Chromosomal Inheritance, Sex-Linked Traits, and Genetic Disorders in Biology
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What did Mendel propose as hereditary units?
Mendel proposed 'hereditary units' as theoretical concepts in 1860.
Who developed the chromosome theory of inheritance?
Sutton and Boveri independently noted parallels between chromosome behavior and Mendel's proposed factors around 1902.
What organism did Thomas Hunt Morgan use for his genetic studies?
Morgan used Drosophila melanogaster, a common species of fruit fly.
Why are fruit flies considered convenient for genetic studies?
They produce many offspring, have a generation that can be bred every two weeks, and have only four pairs of chromosomes.
What are wild type and mutant phenotypes in fruit flies?
Wild type phenotypes are common traits, while mutant phenotypes are alternative traits, such as white eyes instead of red.
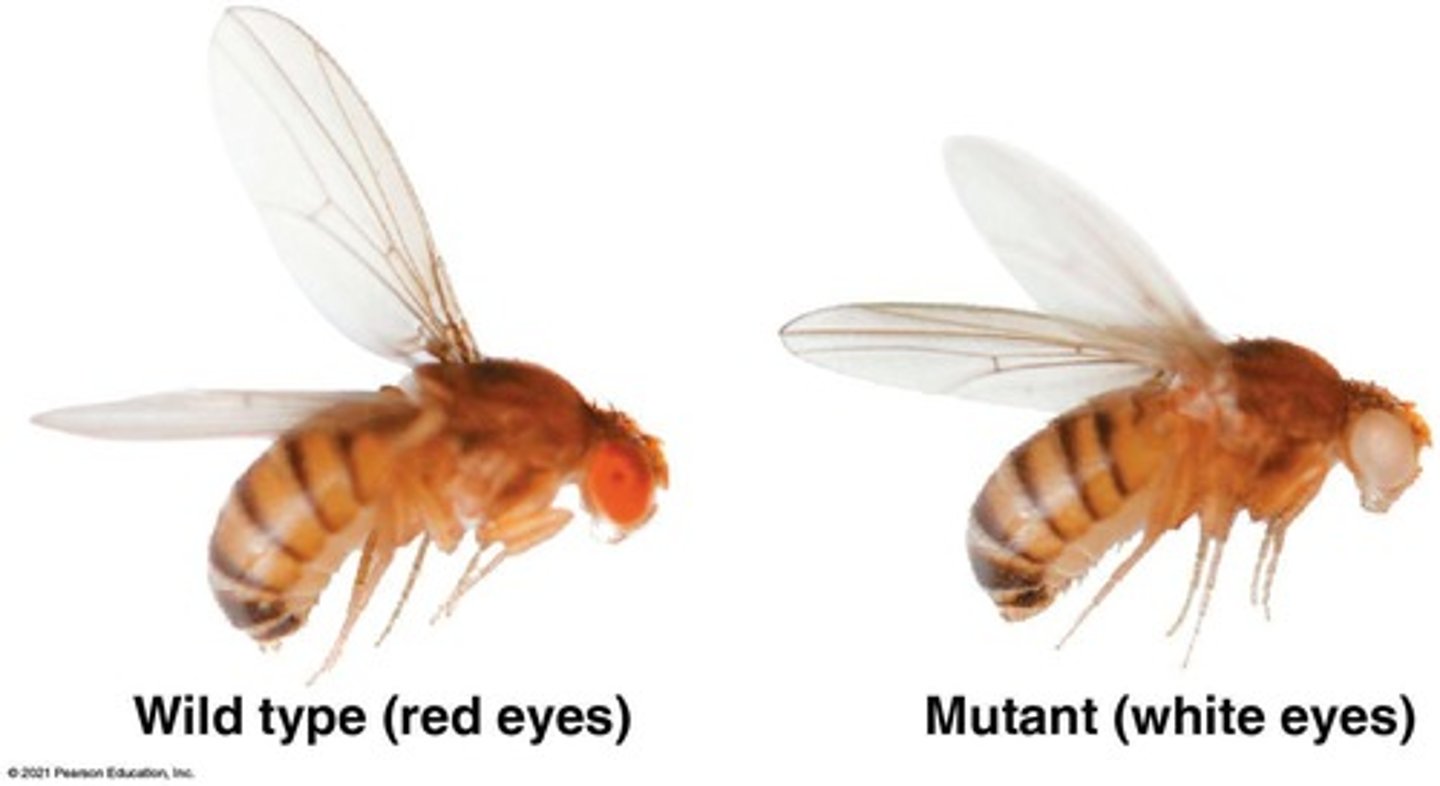

What was the result of Morgan's mating experiment with white-eyed and red-eyed flies?
The F1 generation all had red eyes, and the F2 generation showed a 3:1 red to white eye ratio, with only males having white eyes.
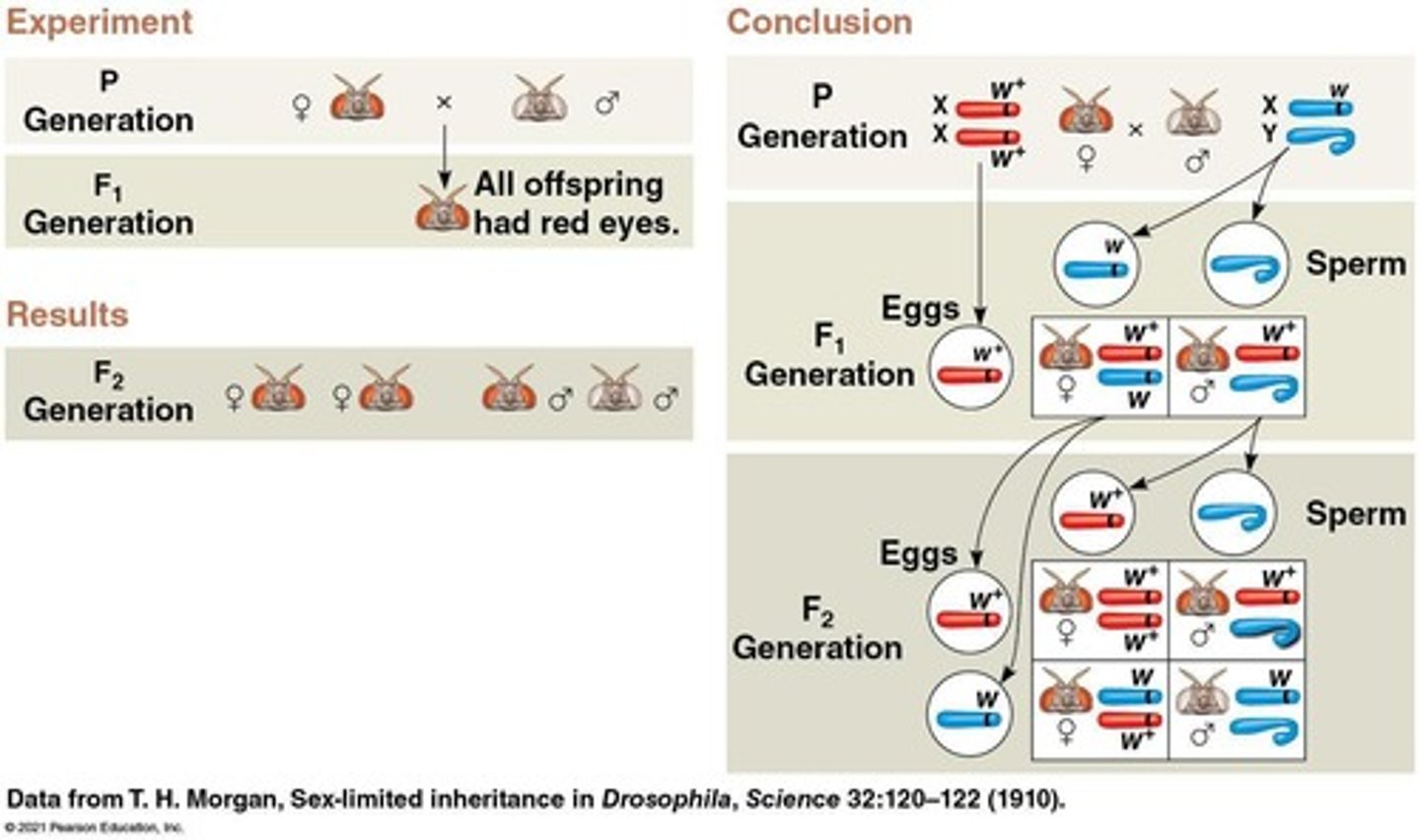
What conclusion did Morgan draw about the white-eyed mutant allele?
Morgan concluded that the white-eyed mutant allele is located on the X chromosome.
What are the two types of sex chromosomes in mammals?
Mammals have a larger X chromosome and a smaller Y chromosome.
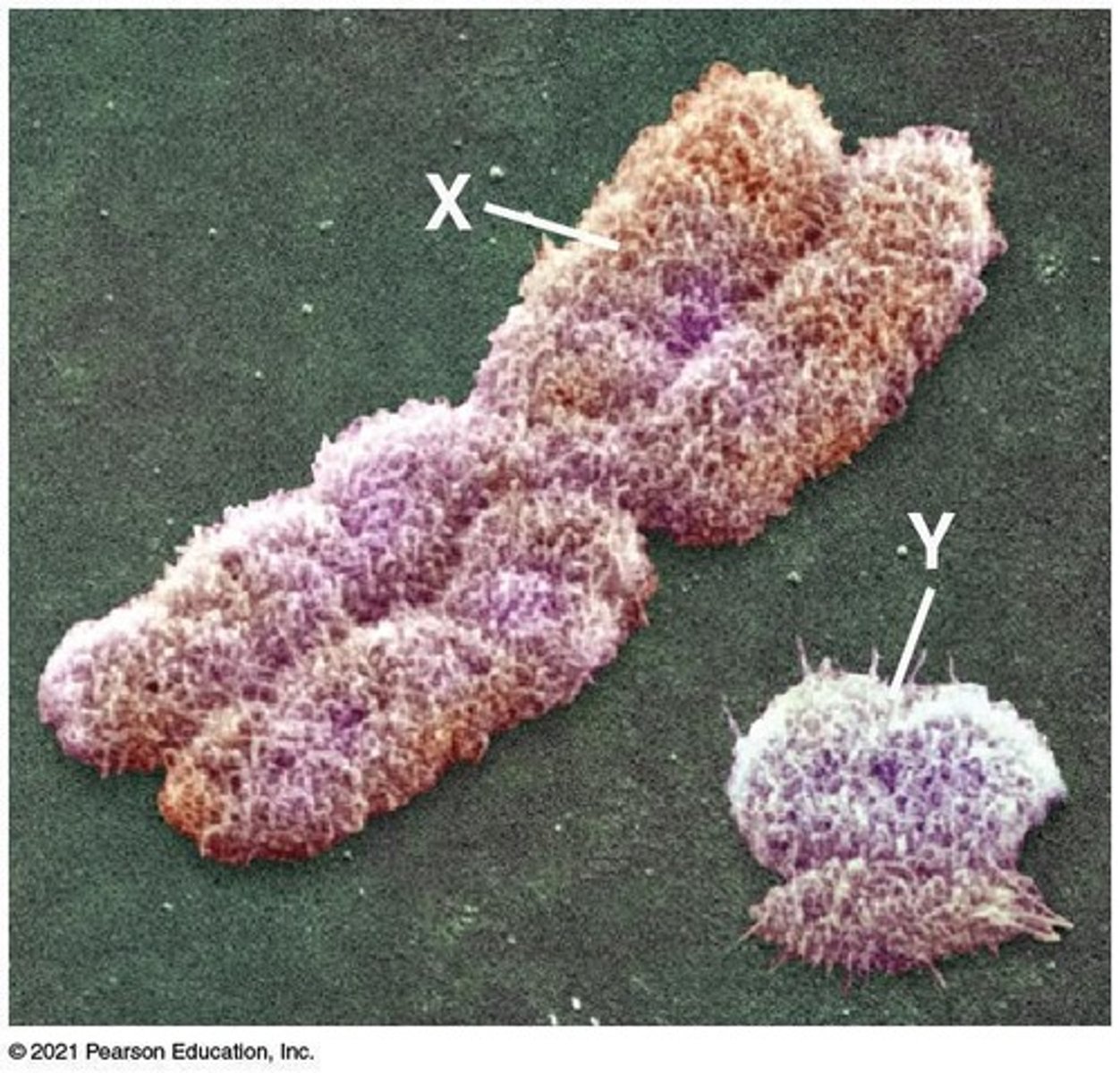
What determines male and female anatomy in humans?
Two X chromosomes usually develop female anatomy, while one X and one Y chromosome develop male anatomy.
What is the role of the SRY gene?
The SRY gene on the Y chromosome is responsible for the development of testes in an embryo.
What are sex-linked genes?
Genes located on either sex chromosome; Y-linked genes are on the Y chromosome, while X-linked genes are on the X chromosome.
How many genes are identified on the human Y chromosome?
Only 78 genes coding for about 25 proteins have been identified on the human Y chromosome.
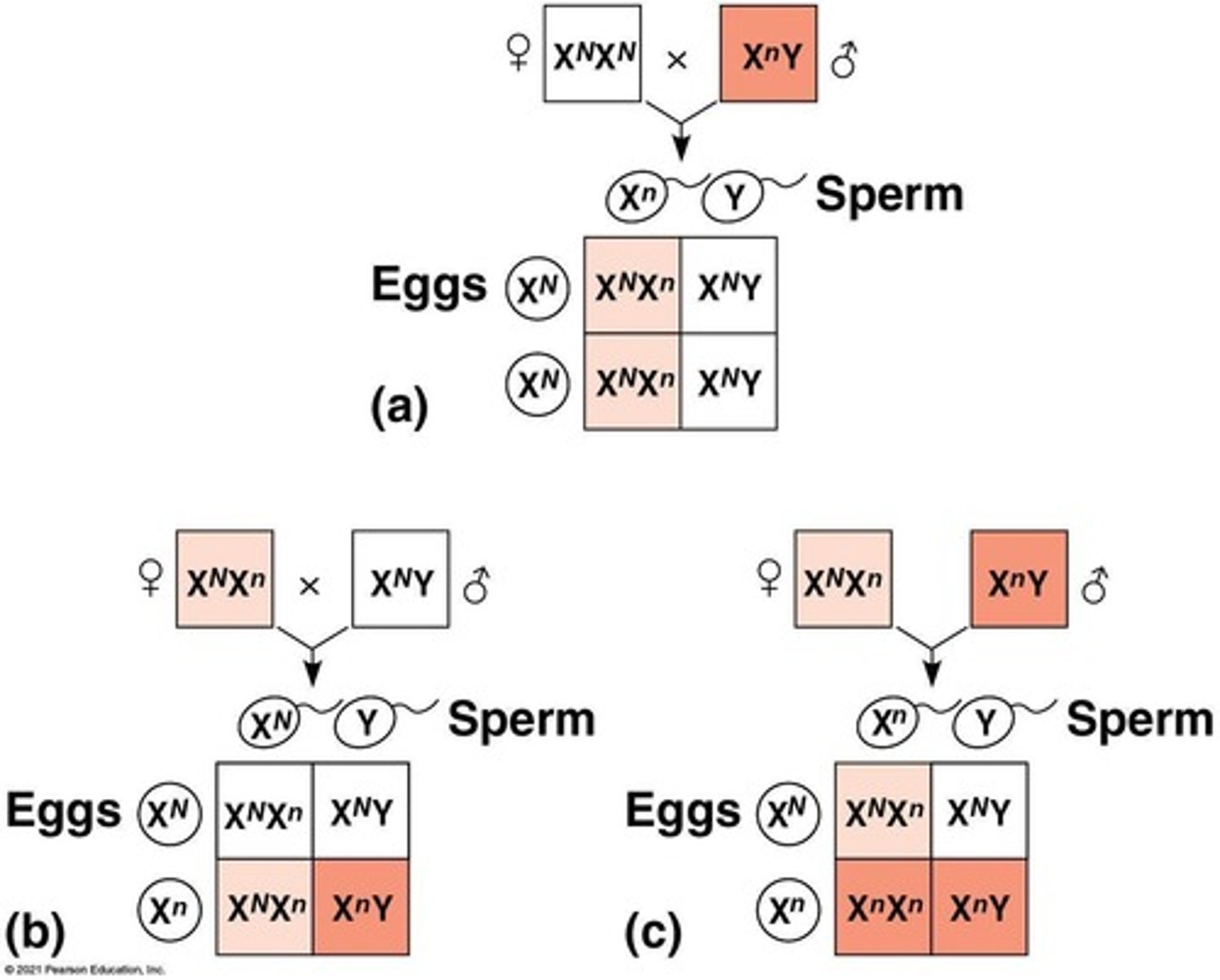
What is required for a recessive X-linked trait to be expressed in females?
A female needs two copies of the allele (homozygous) for the trait to be expressed.
What is required for a recessive X-linked trait to be expressed in males?
A male needs only one copy of the allele (hemizygous) for the trait to be expressed.
Why are X-linked recessive disorders more common in males?
Because males have only one X chromosome, they are more likely to express recessive traits linked to that chromosome.
Name two disorders caused by recessive alleles on the X chromosome.
Color blindness and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
What happens to one of the X chromosomes in female mammals during development?
One of the two X chromosomes is randomly inactivated and condenses into a Barr body.
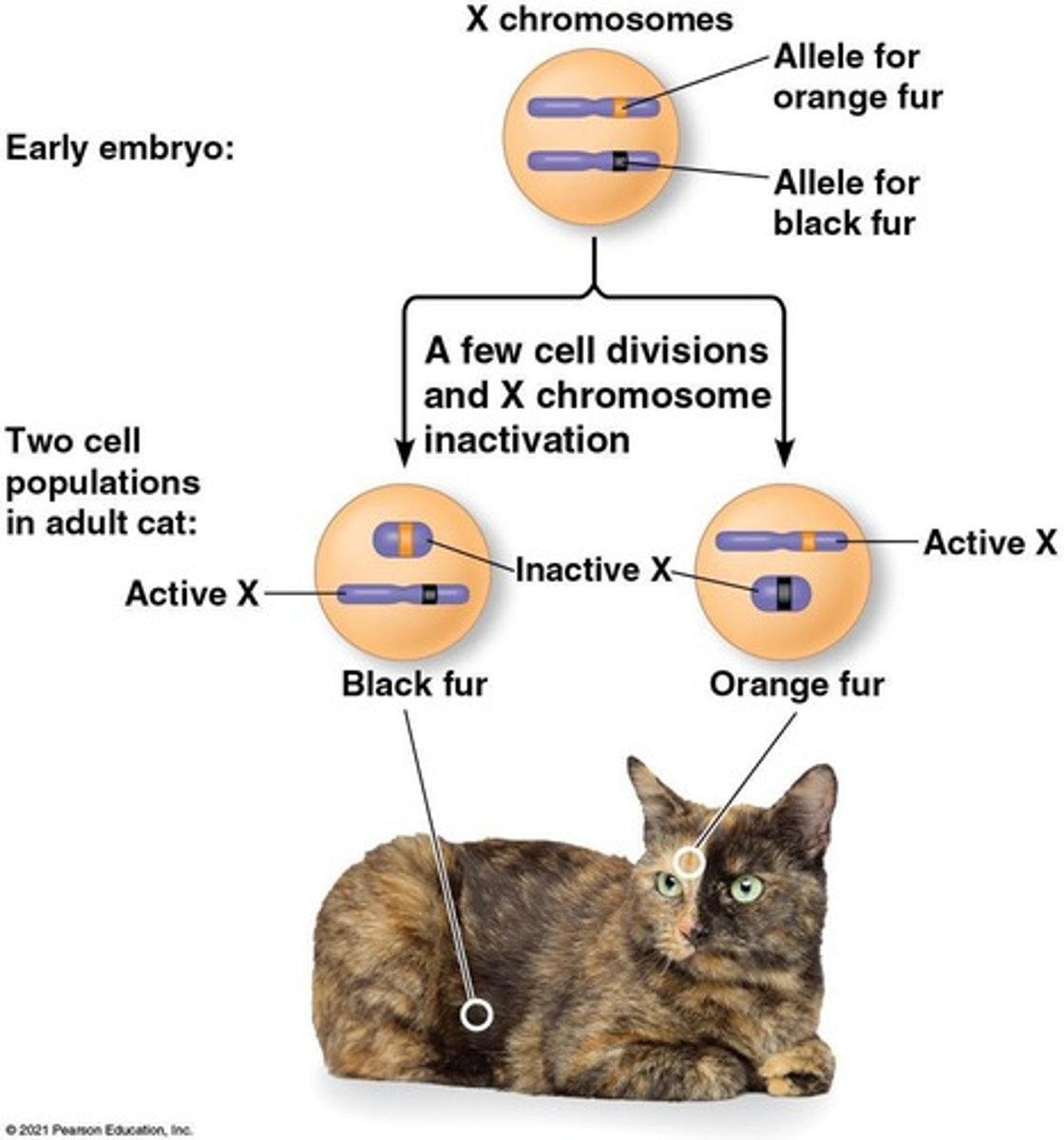
What is the gene responsible for X chromosome inactivation?
The gene is called XIST (X-inactive specific transcript).
What are linked genes?
Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together.
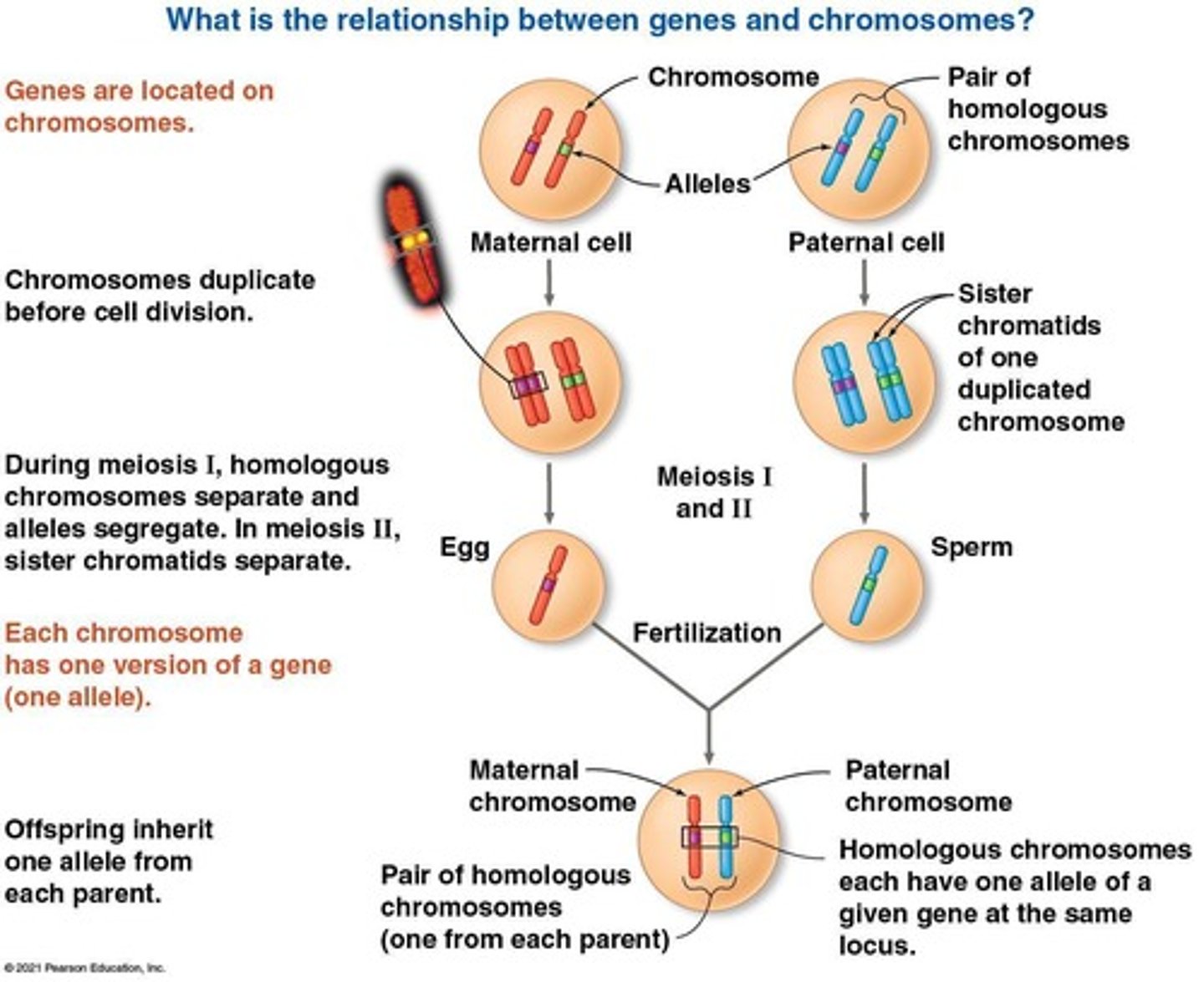
What was the focus of Morgan's experiments with fruit flies?
Morgan focused on how linkage affects the inheritance of traits such as body color and wing size.
What are parental types and recombinant types in offspring?
Parental types match the parental phenotypes, while recombinant types have new combinations of traits.
What is genetic recombination?
The production of offspring with combinations of traits differing from either parent.
What mechanism did Morgan propose for the separation of linked genes?
Morgan proposed that crossing over of homologous chromosomes occasionally breaks the physical connection between linked genes.
What is the frequency of recombination for genes on different chromosomes?
A 50% frequency of recombination is observed for any two genes on different chromosomes.
What is the significance of crossing over in genetics?
Crossing over allows for the production of nonparental allele combinations, contributing to genetic diversity.
What role do recombinant chromosomes play in genetics?
They bring alleles together in new combinations in gametes.
How does random fertilization affect genetic variation?
It increases the number of variant combinations that can be produced.
What is the significance of genetic variation in natural selection?
It is the raw material upon which natural selection works.
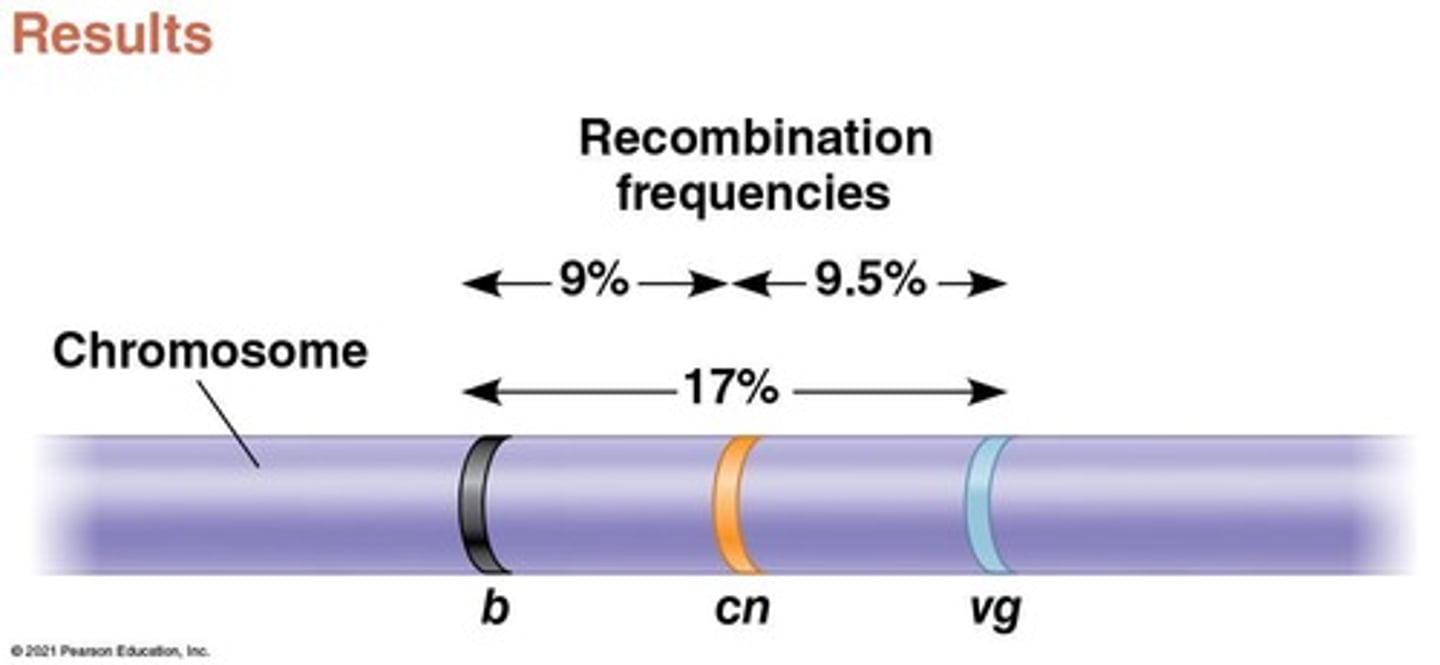
Who constructed the first genetic map?
Alfred Sturtevant, a student of Morgan.
What does a linkage map represent?
It is a genetic map of a chromosome based on recombination frequencies.
What does one map unit represent in genetics?
One map unit represents a 1% recombination frequency.
What happens to genes that are far apart on the same chromosome?
They can have a recombination frequency near 50%, behaving as if on different chromosomes.
What is aneuploidy?
A condition resulting from the fertilization of gametes in which nondisjunction occurred, leading to an abnormal number of a particular chromosome.
What is monosomy?
A condition where a zygote has only one copy of a particular chromosome.
What is trisomy?
A condition where a zygote has three copies of a particular chromosome.
What is polyploidy?
A condition in which an organism has more than two complete sets of chromosomes.
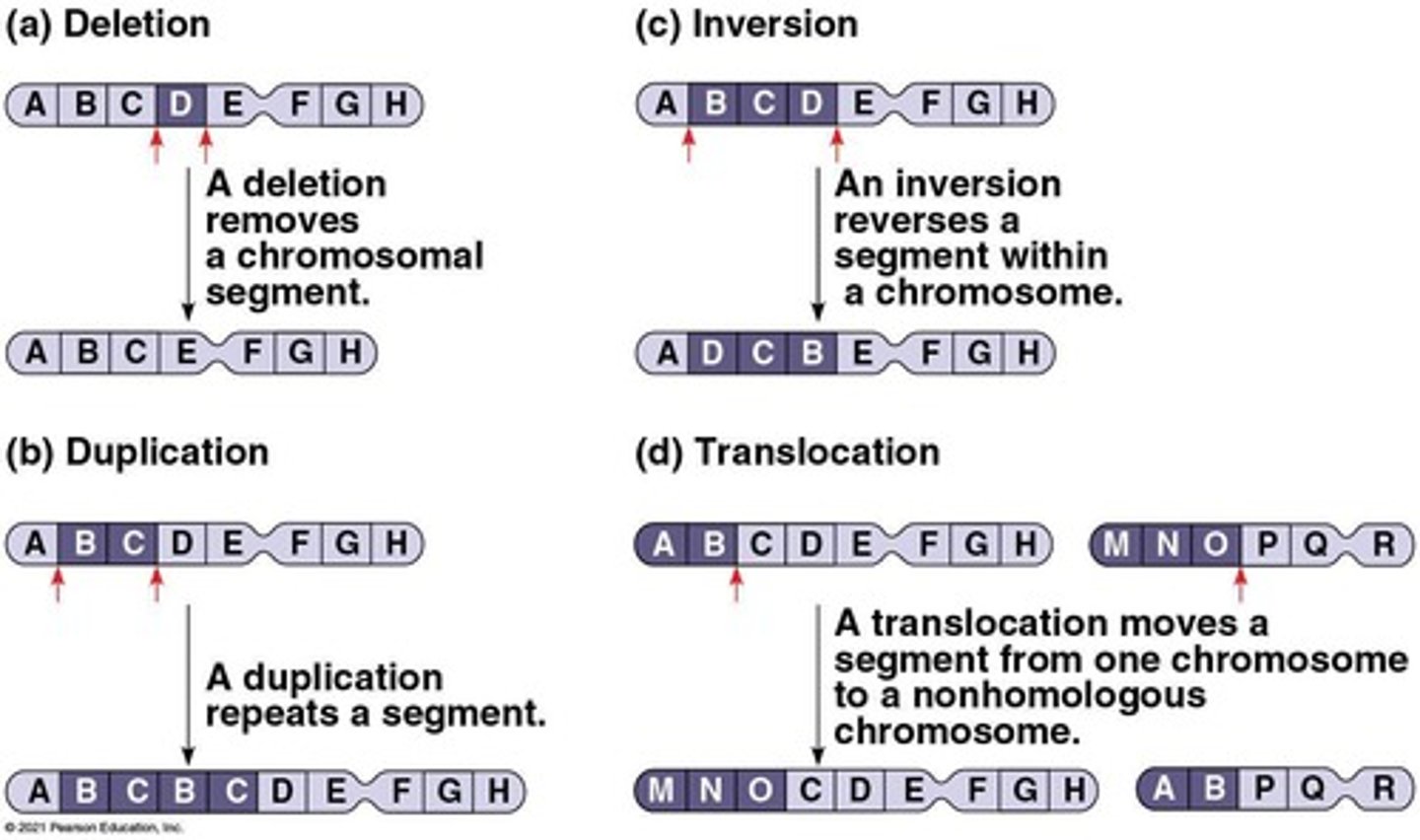
What are the four types of changes that can occur in chromosome structure due to breakage?
Deletion, duplication, inversion, and translocation.
What is Down syndrome?
An aneuploid condition resulting from three copies of chromosome 21.
What is Klinefelter syndrome?
A condition resulting from an extra chromosome in a male, producing XXY individuals.
What is Turner syndrome?
A condition caused by monosomy X, producing X0 females who are sterile.
What is genomic imprinting?
A phenomenon where the phenotype depends on which parent passed along the alleles for certain traits.
What is the role of methylation in genomic imprinting?
It is involved in the silencing of certain genes depending on parental origin.
How are extranuclear genes inherited?
They are inherited maternally because the zygote's cytoplasm comes from the egg.
What are some diseases caused by defects in mitochondrial genes?
Mitochondrial myopathy and Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.
What is a potential method to avoid passing along mitochondrial disorders?
Transferring chromosomes from an affected mother's egg to a healthy donor egg to create a 'two-mother' egg.
What is the significance of chromosomal alterations in humans?
They can lead to spontaneous abortions or a variety of developmental disorders.
What is the relationship between chromosomal alterations and cancer?
Certain cancers, like chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), can be caused by translocations of chromosomes.
What is the frequency of Down syndrome in the United States?
It affects about one out of every 830 children born.
What is the correlation between maternal age and Down syndrome?
The frequency of Down syndrome increases with the age of the mother.
What is the significance of Sturtevant's linkage maps in genetics?
They provided evidence that genes are located on chromosomes.
What is the effect of large-scale chromosomal alterations in humans?
They often lead to spontaneous abortions or developmental disorders.
What are linkage groups in genetics?
Clusters of linked genes identified through linkage maps.
What is the first imprinted gene to be identified?
The mouse gene for insulin-like growth factor 2 (Igf2).