Proteins and Enzymes IB Bio HL
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
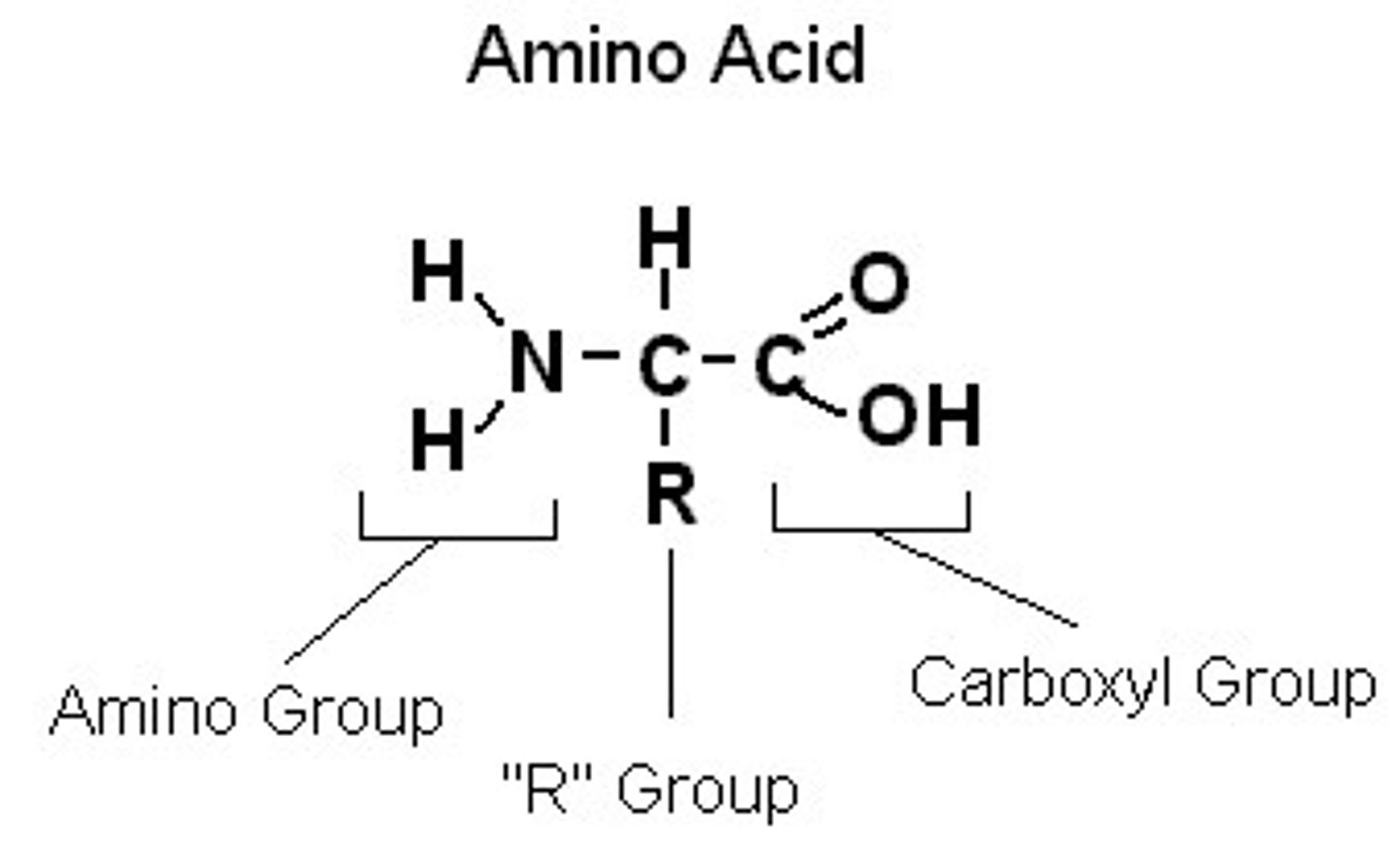
What are the parts of an amino acid?
Amino Group, Carboxyl Group,
R Group (changes)
How many amino acids are there?
20 (9 are essential)
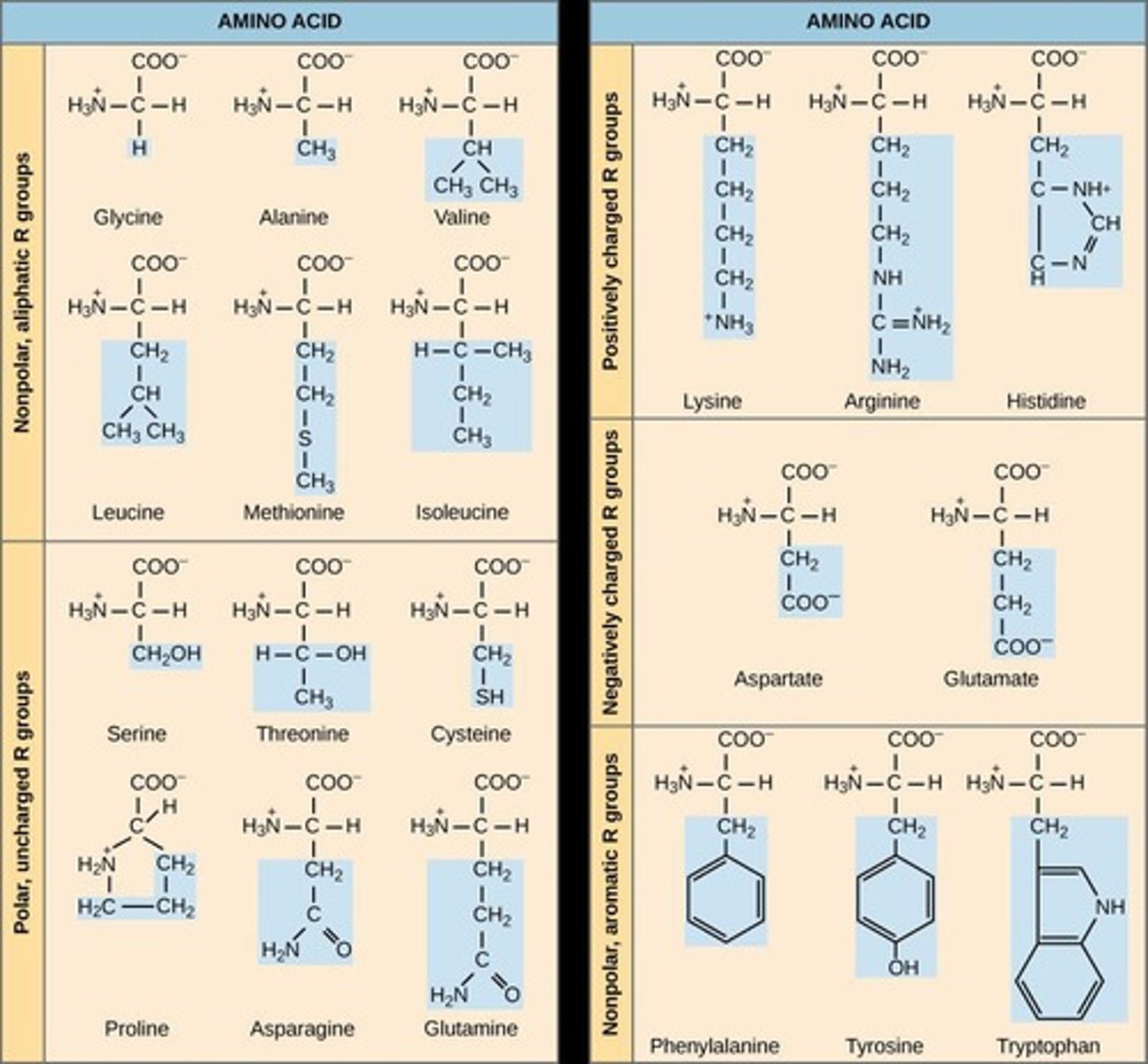
Chemical diversity in R groups
R groups can be...
- positive or negatively charged
- acidic or basic
- polar or non-polar
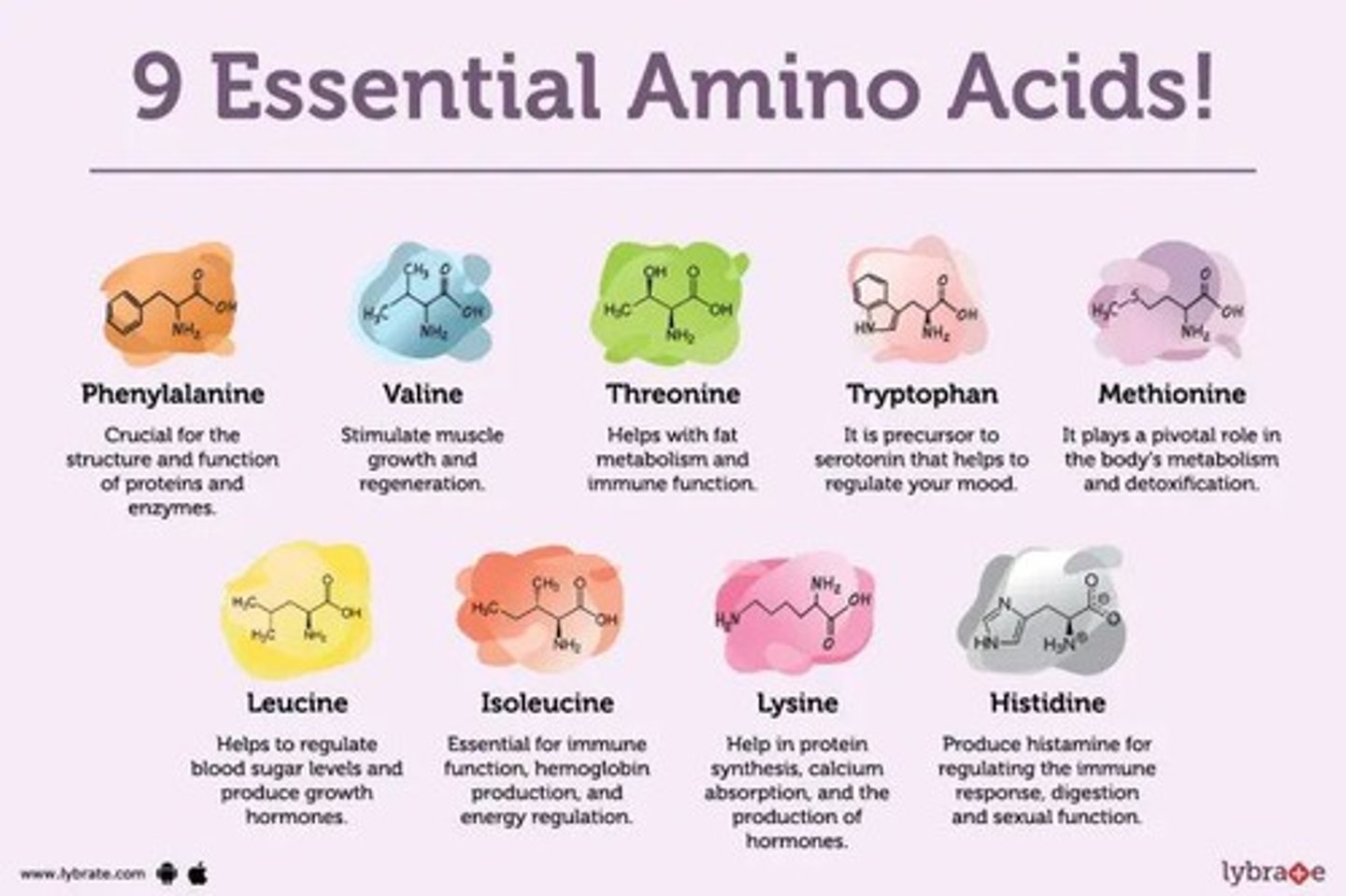
What does it mean if an amino acid is "essential"?
Essential: they cannot be synthesized and must be obtained from food
Non-essential: can be made from other amino acids
How are amino acid chains created?
Condensation Reaction (water OUT to combine) which forms a peptide bond
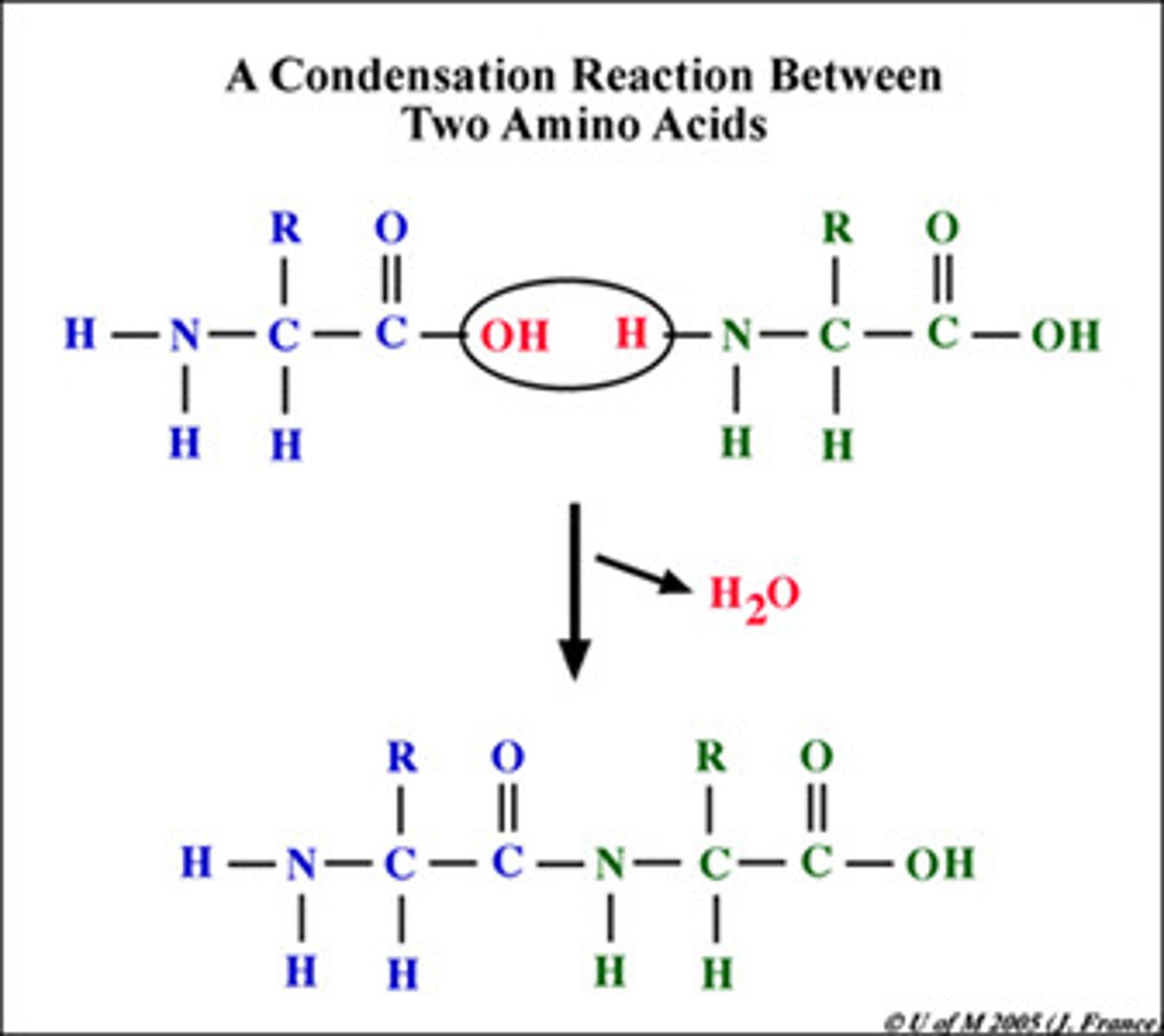
Where do amino acids connect to form dipeptides?
the amine group of one amino acid connects to the carboxyl group of another
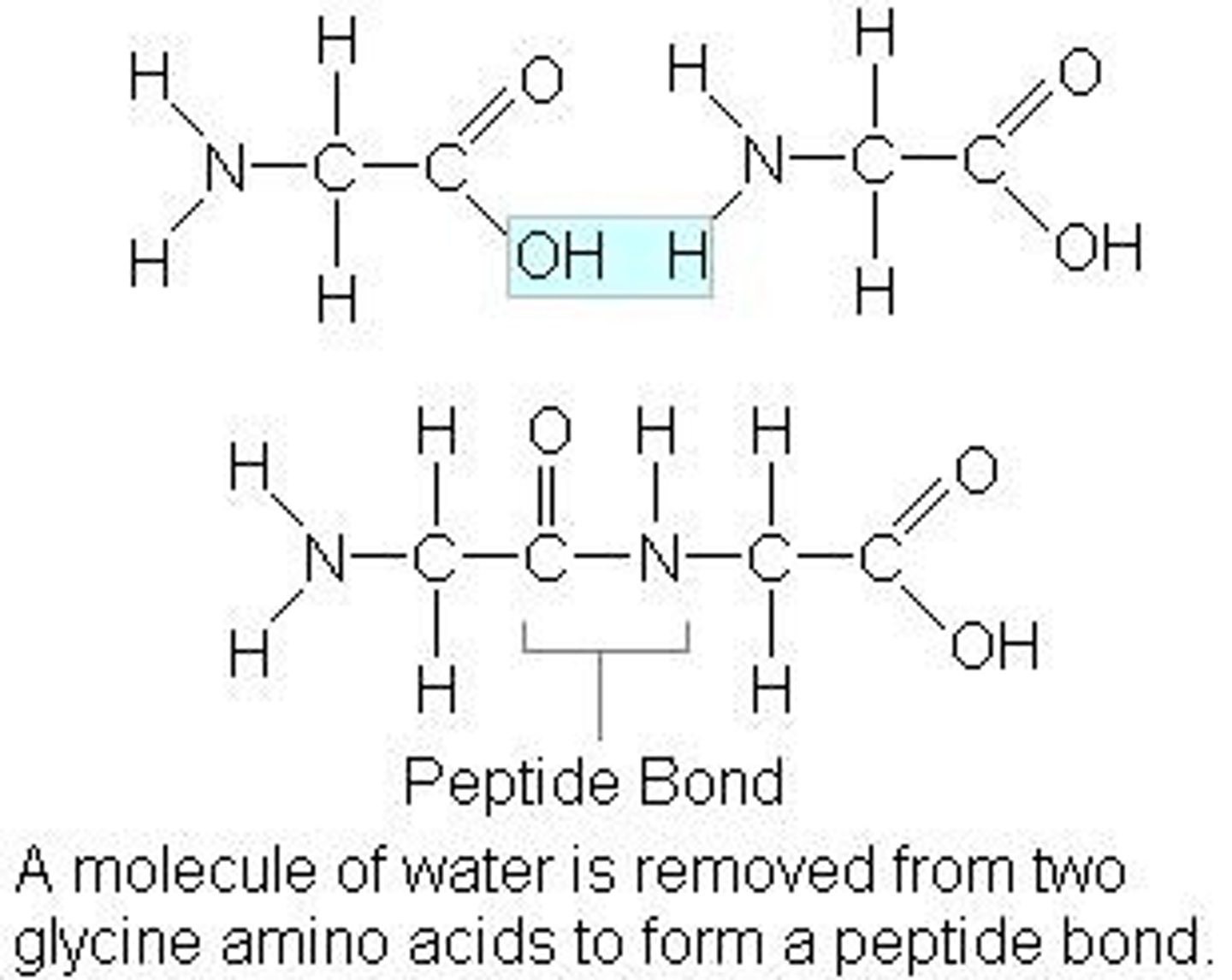
Why is there an infinite combination peptide chains?
- proteins can be ANY length of amino acids
-20 amino acids
Denaturation
changing of a protein's 3D shape (irreversible)
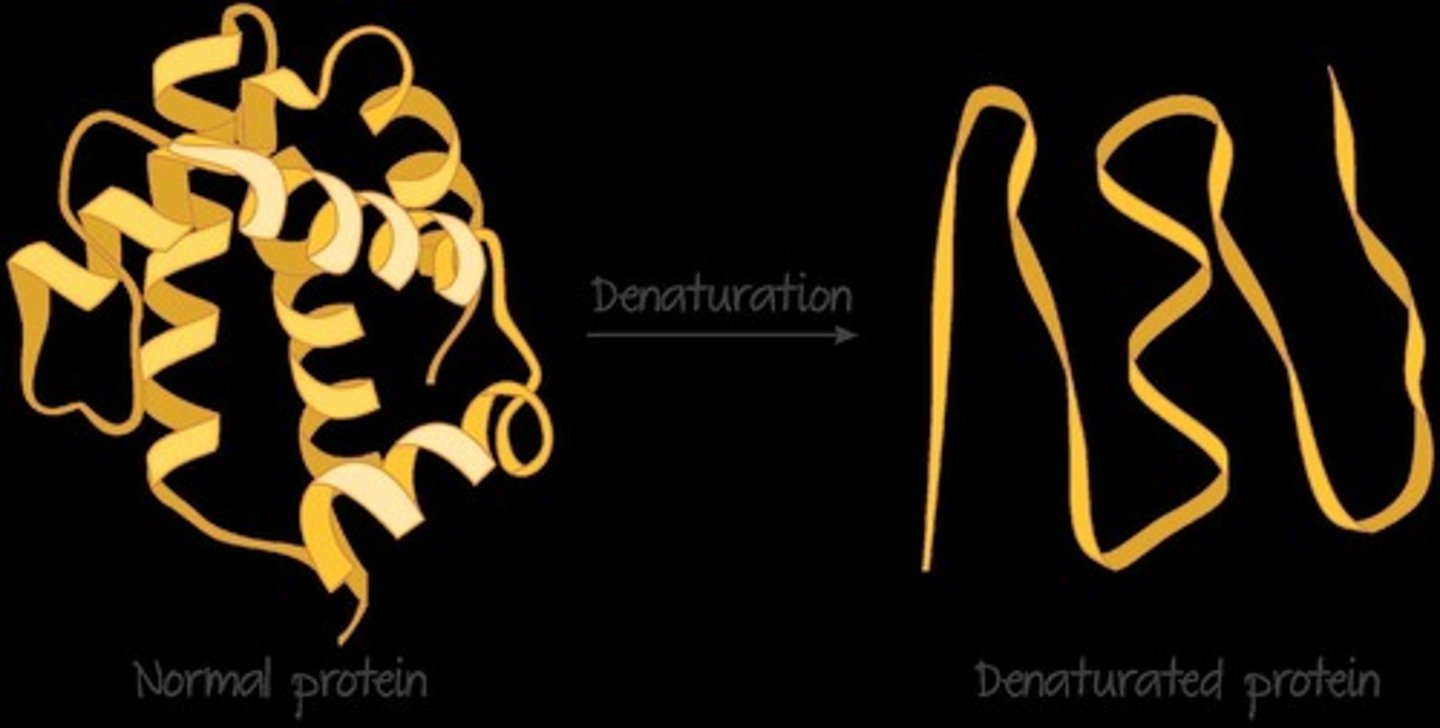
What temperatures are animal proteins stable at (unstable = denaturation)?
animal proteins are stable at body temperatures

What temperatures are plant proteins stable at (unstable = denaturation)?
plant proteins are stable at air temperatures

How does HEAT cause denaturation?
vibrations within the molecule breaks intermolecular bonds or interactions

How do EXTREMES OF pH cause denaturation?
disrupts ionic bonds in proteins

How does COLD cause denaturation?
It doesn't.
Cold does not denature proteins.

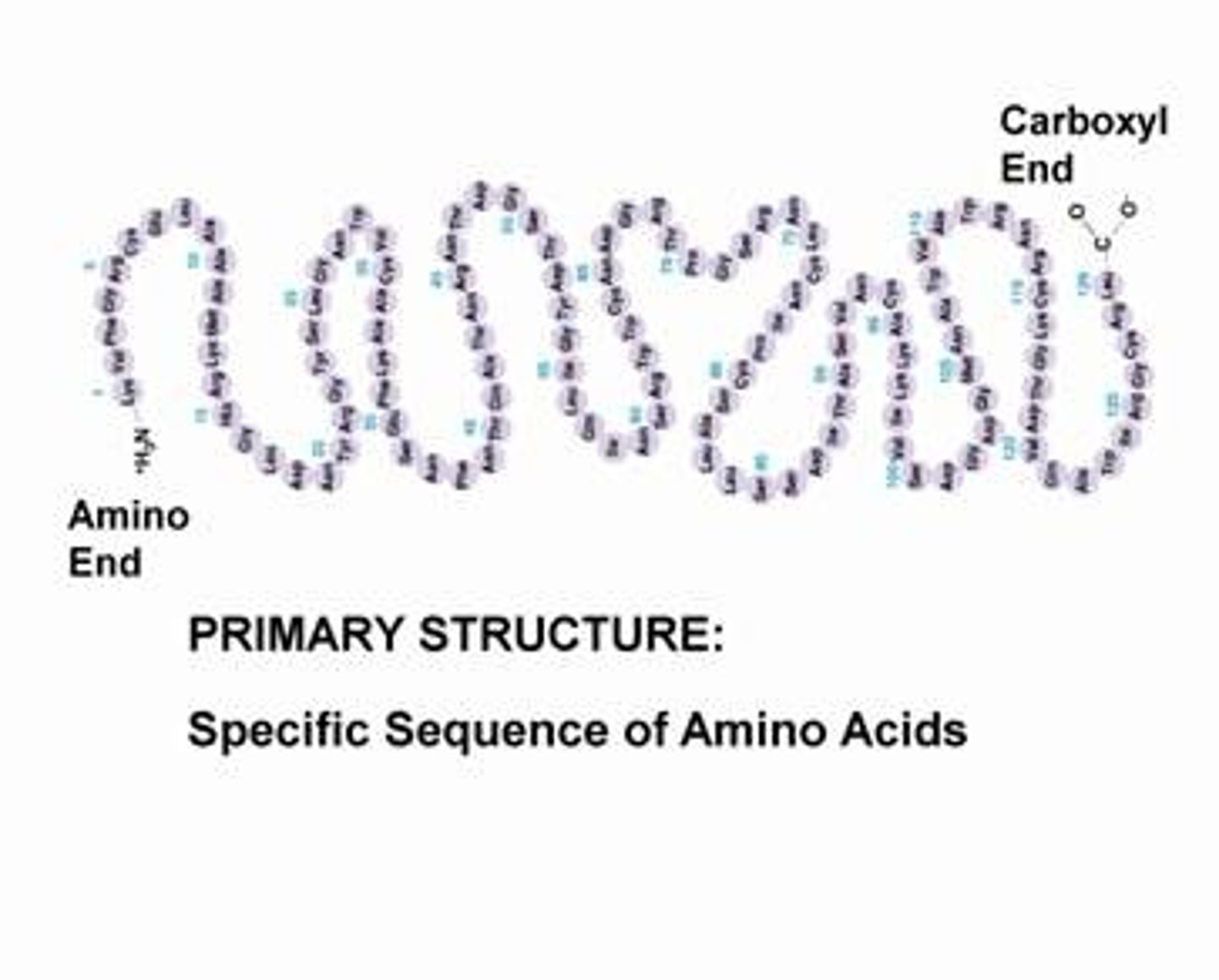
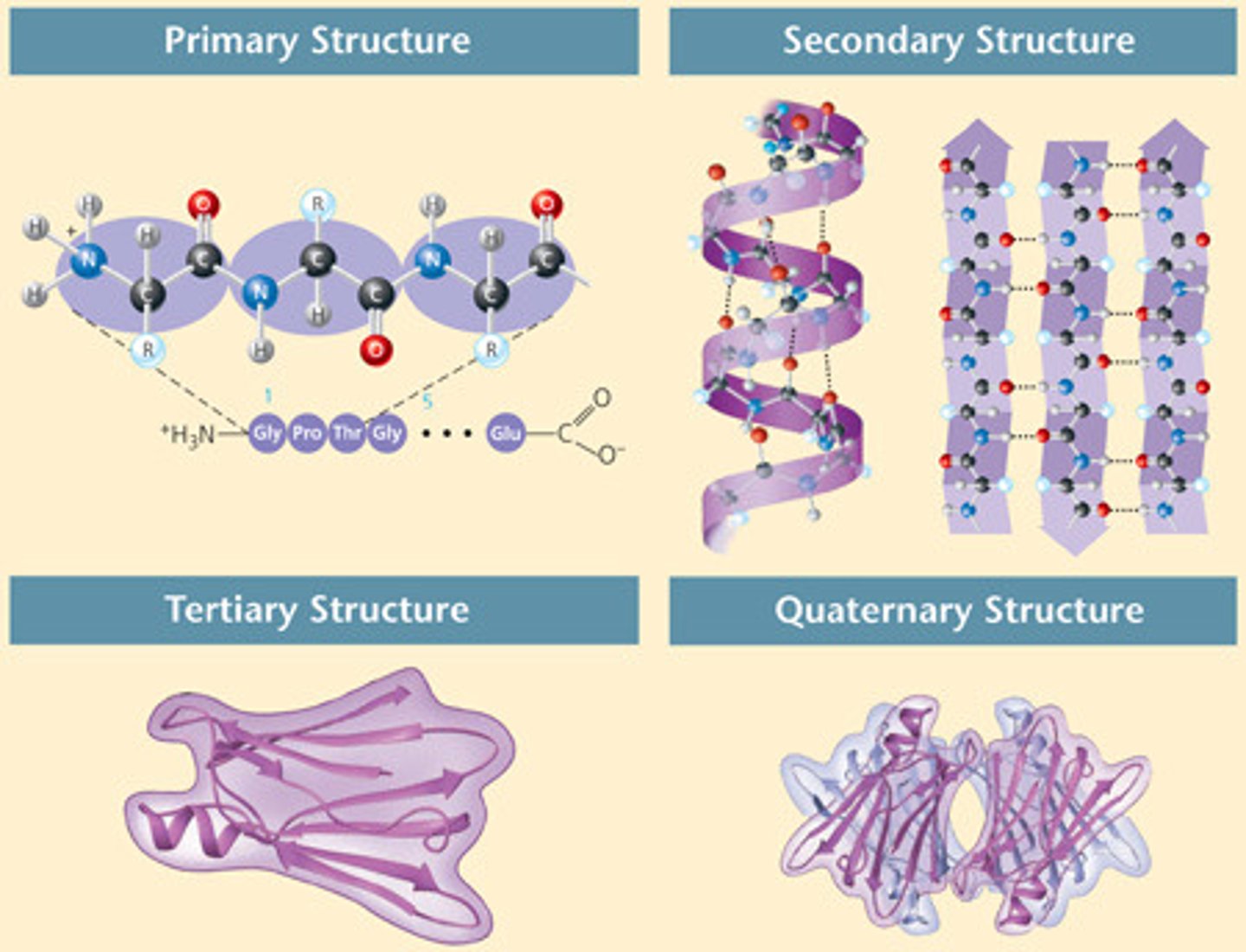
Primary Structure
Sequence of amino acids (like a beaded bracelet) produced as result of gene sequence
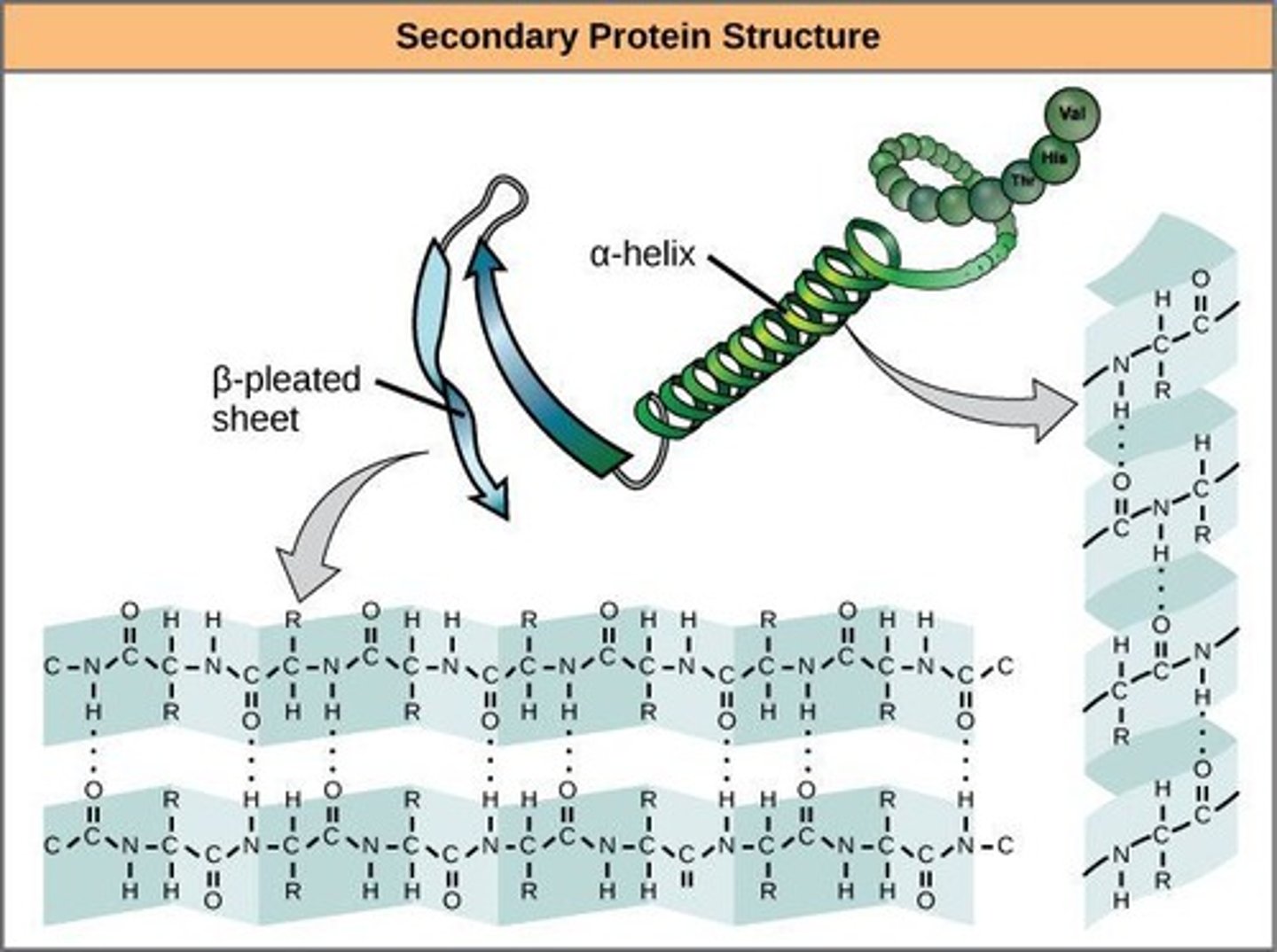
Secondary Structure
Amine and Carbonyl groups will interact to form Hydrogen bonds
two types:
- 𝞪- helix will form a spiral structure
- 𝜷-pleated sheets form
Tertiary Structure
3 dimensional folding as a result of side chain interactions
R group chemistry will matter!

What are examples of side chain interactions (tertiary structure)?
- hydrogen bonds
- ionic bonds
- hydrophobic interactions
- disulfide bridge
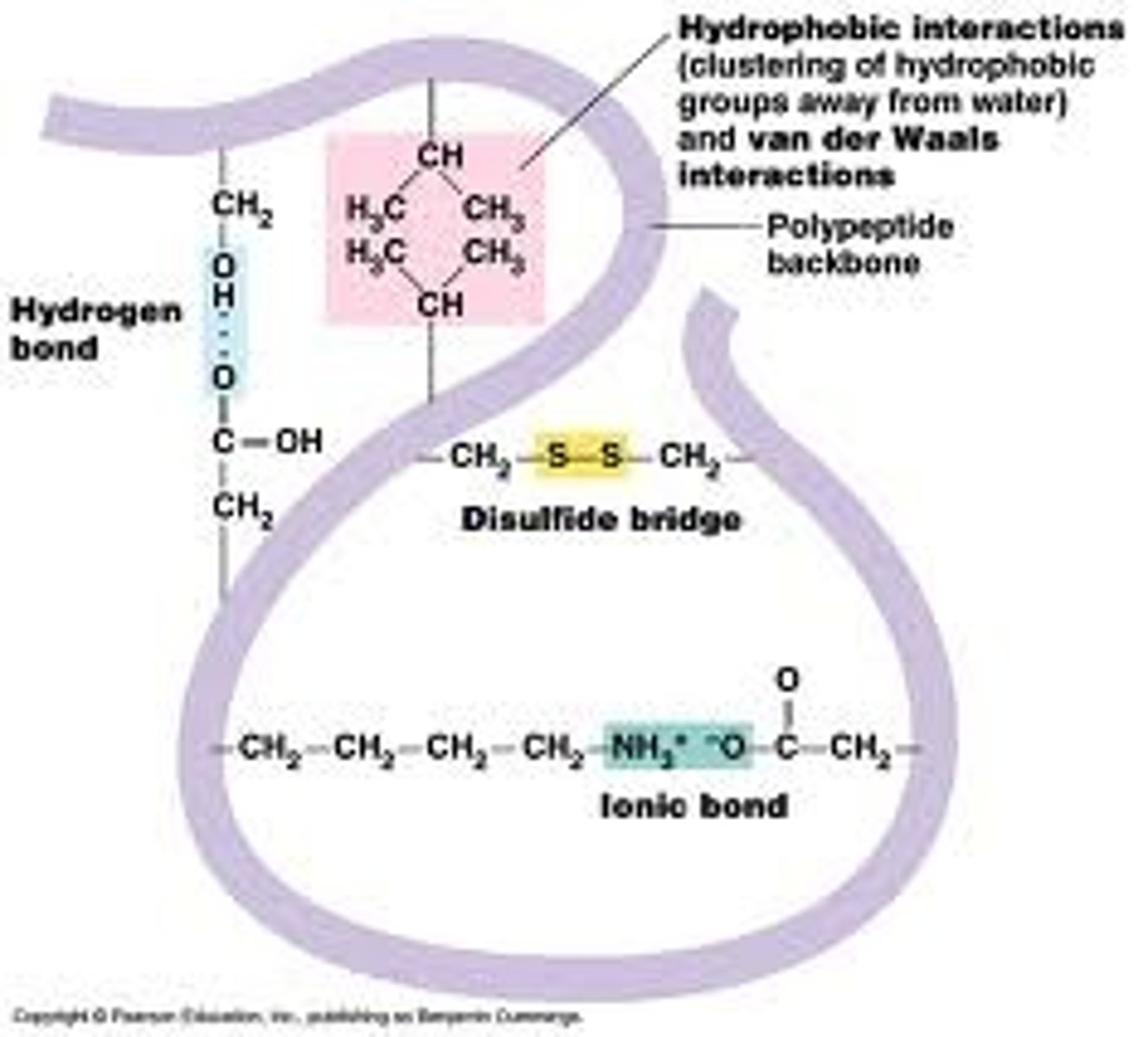
Cysteine in Tertiary Structure
cysteine = amino acid w/sulfur
disulfide bridges (side chain interaction) are critical to lots of tertiary structure
Hydrophobic Amino Acids in Globular Proteins are...
clustered in the middle
Hydrophobic Amino Acids in Integral Membrane Proteins are...
closest to the lipids
Quaternary structure of proteins
multiple polypeptide chains bonded together
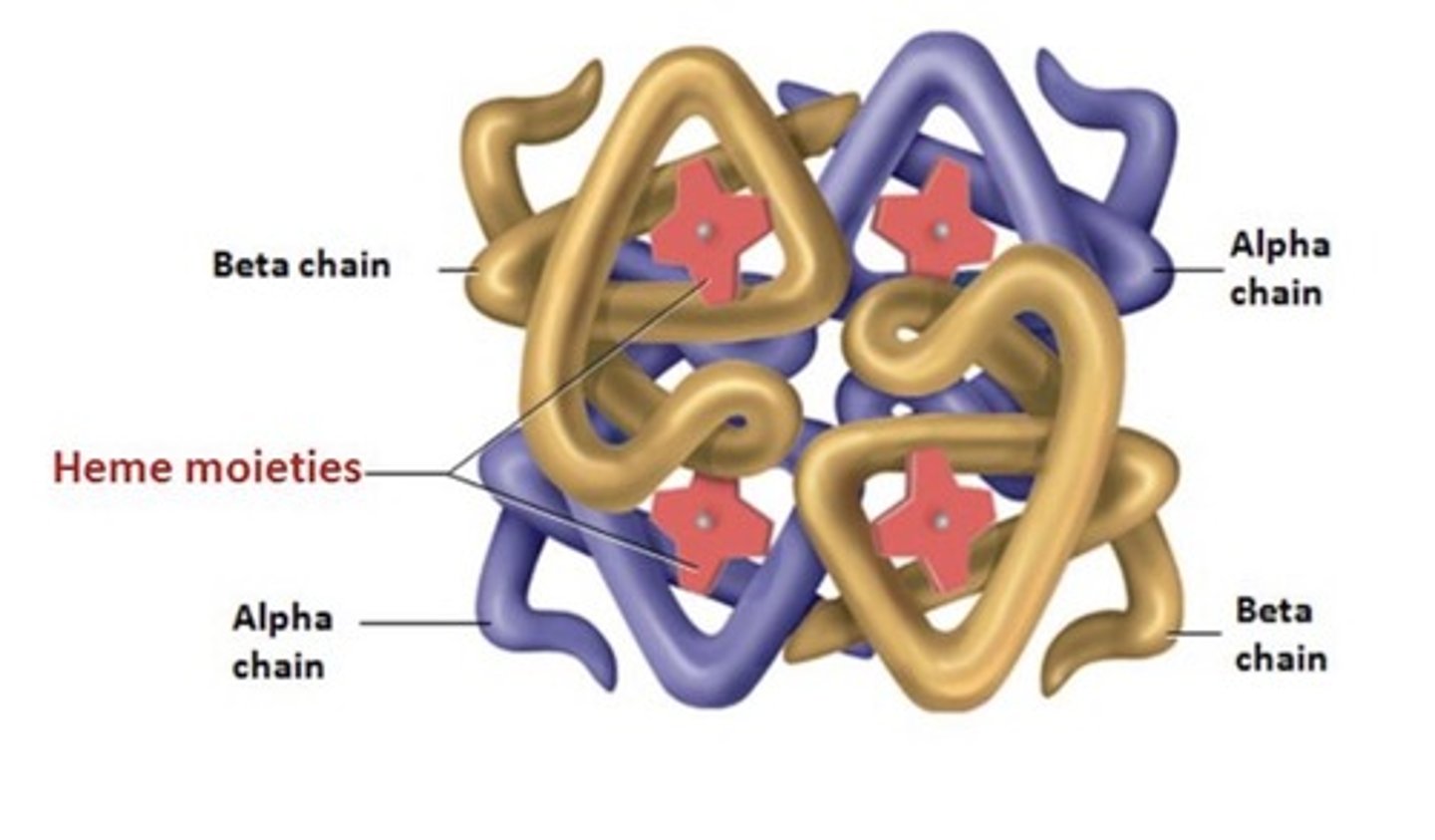
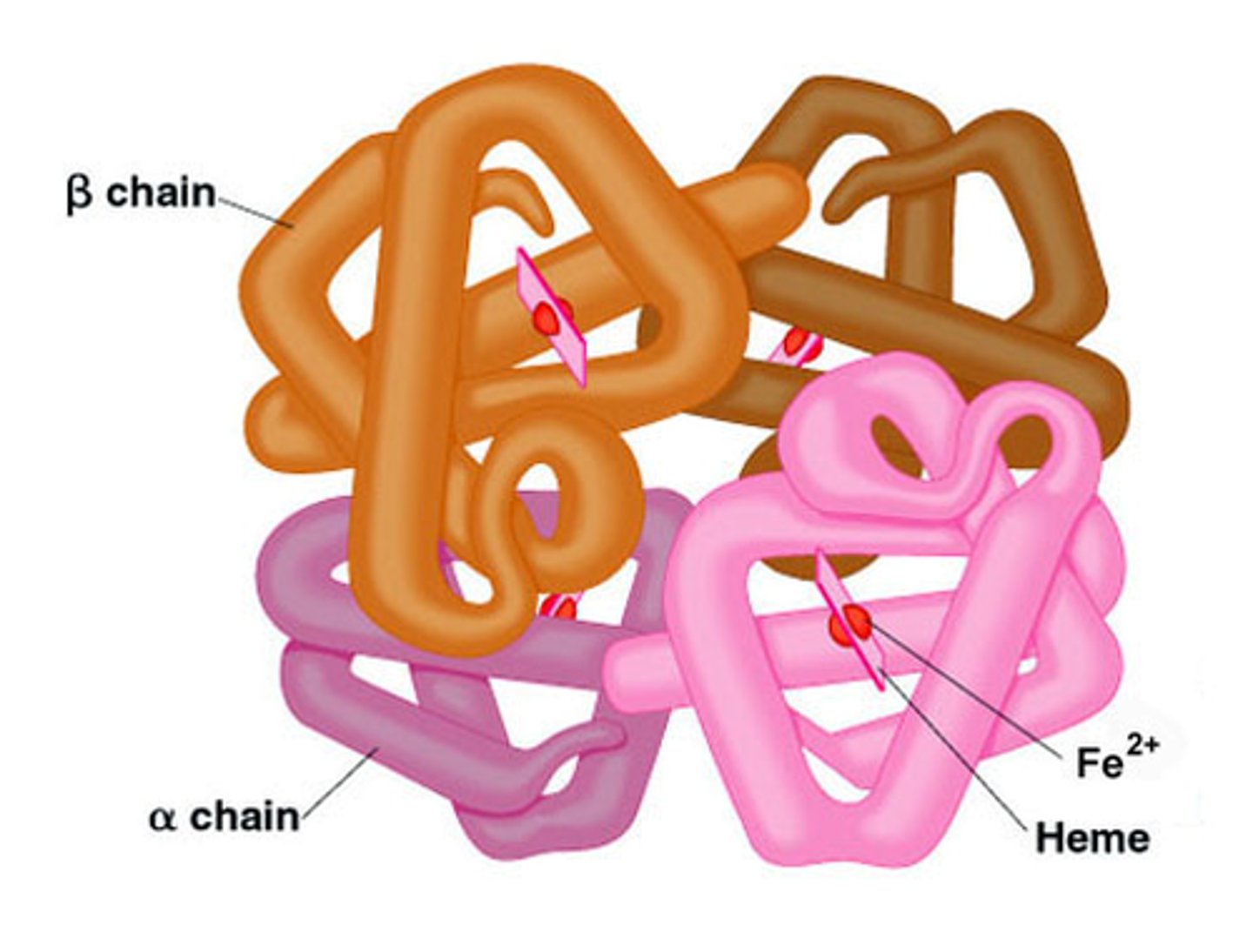
Conjugated Proteins...
have another molecule in their quaternary structure
ex: hemoglobin (has iron!)
Non-Conjugated Proteins...
are purely protein in their quaternary structure
exs: insulin and collagen
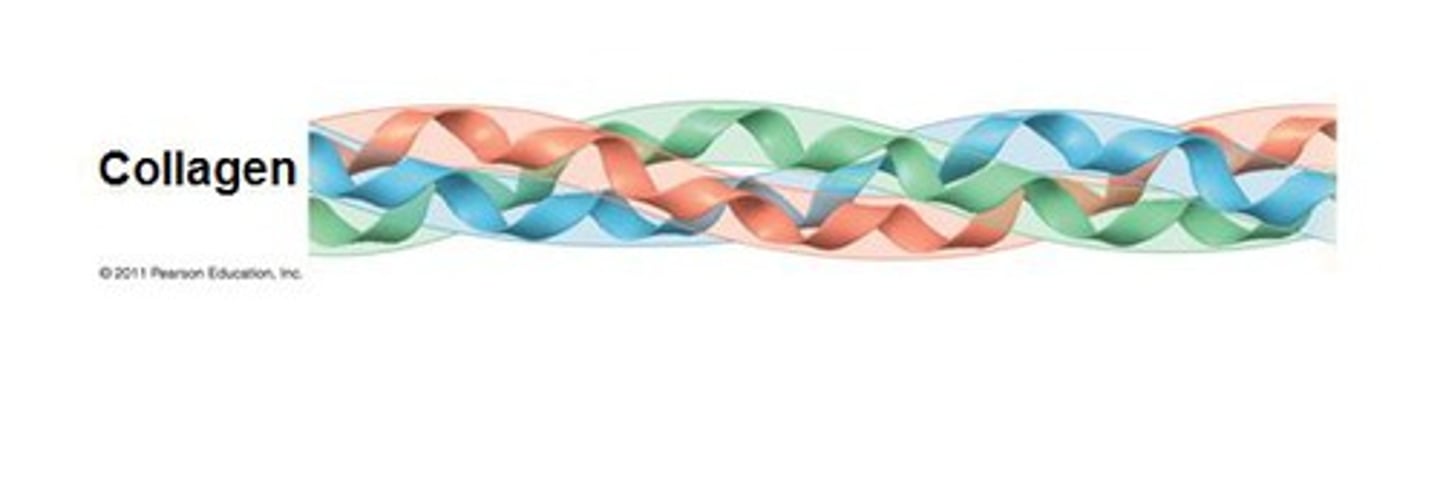
Collagen (Shape and Function)
Shape: long and fibrous
Function: forms fibers that run through tissues (it makes your bones strong and skin "tight")
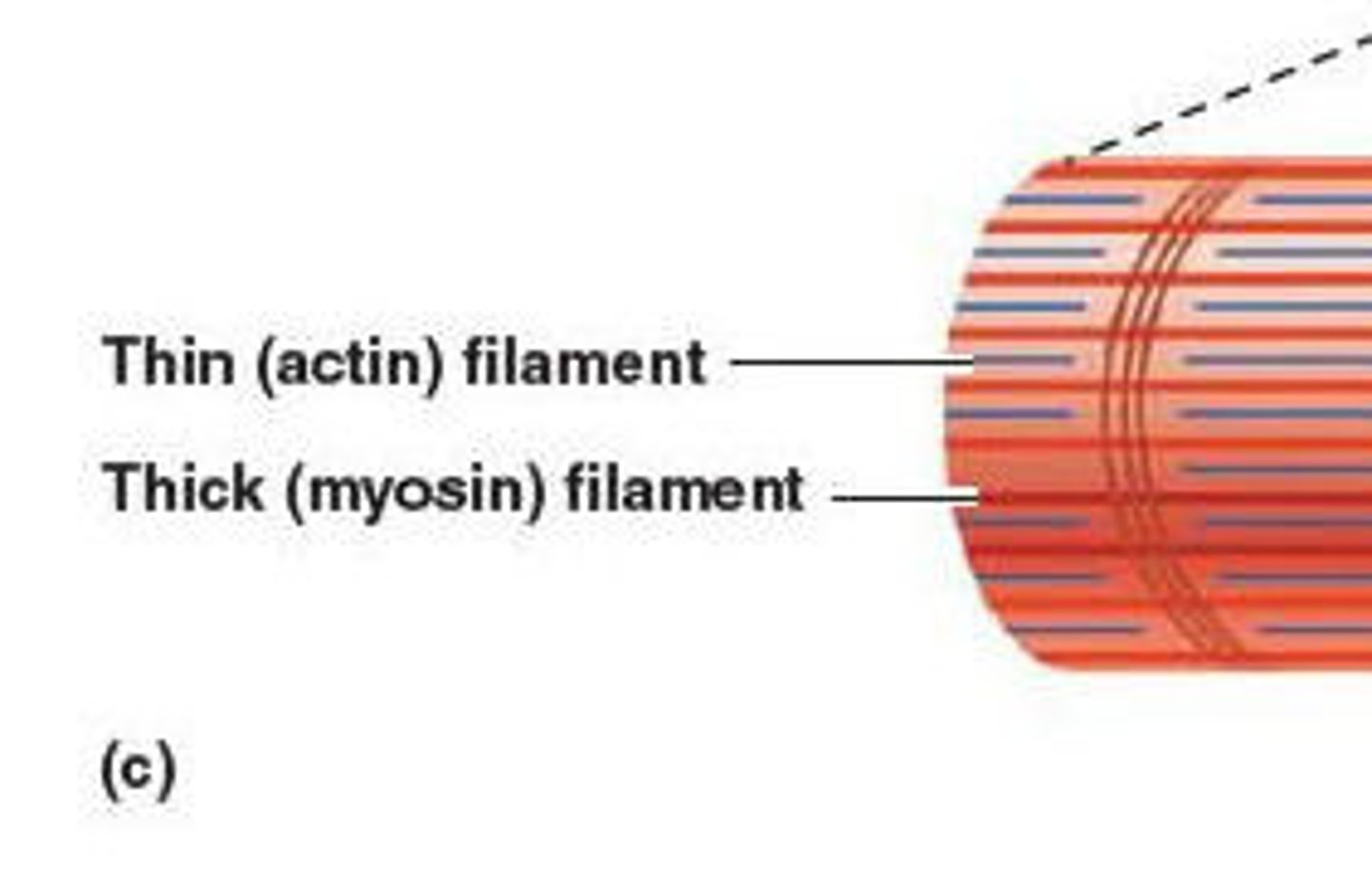
Actin and Myosin (Shape and Function)
Shape: long and fibrous
Function: form cellular cytoskeleton and muscle fibers
Insulin (Shape and Function)
Shape: globular
Function: when insulin binds to the receptor on the membrane, the glucose channel opens (allows glucose to leave blood and enter cells)
Enzyme (Shape and Function)
Shape: globular with a specific 3D shape that can bind other molecules at a specific active site
Function: they can change shape to catalyze reactions
Fibrous vs Globular Proteins
SHAPE
Fibrous: long and narrow
Globular: rounded/spherical
Fibrous vs Globular Proteins
ROLE
Fibrous: structural (strength and support)
Globular: functional (active in cell membrane)
Fibrous vs Globular Proteins
SOLUBILITY (generally)
Fibrous: insoluble in water
Globular: soluble in water
Fibrous vs Globular Proteins
SEQUENCE
Fibrous: repetitive amino acid sequence
Globular: irregular amino acid sequence
Fibrous vs Globular Proteins
STABILITY
Fibrous: LESS sensitive to changes in heat and pH
Globular: MORE sensitive to changes in heat and pH
Fibrous Protein EXAMPLES
collagen, keratin, elastin, actin, myosin
Globular Protein EXAMPLES
insulin, immunoglobin, catalase (enzymes end in -ase!)
Usage of Proteins
- catalysis (enzymes catalyze reactions)
- muscle contraction
- cytoskeletons
- tensile strengthening
- blood clotting
- transport (of nutrients and gas)
- membrane transport
- hormones
- receptors
- packing of dna (histone)
- immunity (antibodies) most diverse group
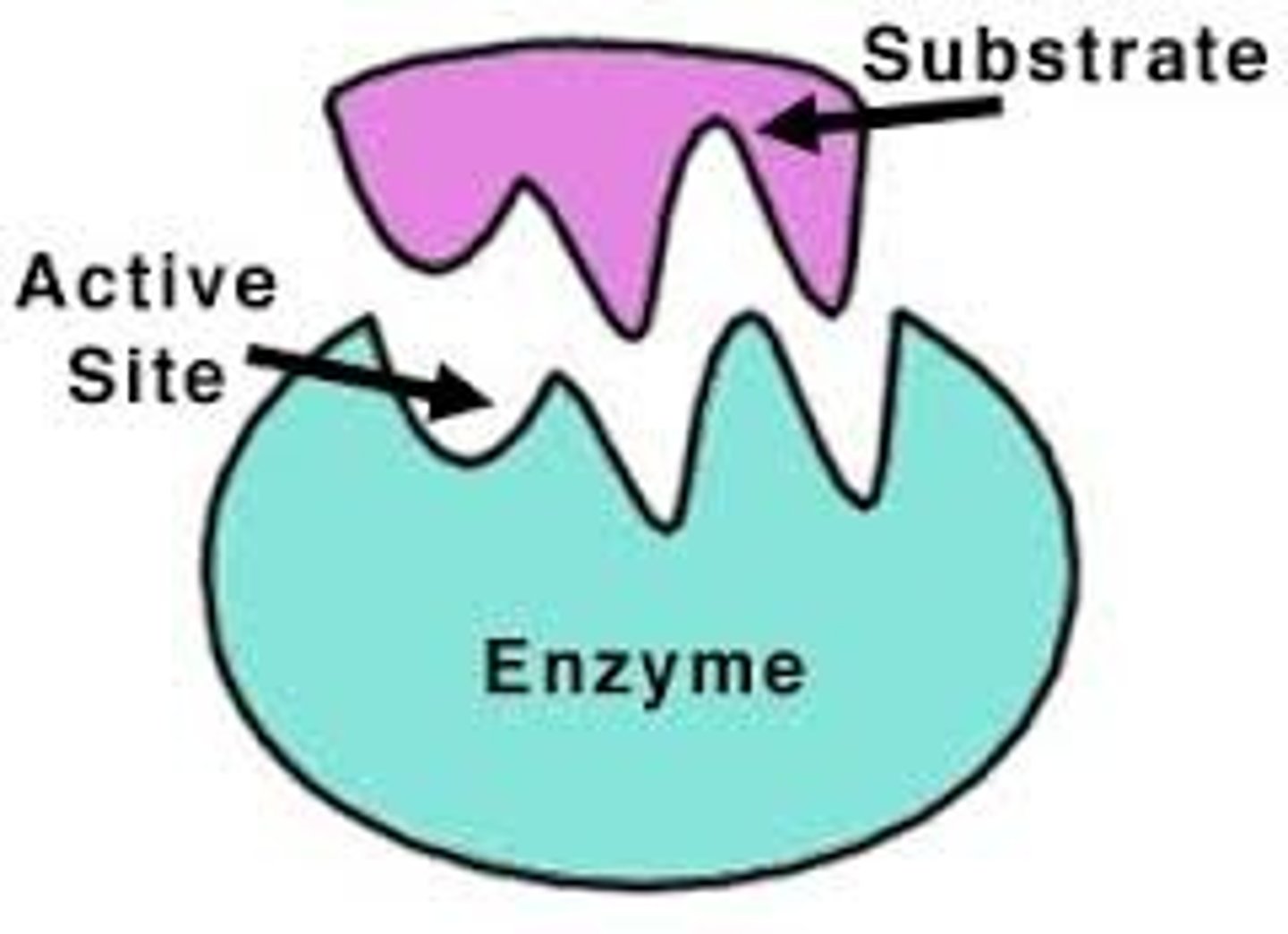
Active Site
region on enzyme where substrate binds
Activation Energy
energy needed to initiate a chemical reaction

Activation Energy GRAPH shows...
the activation energy needed to do the reaction with and without an enzyme

HOW do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction?
In the active site, substrates can chemically change.
- A substrate binding to an enzyme stresses certain bonds, making them less stable (unstable bonds are easier to break)
Enzymes changes bonds and lowers energy needed to make the product
Lock and Key Enzyme Model
substrates must fit enzymes EXACTLY

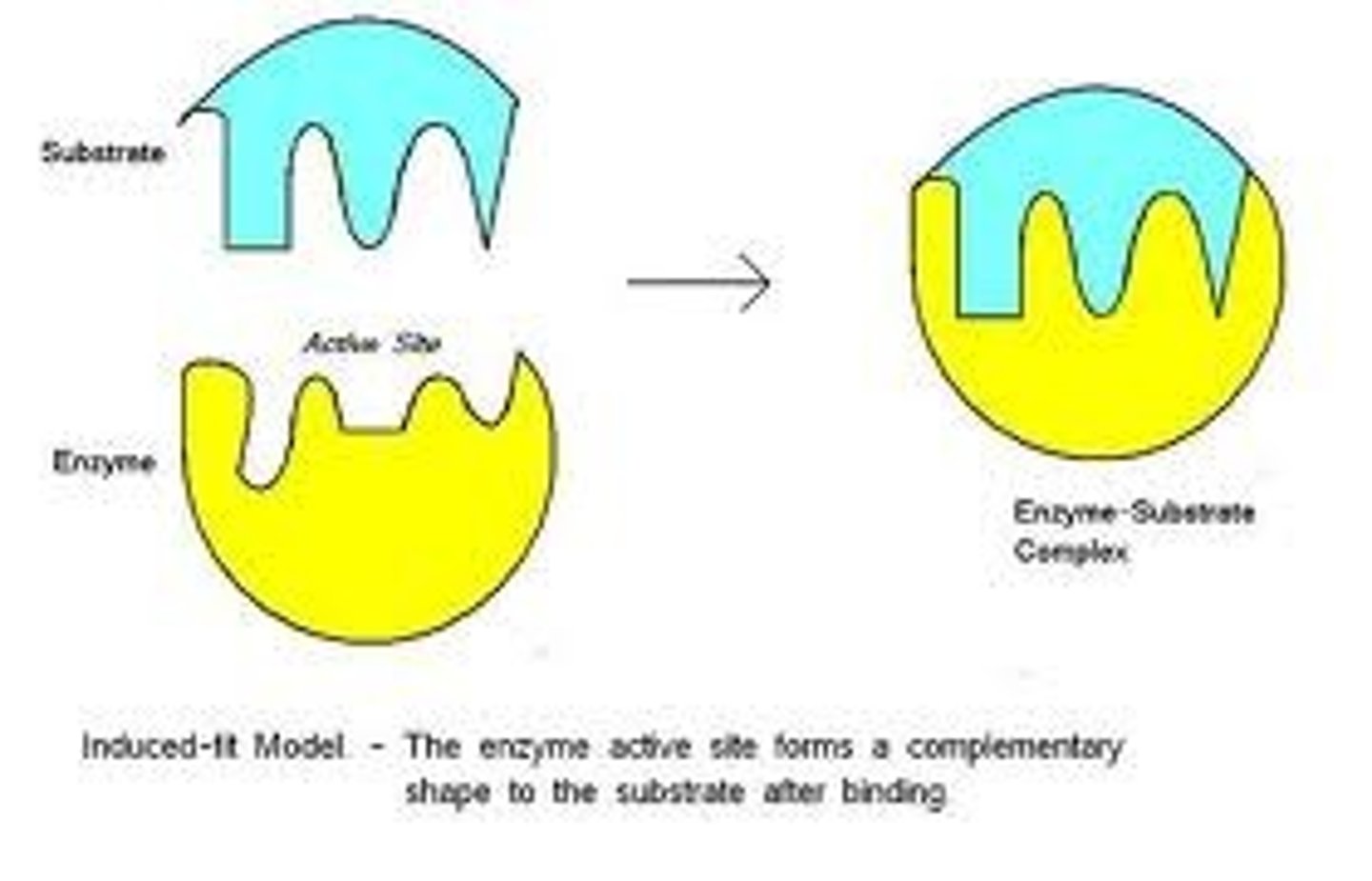
Induced Fit Enzyme Model
enzyme changes shape to fit substrate during binding
Brownian Motion and it's Connection to Enzymes
all particles move randomly!
in order for enzymes to work, they must collide with their substrates in exactly the right position
Immobilized Enzymes
enzymes fixed in place for reuse and stability
Example of Immobilized Enzymes
Lactose-Free Milk
How is Lactose-Free Milk made?
Milk is filtered through lactase in alginate beads ("locks" the enzyme in)
Effect: the lactose is split into glucose and galactose
Factors Affecting the Rate of Enzyme Activity
- temperature
- pH
- substrate concentration

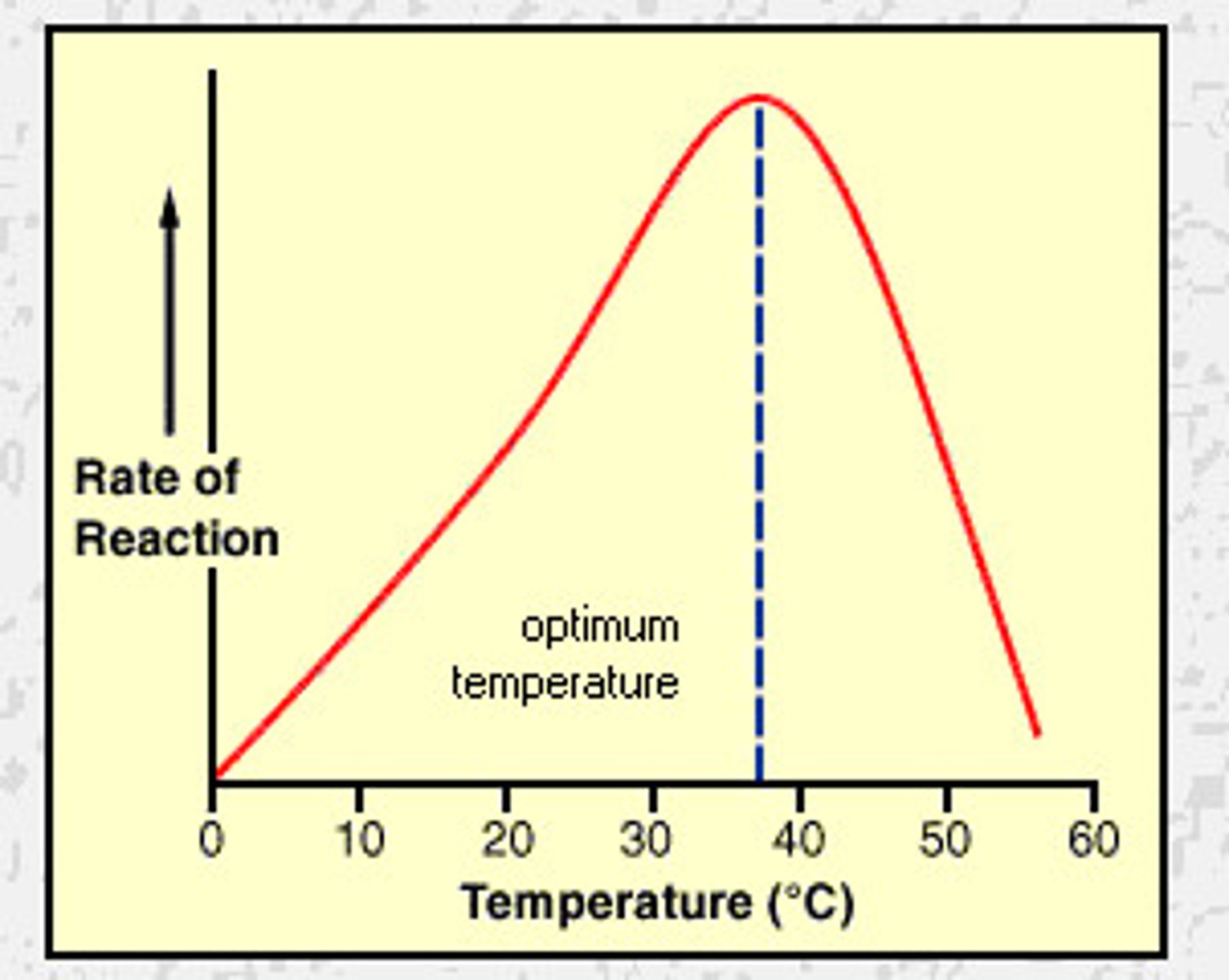
Temperature x Enzyme Activity Graph
as heat increase, collisions increase
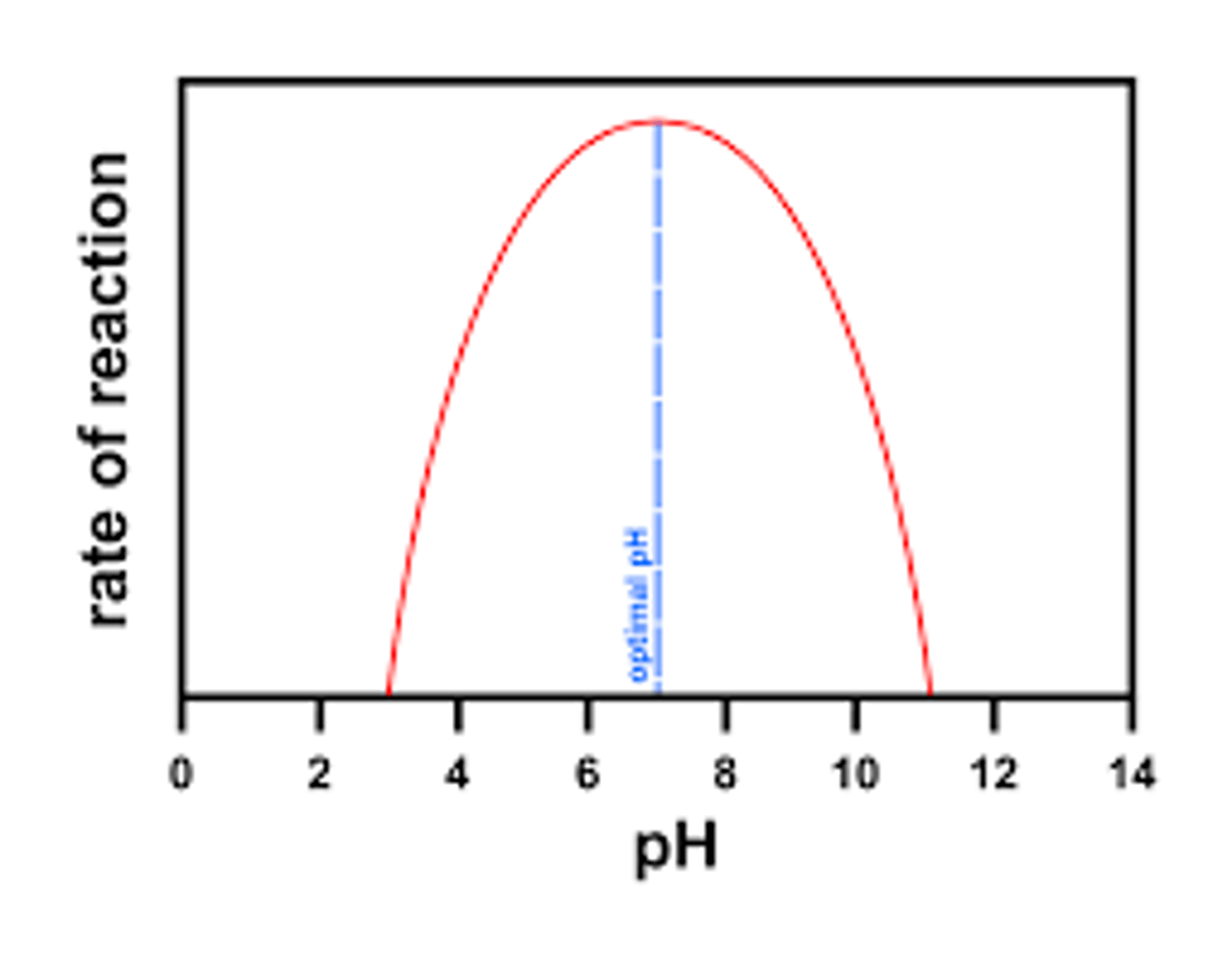
pH x Enzyme Activity Graph
enzymes each have an ideal pH
exs:
- pepsin (in stomach) with an ideal pH of 2
- salivary amylase (in mouth) with an ideal pH of 7.2
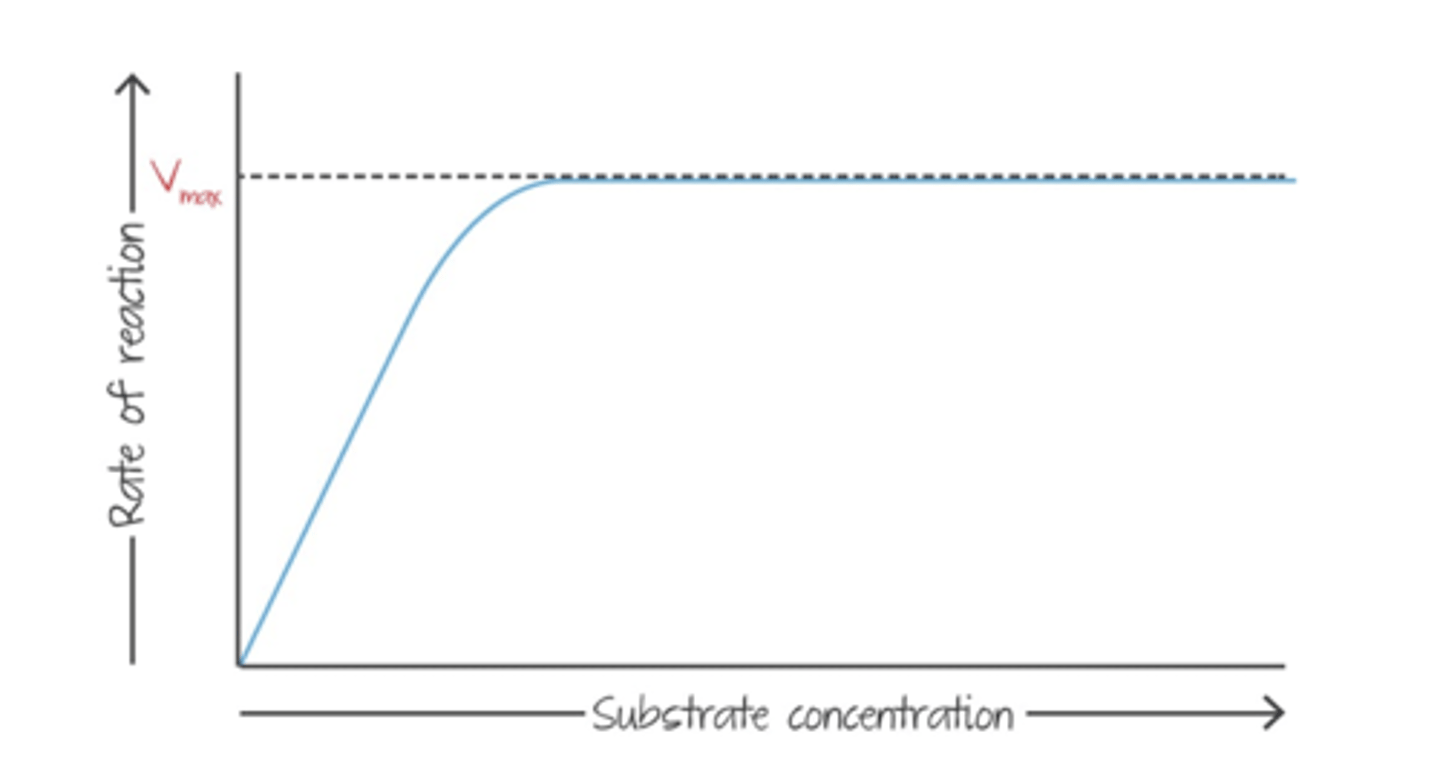
Substrate Concentration x Enzyme Activity Graph
as substrate concentration increases, rate of reaction will increase until Vmax
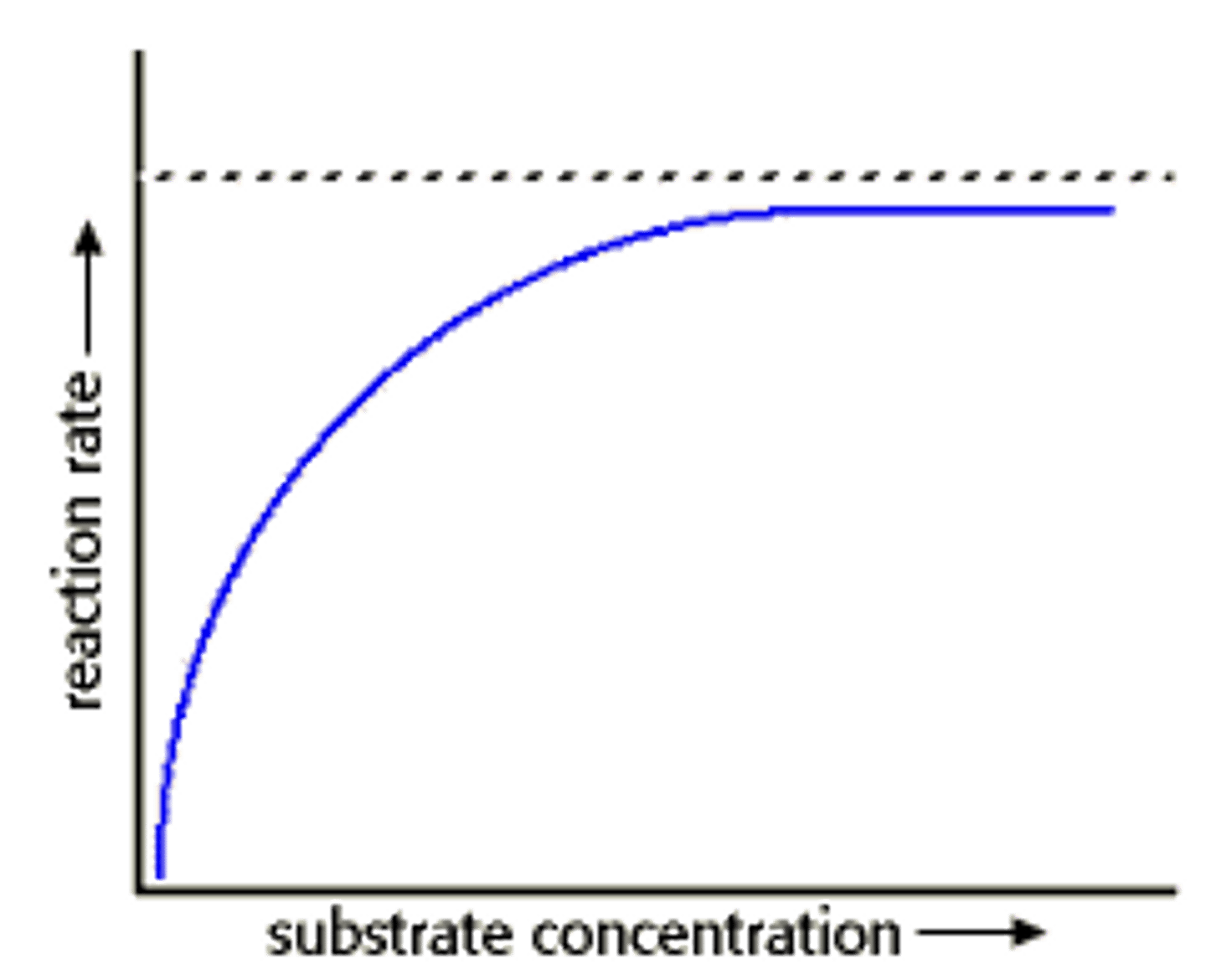
Substrate Concentration
amount of substrate available for enzyme reactions
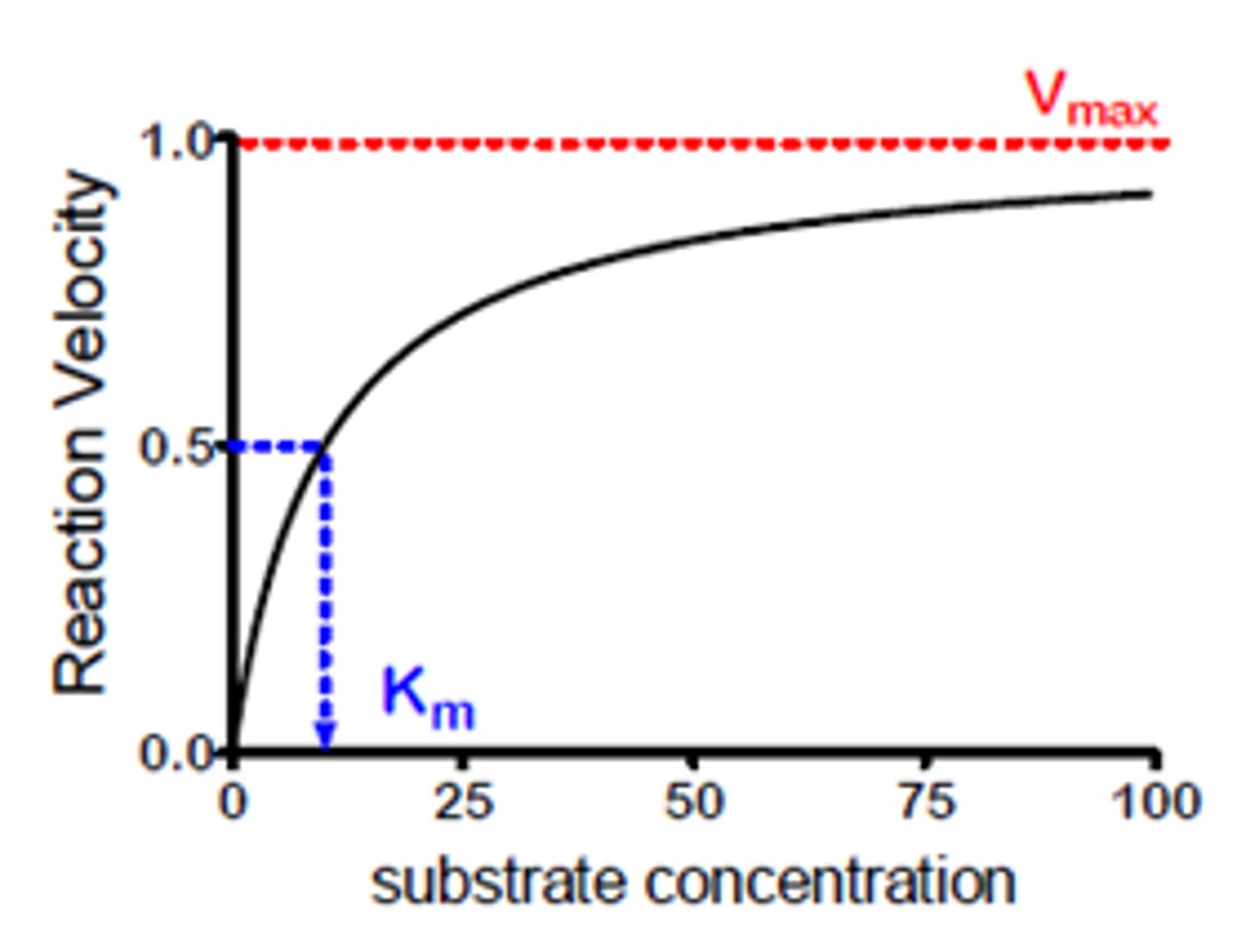
What is "Vmax"?
maximum rate of reaction (the point where every enzyme is working)
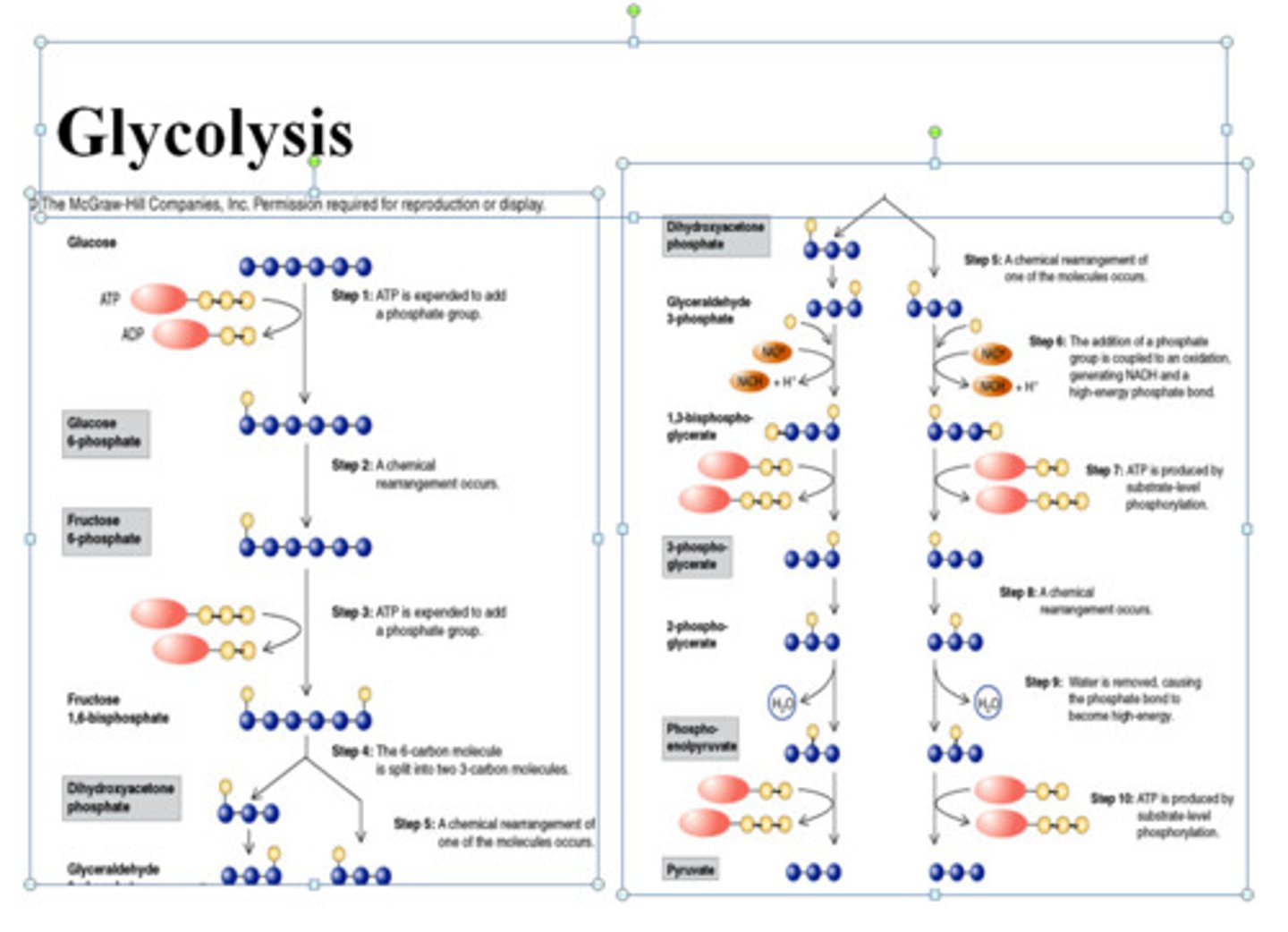
Glycolysis
Intracellular
linear pathway for glucose breakdown
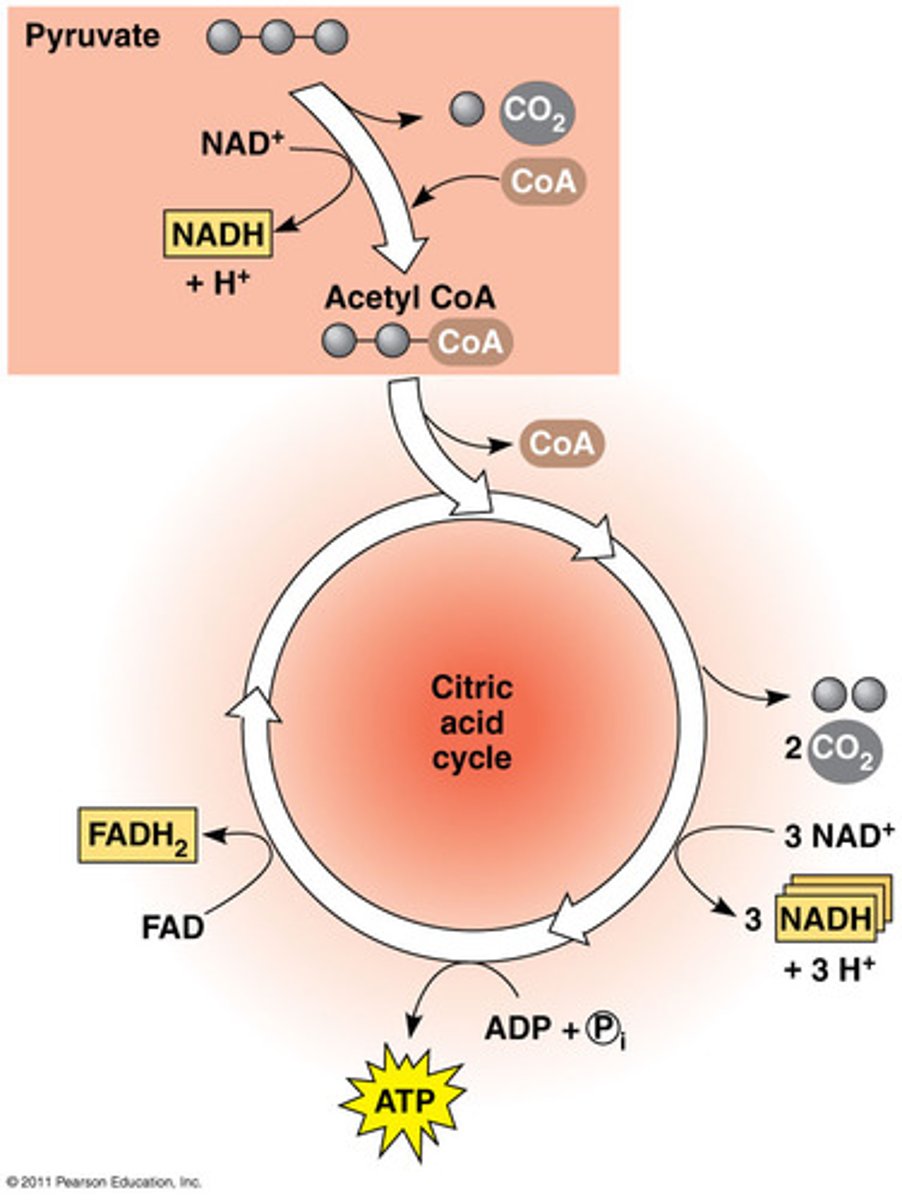
Krebs Cycle
Intracellular
cyclic pathway for energy production
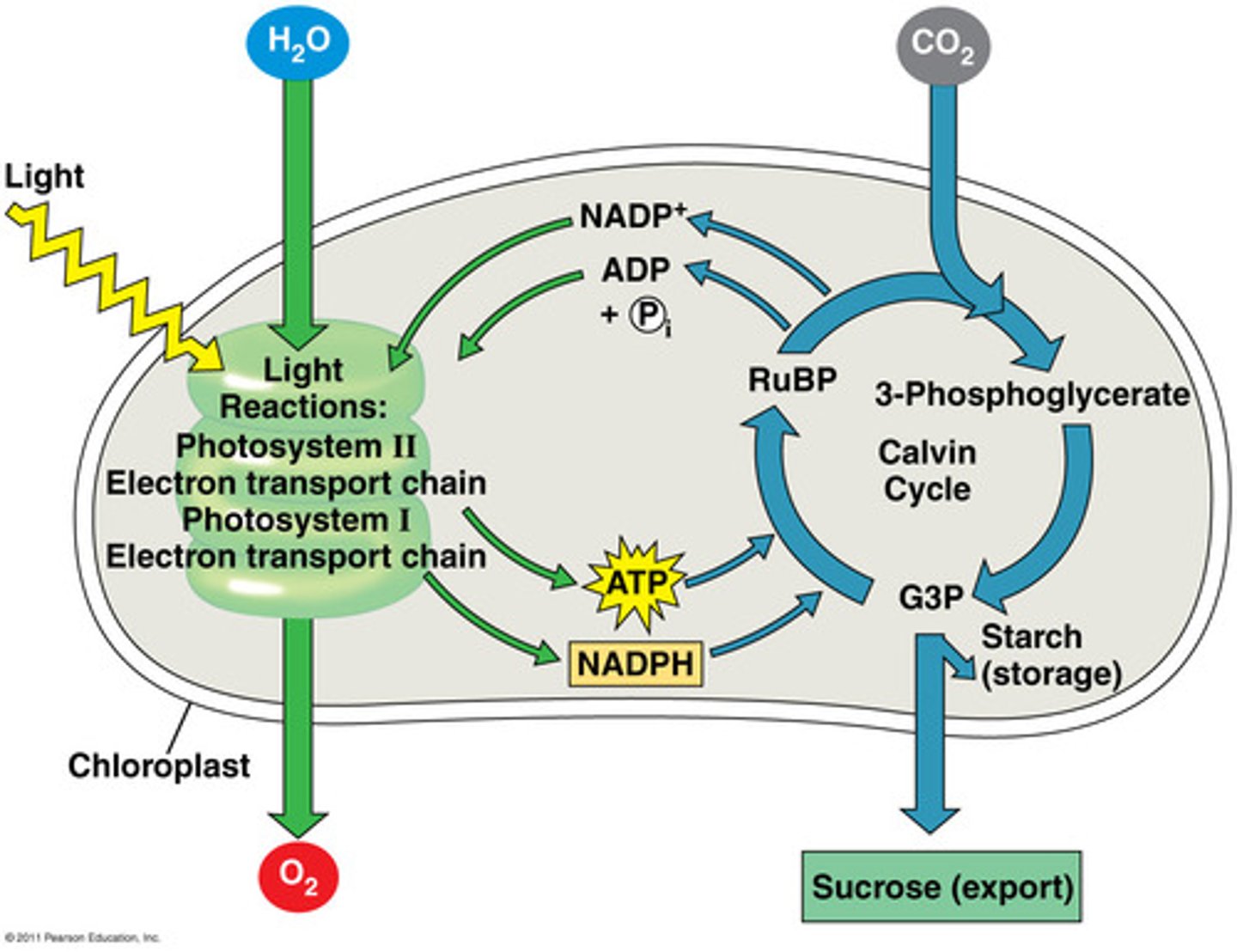
Calvin Cycle
Intracellular
cyclic pathway for carbon fixation (plants photosynthesizing)
Digestion
Extracellular: uses enzymes outside the cell in the lumen (space) of the digestive tract
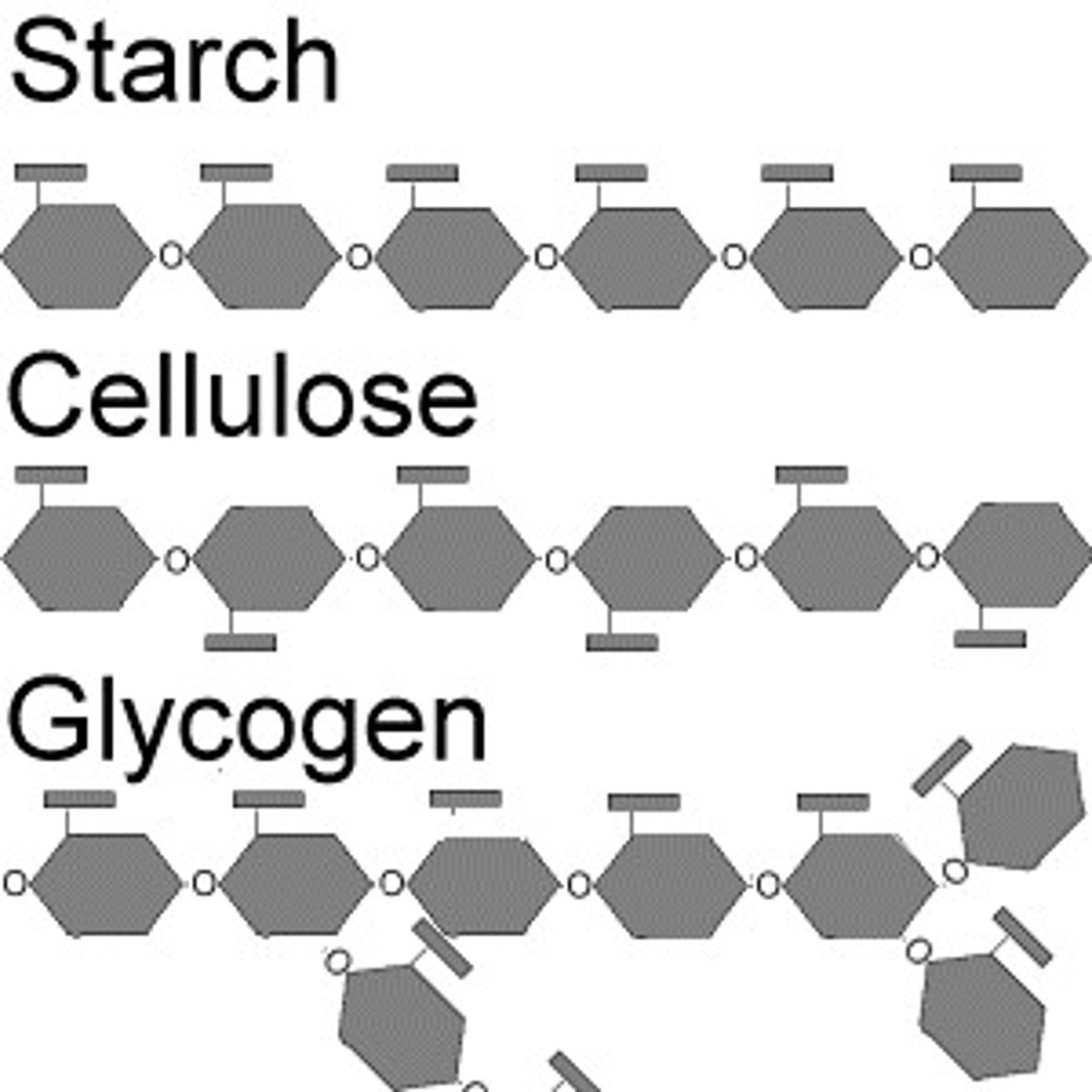
What enzymes does digestion use to break down CARBS?
amylase, maltase, lactase
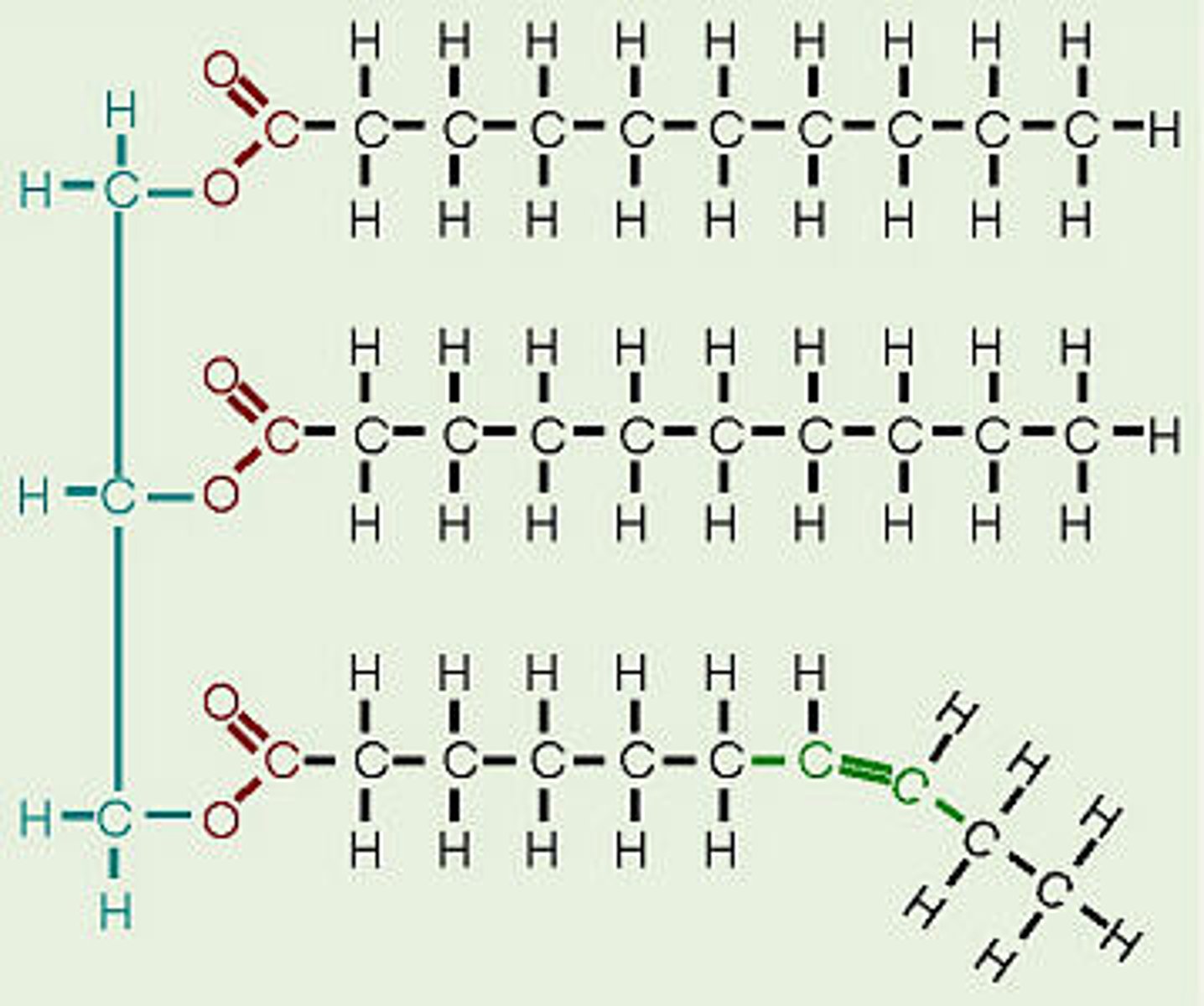
What enzyme does digestion use to break down FATS?
lipase (think lipids)
What enzyme does digestion use to break down PROTEINS?
pepsin, trypsin, peptidase
Heat Generation
metabolic reactions produce heat due to inefficiency
Why is heat generation important sometimes?
some animals depend on heat generated from metabolic reactions to maintain body temperature
Allosteric Site
site on enzyme where non-substrate molecules bind
Non-Competitive Inhibition
inhibitor binds away from active site (on allosteric site), which prevents the enzyme from working (catalysis)
Antabuse
Drug that treat alcoholism by non-competitive inhibition
Impact: acetaldehyde builds up and causes extreme symptoms
Competitive Inhibition
inhibitor competes with substrate for active site
Statins
Drugs that inhibit cholesterol synthesis by competitive inhibition
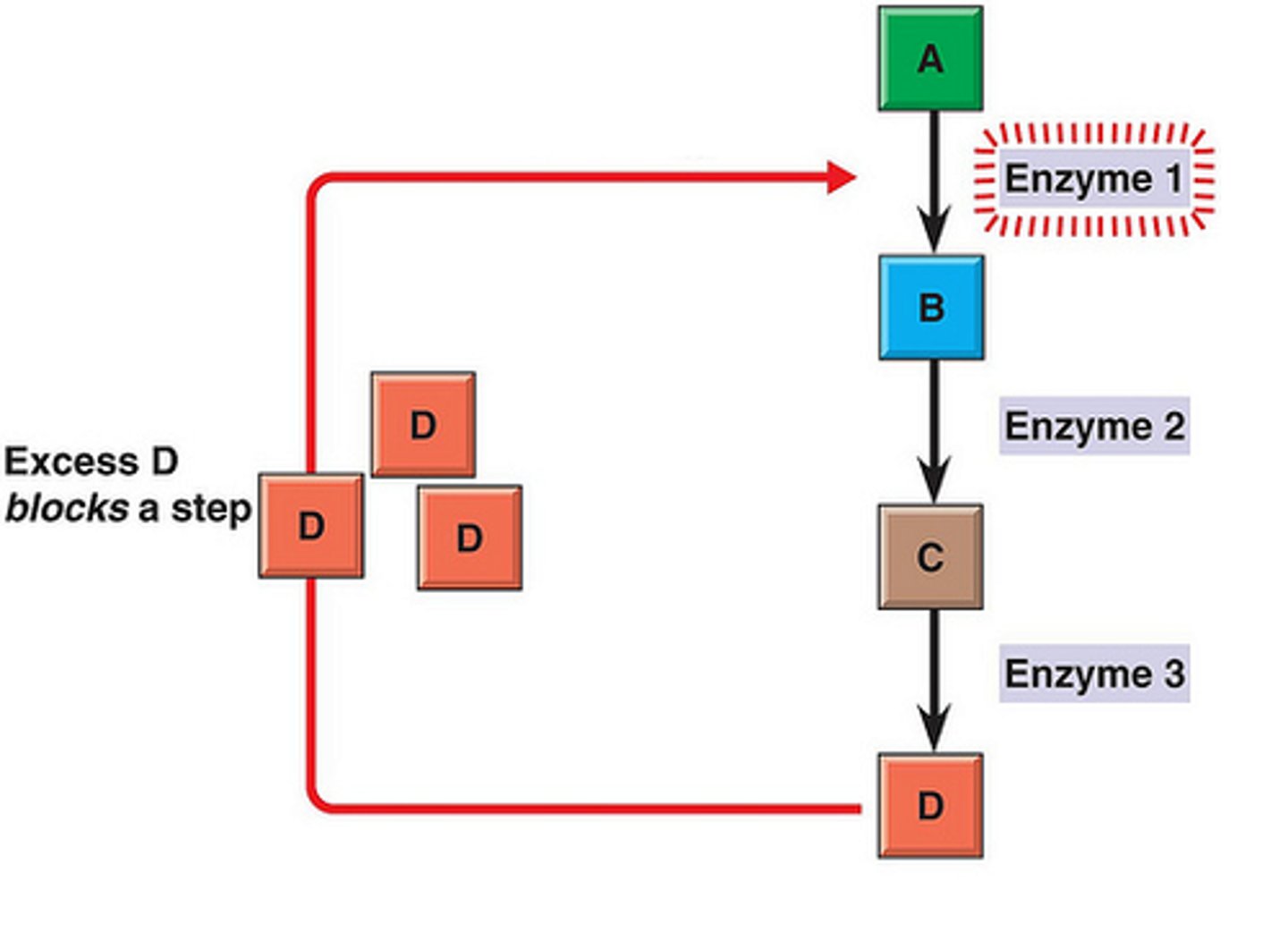
Feedback Inhibition
end product inhibits an earlier enzyme in the pathway
Mechanism-Based Inhibition
irreversible binding of inhibitor (alters active site)