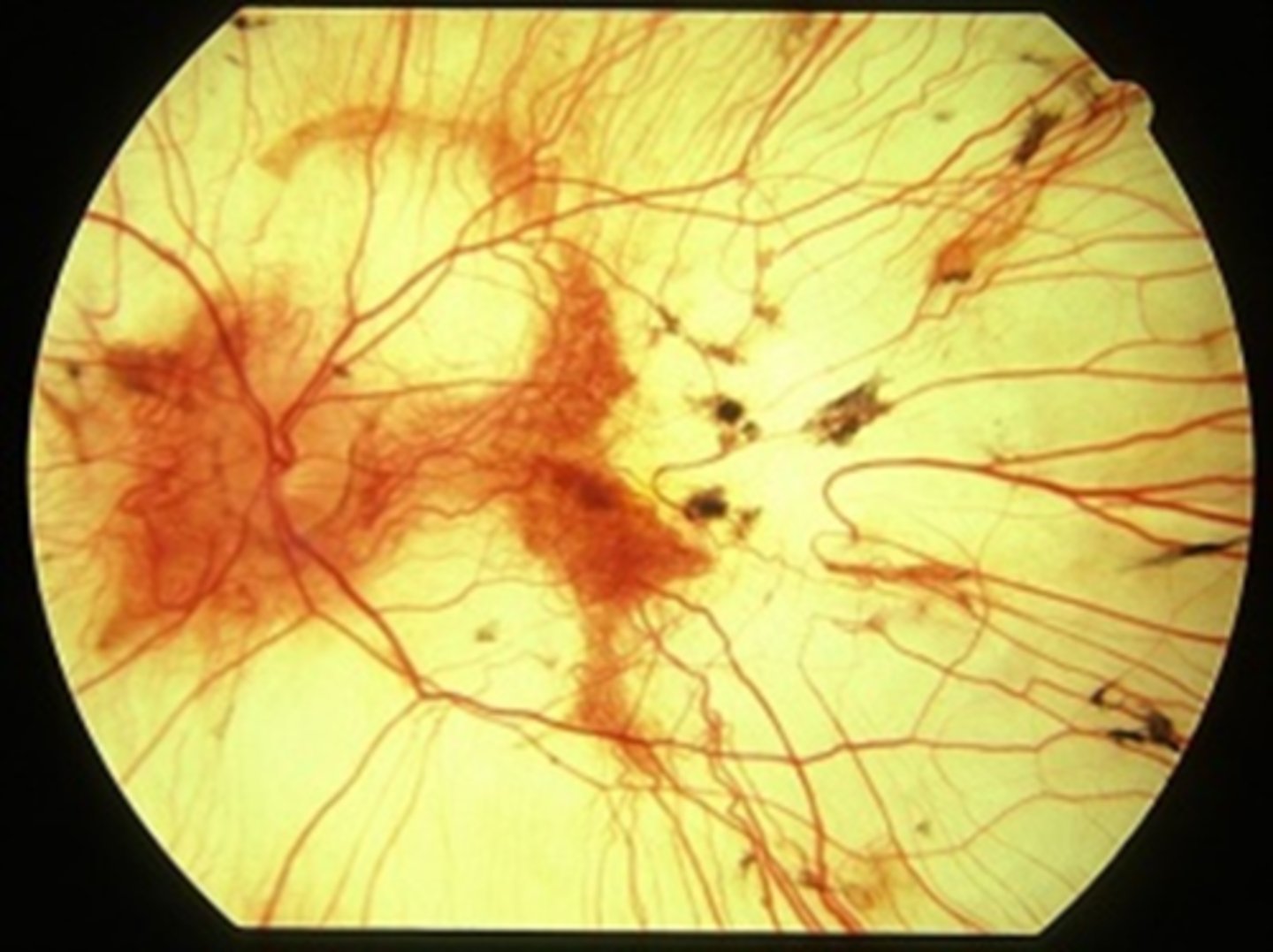
What are 2 NORMAL findings seen in choroidemia?
NORMAL appearing retinal BV
NO optic atrophy
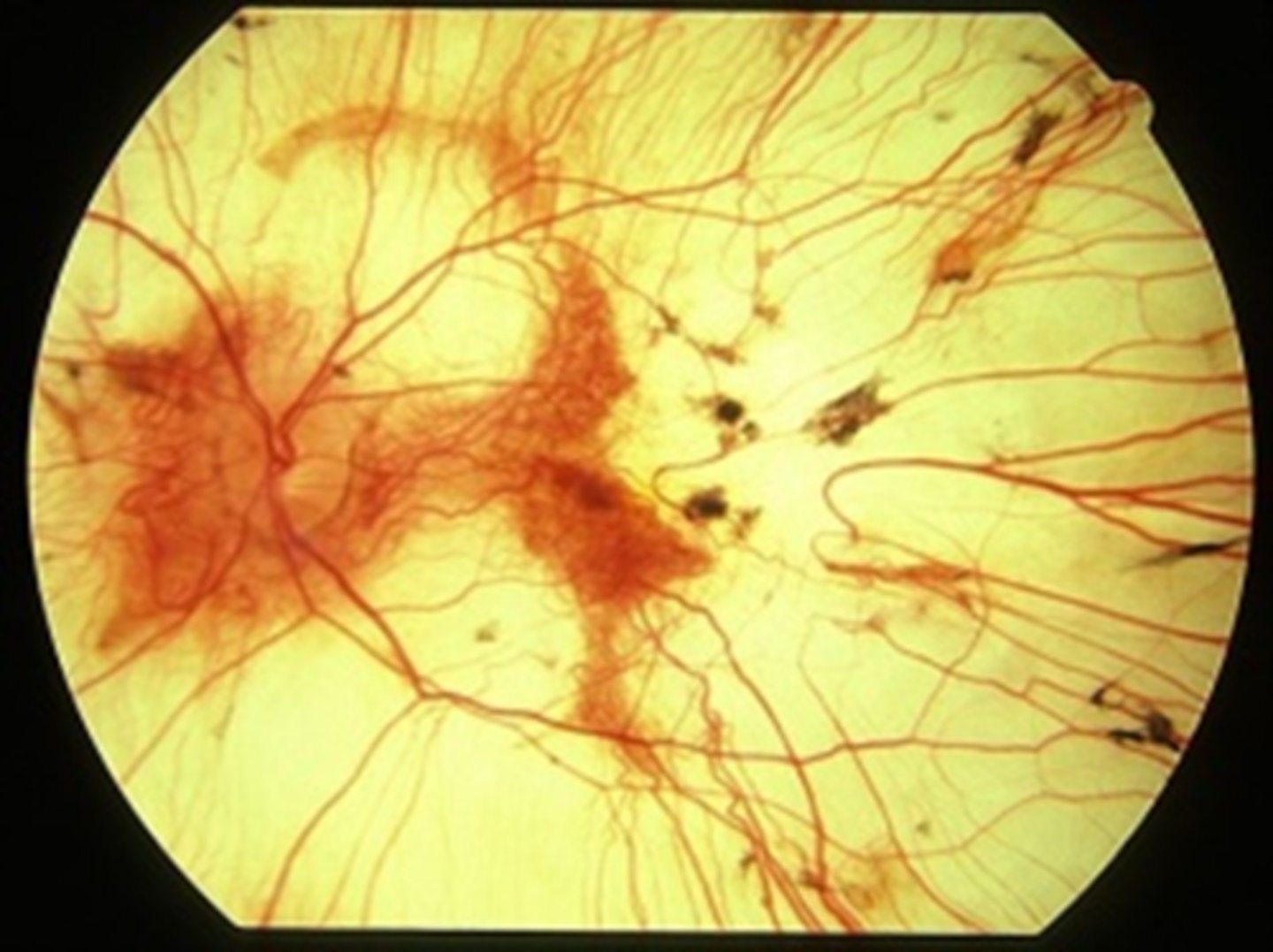
What is the evolution of choroidemia?
first decade = nyctalopia
teenage years = peripheral vision loss, good VA maintained
5th-7th decade = rapid VA and color vision loss
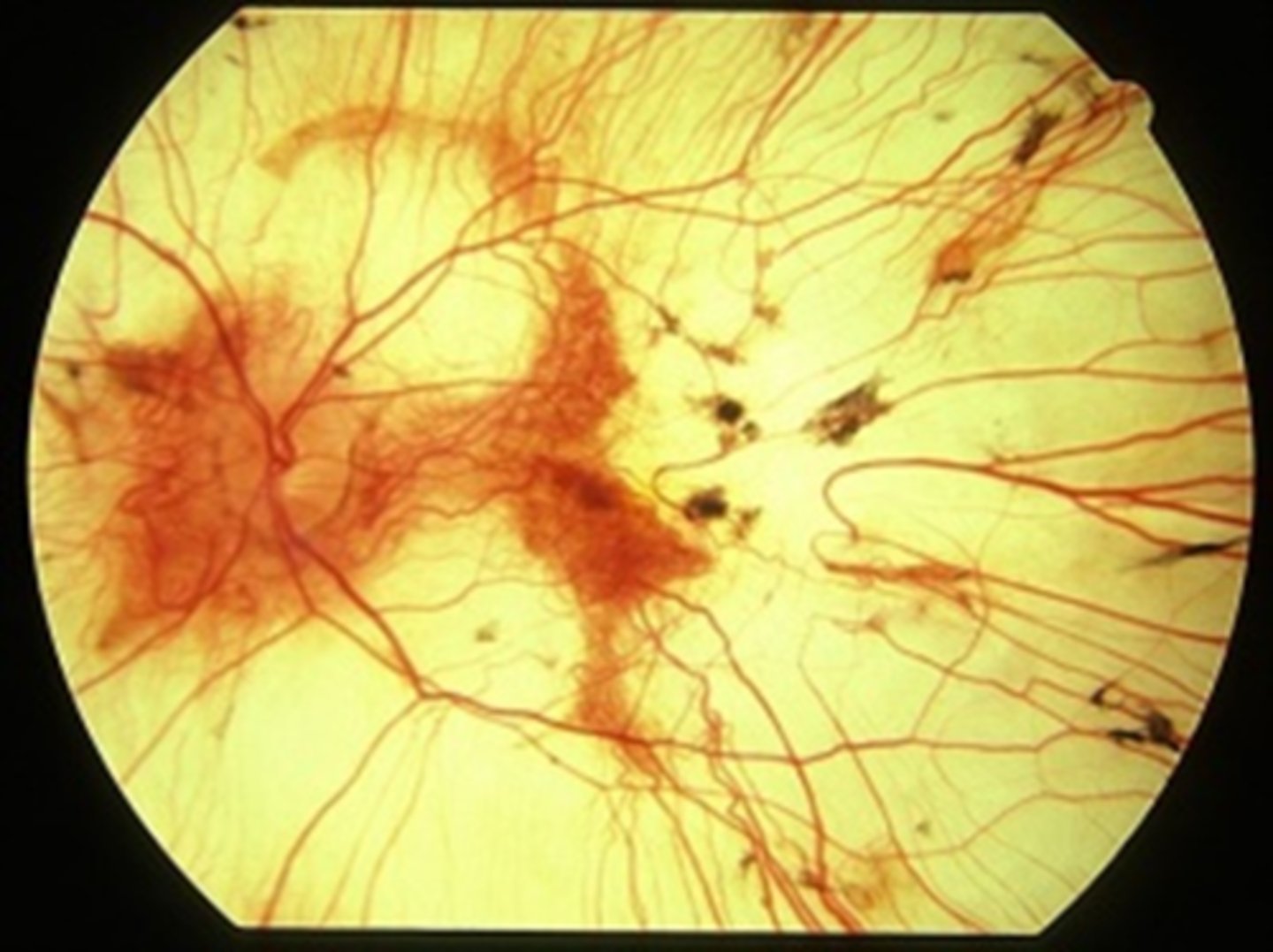
What findings of choroidemia are seen here?
scattered pigment clumping
visible large choroidal vessels
fovea = preserved choriocapillaris at the fovea
extrafovea = deficient choriocapillaris and visible medium, large choroidal vessels
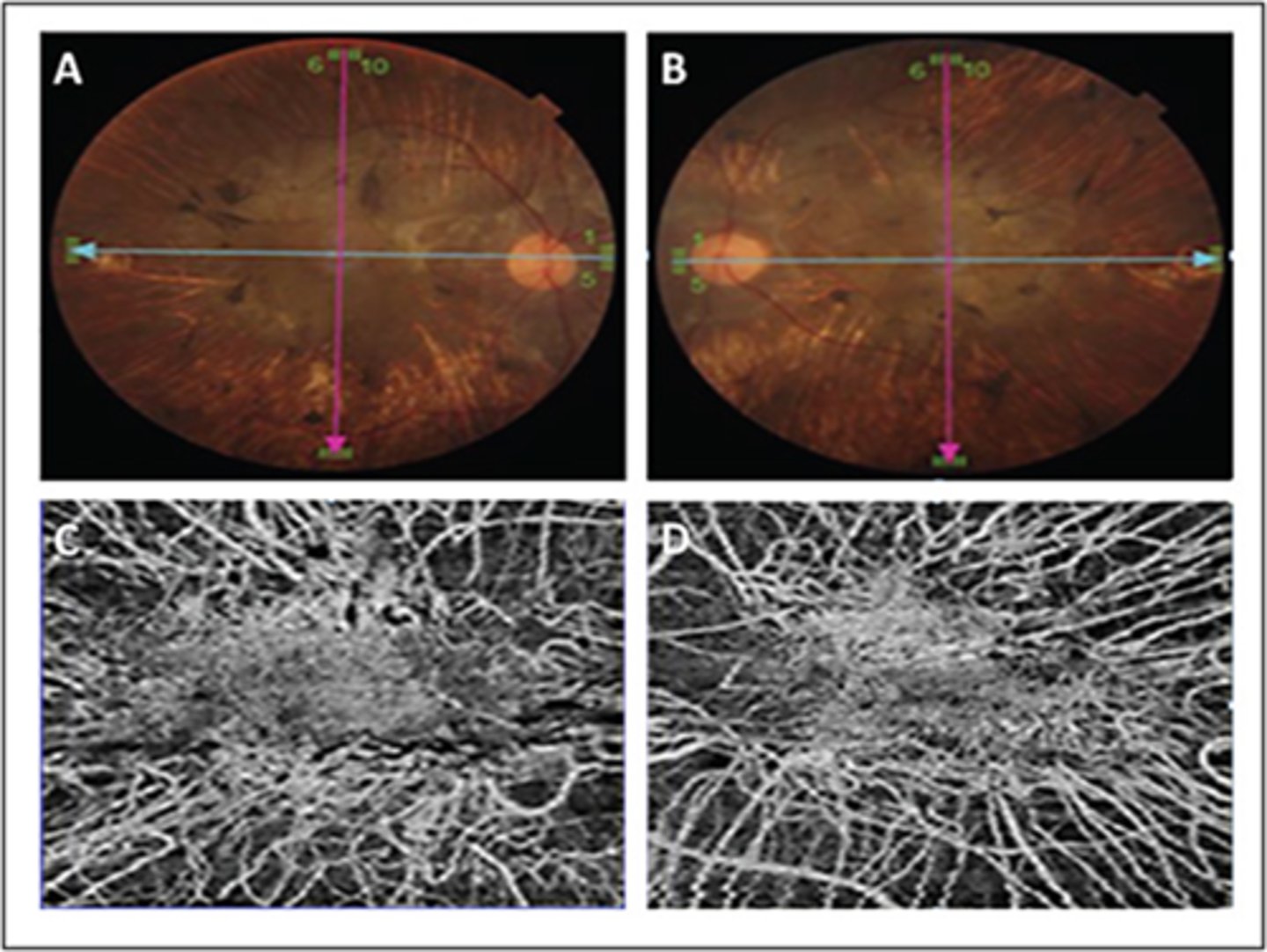
What are some diagnostic testing we can perform for choroidemia?
VF = patchy midperipheral irregular scotomas, then near complete loss of central and peripheral vision later on
ERG = abnormal
genetic testing
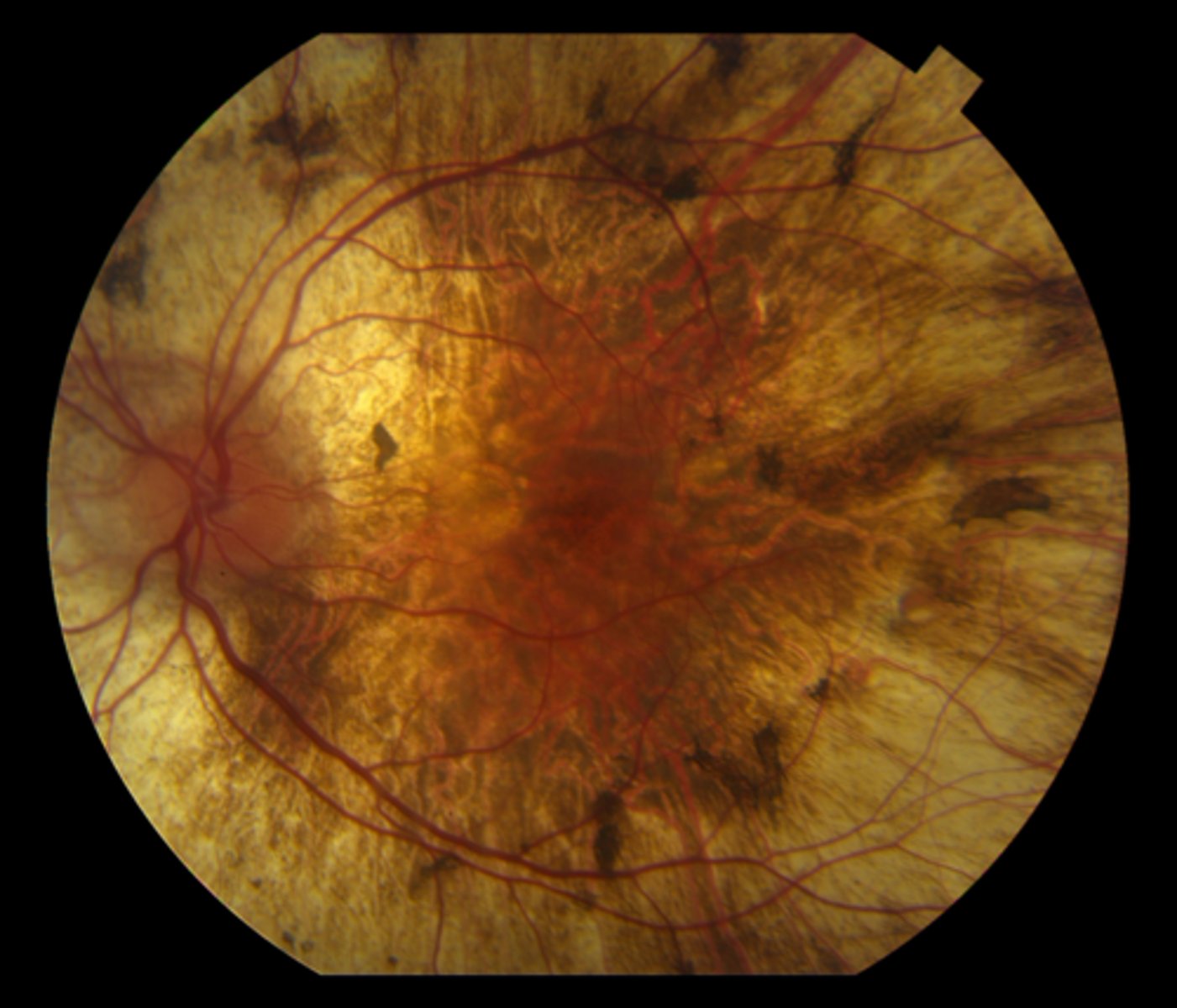
What are 2 complications of choroidemia?
mac edema
CATs
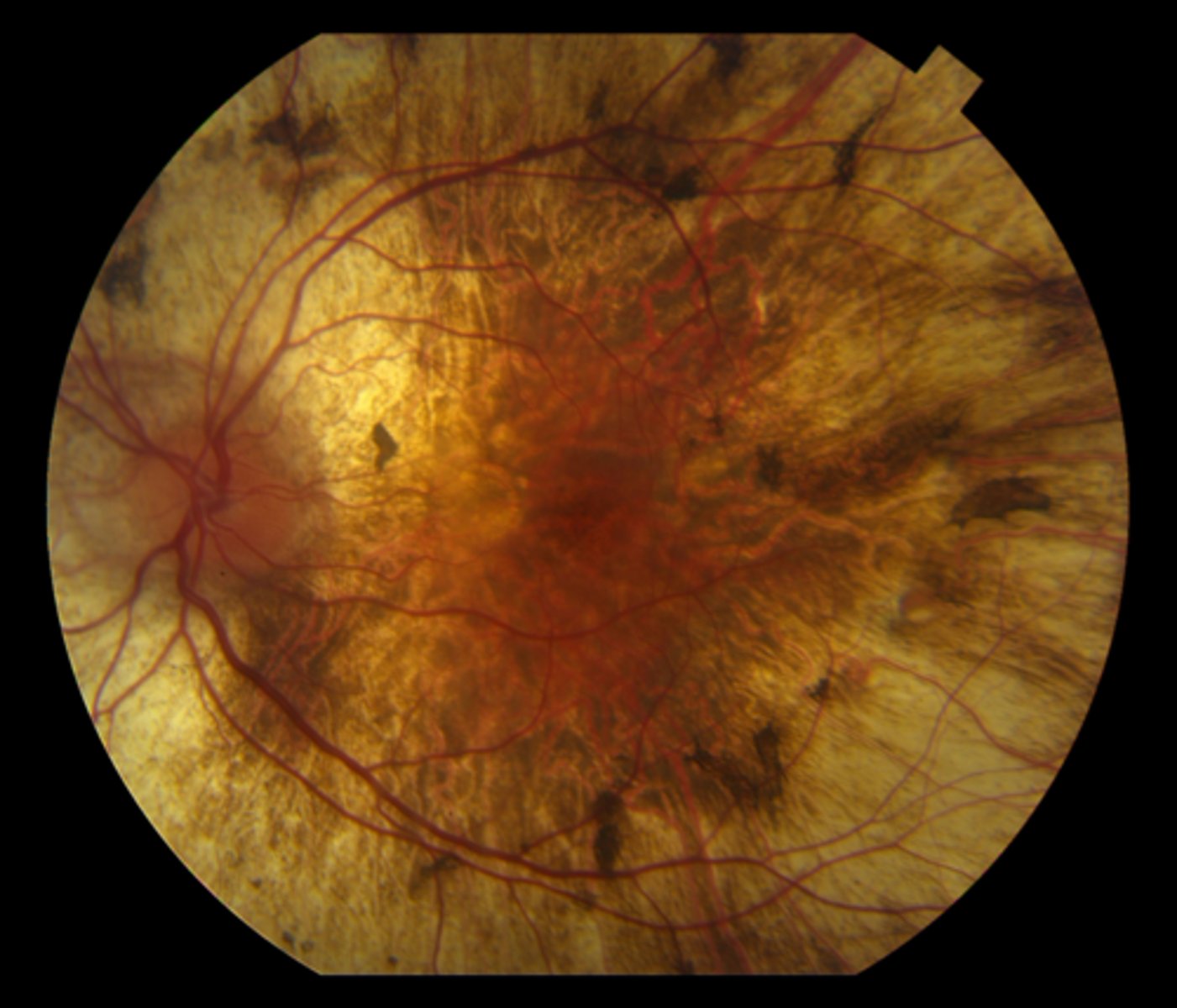
What is the tx for choroidemia?
LV referral
CAI's or anti-VEGF for mac edema
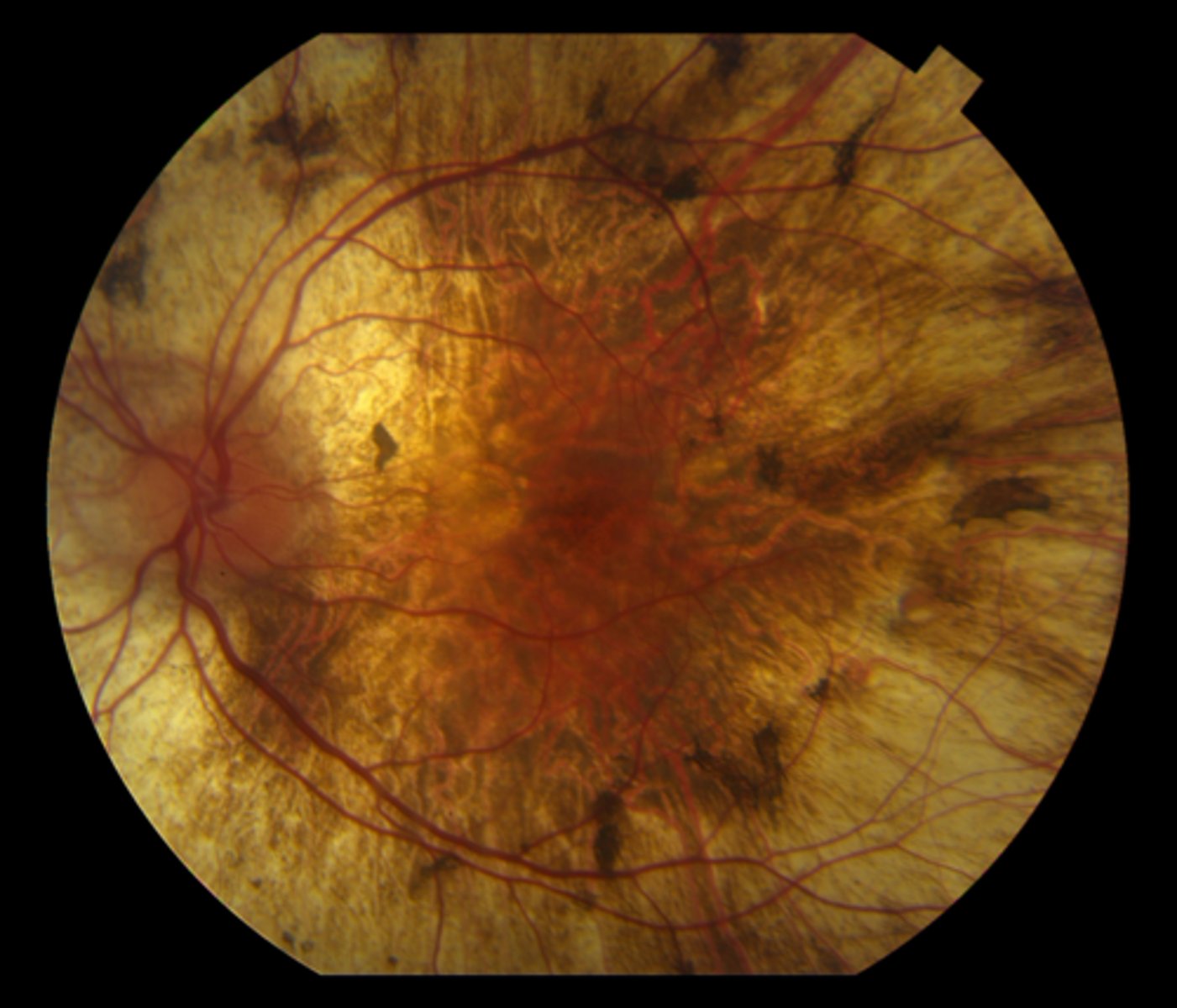
What is gyrate atrophy?
AR dystrophy that is caused by a deficiency in ornithine aminotransferate (OAT) enzyme = increased ornithine in blood

What are the 3 main findings of gyrate atrophy?
bilateral chorioretinal degeneration in the mid-far periphery = patchy, sharply demarcated circles of atrophy with hyperpigmented margins
early CATs
myopia
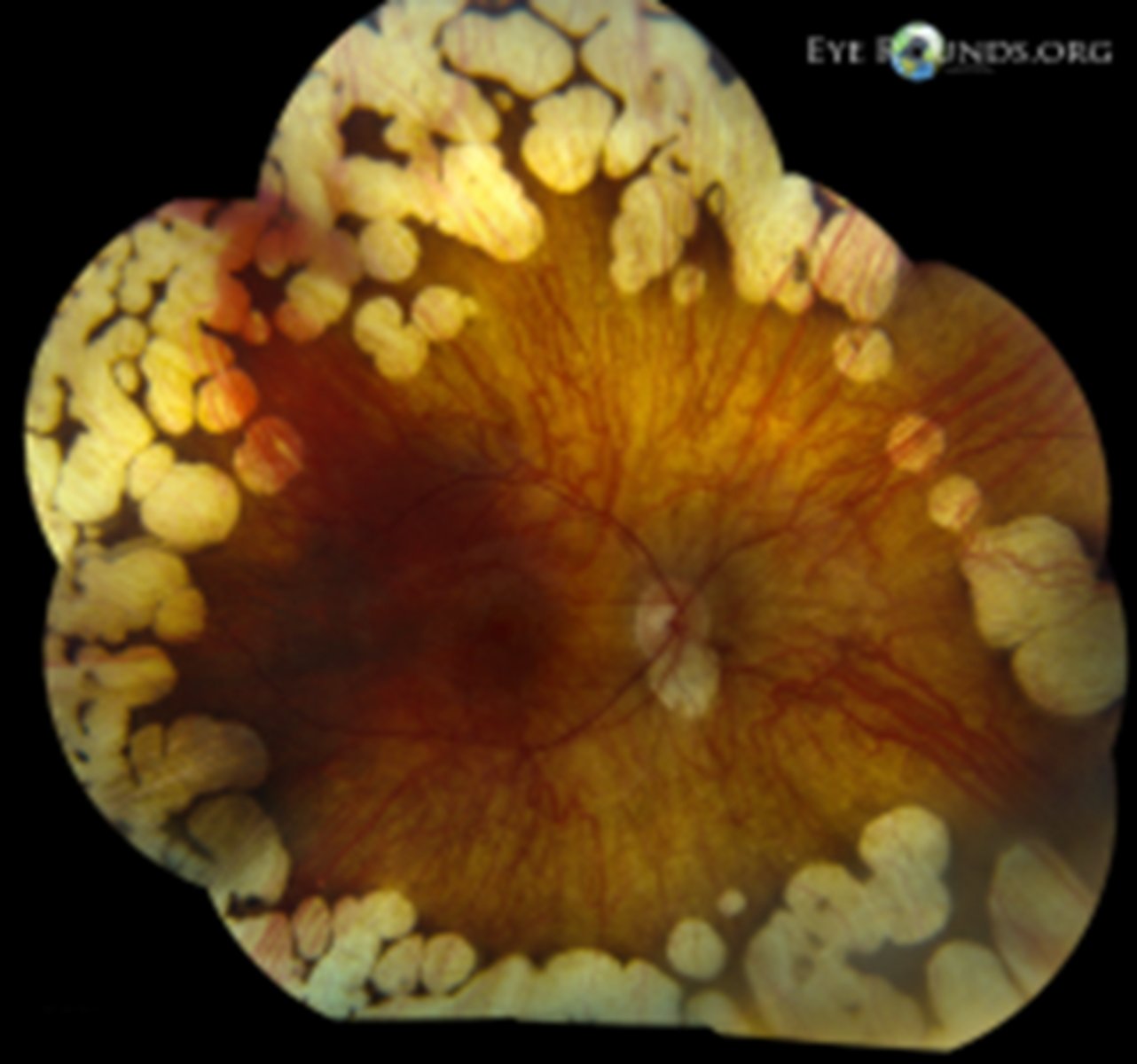
How does gyrate atrophy appear on FAF?
hypoAF in the dark margins
hyperAF in the light atrophic areas
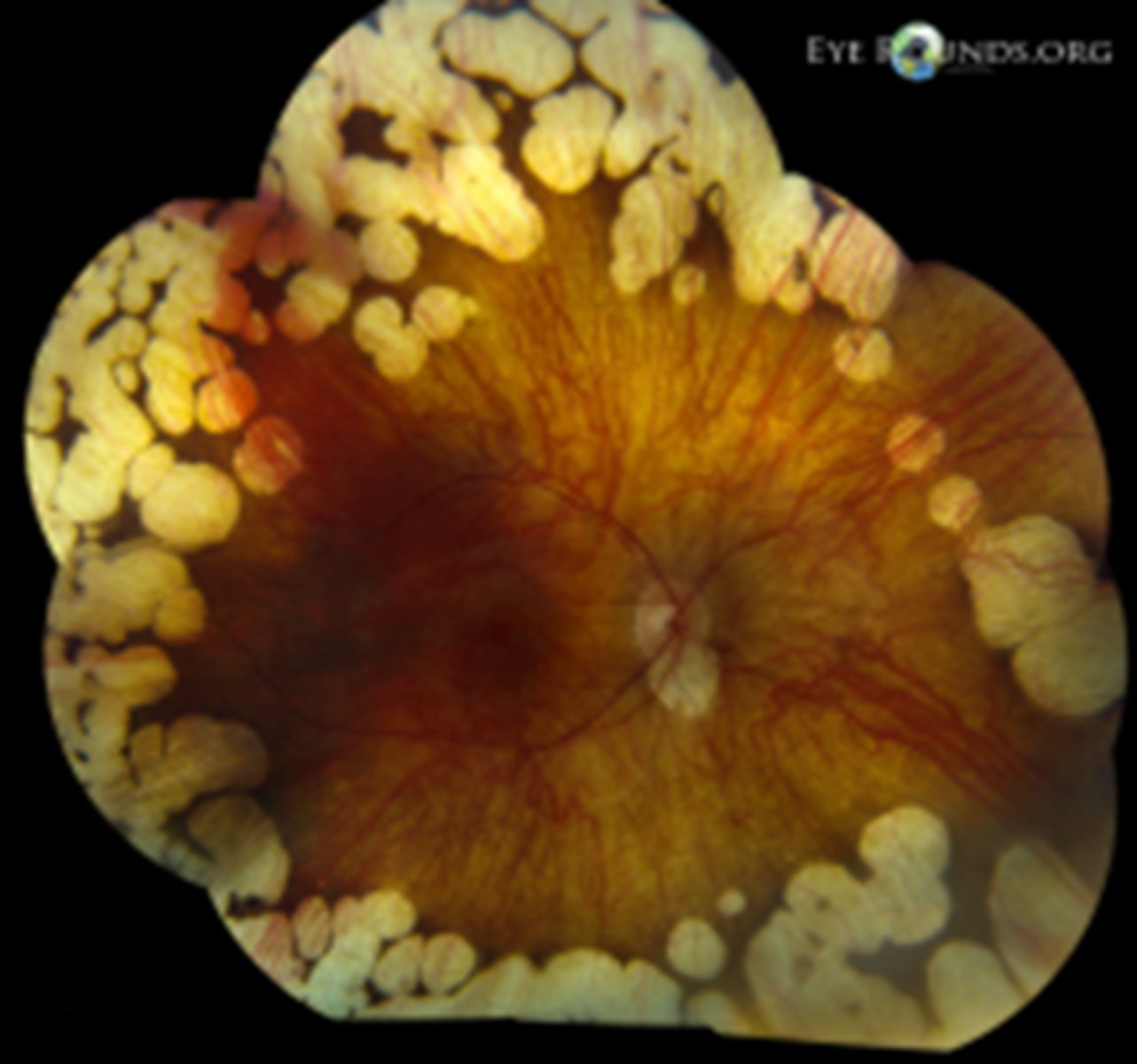
What diagnostic testing can we do for gyrate atrophy?
ornithine blood levels
genetic testing

What are some symptoms of gyrate atrophy?
nyctalopia
peripheral VF loss
VA loss
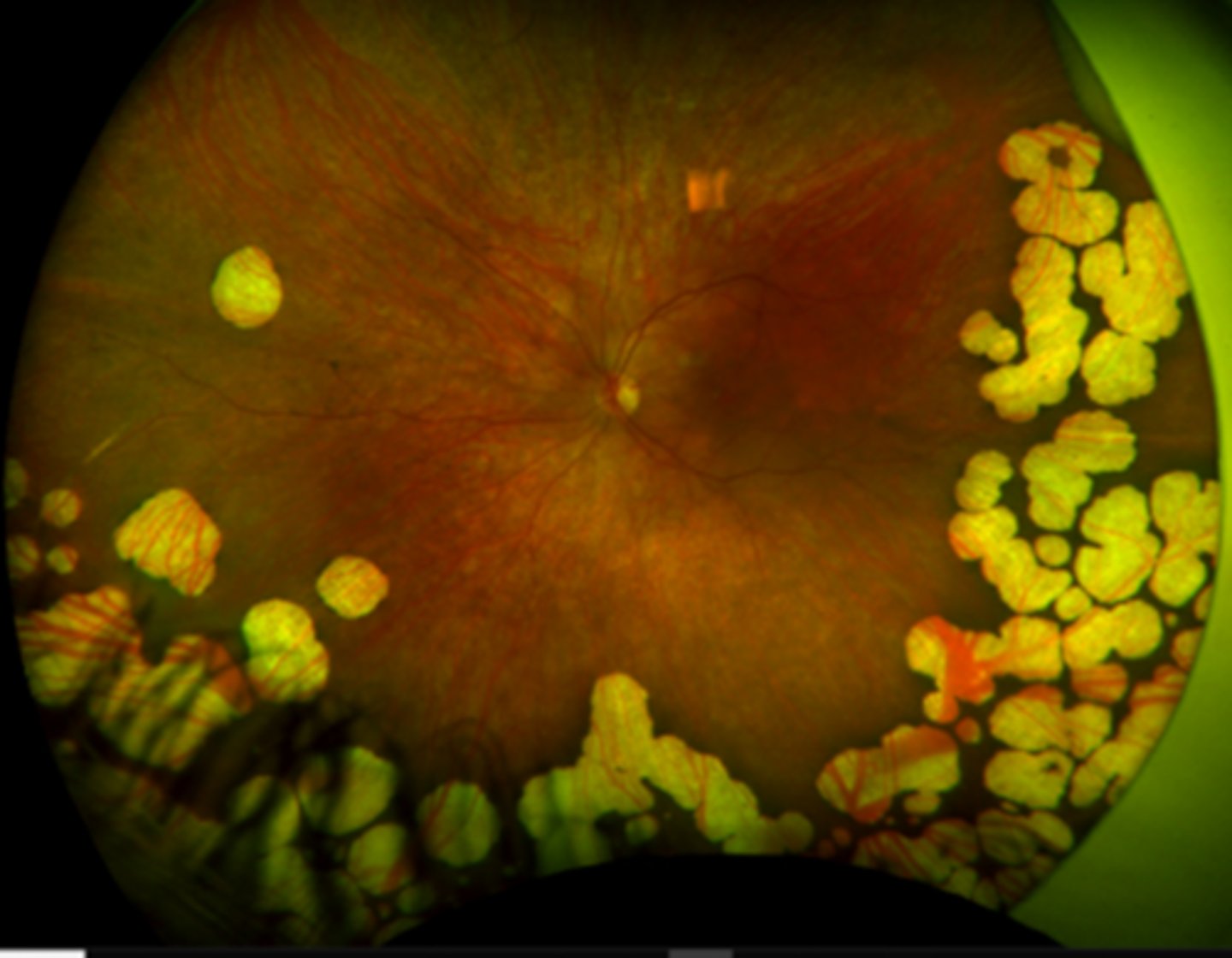
What is the evolution of gyrate atrophy?
first decade = nyctalopia, atrophic patches seen
disease progression = atrophic lesions coalesce and move centripetally towards PP
4th-5th decade = macular involvement
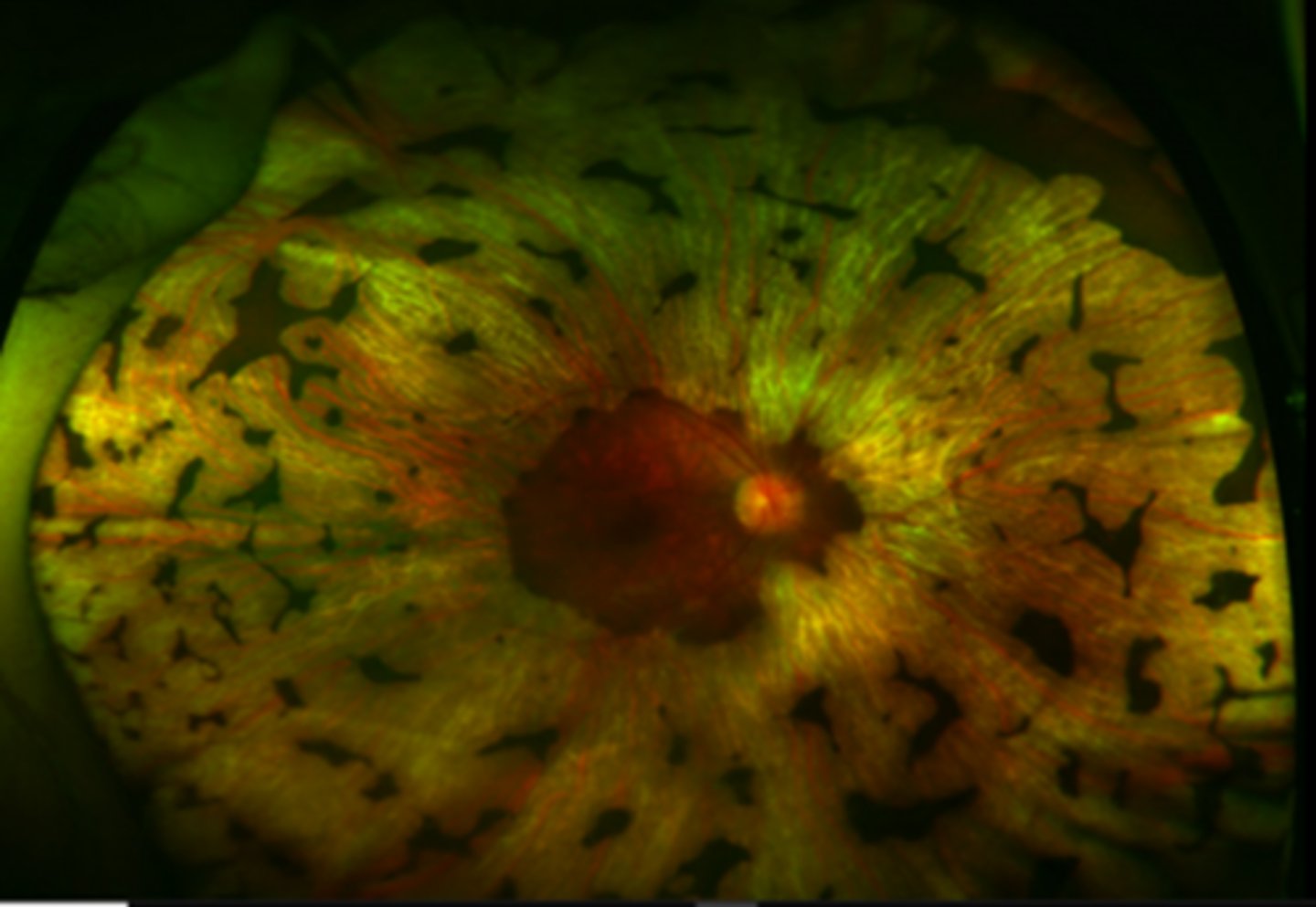
What are 2 possible complications of gyrate atrophy?
dense PSC early in life (2nd decade)
CME
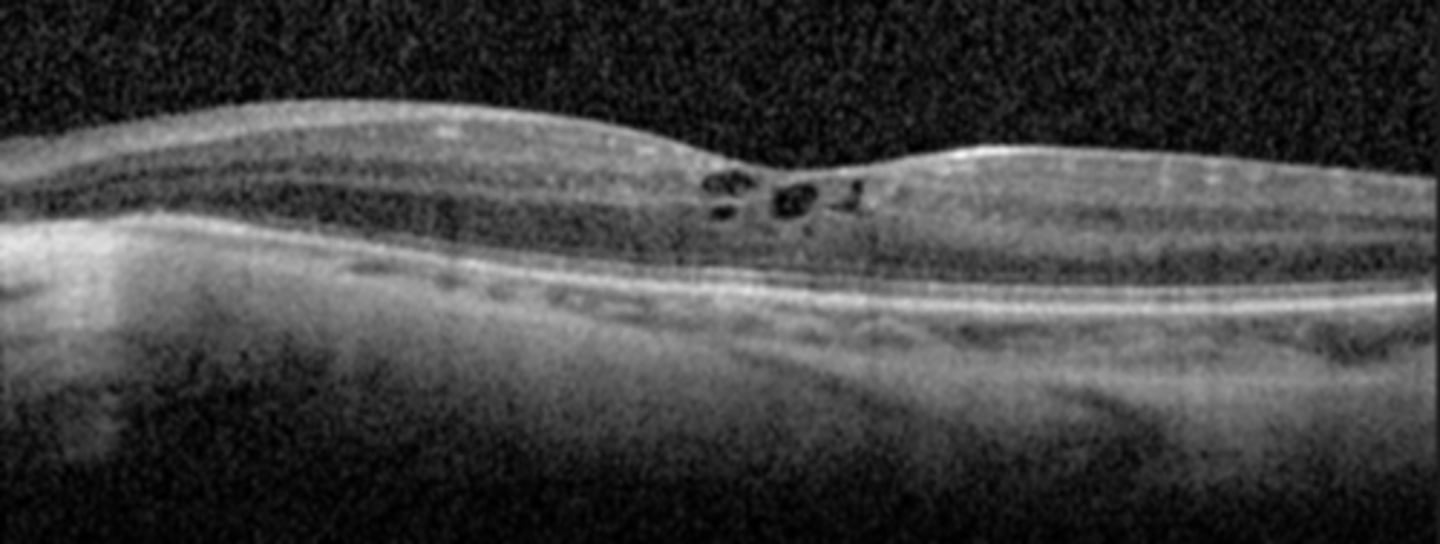
What are some systemic assocations seen with gyrate atrophy?
mild cognitive impairment
delayed language development/speech defects
thin, sparse hair
muscular atrophy
What is the tx for gyrate atrophy?
no cure, but reducing ornithine levels systemically can help with these 3 things:
low-protein, arginine-restricted diet
Vit B6
creatine
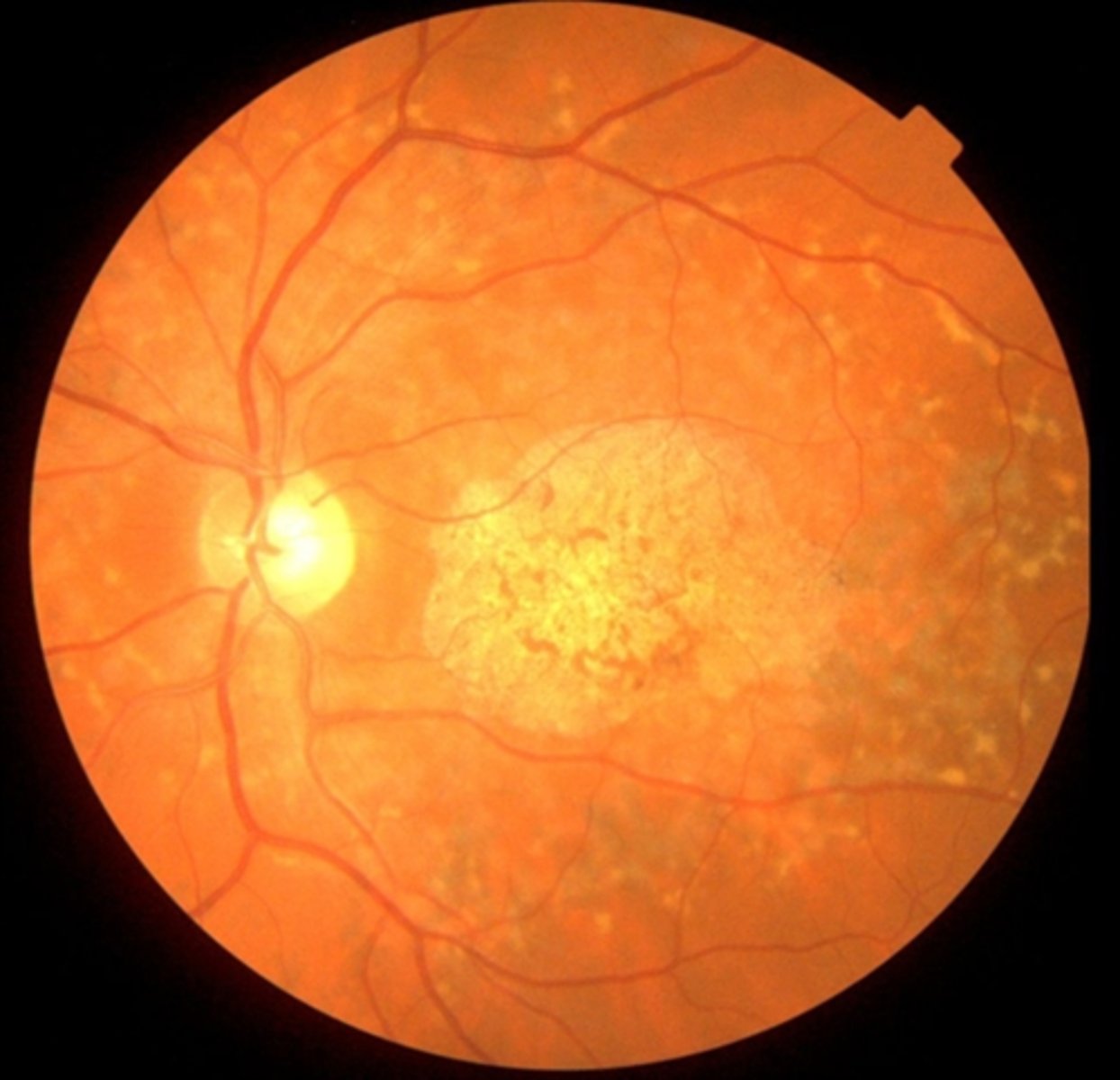
What is Stargardt disease?
mutation in ABCA4 gene = accumulation of visual cycle byproducts in RPE and PR death
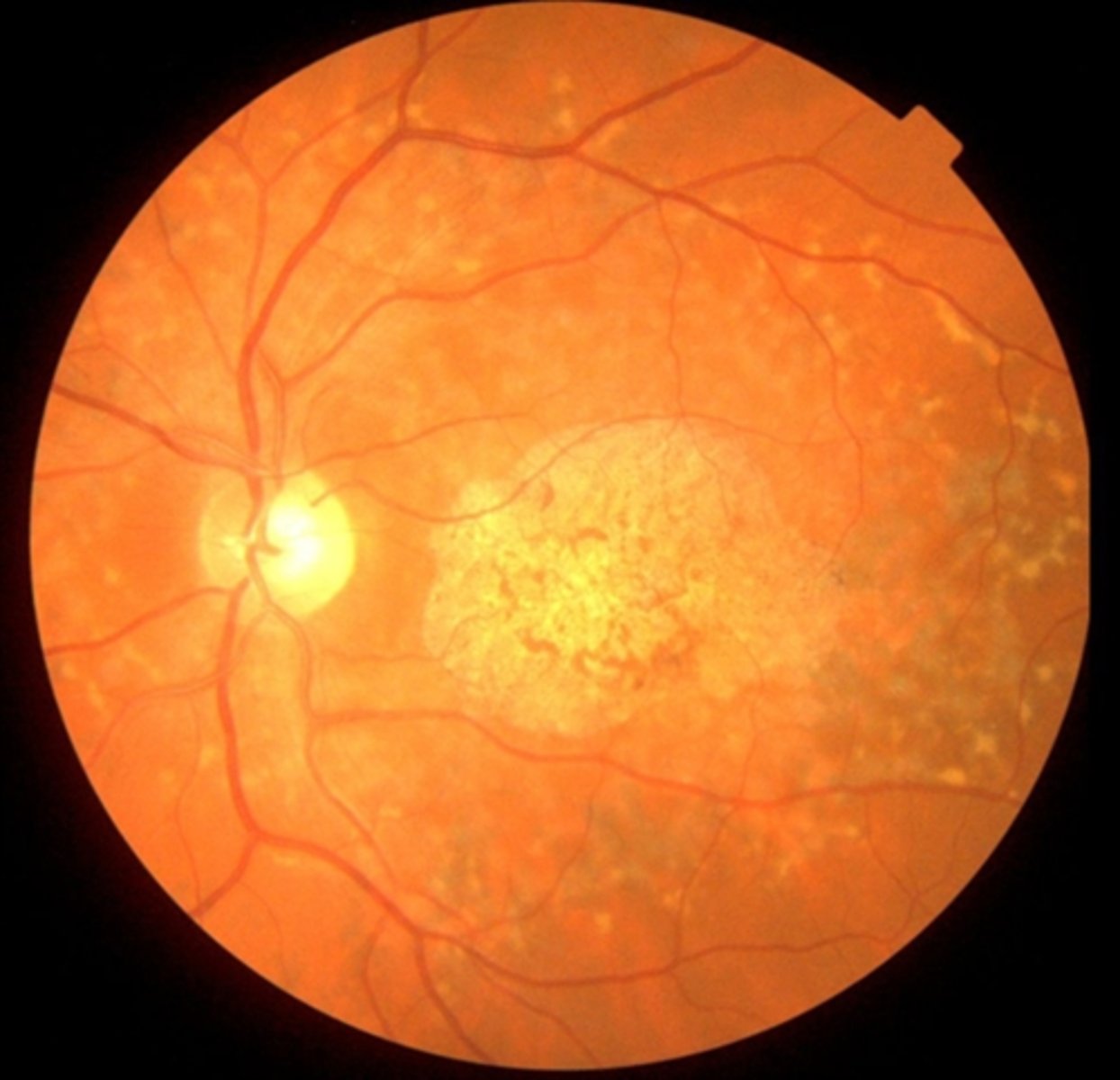
What is the appearance of Stargardt disease?
pigment mottling
"beaten bronze" appearance of macular atrophy
Bullseye maculopathy
fundus flecks = pisciform shaped yellow-white dots of lipofuscin buildup
How does Stargardt disease appear on FAF?
hyperAF of flecks (increased lipofuscin)
hypoAF of RPE damage
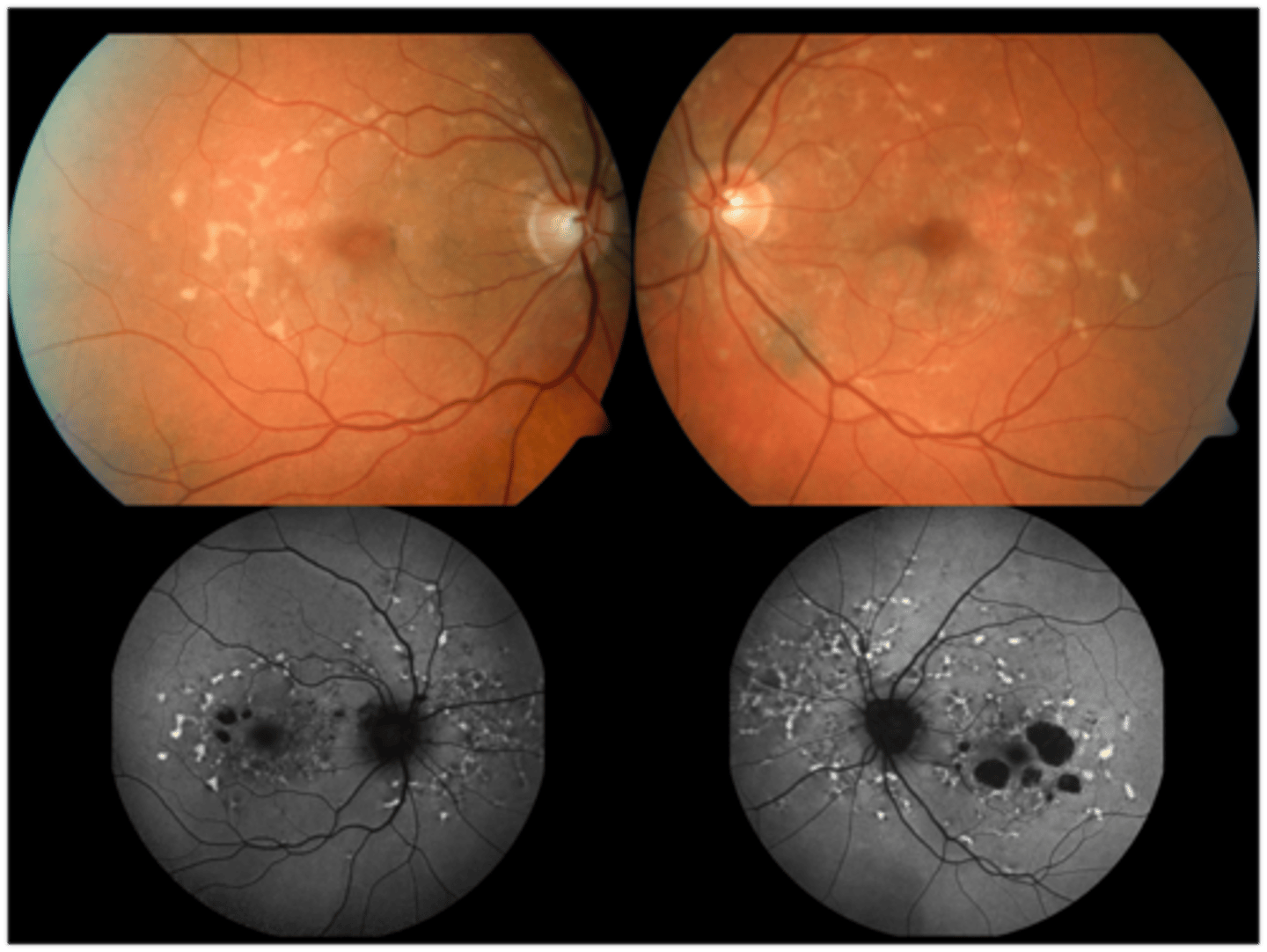
How does Stargardt disease appear on IVFA?
dark choroid due to extreme accumulation of lipofuscin in the RPE that blocks underlying choroid
hyperfluorescent flecks that stain
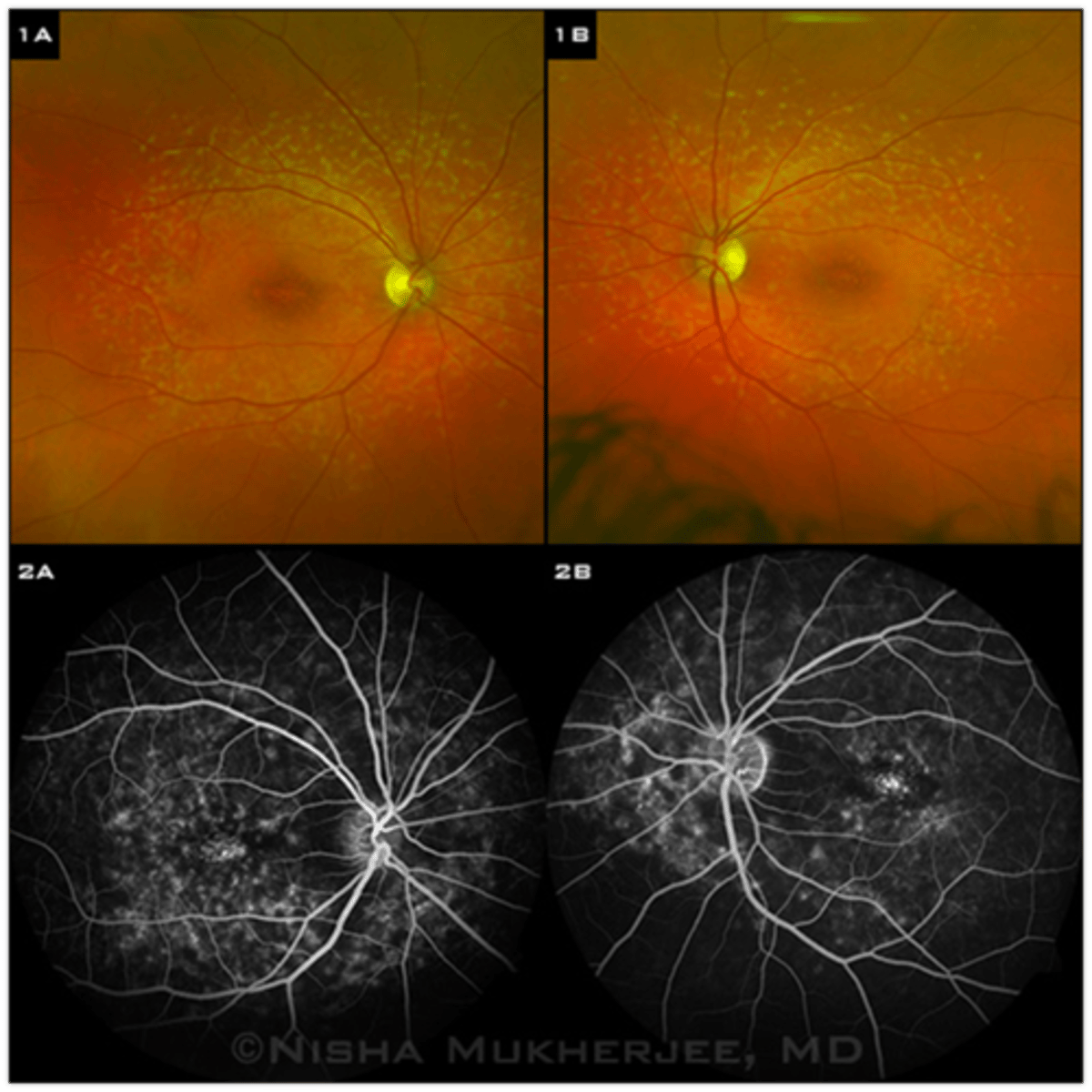
What are some diagnostic tests we can do for Stargardt disease?
OCT = PR atrophy
ERG and EOG = abnormal in later stages
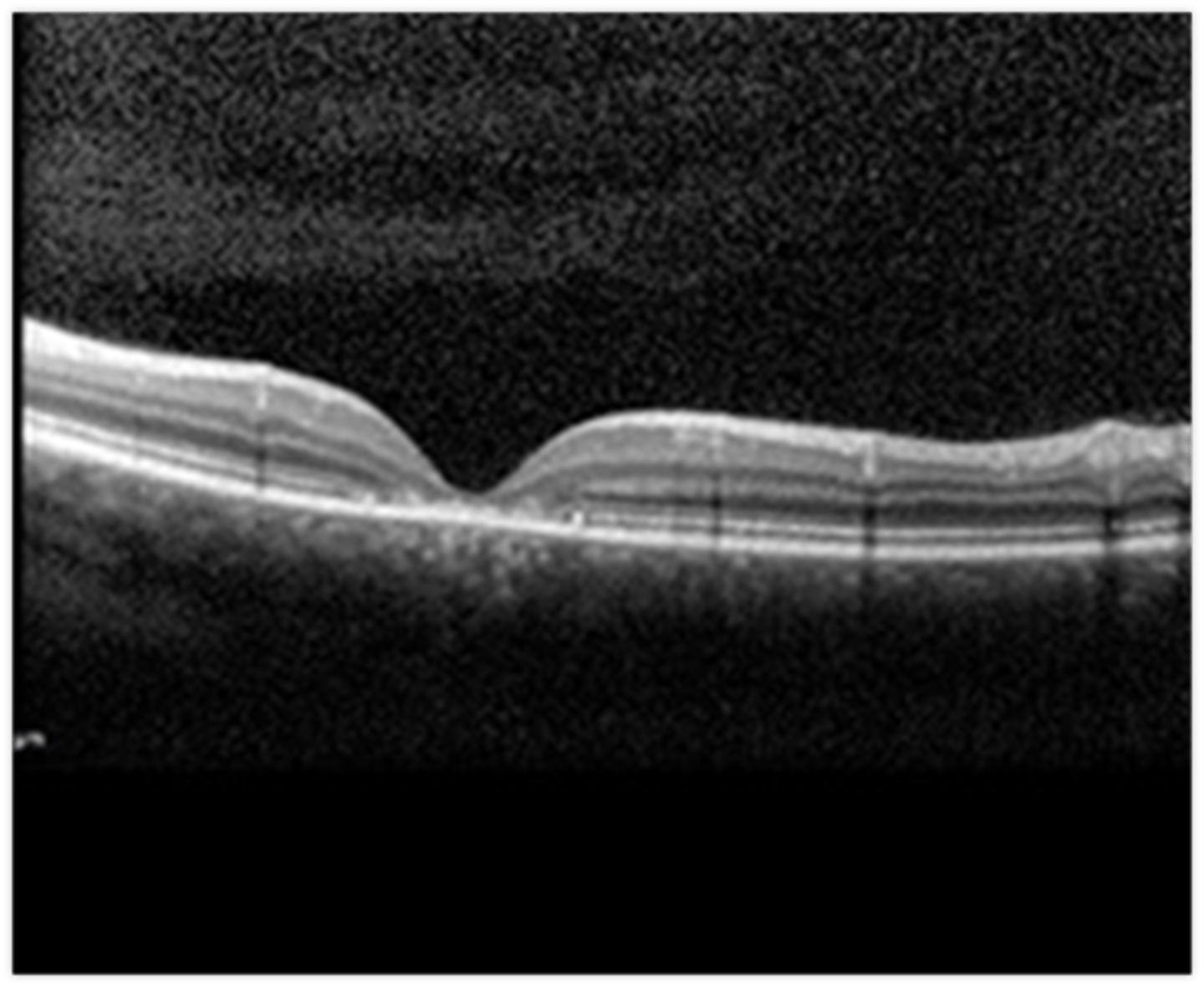
What are some symptoms of Stargardt disease?
bilateral central VA loss
photophobia
color vision anomalies
central scotomas
slow dark adaptation
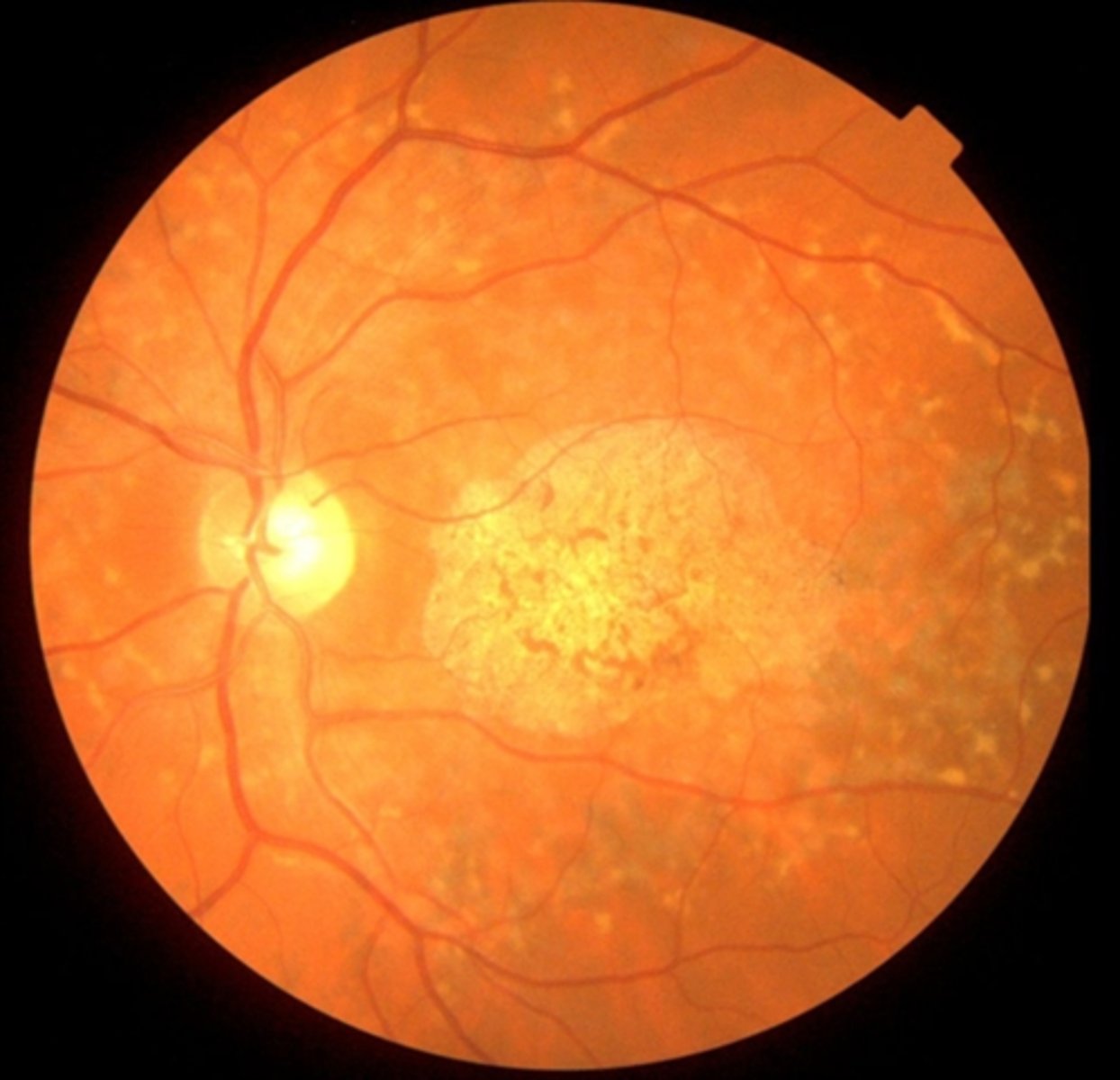
What is the evolution of Stargardt disease?
onset usually between childhood or early adulthood, starting at 20/20-400
rapid vision detioriation that can preceed fundus appearance
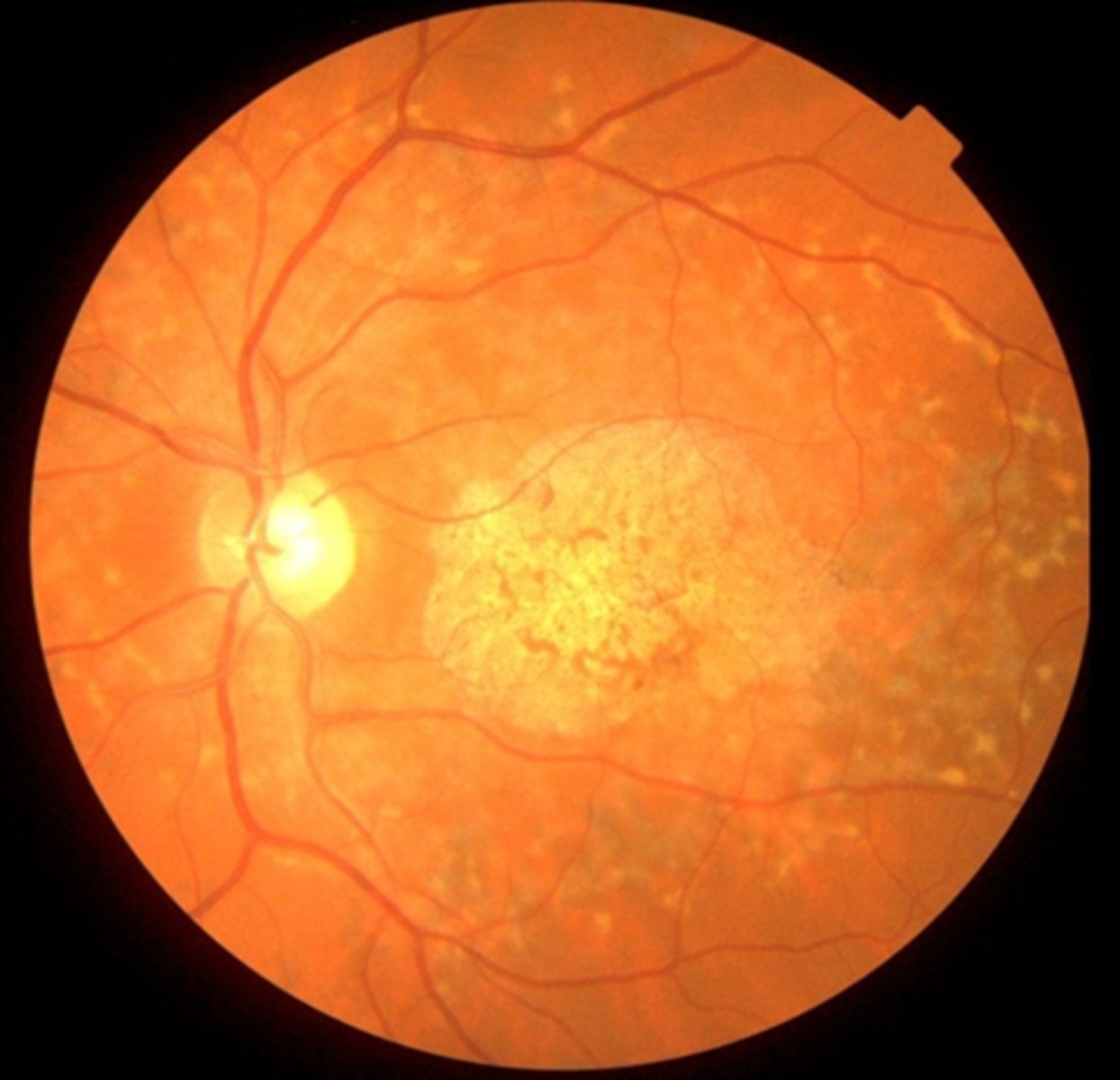
What is fundus flavimaculatus, which is on the Stargardt spectrum?
condition that has...
later onset of the disease
slower detiorioration of vision
more widespread retinal involvment
macula less involved = better VA
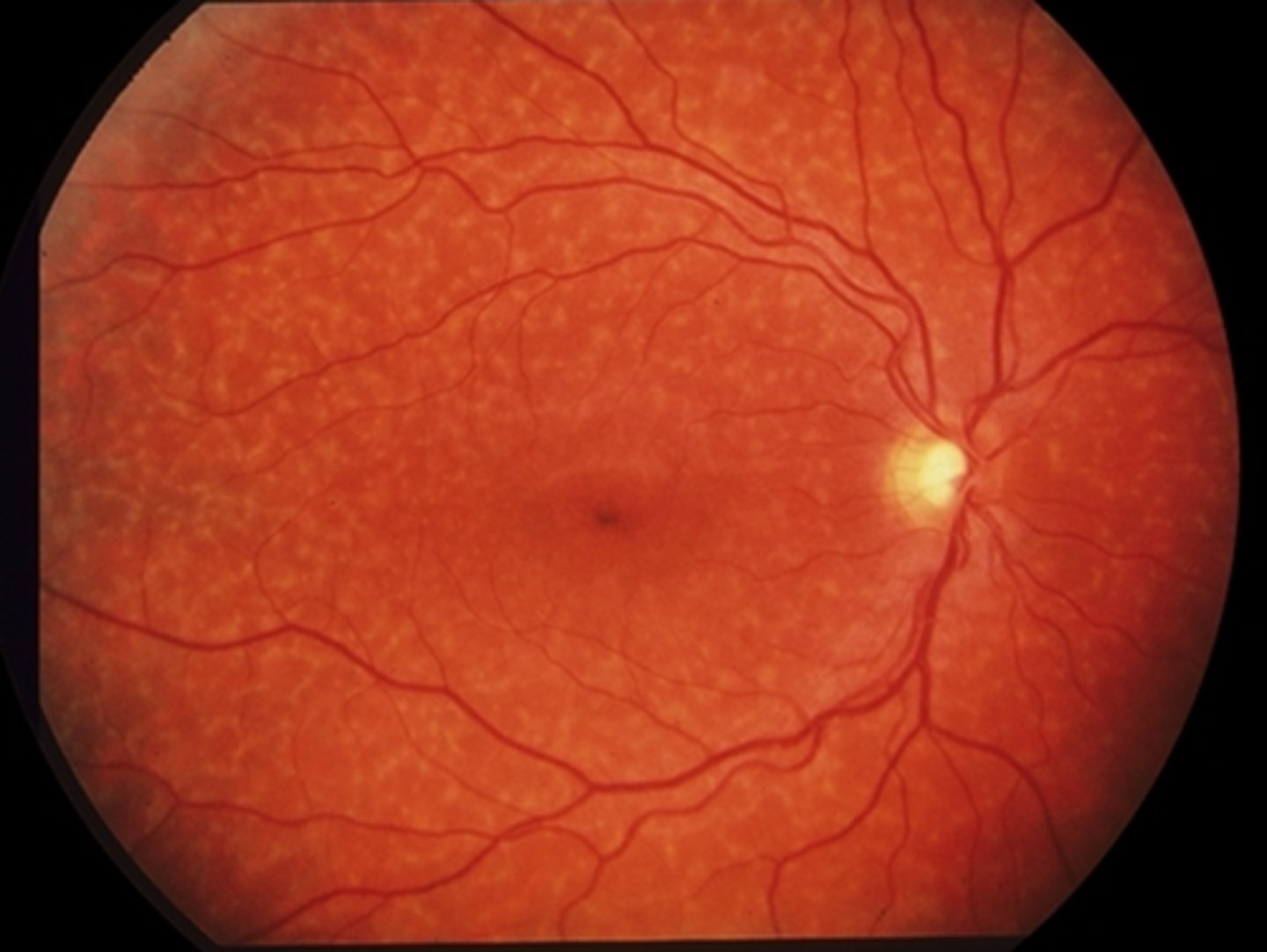
What is the tx for Stargardt disease?
photoprotection as bright light can lead to formation of all-trans-retinal in PR's and contribute to further lipofuscin accumulation
LV referral