Mesoamerican Geography (copy)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
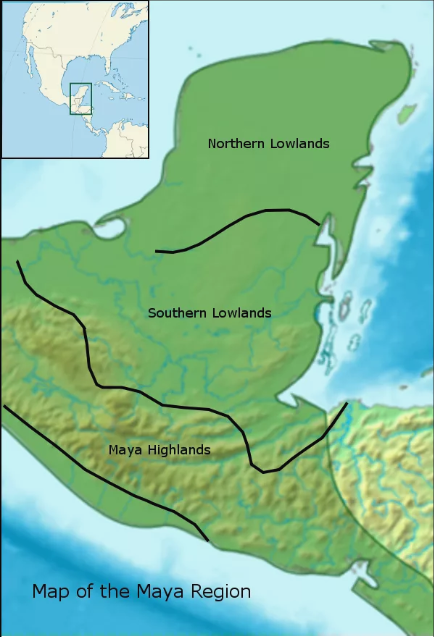
Maya Highlands
The mountainous regions of southern Guatemala and parts of Chiapas, Mexico. This area is characterized by volcanic soil, making it agriculturally productive, and its political centers include Kaminaljuyu and Copan. This area played a key role in the Preclassic and Classic periods as centers of trade and political power.
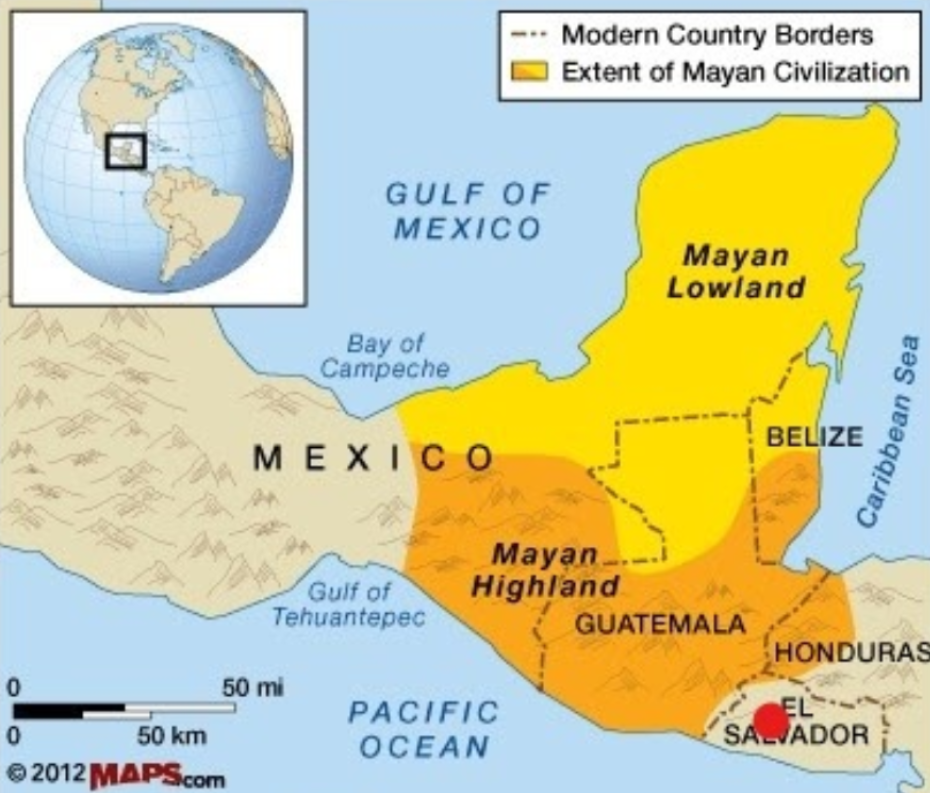
Intermediate Area
The cultural and geographical zone bridging Mesoamerica and South America, including regions like Costa Rica and Panama. This area served as a conduit for trade and cultural exchange, linking the two broader regions with shared artifacts and stylistic influences.
Lowland Veracruz
Coastal region in eastern Mexico, central to Classic Veracruz culture. This area is notable for its monumental architecture, including pyramids and ballcourts, and intricate art, such as the niche pyramids at El Tajín. It was a nexus of cultural exchange, connecting Central Mexico with the Maya region, and played a significant role during the Classic period (AD 300–900).
(Maya) Northern Lowlands
Encompass the Yucatán Peninsula, characterized by a drier climate and cenotes (natural sinkholes) as water sources. This region is known for its Postclassic cities such as Chichen Itza and Uxmal, with distinctive Puuc architecture. Its location facilitated maritime trade, making it an important economic hub.
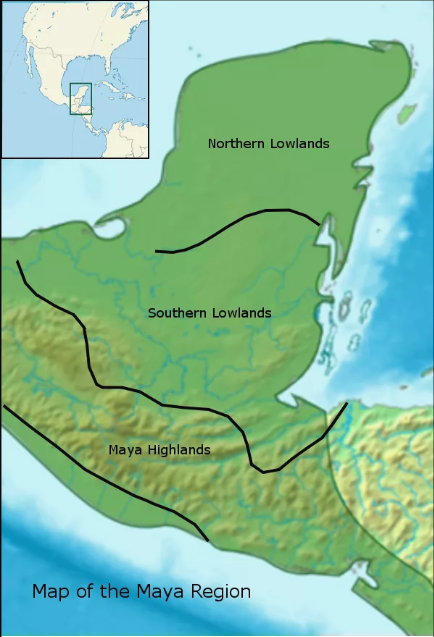
(Maya) Southern Lowlands
Include the tropical rainforests of Guatemala, Belize, and parts of Mexico. This region was the heartland of Classic Maya civilization, featuring cities like Tikal, Calakmul, and Copan. It is noted for monumental architecture, stelae with hieroglyphic inscriptions, and dense urbanization during the Classic period (AD 250–900).
Valley of Mexico
A highland basin surrounded by volcanic mountains, was a political and cultural center of Mesoamerica. It was the home of Teotihuacan (Classic period) and later the Aztec Empire (Postclassic period). Known for its fertile lands and chinampa agriculture, this region played a pivotal role in trade and urbanization.
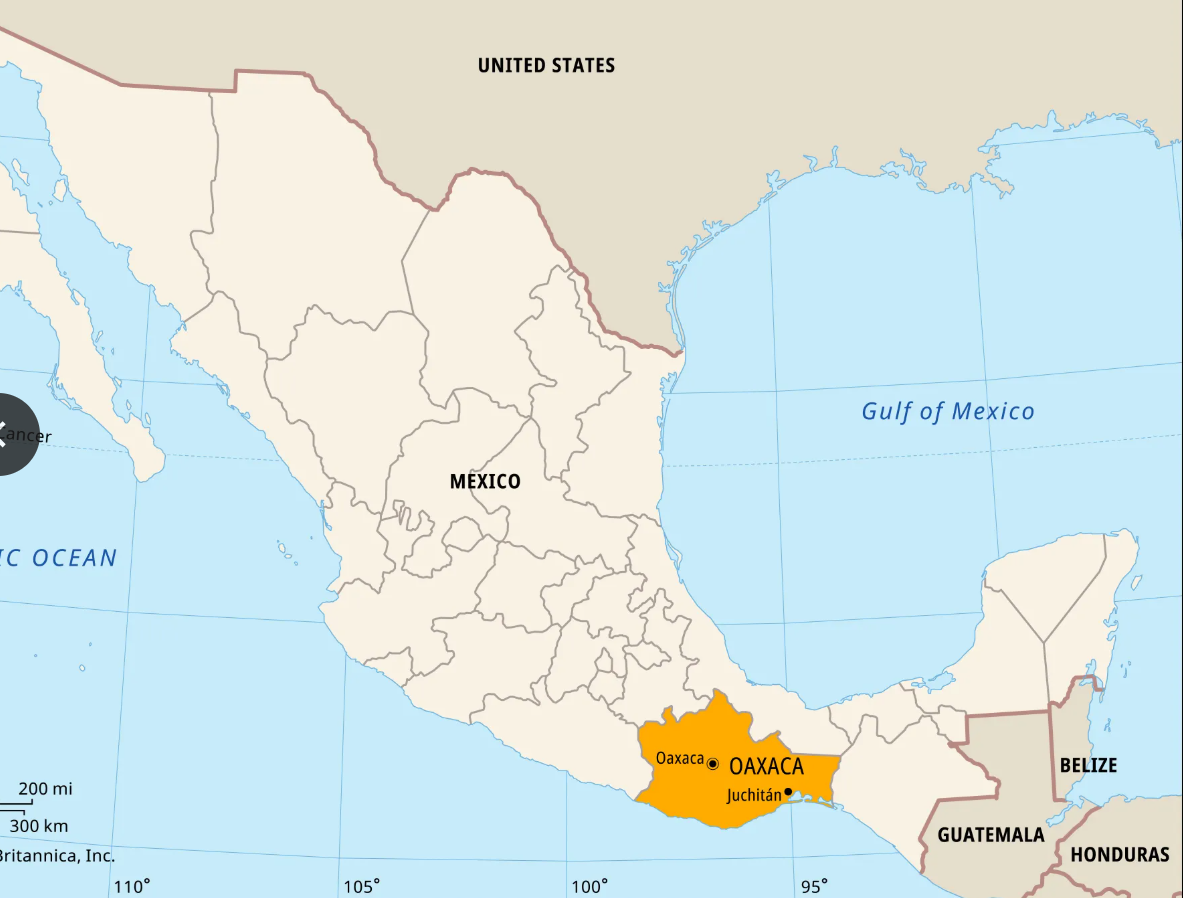
Valley of Oaxaca
A highland region in southern Mexico, characterized by fertile land and terraced agriculture. It was home to the Zapotec civilization, with Monte Albán as its primary city. It’s strategic location fostered cultural exchange between Central Mexico and the southern highlands.