Dent 1111 Test 3
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Hepatitis A
fecal-oral transmission/ route
-not chronic
-vaccine
Hepatitis B
Source
-blood and body fluids
think: hep B= Blood+Body
Transmission
-percutaneous and mucosal tissues
-chronic
-immunization
Hepatitis C
Source
-blood and body fluids
Transmission
-percutaneous and mucosal tissues
-chronic
-no vaccine, perform blood donor screening
Hepatitis D
Source
-blood and body fluids
Transmission
-percutaneous and mucosal tissues
-chronic
-HBV vaccine
Hepatitis E
fecal-oral transmission/ route
-not chronic
-ensure safe drinking water
Hepatitis A+E
= same
Hepatitis B, C, D
= same
Types of Human Herpesviruses
-Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
-Herpes zoster virus (HZV)
-Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
-Epstein- Barr virus (EBV) *
Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
2 types:
-Type 1
-Type 2
Herpes simplex virus Type 1
-seen in the dental office (cold sores)
-causes primarily oral lesions
*known as fever blisters or cold sores
Herpes simplex virus Type 2
-causes primarily genital lesions
-common sexually transmitted disease (STD)
-mother giving birth can pass virus to baby
Herpes zoster virus (HZV)
-causes herpes zoster, shingles and chickenpoxs
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
-normally latent (does not cause disease)
-may become active when the immune system is damaged
-once active, highly contagious
-transmitted through most body fluids
-can affect the fetus, some born deaf or intellectually disabled
Epstein- Barr virus (EBV) *
-causes infectious mononucleosis and Burkitts lymphoma, which is a malignancy of the lymph tissue
-transmitted by kissing
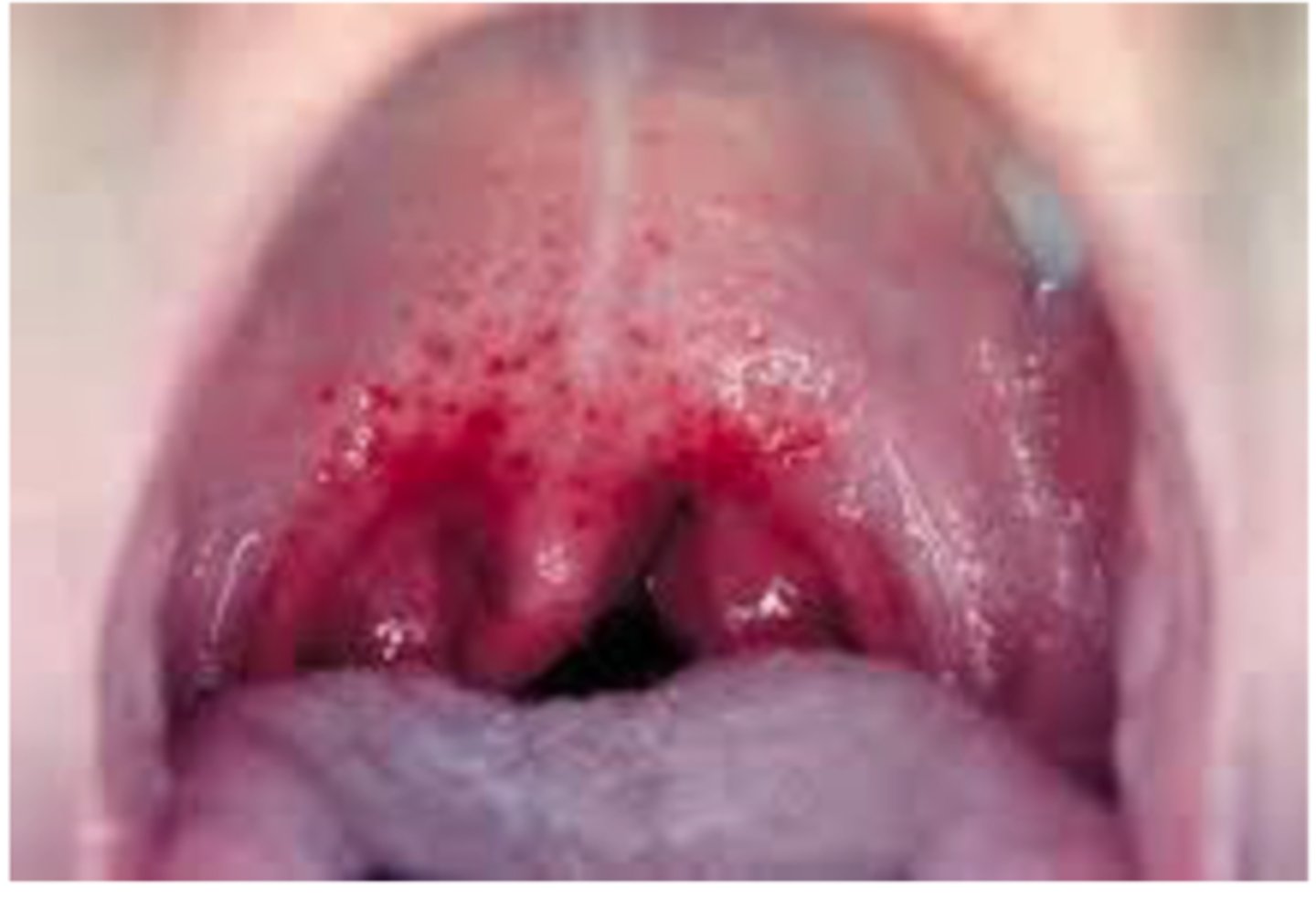
Tuberculosis
-spread through the air when a person sneezes, coughs and talks
Symptoms:
-
Legionnaire's disease
-bacteria is transmitted through aersolization and aspiration of contaminated water
-from dental water lines
-causes very severe pneumonia
-can be fatal
Syphilis
-STD, caused by treponema palladium spirochetes
-direct cross infection may occur in the dental operatory through contact with oral lesions
-chancre
-split papules at the corners of the mouth
-grayish white, moist "mucous patches" on the tongue, roof of the mouth, tonsils or inner surfaces of the lips
-generalized measles type rash, pox like pustules, oozing sores and hair falling out of the scalp
Ebola
-bleeding inside and outside the body
-epidemic
-spread through direct contact (broken skin or mucous membrane), blood and body fluids (urine, feces, saliva, vomit and semen) from a person who has ebola
Tetanus
-aka lockjaw
-caused by a spore forming bacillus found in soil, dust or animal or human feces
-microbe enters through wound or break in the skin
-can be fatal
-causes severe muscle spasms and rigidity
The chain of infection
1. Infectious Agent
2. Reservoir
3. Portal of Exit
4. Mode of Transmission
5. Portal of Entry
6. Susceptible Host
1) Infectious agent
-a pathogen, such as a bacterium or virus that can cause a disease must be present in sufficient numbers
-organism must be virulent (strong ability to cause disease)
-hep B virus vaccine can help body protect itself
2) Reservoir
-place where organisms can live and reproduce
ex. humans, animals, food, water, contaminated surfaces and bioburden (blood and saliva)
-stay healthy, sterilization, disinfection, water asepsis, rubber dam
3) Portal of exit
-where pathogen exits reservoir
-secretions, excretions, droplets, aerosols
ex. respiratory tract (nose, mouth), intestinal tract and the urinary tract and through blood
-hand hygiene, barriers, minimize spatter, waste containment
4) Mode of transmission
-direct transmission
-indirect transmission
-airborne transmission
-hand hygiene, surface Barries, gloves, mask, aseptic techniques, sterilization, disinfection, eyewear
Direct transmission
-person to person contact
ex. droplets through sneezing or coughing or spatter produced during dental treatment
-unprotected contact with an infectious lesions of infected body fluids such as blood, saliva, semen or vaginal secretions
Indirect transmission
-when micro-organisms first are transmitted to an object or surface then to another person who touches it
ex. dental chart handled by dental assistant with contaminated gloves then the receptionist touches it with bare hands
Airborne transmission
aka droplet infection
-spread of disease through droplets of moisture that contain bacteria or viruses
5) Portal of entry
-portal of entry for airborne pathogen are the mouth and nose
-blood borne pathogens must have access to the blood supply as a means of entry
ex. through break in the skin caused by a needle, stick, cut or even a human bite that breaks the skin or mucous membranes of the nose and mouth
-PPE
6) Susceptible host
-person who is unable to resist infection by a particular pathogen
-someone with poor health, chronically fatigued, under extreme stress or has a weakened immune system is likely to become infected
-immunizations
-manage underlying health
Parenternal transmission
Parenternal= through the skin
-from cuts or punctures, needlestick injury, human bites, cuts, abrasions or any breaks in the skin
Acute infection
-symptoms are severe and appear soon after the initial infection occurs
-short duration
ex. common cold
Chronic infection
-microorganism is present for long duration
-some may persist for life
-person may be asymptomatic
ex. HCV or HIV
Latent infection
-persistent infection with recurrent symptoms that "come and go"
-virus will sit away from the surface in the nerve cell until it gets triggered by something (fever, sunburn or stress) then it will leave the nerve cell and appear back on the surface
ex. chickenpox leads to shingles
ex. cold sores (herpes simplex) and genital herpes
Opportunistic infection
-caused by normally nonpathogenic organisms
-occurs in individuals whose resistance is decreased or compromised
ex. individual who is recovering from influenza may get pneumonia or an ear infection
think: the infection is taking the OPPORTUNITY (opportunistic) to make the person more sick
Protocol for cleaning an operatory after patient treatment
1. put on utility gloves, eyewear and protective clothing
2. make sure that the precleaning/ disinfecting product has been prepared correctly and is fresh
-read and follow manufacturers instructions
3. pre-clean; spray the paper towel or gauze pad with the product and vigorously wipe the surface
-if cleaning a large area, use several towels or gauze pads
4. disinfect, spray a fresh paper towel or gauze pad with the product
-let the surface remain moist for the manufacturers recommended time for tuberculocidal action (usually 10 mins)
5. if the surface is still moist after kill time and you are ready to seat the patient, wipe the surface dry
-use water to rinse instruments if still wet
Categories of disinfecting and sterilizing chemicals
-sterilant
-high level disinfectant
-intermediate level disinfectant
-low level disinfectant
Sterilant
-destroys ALL microorganisms including high numbers of bacterial spores
-used on heat sensitive reusable items
-immersion only
ex. gluteraldehyde, gluteraldehyde phenate, hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen peroxide with peracetic acid, peracetic acid
High level disinfectant
-destroys all microorganisms but NOT necessarily high numbers of bacterial spores
-used on heat sensitive reusable items
-immersion only
ex. gluteraldehyde, gluteraldehyde phenate, hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen peroxide with peracetic acid, peracetic acid, orthophthalaldehyde
Intermediate level disinfectant
-destroys vegetative bacteria, most fungi and most viruses
-inactivates mycobacterium tuberculosis var. bovis (is tuberculocidal)
-clinical contact surfaces
-non critical surfaces with visible blood
ex. EPA registered hospital disinfectant with label claim of tuberculocidal activity (eg. chlorine based products, phenolics, iodophors, hydrogen peroxide, quaternary ammonium compounds with alcohol, bromides)
Low level disinfectant
-destroys vegetative bacteria, SOME fungi and some viruses
-does not inactivate M. tuberculosis var. bovis (not tuberculocidal)
-housekeeping surfaces (floors, walls)
-noncritical surfaces without visible blood
-clinical contact surfaces
ex. EPA registered hospital disinfectant with label claim of tuberculocidal activity (eg. quaternary ammonium compounds)
7 steps for instrument processing
1. transport
2. cleaning
3. packaging
4. sterilization
5. storage
6. delivery
7. quality
1. Transport
-transport contaminated instruments to the processing area in a manner that minimizes the risk of exposure to persons and the environment
-use appropriate PPE and a rigid, leakproof container
2. Cleaning
-clean instruments with a hands-free, mechanical process such as use of an ultrasonic cleaner or instrument washer
-if instruments cannot be cleaned immediately, use a holding solution
3. Packaging
-wrap/ package instruments in appropriate materials
-place a chemical indicator inside the package with the instruments
-if an indicator is not visible on the outside of the package, place an eternal process indicator on the outside of the package
4. Sterilization
-load the sterilizer according to the manufacturer's instructions
-label packages
-do not overload the sterilizer
-place packages on their edges in single layers or on racks to increase circulation of the sterilizing agent around the instruments
-operate the sterilizer according to the manufacturer's instructions
-allow packages to cool before removing them from the sterilizer
-allow packages to cool before handling
5. Storage
-store instruments in a clean, dry environment in a manner that maintains the integrity of the package
-rotate packages so that those with the oldest sterilization dates will be used first
6. Delivery
-Deliver packaged instruments to their proper location/person
-INSPECT prior to use!
7. Quality
-an effective quality assurance program should incorporate training, record keeping, maintenance, and the use of biologic indicators
What to do if a sterilized package comes out of the sterilizer wet?
-instruments must be repackaged with a integrator and indicator and reprocessed in the sterilizer
What happens if sterilized packages come out wet?
-to maintain sterility packages must be allowed to dry while inside the steam sterilizer
-wet or damp packages can be easily torn or damaged
-when wet or damp packages are allowed to dry outside of the sterilizer, WICKING can occur
Wicking
-when bacteria from the air or contaminated surfaces are drawn through the wet packaging material and contaminate the instruments inside
Biological monitoring
aka spore testing
-only way to determine whether sterilization has occurred and to confirm that all bacteria and endospores have been killed
· Know about standard precautions and what is the list of protocols involved chapter 18-24
FDA cleared instrument IMMERSION DISINFECTANTS for dentistry
Glutareldehyde ; 2.4%-3.4% alkaline and acidic formulations
-6 to 10 h at 20, 22 or 25C (steri)
-20 to 90 mins at 20, 22 or 25C (disinfect)
Hydrogen peroxide; 7.3%
-6h at 20 C (steri)
-30 min at 20 C (disinfect)
Ortho phthaladehyde; 0.55%
-not indicated for sterilization
-12 min at 20C (disinfect)
Glutareldehyde*
-classified as a high level disinfectant/ sterilant
-can be used as a liquid sterilant when the immersion time is greatly increased
-times for disinfection range from 10 to 90 mins (read manufacturers label)
-useful for plastics and other items that cannot withstand heat sterilization
-some gluteraldeyhde products are effective for only 28 days after activation
Idophors*
-EPA registered intermediate level hospital disinfectants with tuberculocidal action
-recommended for disinfecting surfaces that have been soiled with potentially infectious patient material
-usually effective within 5 to 10 mins
-can be used as immersion disinfectant for non hydrocolloid impressions
-inactivated by hard water, MUST BE mixed with soft or distilled water
-may corrode or discolour certain metals or temporarily cause red or yellow stains on clothing and other surfaces because they contain IODINE
Synthetic phenol compound*
-EPA registered intermediate level hospital disinfectant with broad spectrum activity
-they can kill a wide range of microbes
-phenols can be used on metal, glass rubber or plastic
-can be used as holding solution for instruments but they leave a residual film on treated surface
-prepared daily
-also may be used to disinfect impressions
Chlorine dioxide*
-classified as a high level disinfectant/ sterilant
-can be used as effective rapid acting, environmental surface disinfectants (3 mins) or chemical sterilants (6 hrs)
-do not readily penetrate organic debris and must be used with a separate cleaner
-must be prepared fresh daily
-must be used with good ventilation
-corrosive to aluminum containers
Alcohol
-not effective in the presence of bioburdens such as blood and saliva
-rapid rate of evaporation limits the antimicrobial activity of alcohol
-damaging to plastics and vinyl, which are prevalent
Sodium hypochlorite *
-intermediate level disinfectant
-main ingredient is household bleach
-fast acting, economical and broad spectrum disinfectant
-not EPA registered disinfectant
Disadvantages of sodium chlorite
-unstable and needs daily preparation
-has a strong odour and is corrosive to some metals
-destructive to fabrics and may eventually cause plastic chair covers to crack
-irritating to the eyes and skin
Methods of sterilization
-steam autoclave
-unsaturated chemical vapour
-dry heat oven type (static air)
Steam autoclave
Advantages:
-short time
-no corrosion
-instruments dry quickly following cycle
Disadvantages:
-damages some plastic and rubber items
-requires use of distilled water
-may rust non stainless steel instruments and burs
-cannot use closed containers
Unsaturated chemical vapor
Advantages:
-short time
-good penetration of steam
-commonly used in dental offices
Disadvantages:
-instruments must be dry
-damages some plastic and rubber items
-requires special solution
-requires good ventilation
-cannot sterilize liquids
-cannot use closed containers
-CLOTH WRAP MAY ABSORB CHEMICALS
Dry heat oven type (static air)
Advantages:
-no corrosion
-can used closed containers
-items are dry after cycle
Disadvantages:
-long sterilization time
-instruments must be pre dried
-damages some plastic and rubber items
-cannot sterilize liquids
Management of an exposure incident
-document the routes of exposure and the circumstance in which the incident occurred (ex, needlestick, cut or blood splash)
-identify and document the source (patient whose blood or body fluid is involved in the exposure incident) unless the employer can establish that identification is not possible or is prohibited by state or local law
-request that the source individual has their blood tested for HIV, HBV (source individual can refuse request)
-advise the employee to have their blood tested for HIV, HBV
-provide medically indicated prophylactic treatment (vaccine or booster)
-provide appropriate counselling
-evaluate reported illnesses after the incident
Classification of waste
-general waste
-hazardous waste
-contaminated waste
-infectious or regulated waste (Biohazard)
General waste
-Paper towels, paper mixing pads, empty food containers
-discard in covered containers made of durable materials such as plastic or metal
Hazardous waste
-waste that present a danger to humans or to the environment (toxic chemicals)
-follow your specific state and local regulations
Contaminated waste
-waste that has been in contact with blood or other body fluids (used barriers, patient napkins)
-in most states, dispose of with the general waste
Infectious or regulated waste (biohazard)
-waste that is capable of transmitting an infectious disease
-follow your specific state and local regulations
Donning PPE
-gown
-mask
-goggles
-handwash
-gloves
Doffing PPE
-remove gloves
-wash hands
-glasses off
-mask off
-gown off
Alcohol-based hand rubs
-Waterless antiseptic agents are alcohol-based products that are available in gels, foams, or rinses
-this product is simply applied to the hands which are then rubbed together to allow the product to cover all surfaces
-more effective than plain soap or even antimicrobial hand wash at reducing microbial flora
Applying alcohol based hand rubs
-60-95% concentration
-dough sensitive
1. check your hands and make sure they're not contaminated with any blood or saliva
2. dispense enough sanitizer to cover all surfaces of your hands
3. rub the palms of your hands together, between your fingers and over the back of your hands, making sure your hands stay wet for 20 seconds
Utility gloves
-not used for direct patient care
-worn when the treatment room is cleaned and disinfected in between patients
-while contaminated instruments are being cleaned or handled
-for surface cleaning and disinfecting
-must be chemical resistant, heat resistant and puncture resistant
-must properly disinfect or sterilize them after use
Latex allergies
-latex gloves have been proven to be one of the most effective means of protecting workers for transmissible diseases
-number of health care workers and patients who have become hypersensitive to latex has increased dramatically
Irritant dermatitis
-nonimmunologic process (does not involve bodys immune system)
-caused by contact with a substance that produces a chemical irritation to the skin
-skin becomes reddened, dry, irritated and cracked
Type I allergic reaction
-most serious type of latex allergy and can result in death
-occurs in response to latex proteins in the gloves
-sever immunological response occurs
-usually 2 to 3 minutes after latex contact with the skin or mucous membranes
-proteins from the latex adhere to the cornstarch powder particles inside the gloves
-sensitive ppl can experience coughing, wheezing, runny nose and eyes, shortness of breath and respiratory distress
Anaphylaxis
-primary cause of death associated with latex allergies
-most severe form of allergic reaction
-death results from closure of the airway caused by swelling
Type IV allergic reaction
-most common type
-delayed contact reaction that involves the immune system
-may take 48 to 72 hours for the red, itchy rash to appear
-reactions are limited to areas of contact and does not involve the entire body
-the chemical used to process the latex in these gloves cause an immune response
-PROTEINS in the latex DO NOT CAUSE it
Why should latex gloves never be worn when handling chemicals?
-gluteraldehyde and acrylates readily pass through latex gloves and can irritate the skin
-this irritation may be mistaken for an allergic reactions to the chemicals in the latex gloves
CDC Classification of Instruments and Procedures
-critical
-semicritical
-noncritical
Critical
Function:
-touch bone or penetrate soft tissues
ex. surgical and other instruments used to penetrate soft tissue or bone, including forceps, scalpers, bone chisels, scalers and burs
-intraoral use
-very high risk of disease transmission
-must sterilize
Noncritical
Function:
-contact only with intact skin
ex. external dental x ray head (PID)
-no intraoral use
-very low or no risk of disease transmission
-intermediate to low level disinfectant or basic cleaning
Semicritical
Function:
-touch mucous membranes but will not touch bone or penetrate soft tissues
ex. mouth mirrors, amalgam condensers
-intraoral use
-moderate risk of disease transmission
-sterilization or high level disinfectant
Holding solutions
-if instruments cannot be cleaned immediately after a procedure is performed, they should be placed in a holding solution to prevent the drying of blood and debris on the instruments
-may be any noncorrosive liquid
-a commercial enzymatic solution that partially dissolves organic debris may be used
-dishwasher detergent makes a good holding solution bc low cost, low foaming and readily available
What labels are required on holding solutions
-the container must have a lid and be labeled with both a BIOHAZARD label (bc contaminated instruments) and a CHEMICAL label (bc of the cleaner/ detergent)
How often should the holding solution be changed?
-at least twice daily
-more frequently if it becomes clouded
Ultrasonic cleaner
-used to loosen and remove debris from instruments
-reduce the risk for hand injury from cuts and punctures during the cleaning process
-instruments should be process until they are visibly clean
-may take 5 to 15 mins depending on the amount and type of material on the instruments and efficiency of ultrasonic cleaner
Operating the ultrasonic cleaner
-puncture resistant utility gloves must be worn, mask, eyewear and a gown should always be worn when using the ultrasonic
-keep a set of tongs to remove the instruments from the cleaner to further avoid contaminated instruments
How does the ultrasonic cleaner work?
-by producing sound waves beyond the range of human hearing
-these sound waves which can travel through metal and glass containers cause CAVITATION (formation of bubbles in liquid)
-bubbles, which are too small to be seen burst by implosion
-the mechanical cleanings action of the ultrasonic solution removes the debris from the instruments
Testing the ultrasonic cleaner
-to determine whether the ultrasonic cleaner is working properly, hold a 5-by-5-inch sheet of lightweight aluminum foil vertically (like a curtain) half-submerged in fresh, unused solution
-run the unit for 20 seconds, then hold the foil up to the light
-the surfaces that were submerged in the solution should be evenly marked with a tiny pebbling effect over the entire surface
-an area without pebbling of more than ½ inch indicates a problem with the unit, and it needs to be serviced by the manufacturer
Chemical monitoring
-external and internal
-involves the use of a heat sensitive chemical that changes color when exposed to certain conditions
2 types: process indicators and process integrators
Process indicator
(External)
-placed outside of instrument packages before sterilization
-simply identify instrument packs that have been exposed to a certain temp
-DO NOT measure duration or pressure
ex. autoclave tape and color change markings on packages or bags
Process integrator
(Internal)
-placed inside the instrument packages
-they respond to a combination of pressure, temperatures, and time
-aka multiparameter indicators
-all sterilization factors are integrated
-penetration of sterilization agent is ensured
ex. strips, tabs and tubes of coloured liquid
Biological indicator
aka spore tests
-vials or strips of paper that contain harmless bacterial spores (spores are highly resistant to heat)
-3 are used in testing
-2 are placed inside instrument packs and the sterilizer is operated under normal conditions, 3rd test is set aside as a control
-after load is sterilized the indicators are cultured
-if the spores survive the sterilization cycle (test came back positive) then sterilization has failed
-if the spores are killed (came back negative) then the sterilization is successful
What does the Alberta sterilization standards require for biological tests?
-tests must be run for each type of load in each sterilizer DAILY
The regulatory agency responsible for regulating the manufacturing and labeling of medical devices. chapter 22
FDA
Biofilm
-forms inside dental unit waterlines
-found in virtually all places where moisture and a suitable surface exist
-microbes that adhere to surfaces and form a protective slime layer