A&P Chapters 13-15 Exam
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
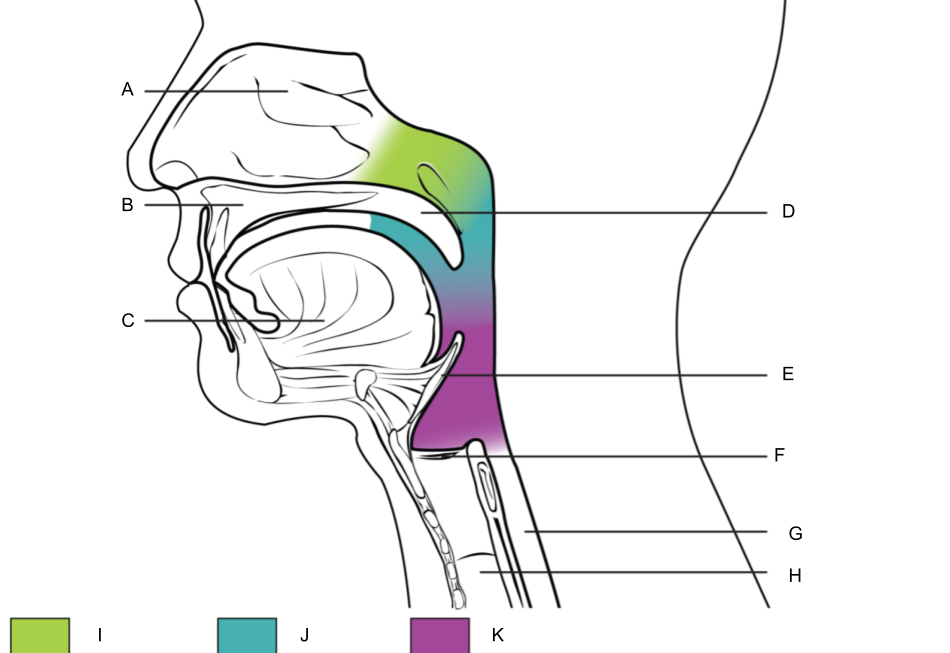
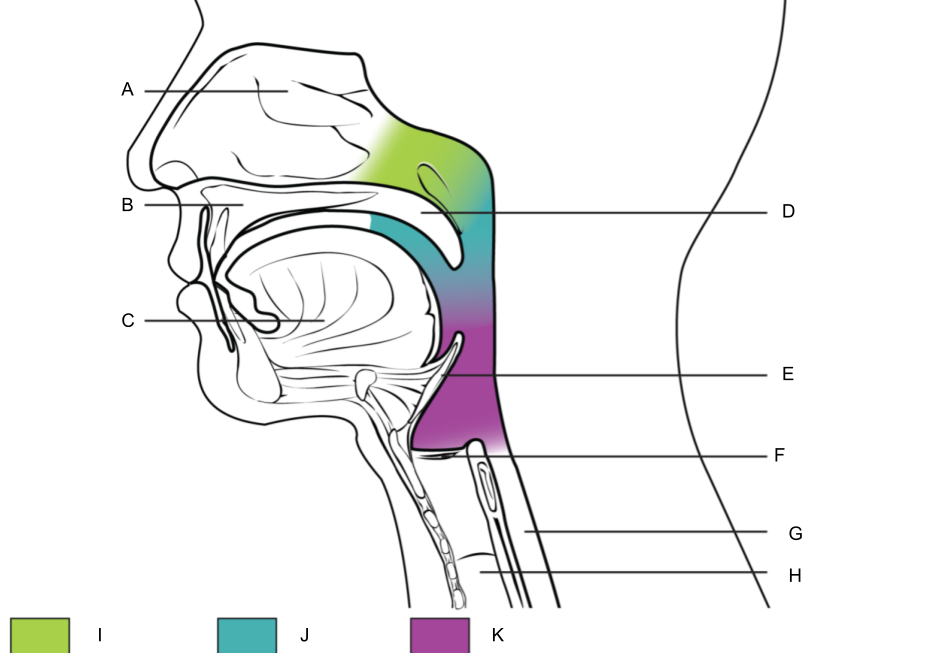
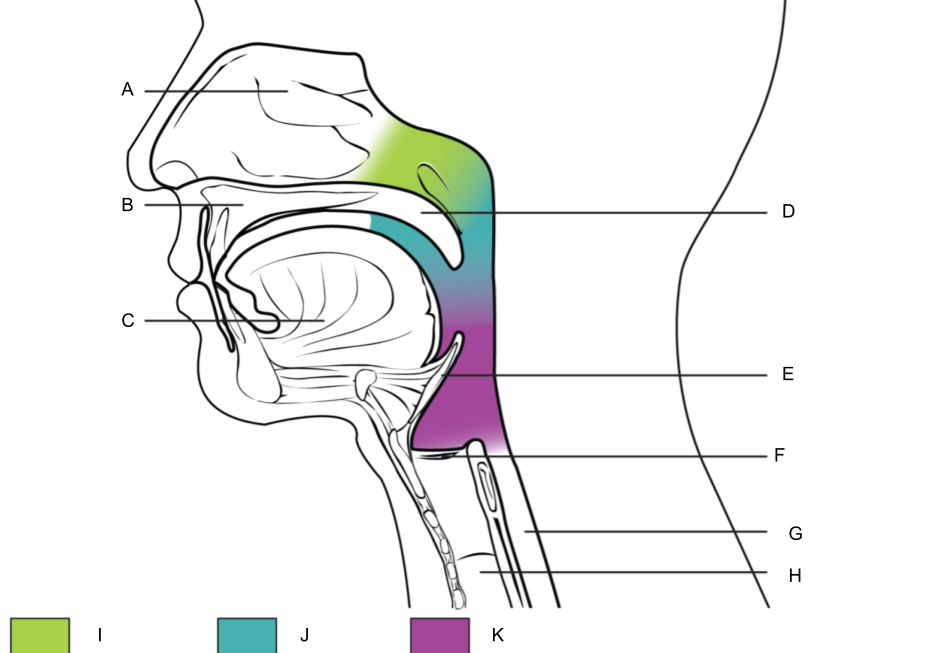
What is A?
nasal cavity
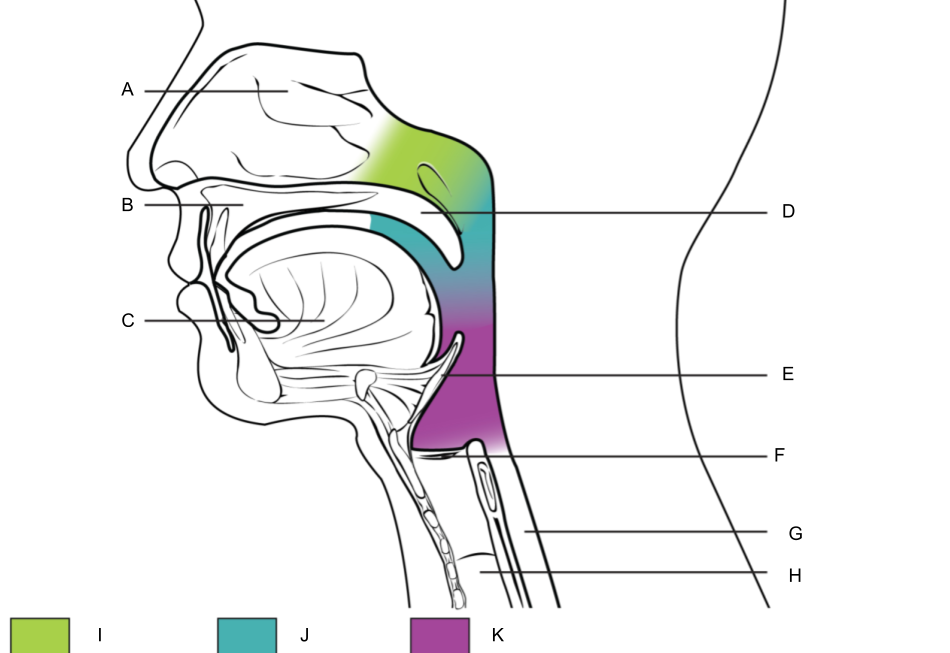
What is B?
hard palate
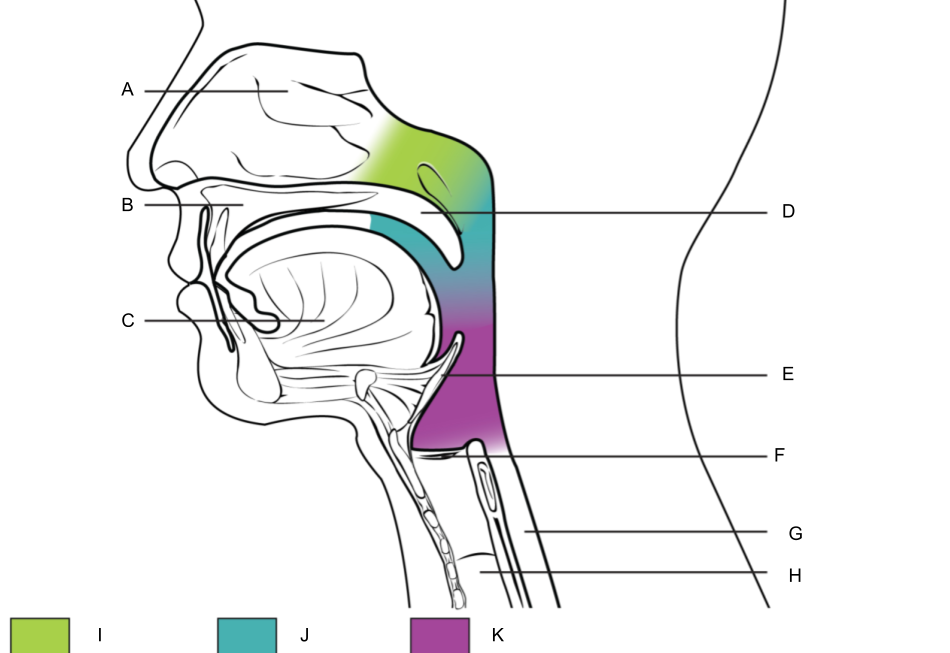
What is C?
tongue
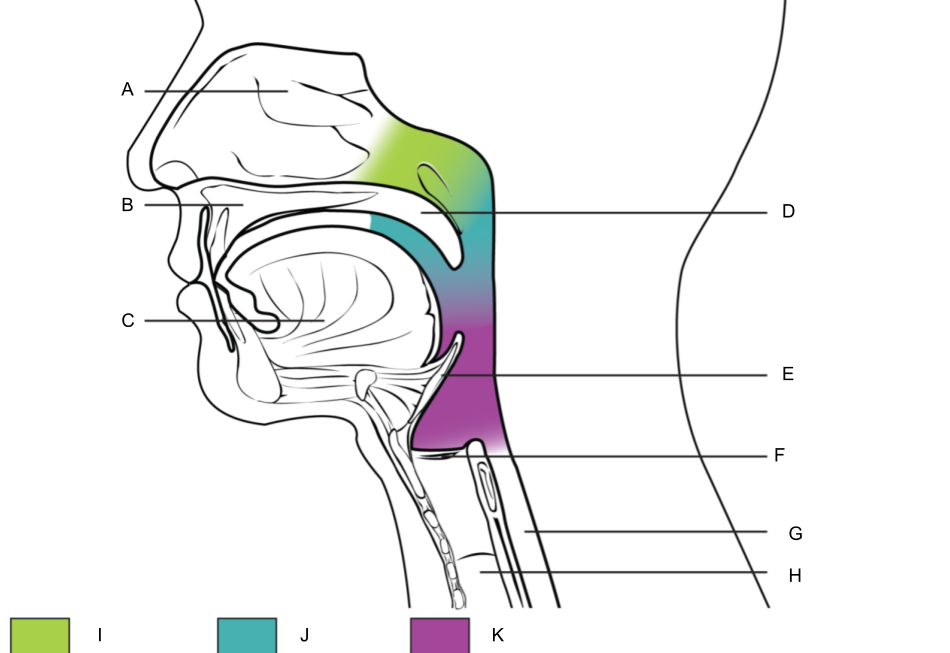
What is D?
soft palate
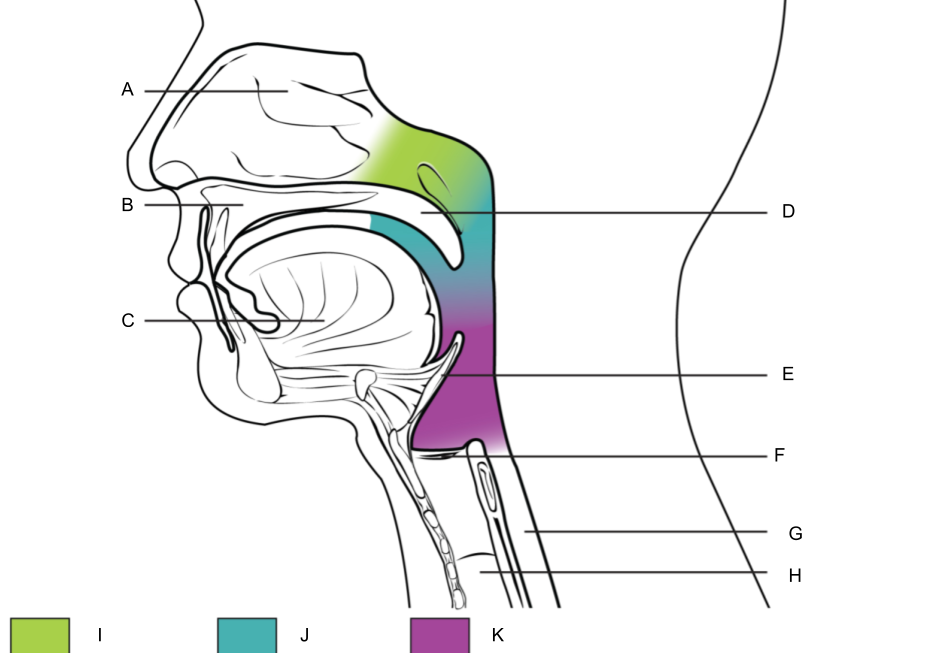
What is E?
epiglottis
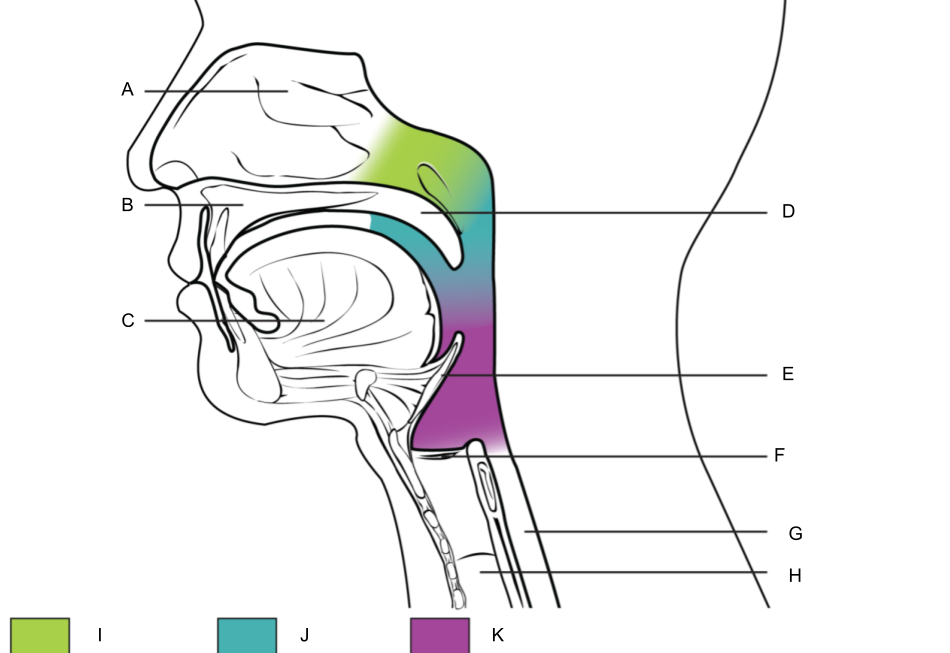
What is F?
larynx (voice box)
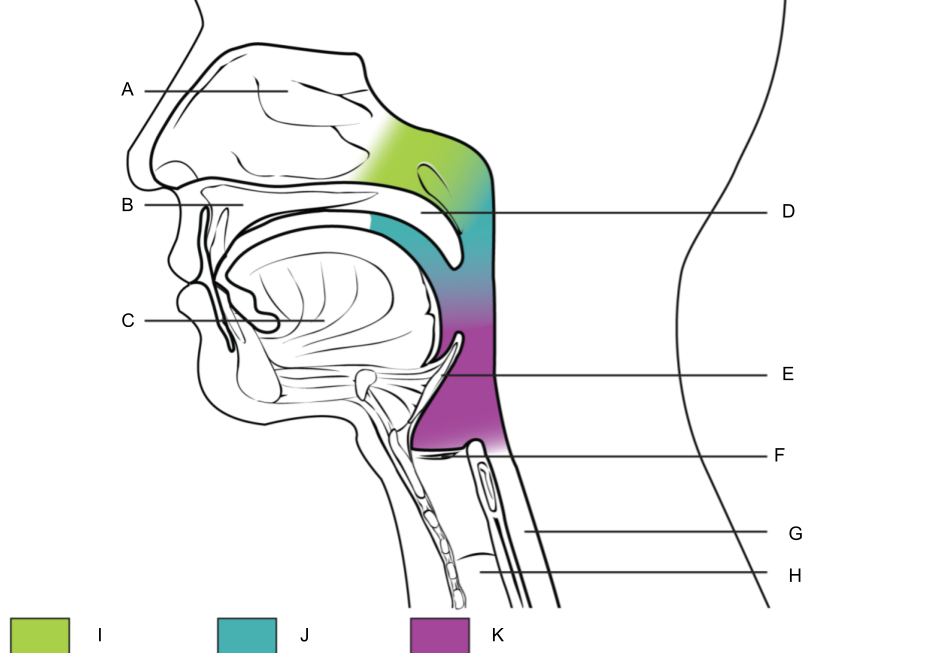
What is G?
esophagus
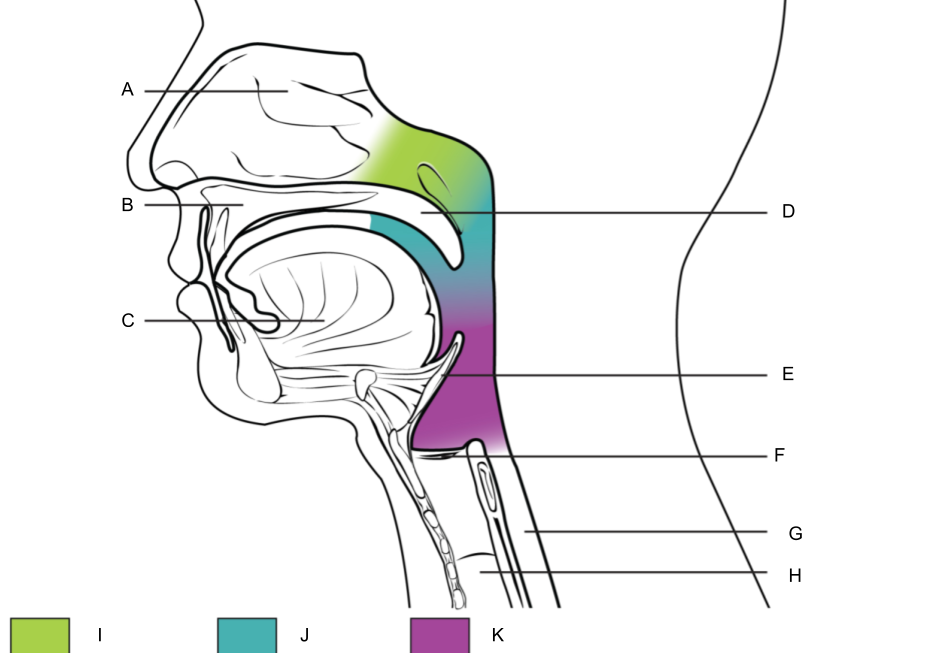
What is H?
trachea
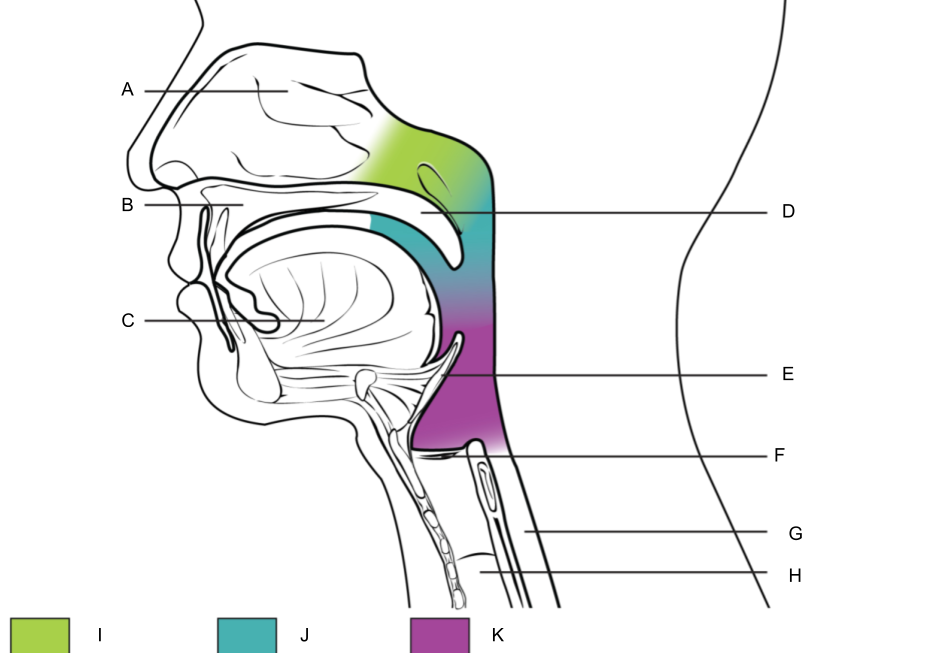
What is I?
nasopharynx
What is J?
oropharynx
What is K?
laryngopharynx
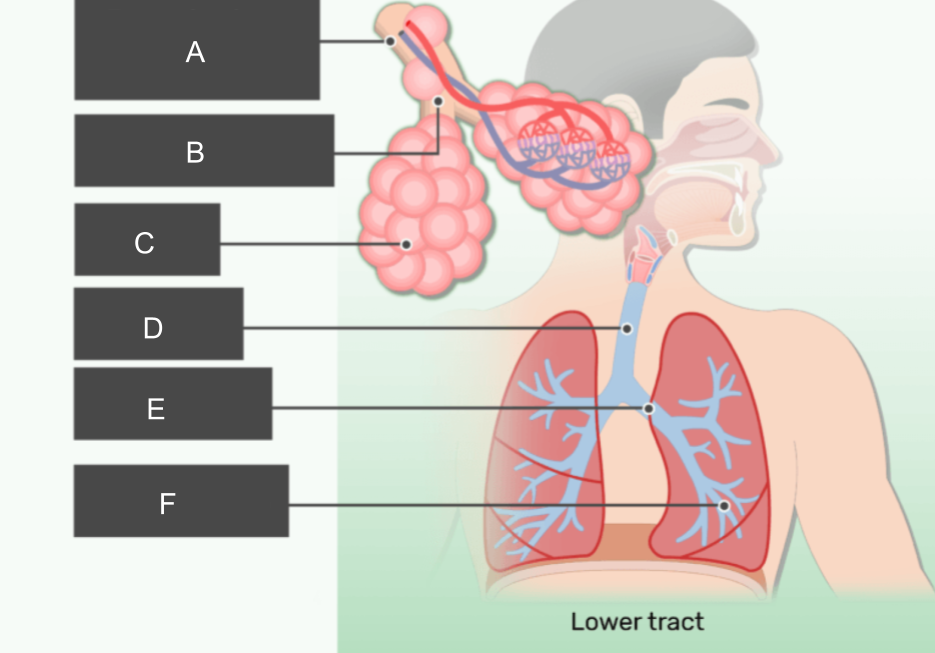
What is A?
respiratory bronchiole
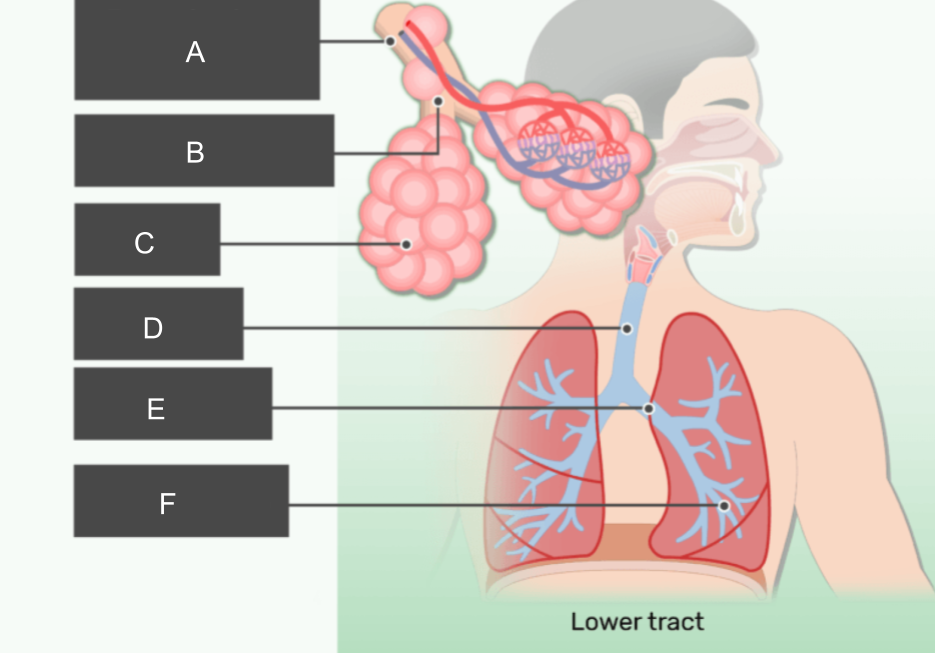
What is B?
alveolar duct
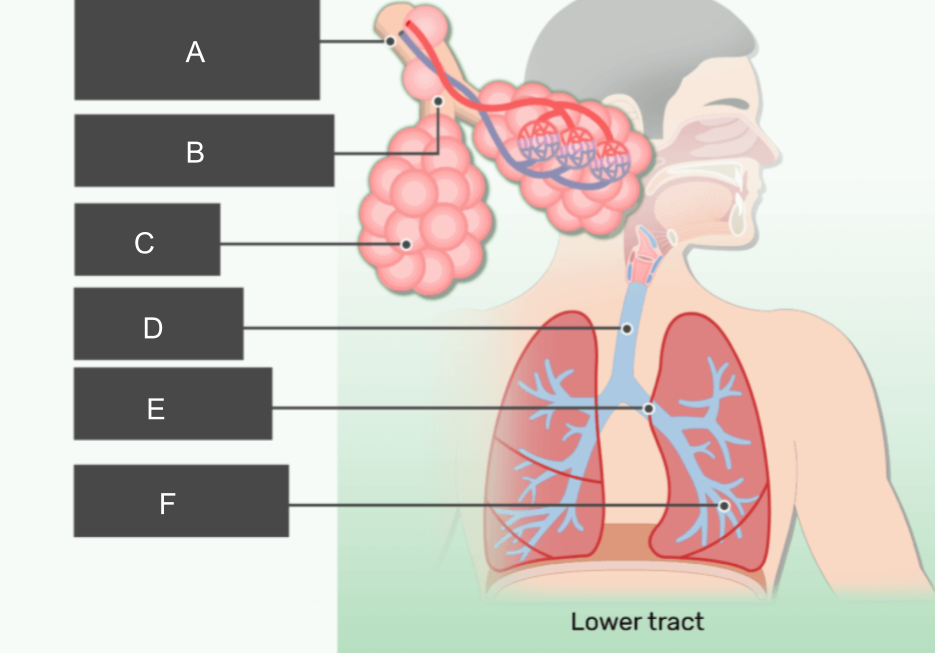
What is C?
alveoli
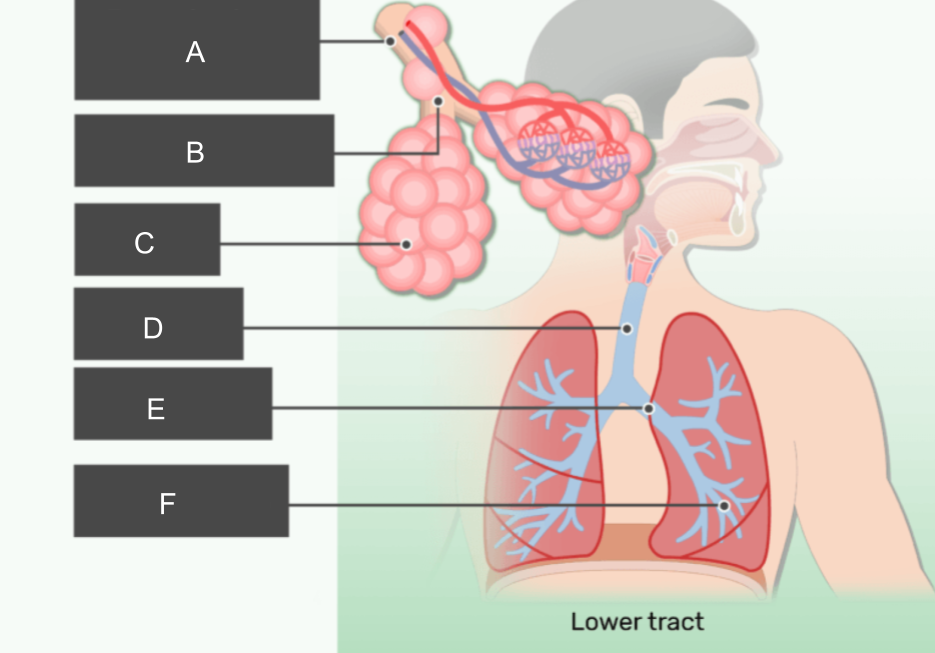
What is D?
trachea
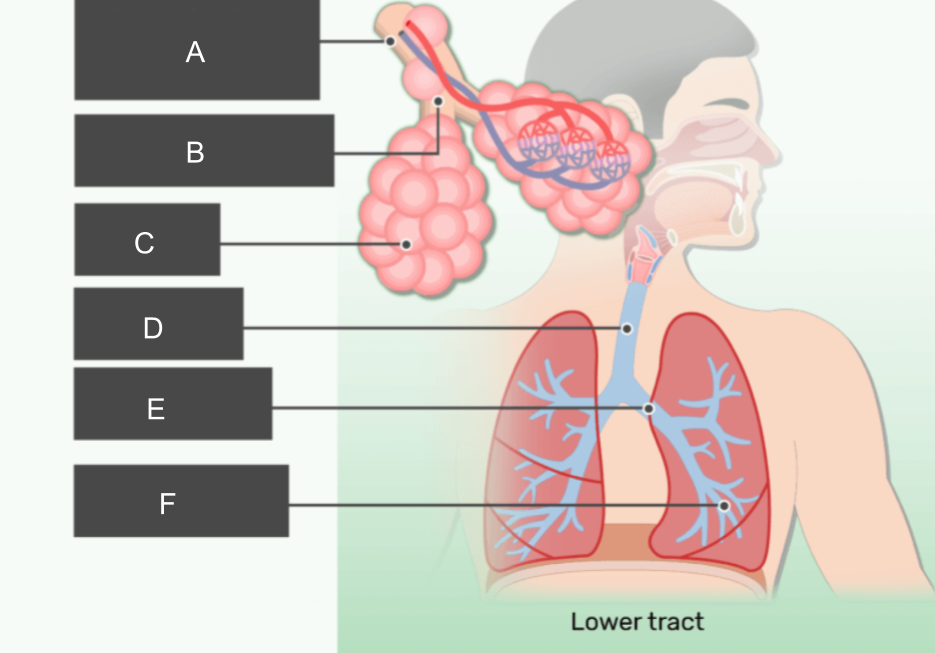
What is E?
bronchus
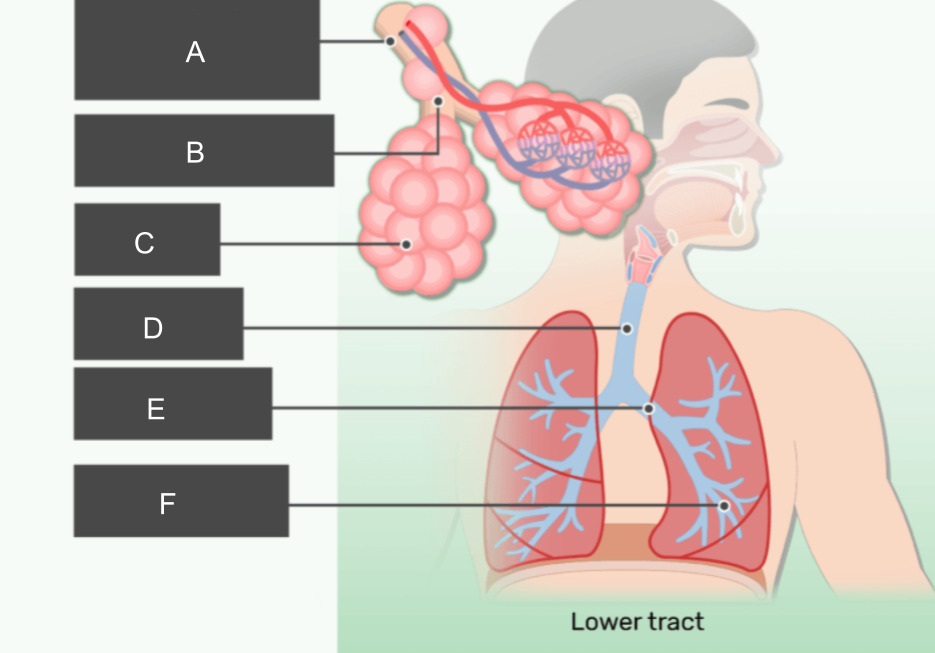
What is F?
bronchiole
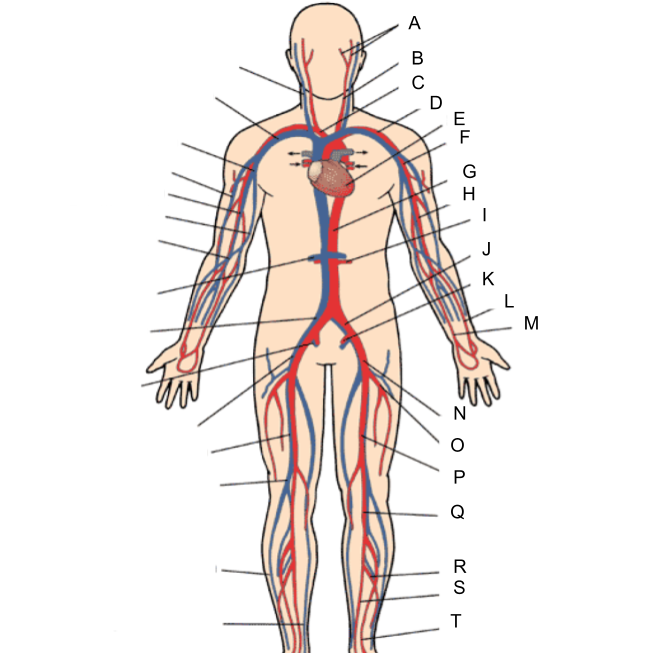
What is A?
external and internal carotid artery
What is B?
common carotid artery
What is C?
brachiocephalic artery
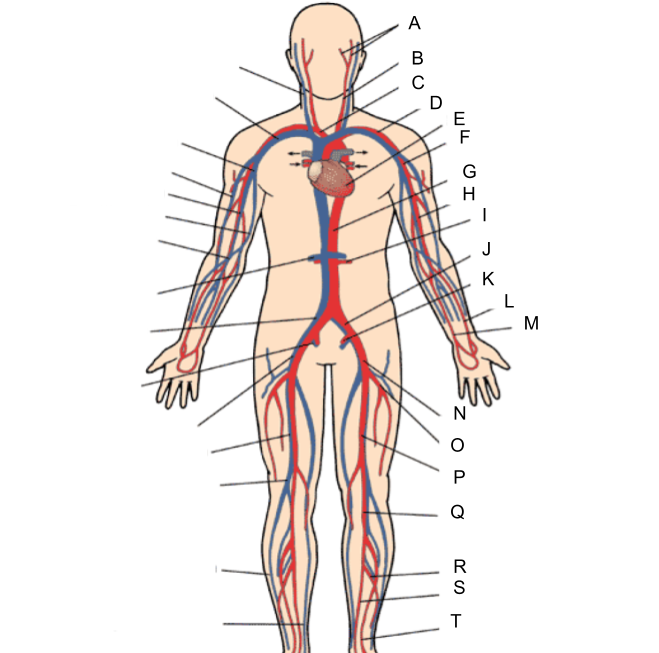
What is D?
subclavian artery
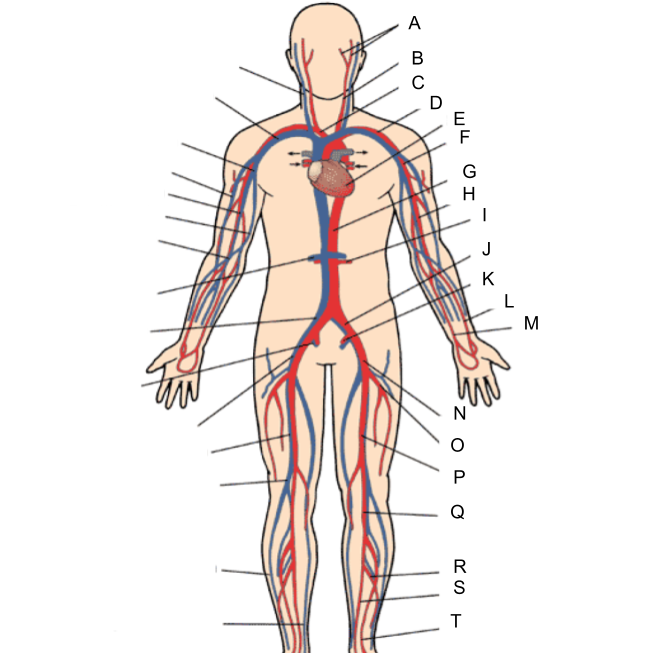
What is E?
heart
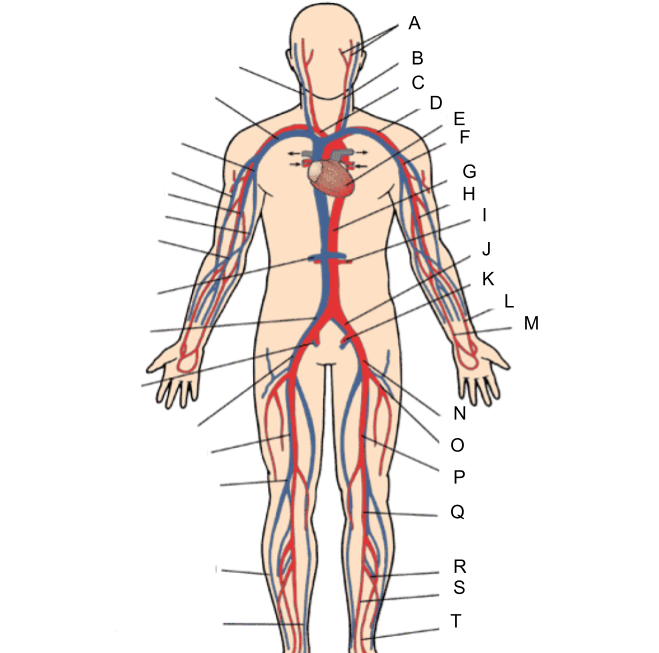
What is F?
axillary artery
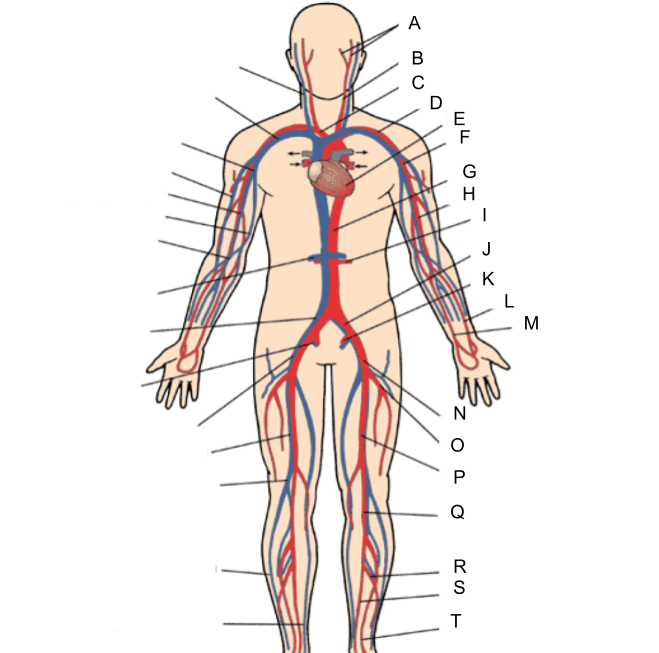
What is G?
abdominal aorta
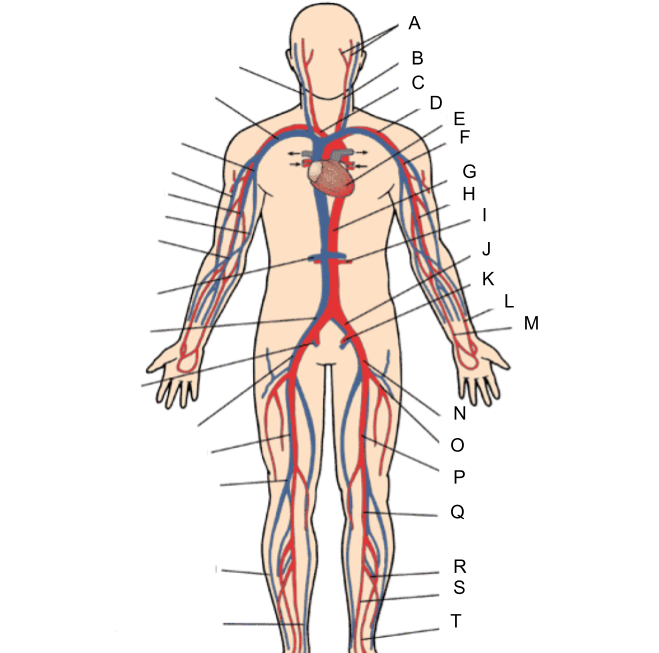
What is H?
brachial artery
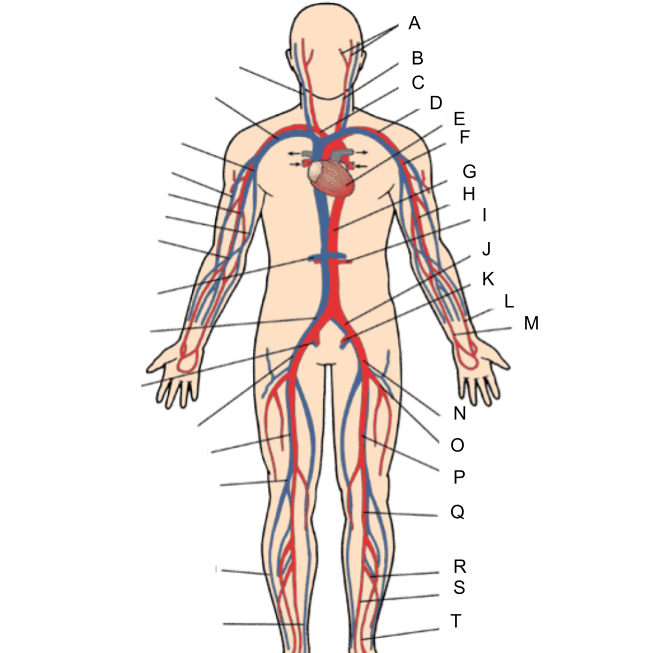
What is I?
renal artery
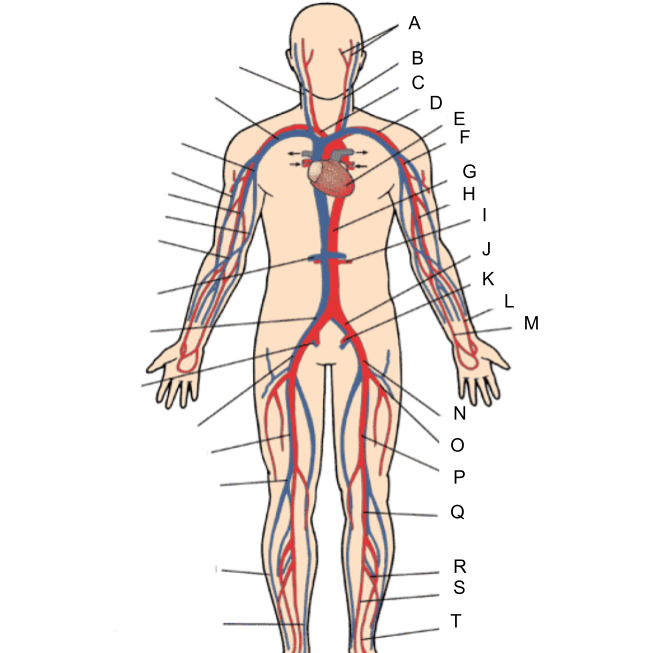
What is J?
common iliac artery
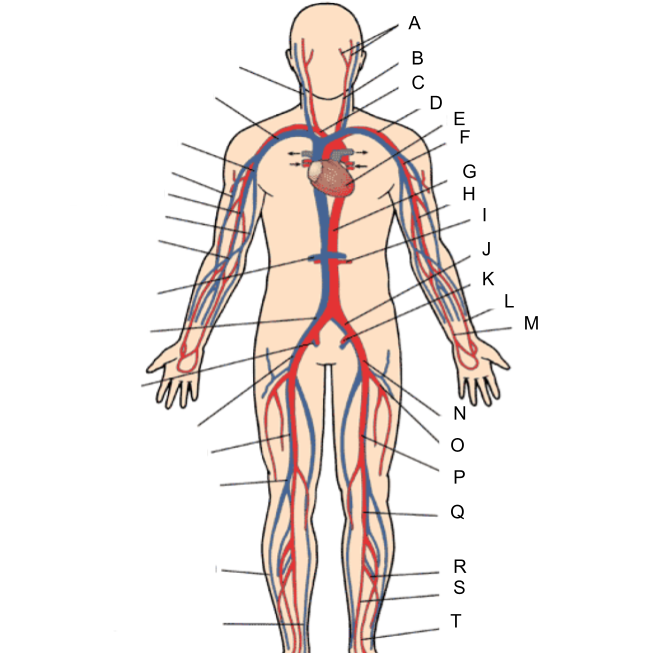
What is K?
internal iliac artery
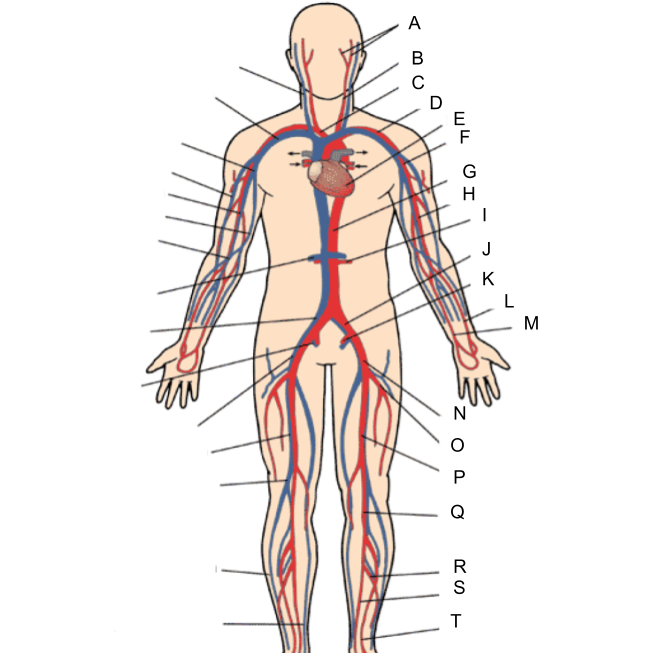
What is L?
radial artery
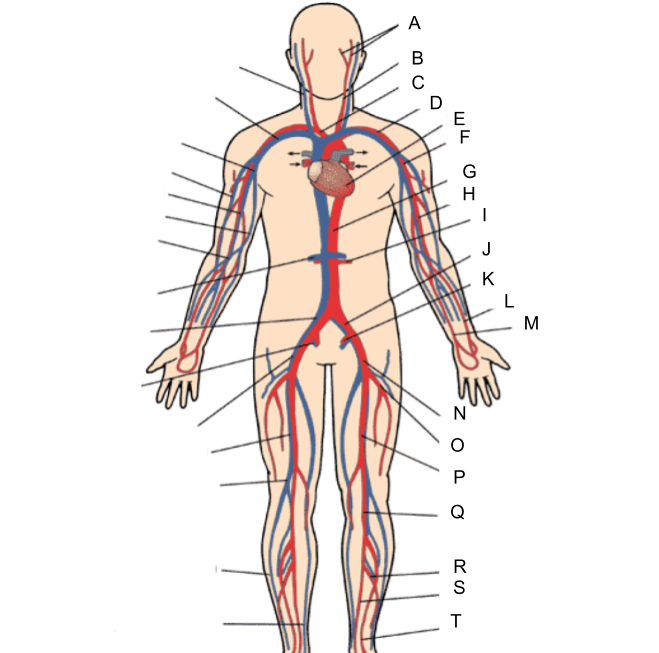
What is M?
ulnar artery
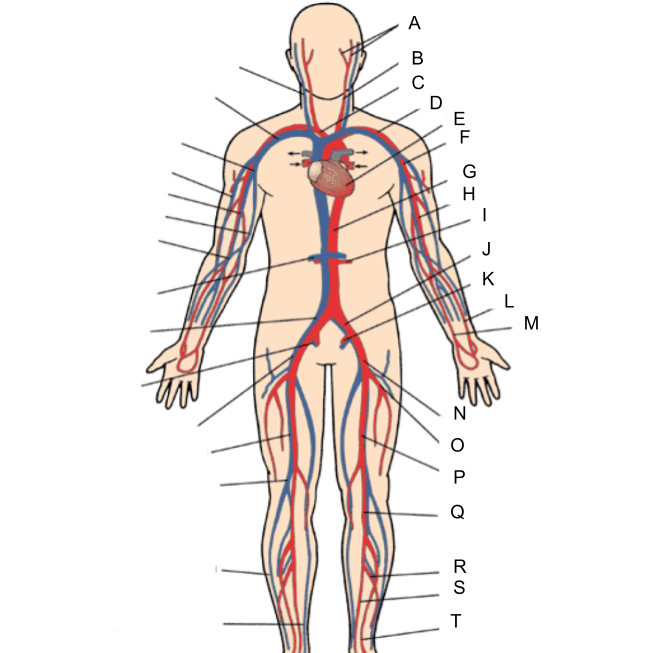
What is N?
external iliac artery
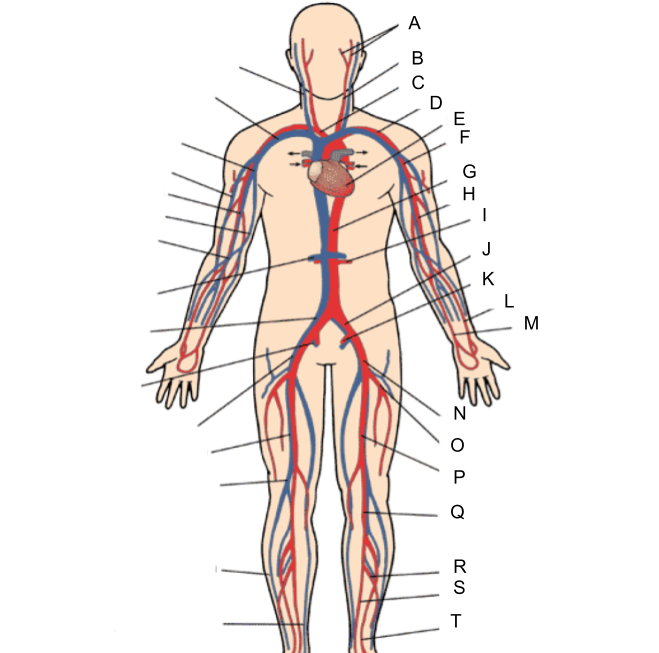
What is O?
deep femoral artery
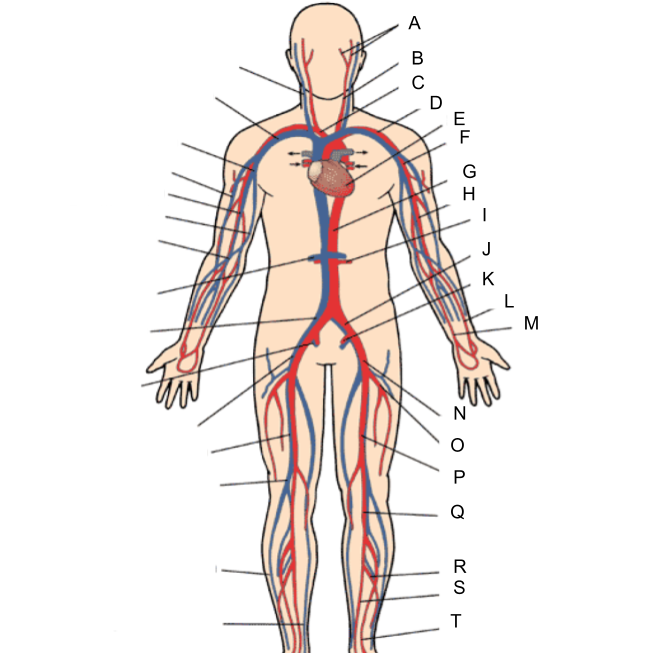
What is P?
femoral artery
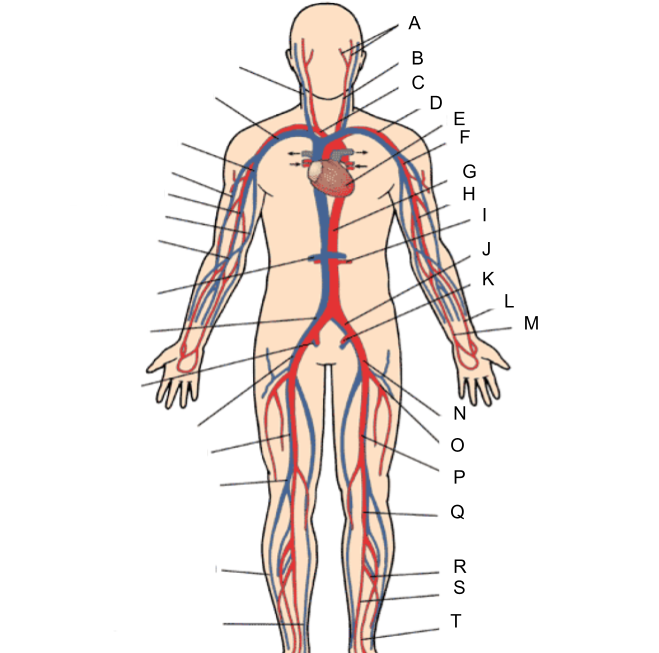
What is Q?
popliteal artery
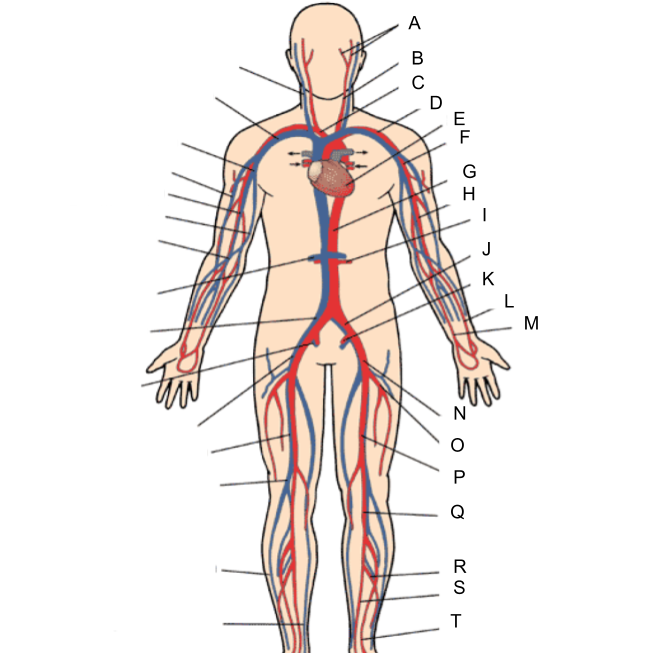
What is R?
peroneal artery
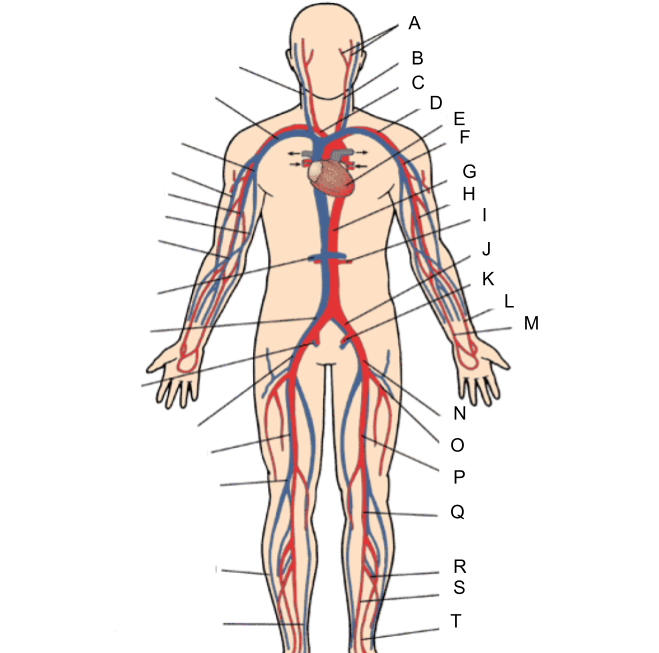
What is S?
posterior tibial artery
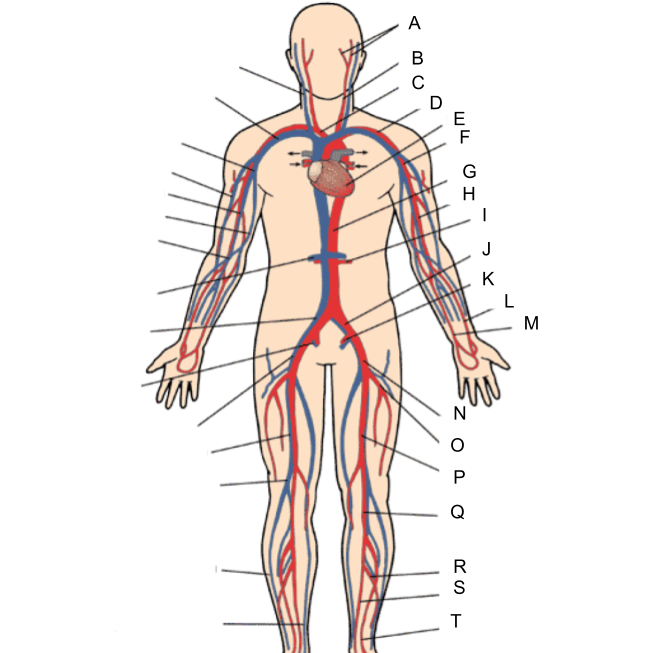
What is T?
anterior tibial artery
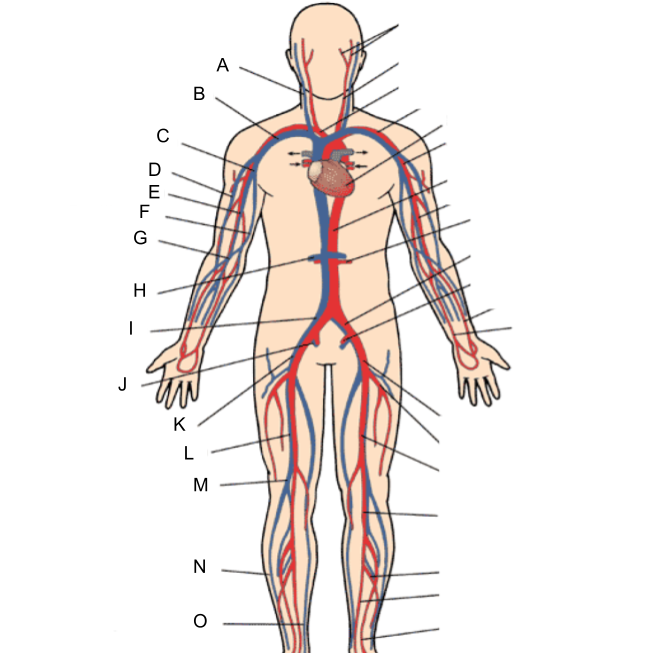
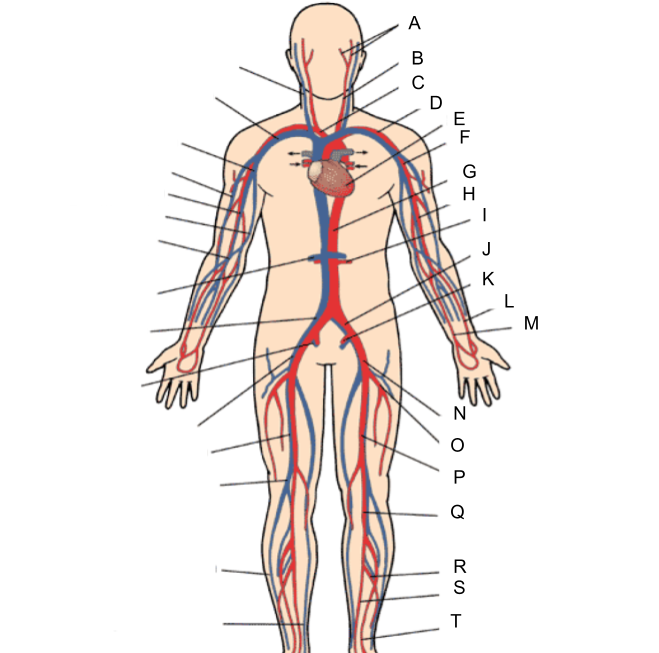
What is A?
internal jugular vein
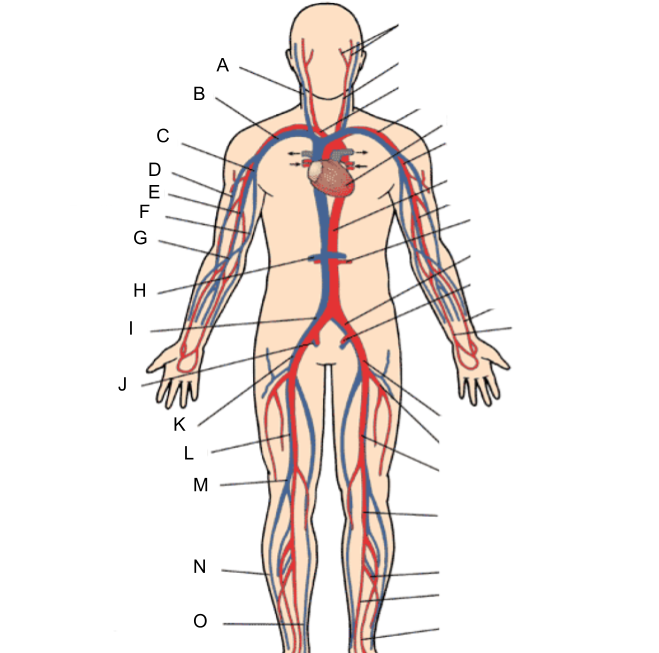
What is B?
subclavian vein
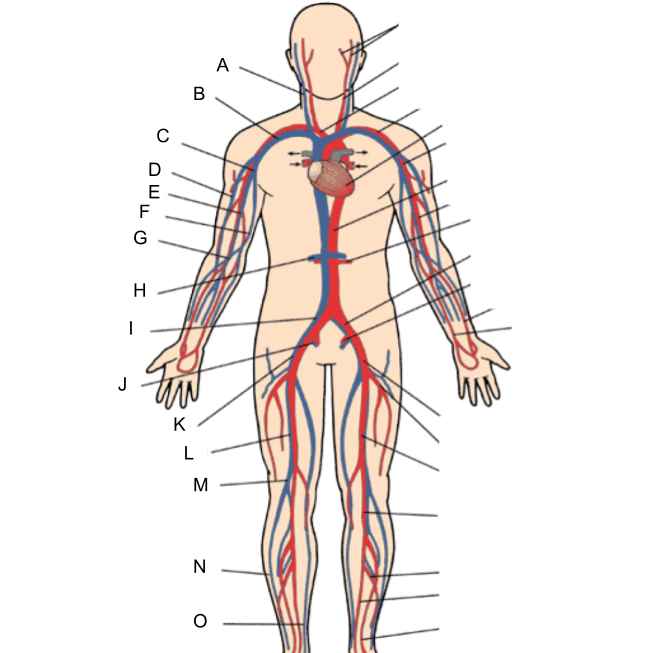
What is C?
axillary vein
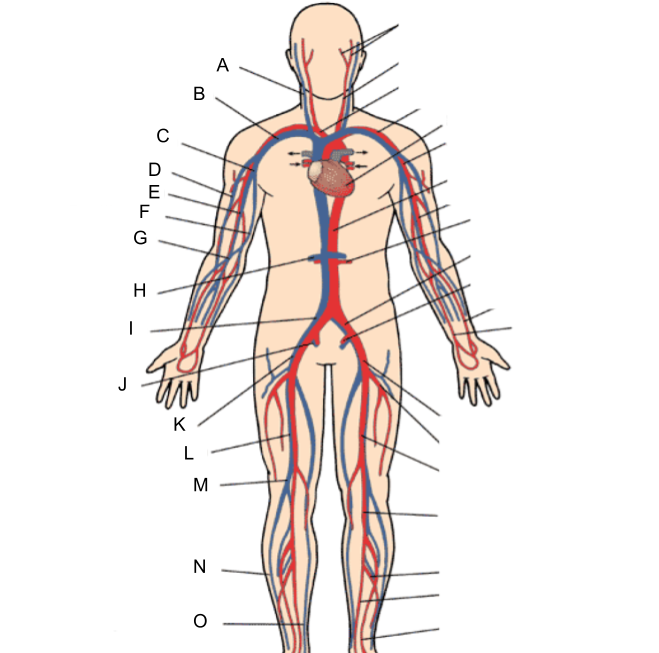
What is D?
cephalic vein
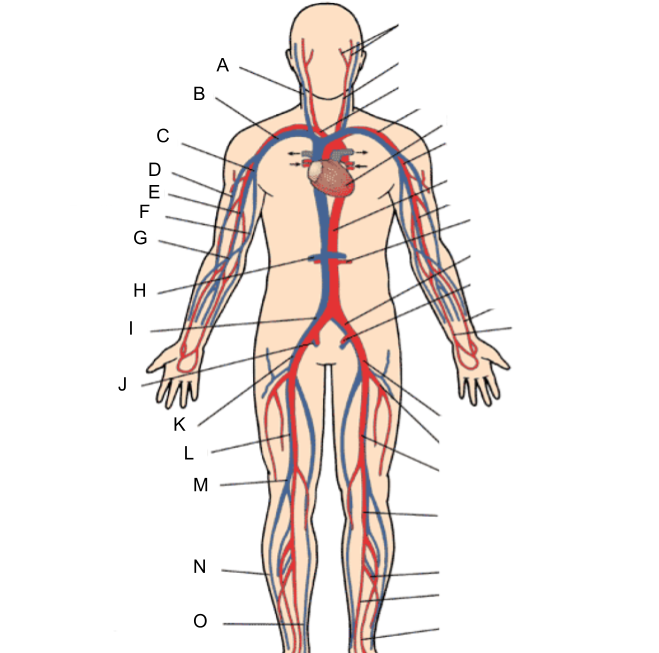
What is E?
brachial vein
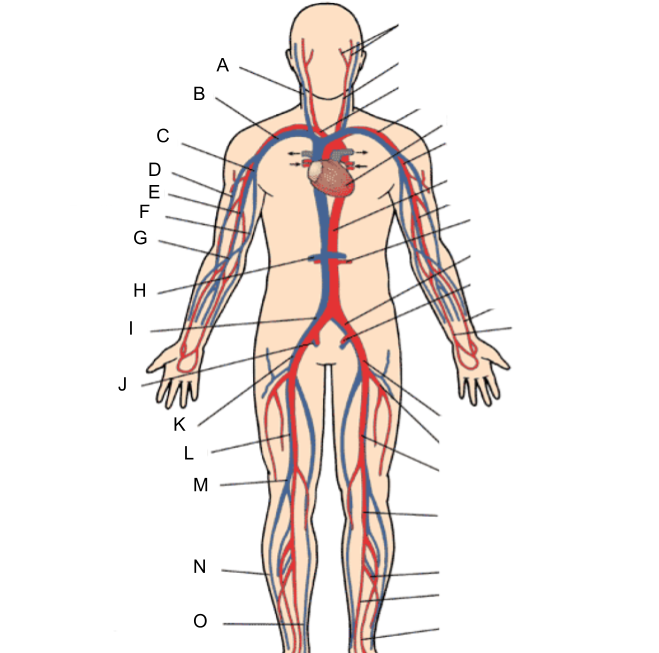
What is F?
basilic vein
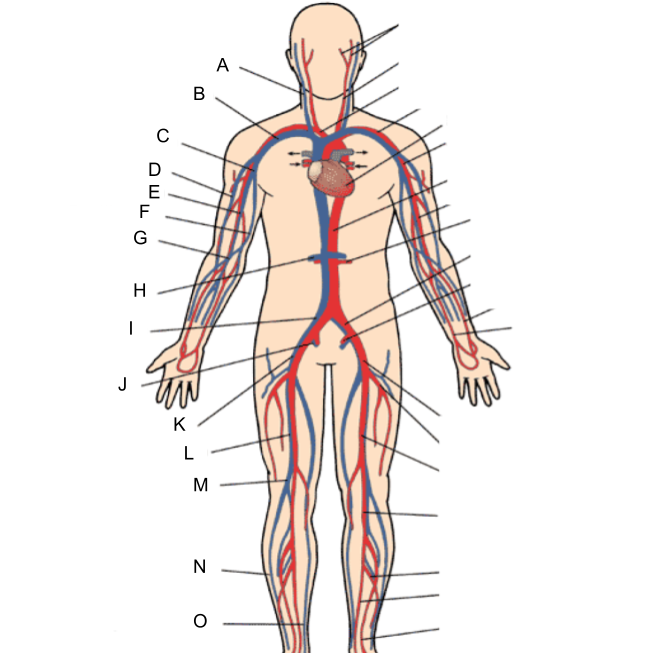
What is G?
median cubital vein
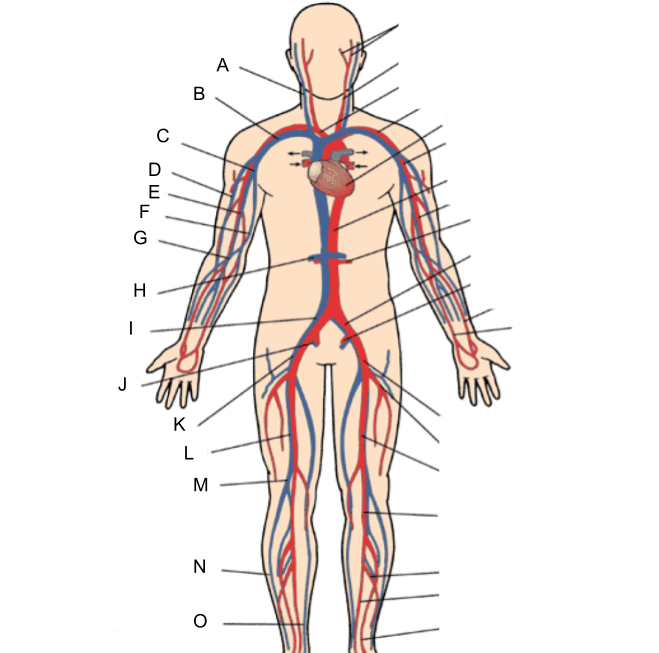
What is H?
renal vein
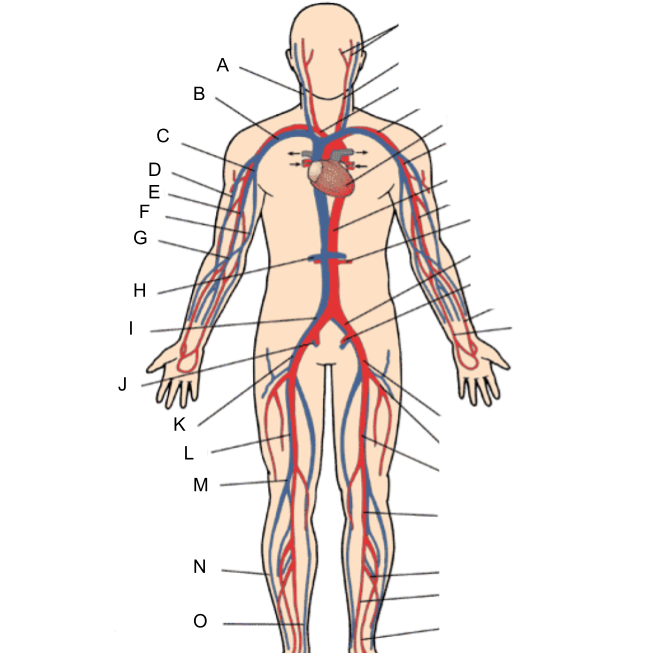
What is I?
common iliac vein
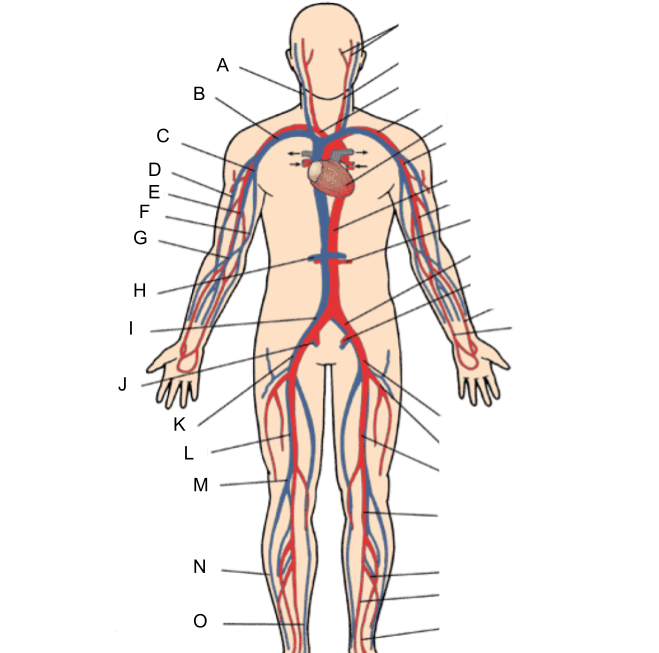
What is J?
internal iliac vein
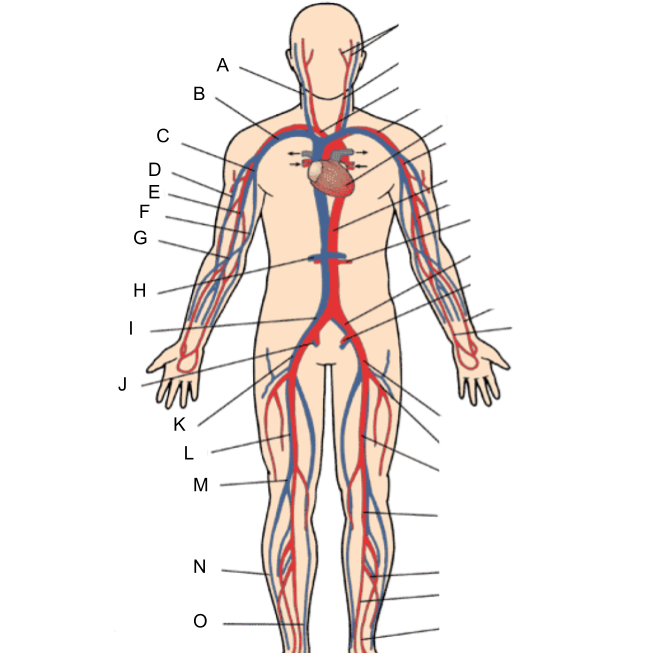
What is K?
external iliac vein
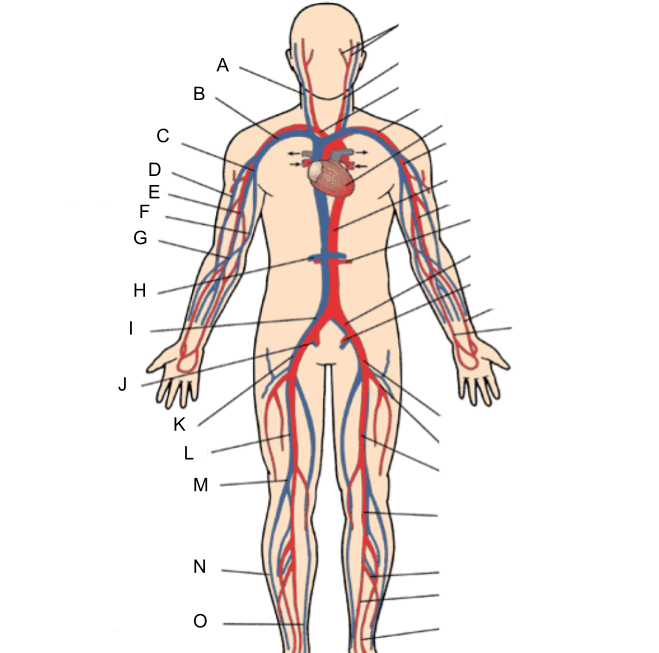
What is L?
femoral vein
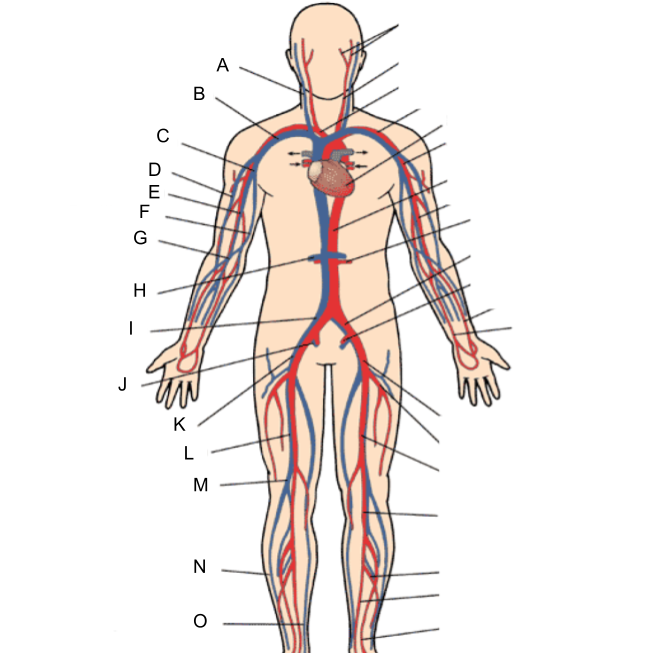
What is M?
popliteal vein
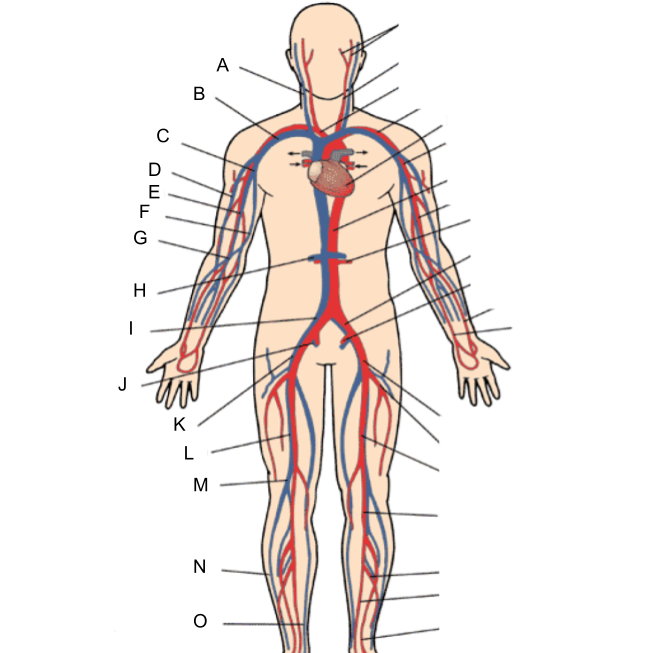
What is N?
peroneal vein
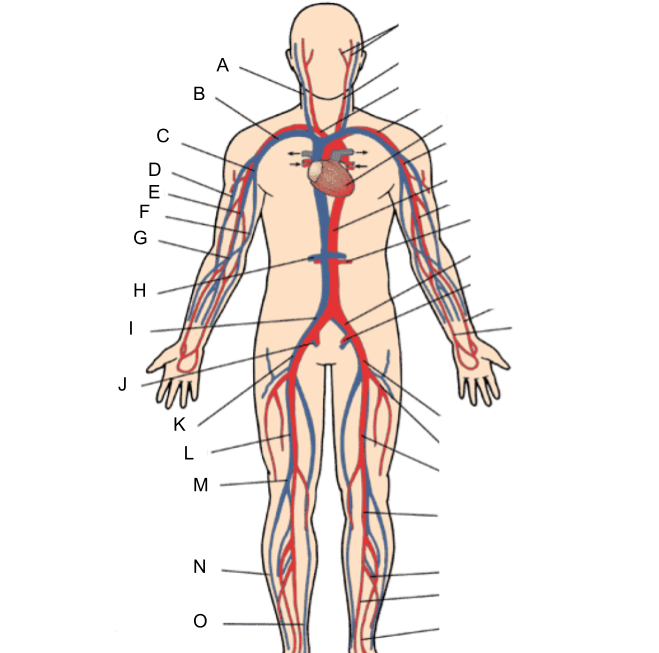
What is O?
great saphenous vein
What is actually happening during an asthma attack?
airway fills with mucus causing airway muscles to contract resulting in swelling
How do we change our voice’s pitch?
increase/decrease tension of our vestibular folds
How do we change our voice’s loudness?
force more or less air out
What are serous membranes?
tissues that line certain internal cavities
What do serous membranes do?
lubricate the membrane to reduce friction from other organs/cavity wall
What happens during inspiration/breathing in?
increased thoracic volume→decreased pleural pressure→increased alveolar volume→decreased alveolar pressure→air flows into lungs
What happens during expiration/breathing out?
decreased thoracic volume→increased pleural pressure→decreased alveolar volume→increased alveolar pressure→air flows out of lungs
What is a surfactant?
surface acting agent
What do surfactants do?
prevent lung collapse by reducing surface tension of alveoli which keeps them open making respiration easier
What organs are a part of the lymphatic system?
tonsils, nodes, spleen, thymus
What does SIV and other immunodeficiency disorders have to do with the lymphatic system?
the lymphatic system regulates the immune system
What protein stabilizes binding and does a “double handshake?”
t cells
What type of cell sends chemical signals between cells that are being activated?
cytotoxic t cells
What is the CO2 transport equation?
CO2+H2O→HCO3-+H+
What is hyperventilation?
rapid breathing resulting in exhaling more CO2 than inhaling
What do precapillary sphincters do?
regulate blood flow and capillaries
What are precapillary sphincters?
smooth muscle cells that help blood flow to capillaries
What are small veins called?
venules
What are small arteries called?
arterioles
What is the difference between a vein and an artery?
arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood back to the heart