Session 3: The Immunological Response
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Disease
A condition that disturbs the normal functioning of the body
Illness
A deterioration in the state of normal health (a disease may cause illness)
Pathogen
An infectious agent that causes disease or illness in a host
Symptom
Phenomenon experienced by the individual affected by the disease (by the patient)
Subjective evidence of disease e.g., pain
Sign
Manifestation of the disease process that can be detected by others (physician)
Objective evidence of disease e.g., fever
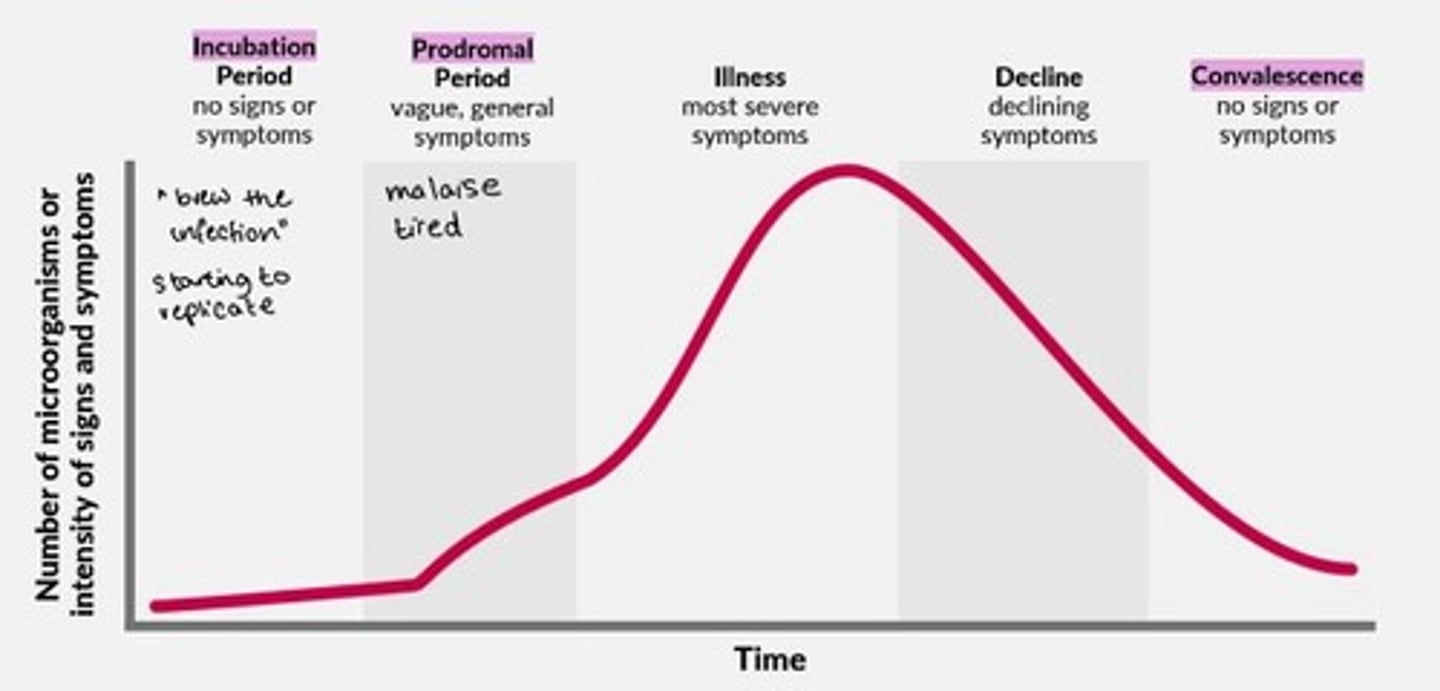
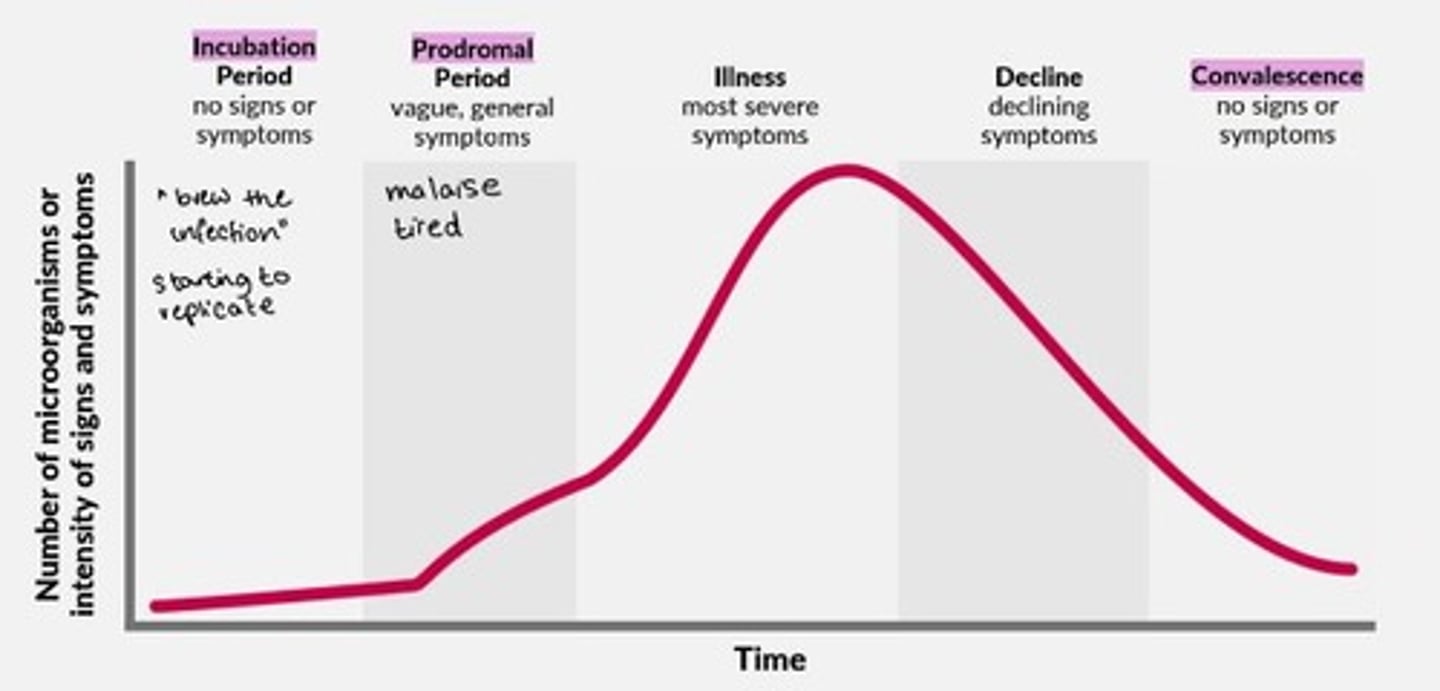
Infectious disease development and stages
1) Incubation period = no signs/symptoms
2) Prodromal period = vague, general symptoms
3) Illness = most severe symptoms
4) Decline = declining symptoms
5) Convalescence = no signs or symptoms
The five cardinal signs of inflammation
1) Heat = calor
2) Redness = rubor
3) Swelling = tumor
4) Pain = dolor
5) Loss of function = functio laesa
Chemical barriers in body
Lysozymes = saliva, tears
Low pH = stomach, urinary tract, vagina
Physical barriers in body
Ciliated mucosa
GI tract mucosa
Skin
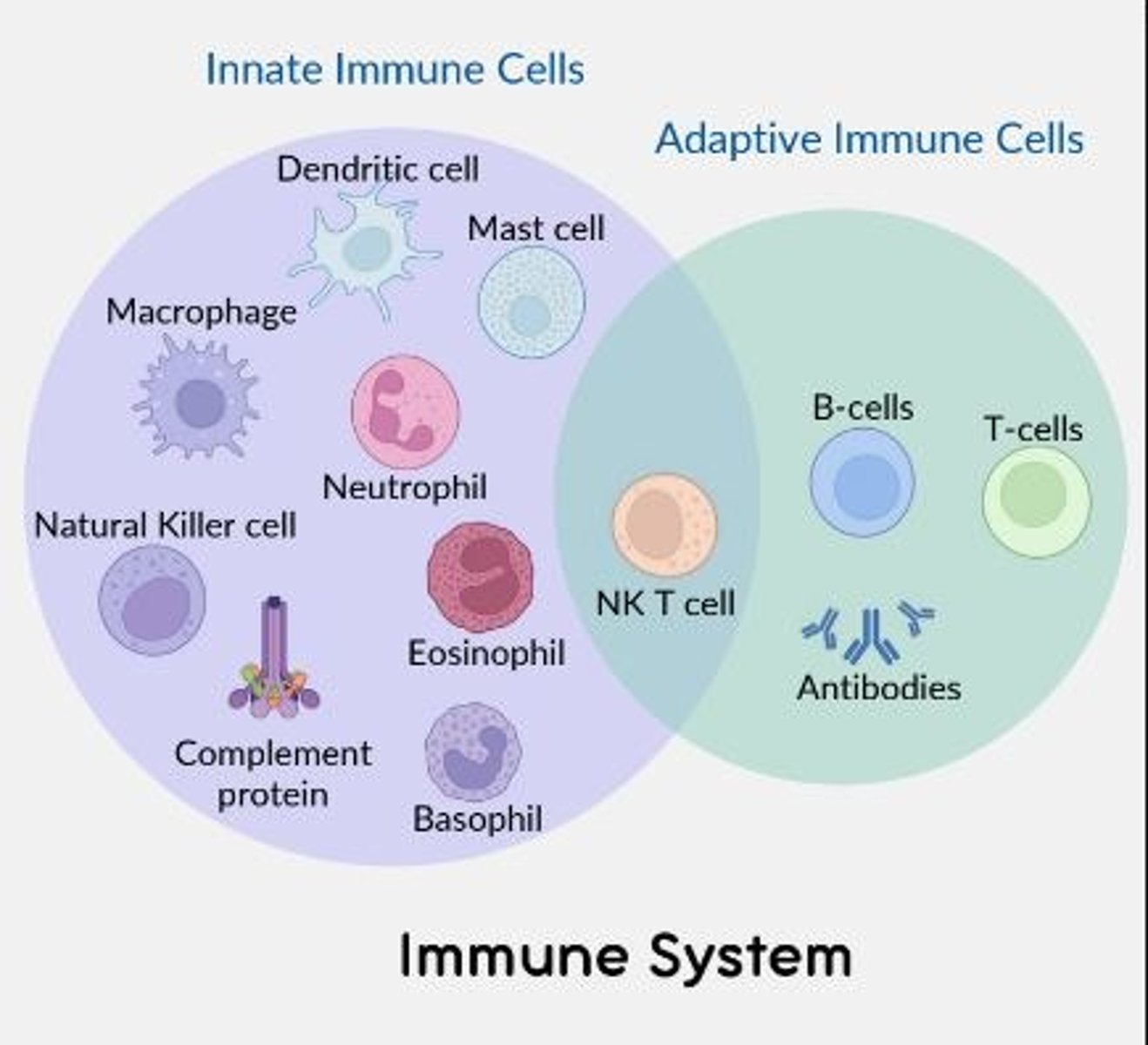
Immune effector cells involved in innate immunity only
Macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells, neutrophils, complement proteins, basophils
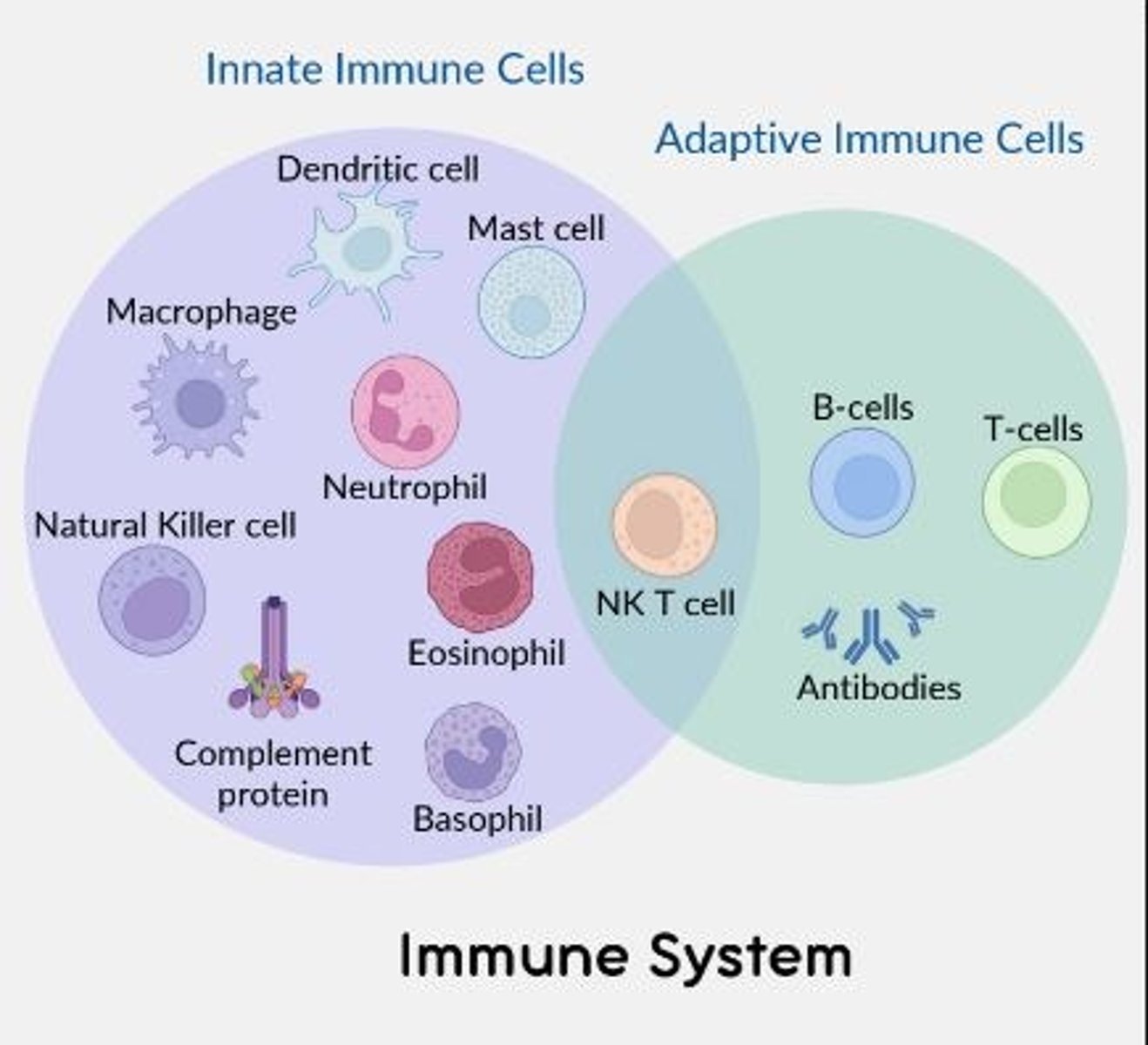
Immune effector cells involved in adaptive immunity only
B cells, T-cells (and antibodies)
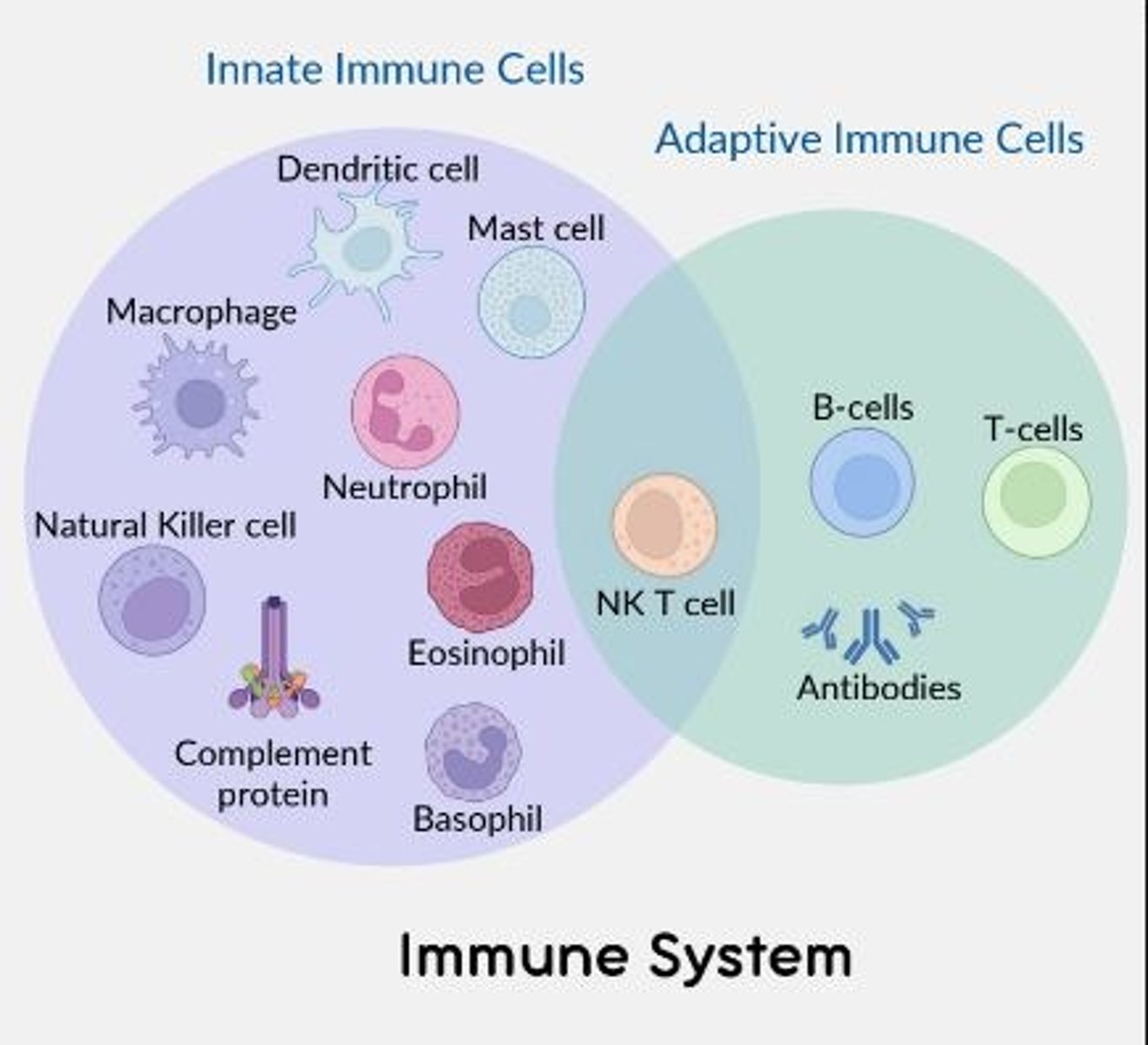
Immune effector cells involved in both the innate and adaptive immune response
NK T cell
White blood cells (WBC) are derived from a ___ progenitor cell, before maturing into different lineages.
Myeloid
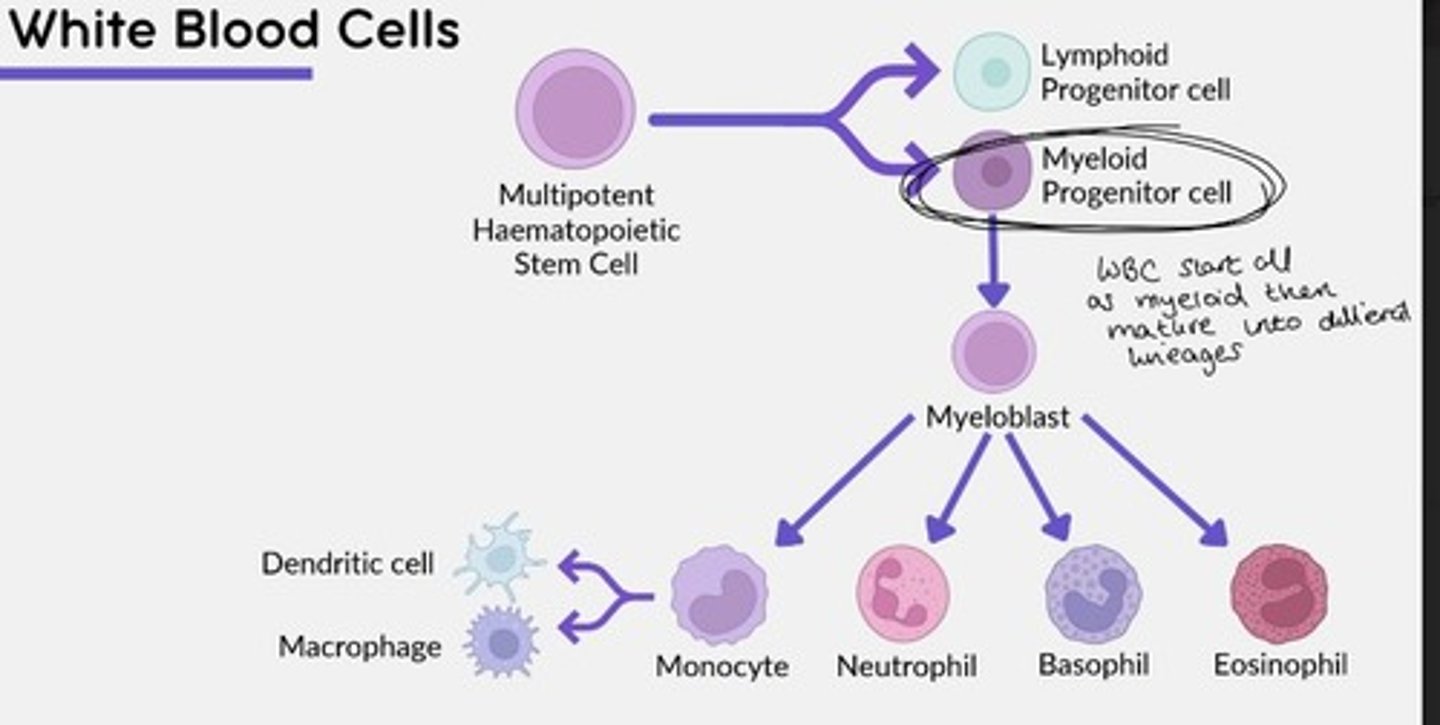
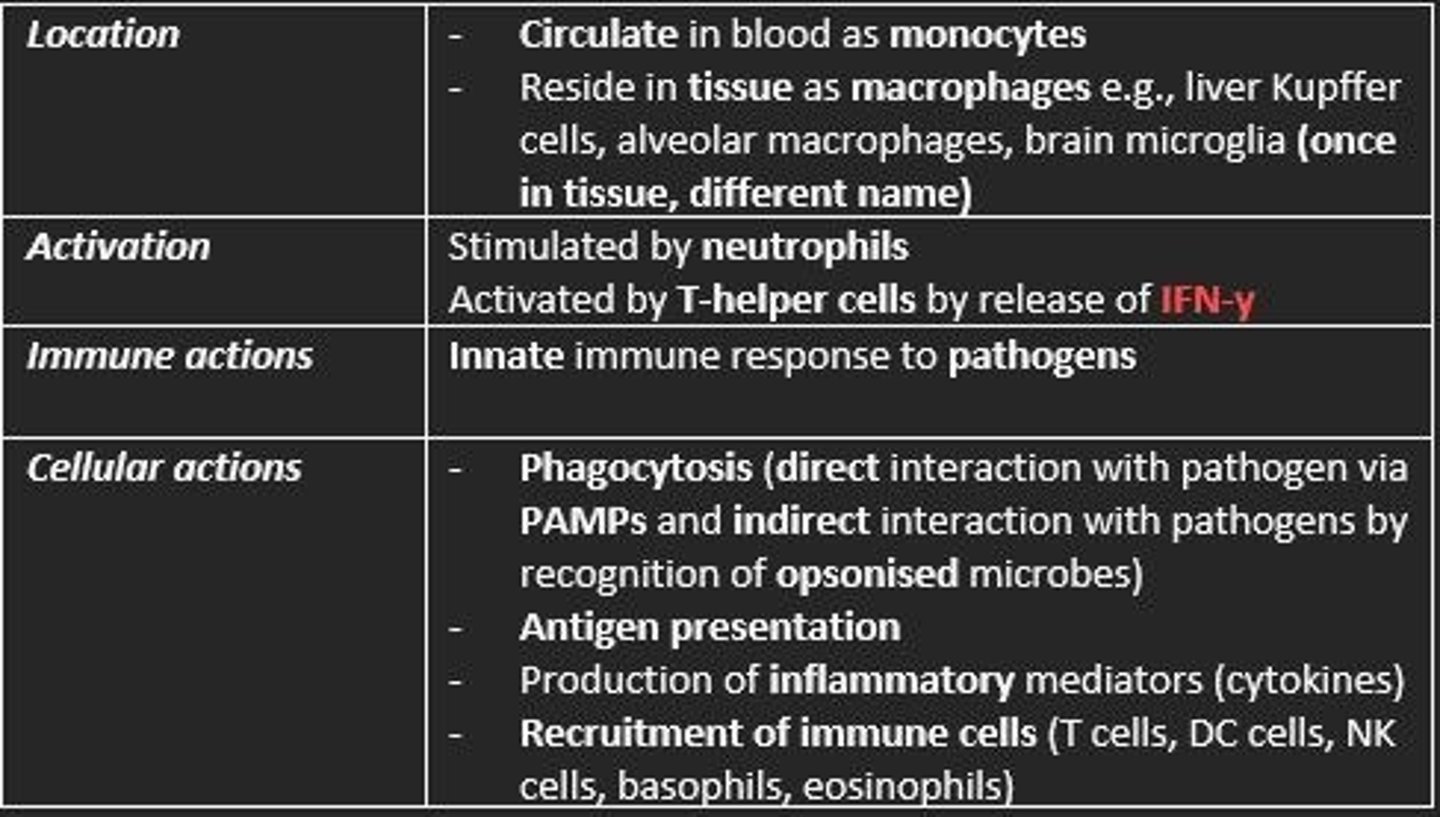
Macrophages
Location, activation, immune actions, cellular actions
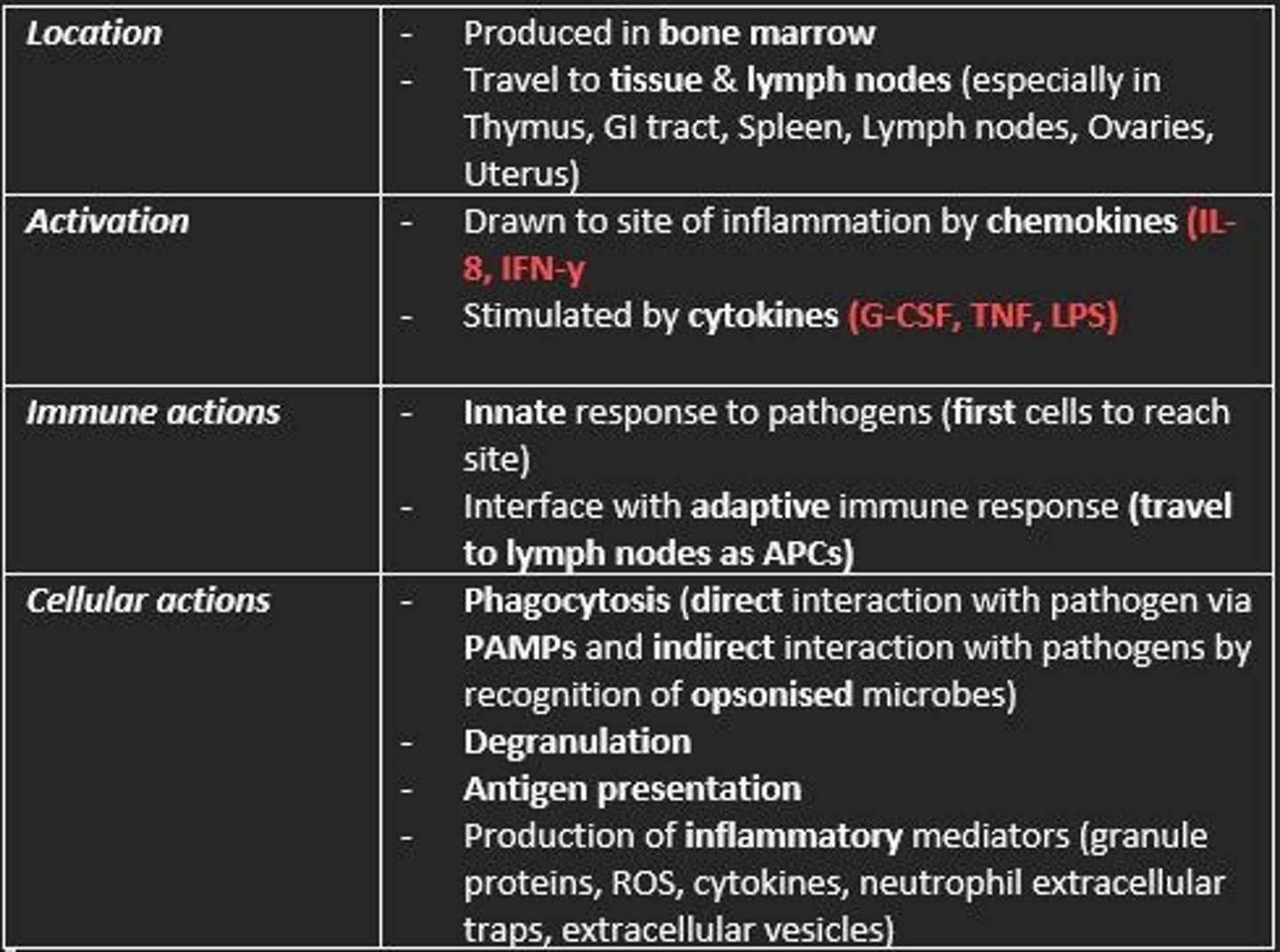
Neutrophils
Location, activation, immune actions, cellular actions
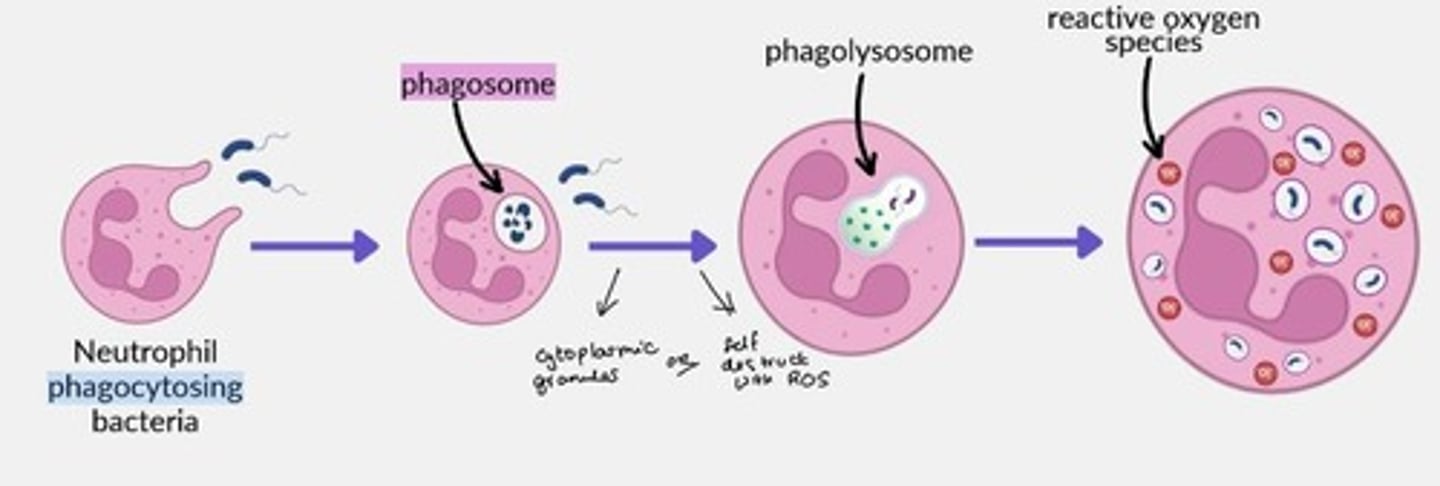
Describe how neutrophils phagocytose bacteria
- Bacteria engulfed into phagosome
- Phagosome fused with lysosome to form phagolysosome
- Destruction via cytoplasmic granules (anti-microbial proteins) or via ROS
Examples of anti-microbial proteins found in granules of neutrophils
- Defensins
- Myeloperoxidase
- Catalase
- Elastase
- Metalloproteinases
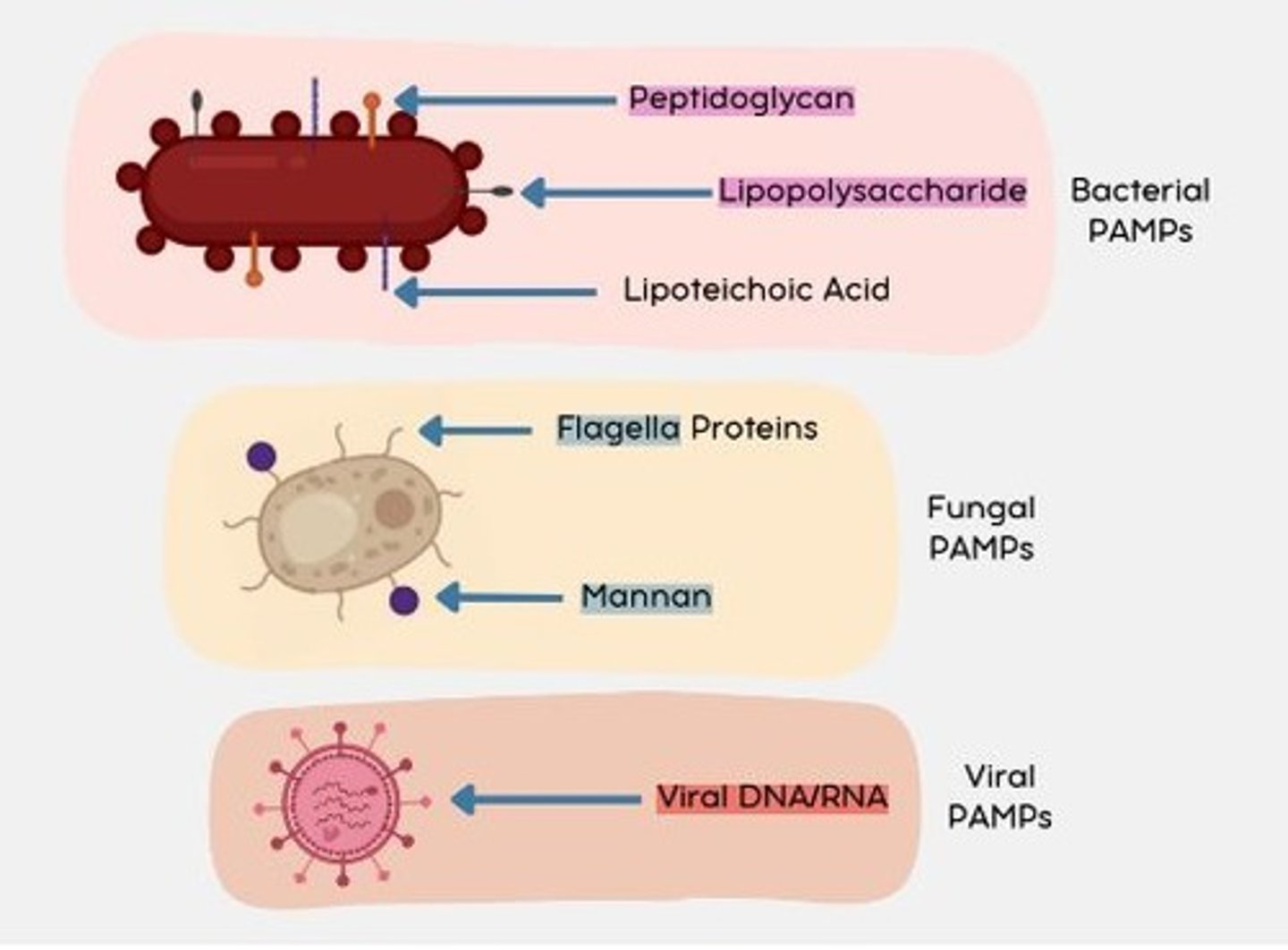
PAMPs
(Pathogen-associated molecular patterns) molecules associated with groups of pathogens, that are recognized by cells of the innate immune system.
Bacterial PAMPs
Peptidoglycan
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Lipoteichoic acid
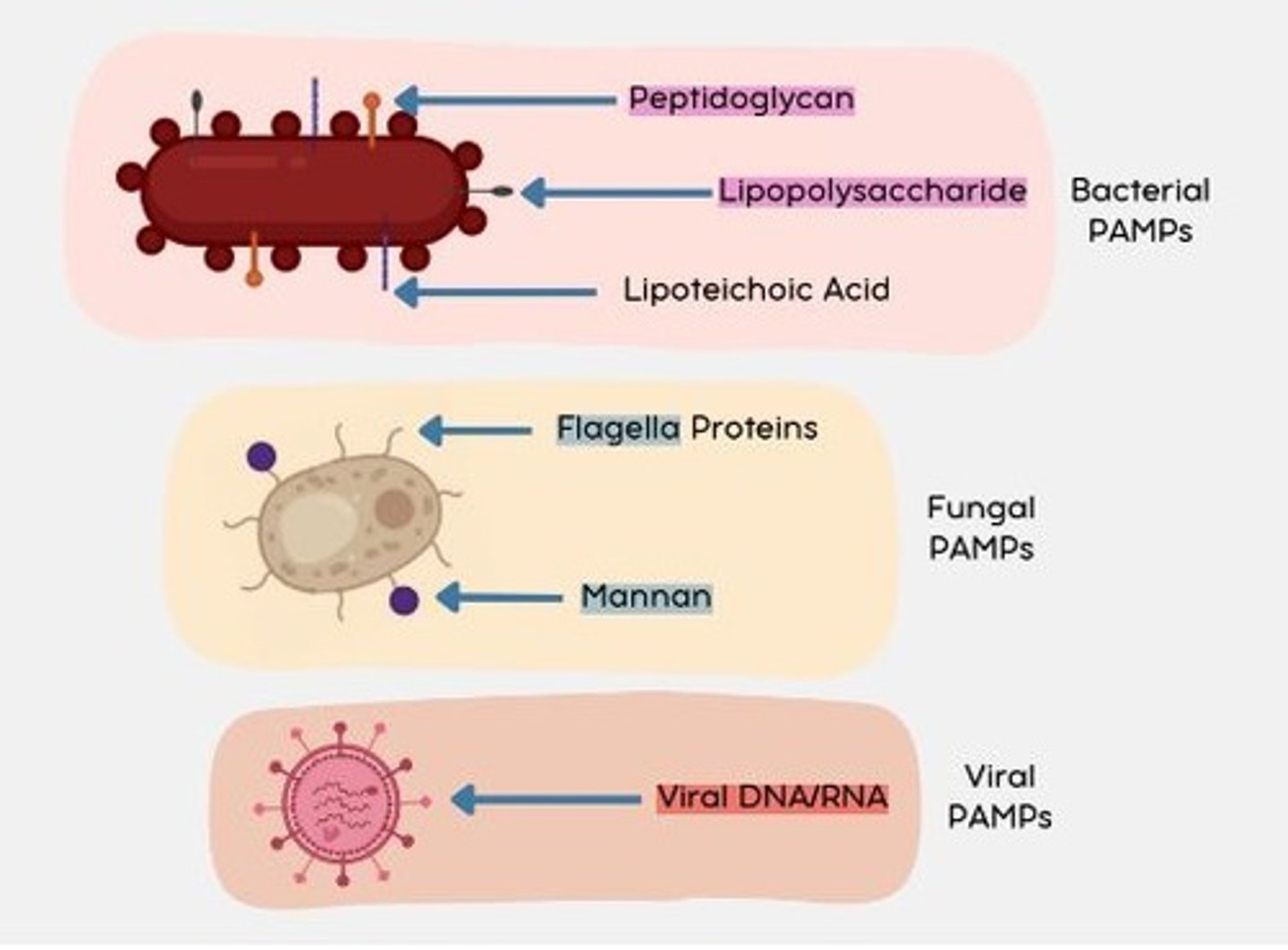
Fungal PAMPs
Flagella proteins
Mannan
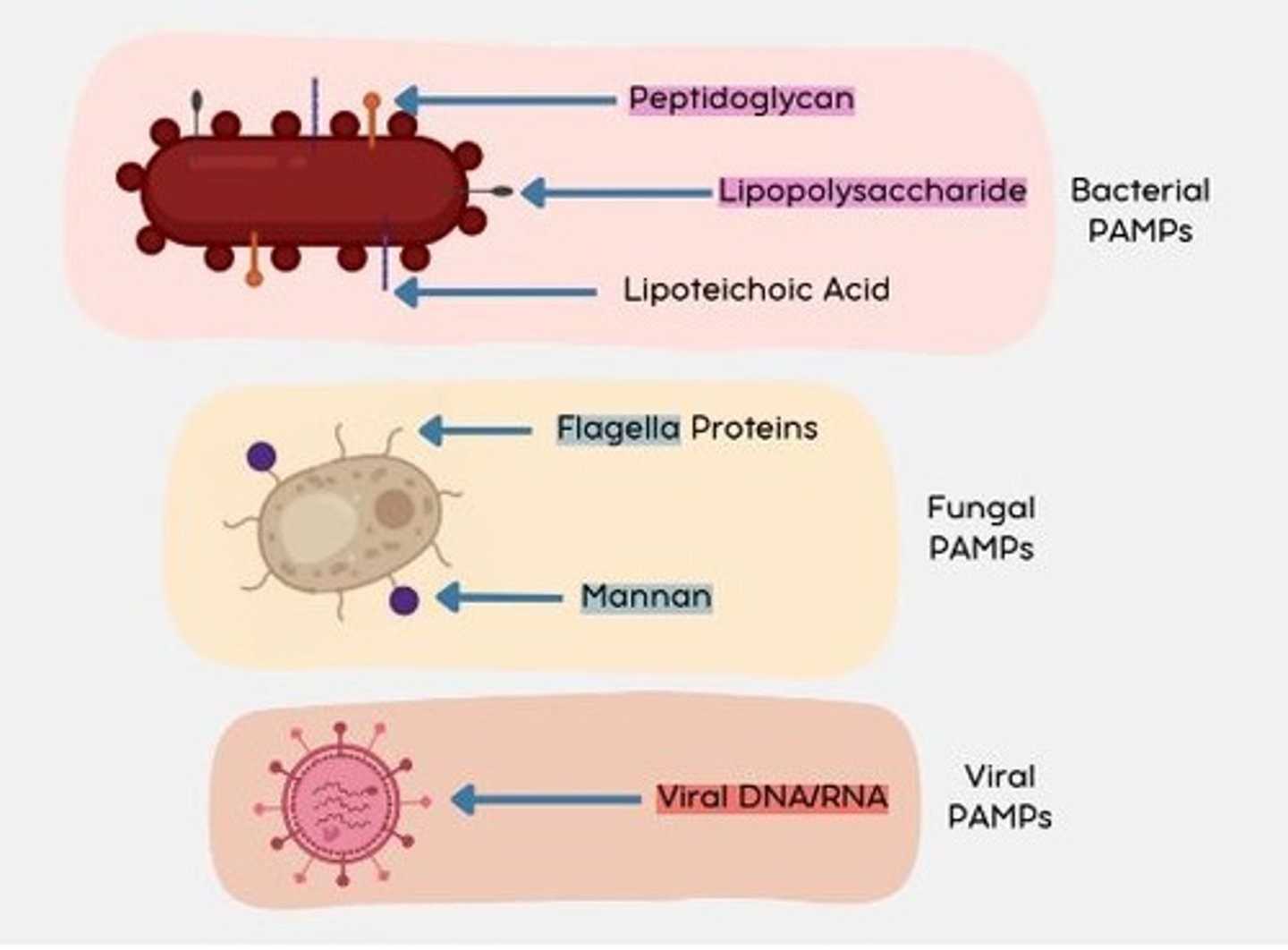
Viral PAMPs
Viral DNA/RNA (nucleic acids)
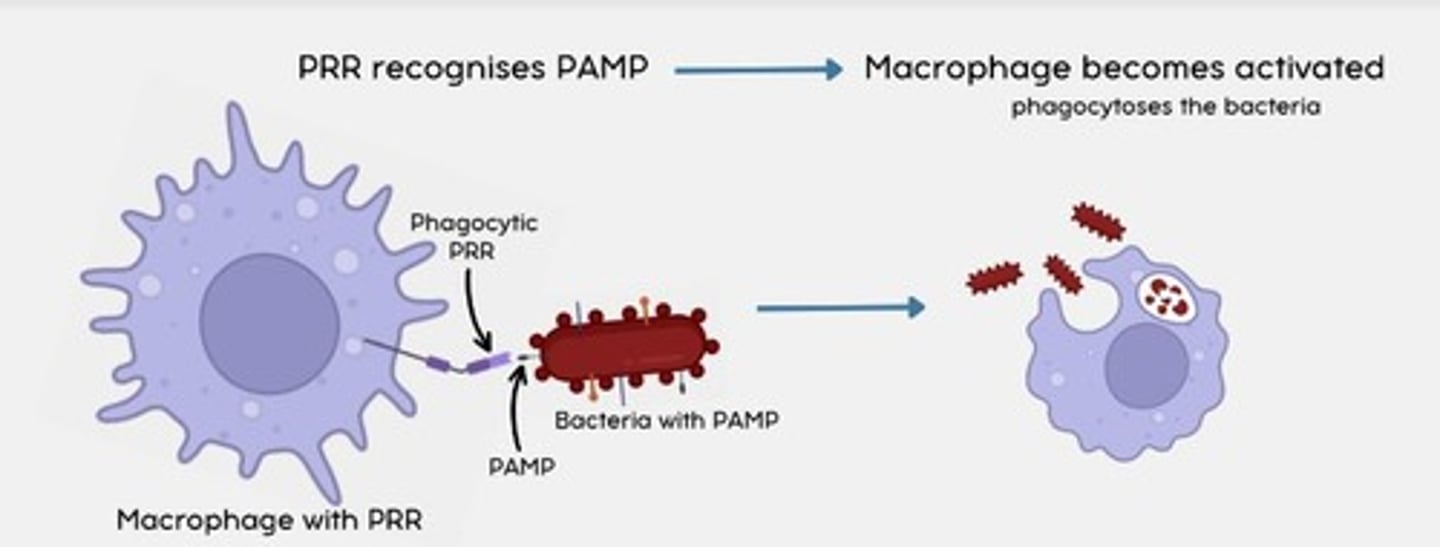
PRRs
Pathogen recognition receptors = recognize PAMPs
What immune cells can PHAGOCYTIC PRRs be found on?
- Macrophages
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
- Mast cells
How do PHAGOCYTIC PRRs work?
When a phagocytic PRR detects a PAMP, the macrophage becomes activated.
This leads to phagocytosis of the bacteria by the macrophage.
What immune cells can SIGNALLING PRRs be found on?
- Leukocytes
- Epithelial cells
- Endothelial cells
How do SIGNALLING PRRs work?
When a macrophage with a signalling PRR detects a PAMP, the signalling PRR stimulates the release of cytokines
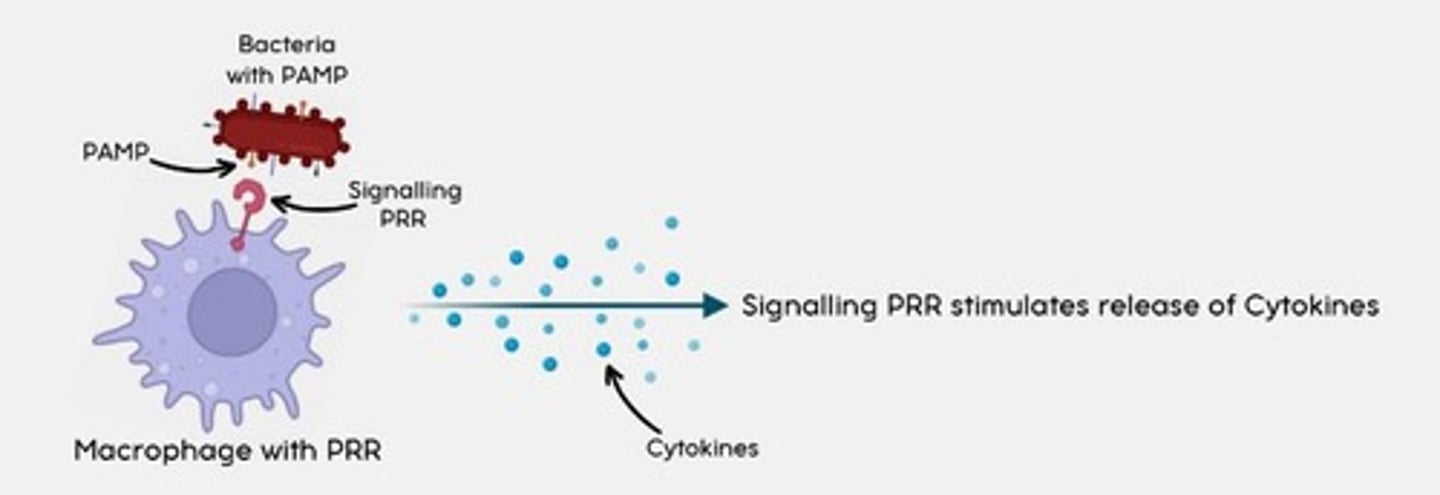
Most important SIGNALLING PRR?
Toll-like receptors (TLR)
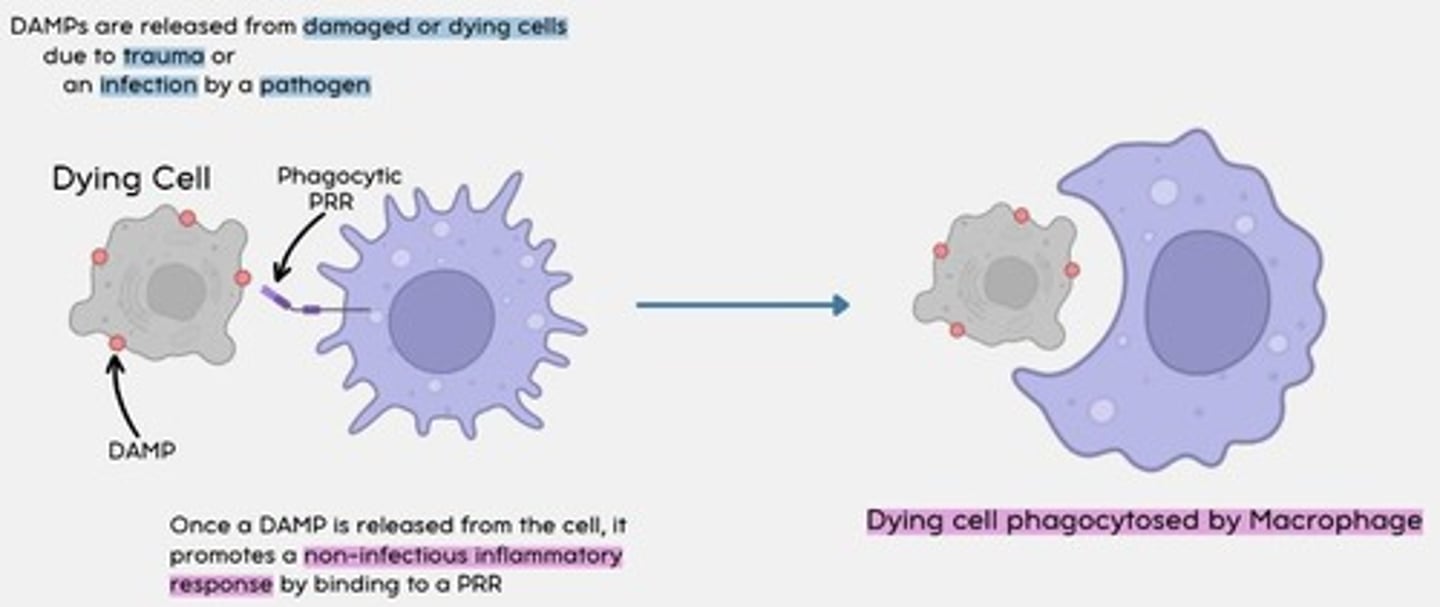
DAMPs
Damage associated molecular patterns are molecules released by necrotic (dying) or damaged cells
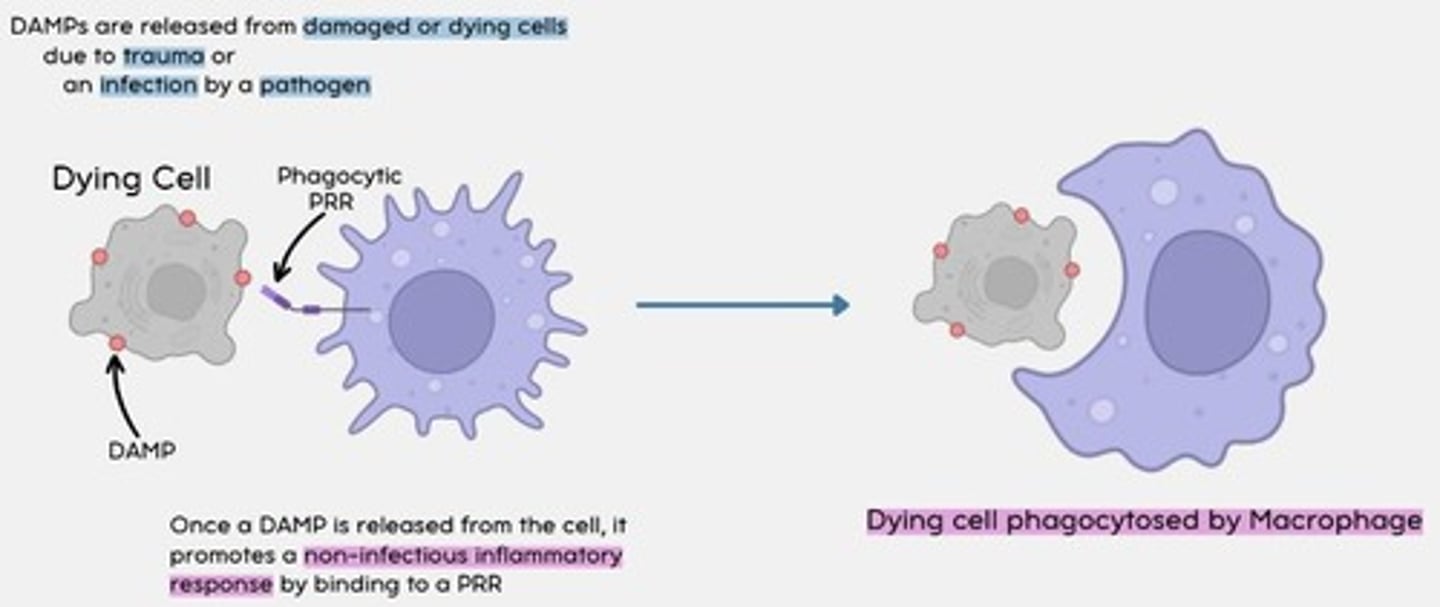
How do DAMPs work?
Once a DAMP is released from the cell, it promotes a non-infectious inflammatory response by binding to a phagocytic PRR.
The dying cell is then phagocytosed by a macrophage.
Neutropenia
Deficiency of neutrophils
Medication - cause of neutropenia
Chemotherapy
- Increased risk of neutropenic sepsis (complication)
- Must always check for clinical features = fever, tachycardia and hypotension
Bone marrow disorders that cause neutropenia
- Leukaemia
- Lymphoma
- Aplastic anaemia
Other causes of neutropenia
- Autoimmune disease
- Hepatitis
- TB
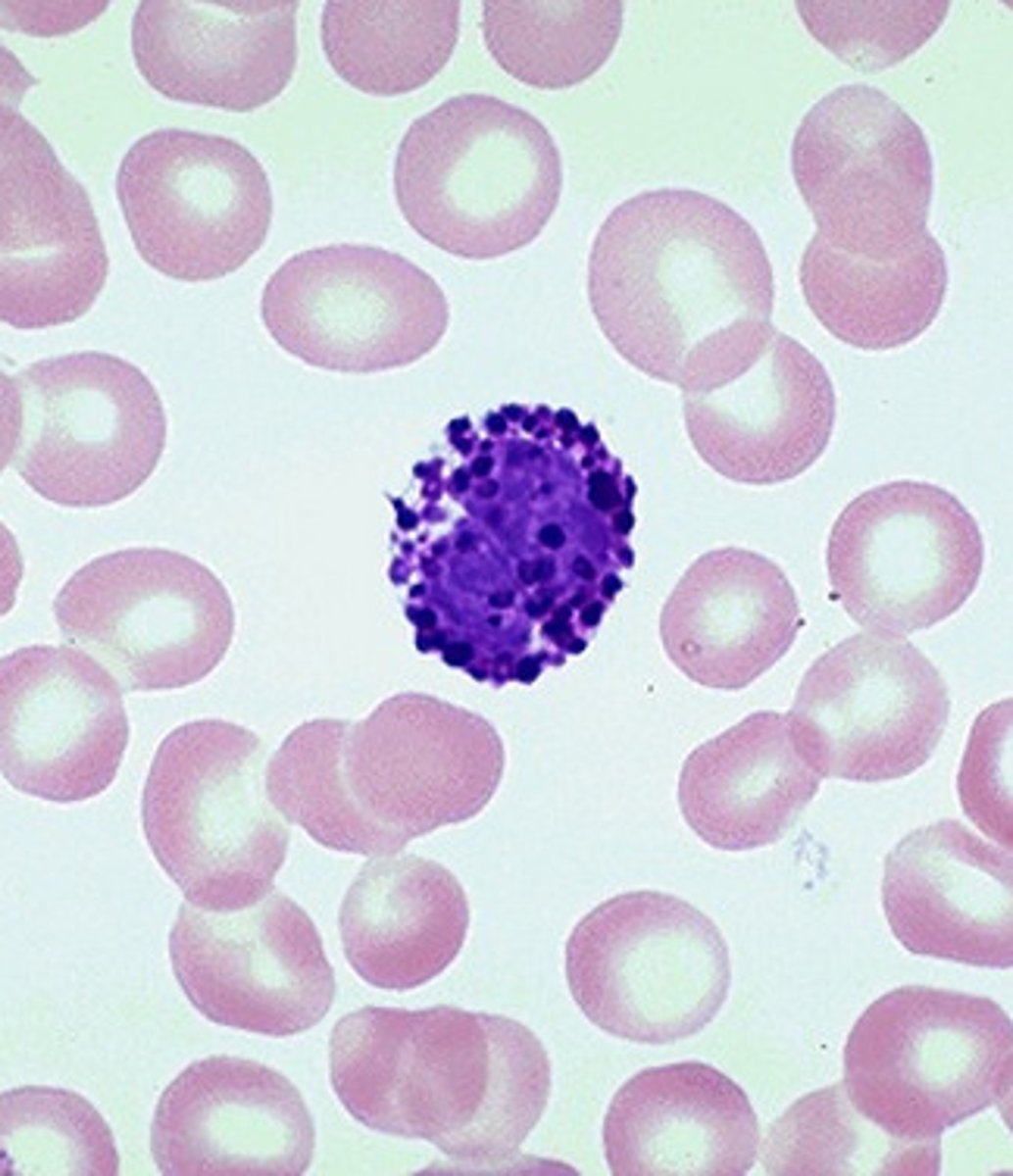
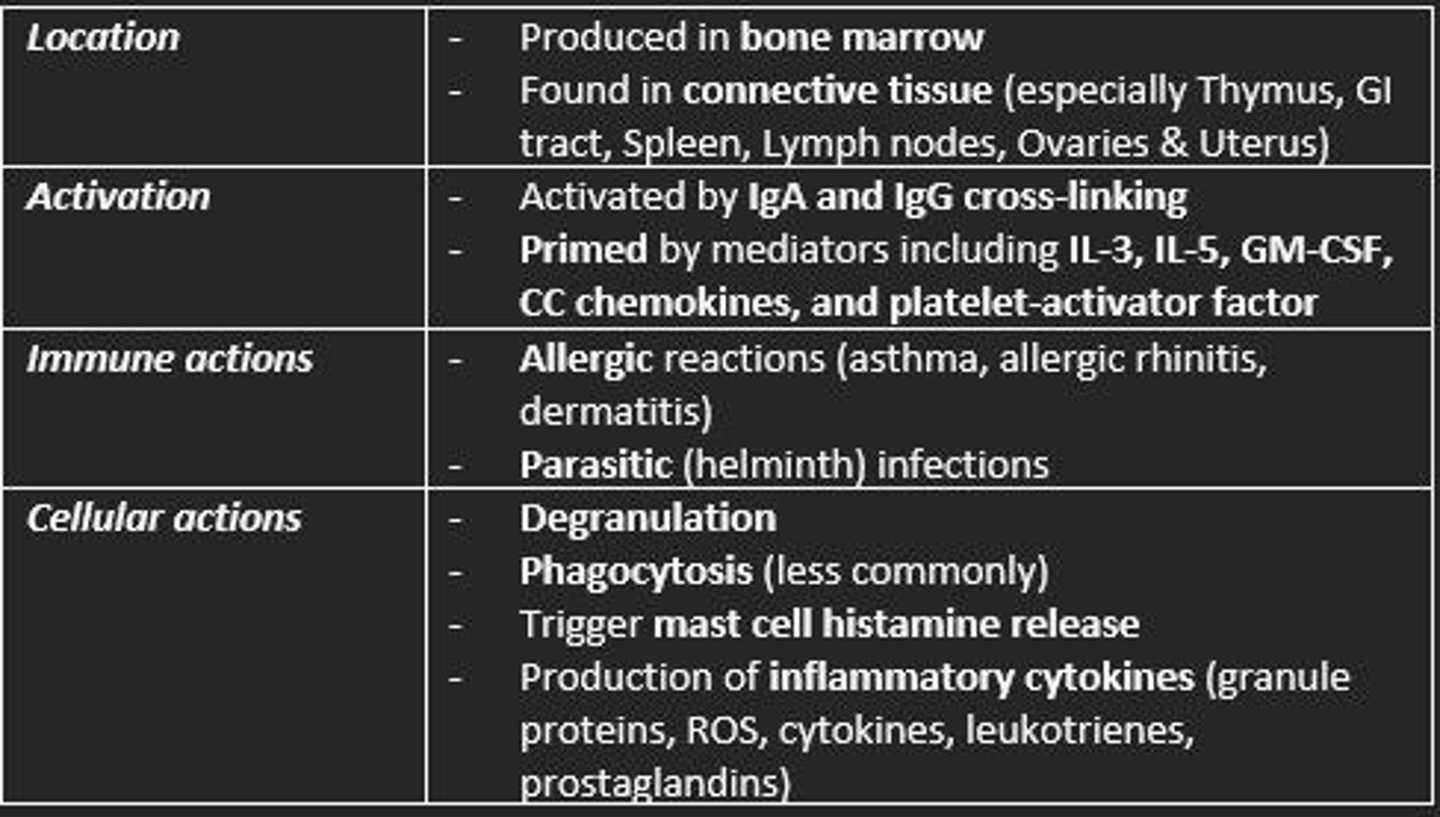
Eosinophil function
Allergic reactions; defense against parasites
Degranulation releases histamine
Capable of phagocytosis and APC
Basophil function
Viral infections, type 1 hypersensitivity reactions
Granules = histamine, heparin, serotonins, pro-inflammatory
Capable of phagocytosis and APC
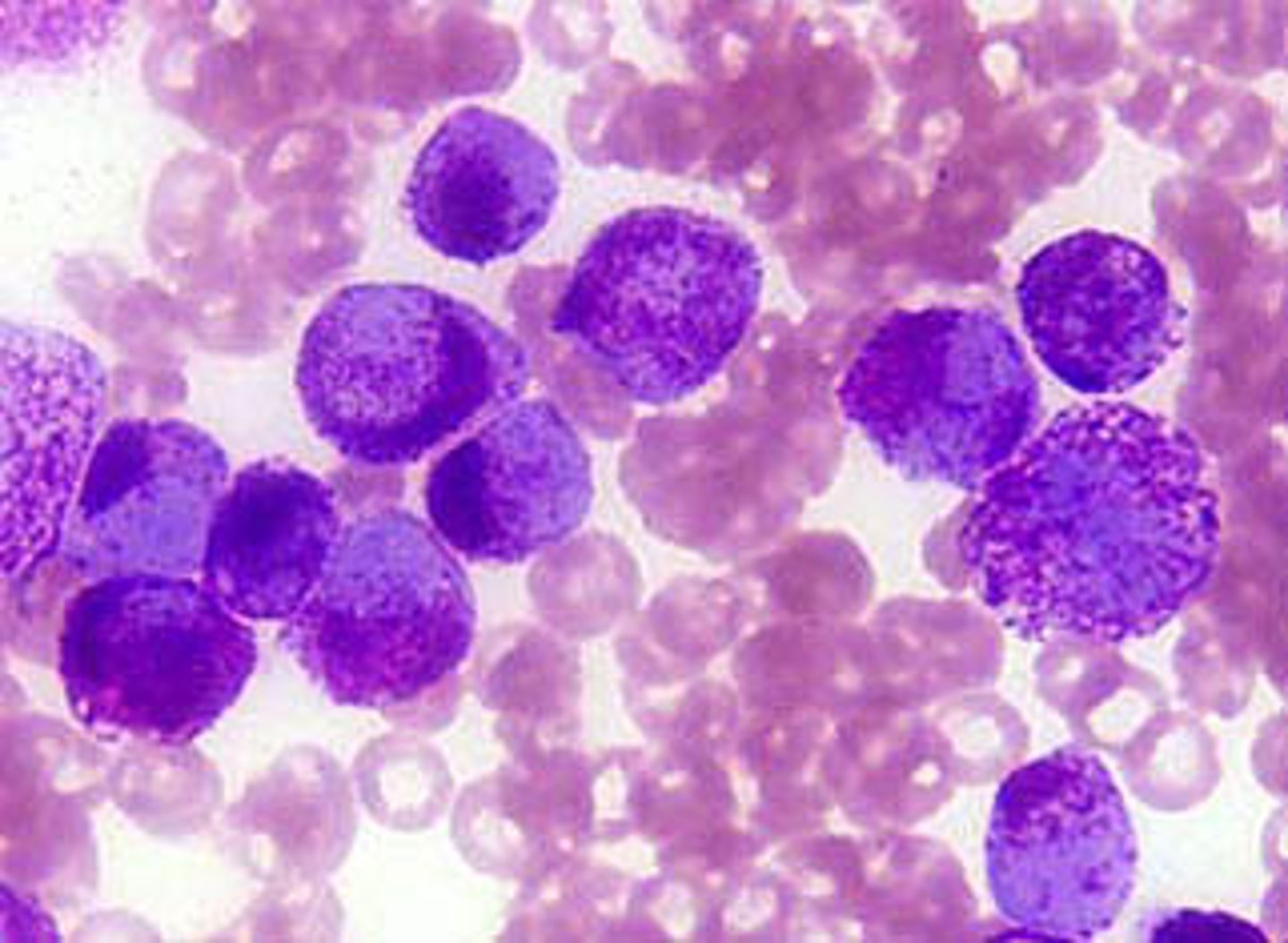
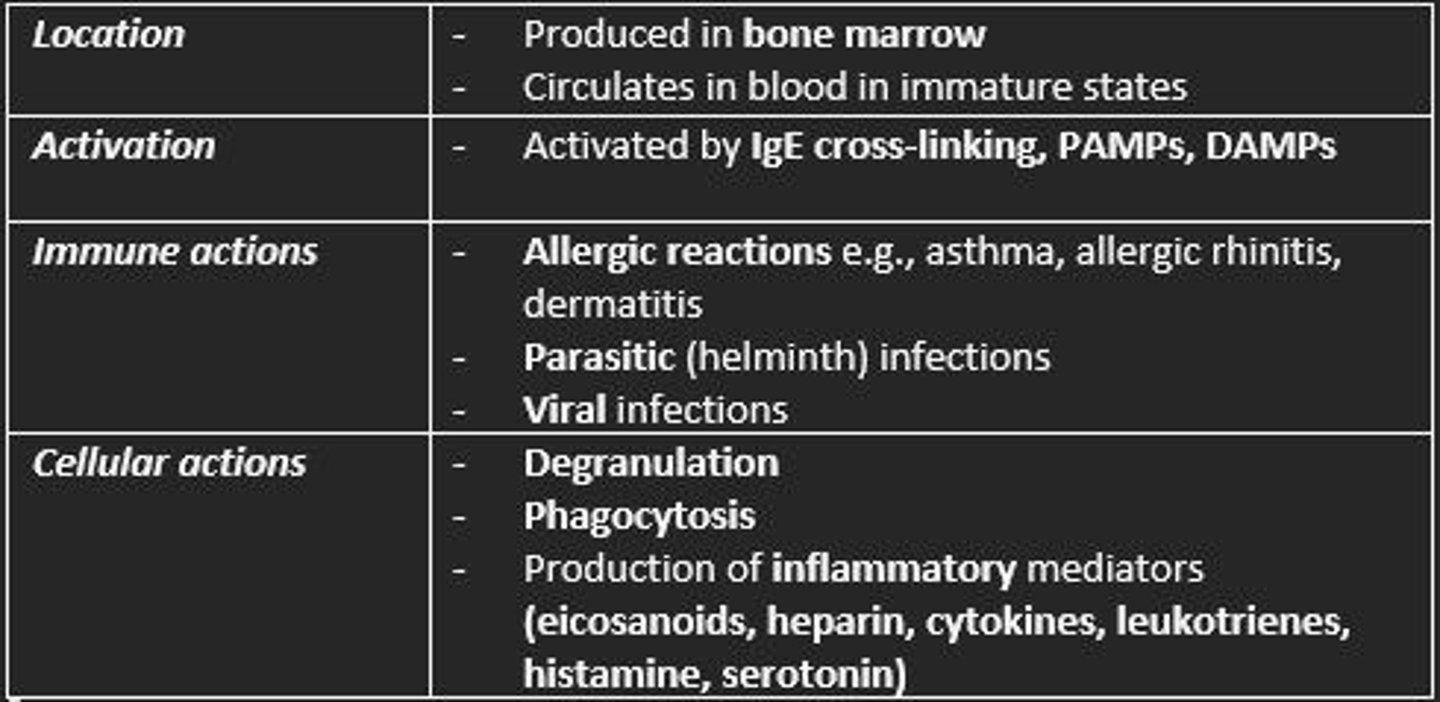
Mast cell function
Produced in bone marrow - circulate in blood
Part of innate immune system and inflammation in allergies
Granules = heparin, histamine & cytokines
Eosinophil
Location, activation, immune actions, cellular actions
Basophil
Location, activation, immune actions, cellular actions
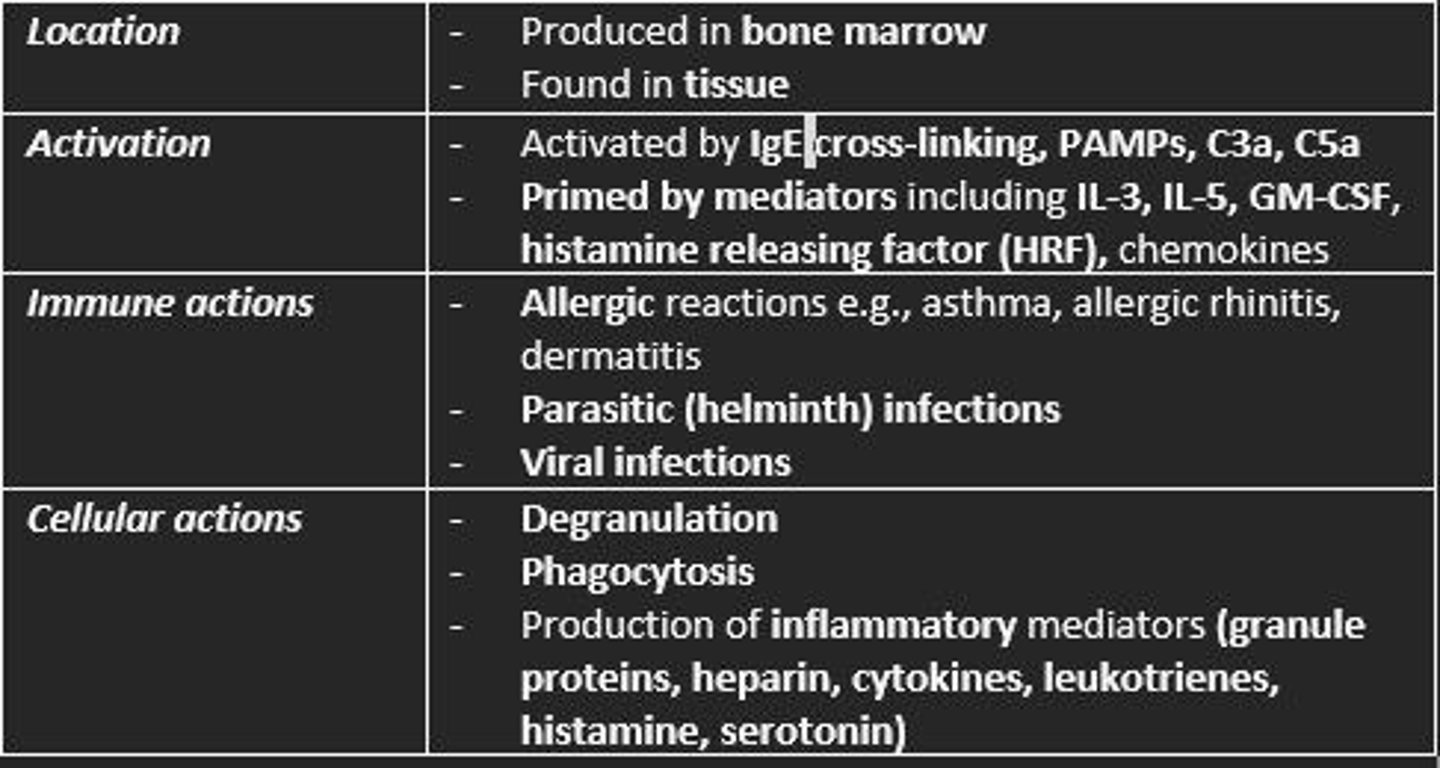
Mast cells
Location, activation, immune actions, cellular actions
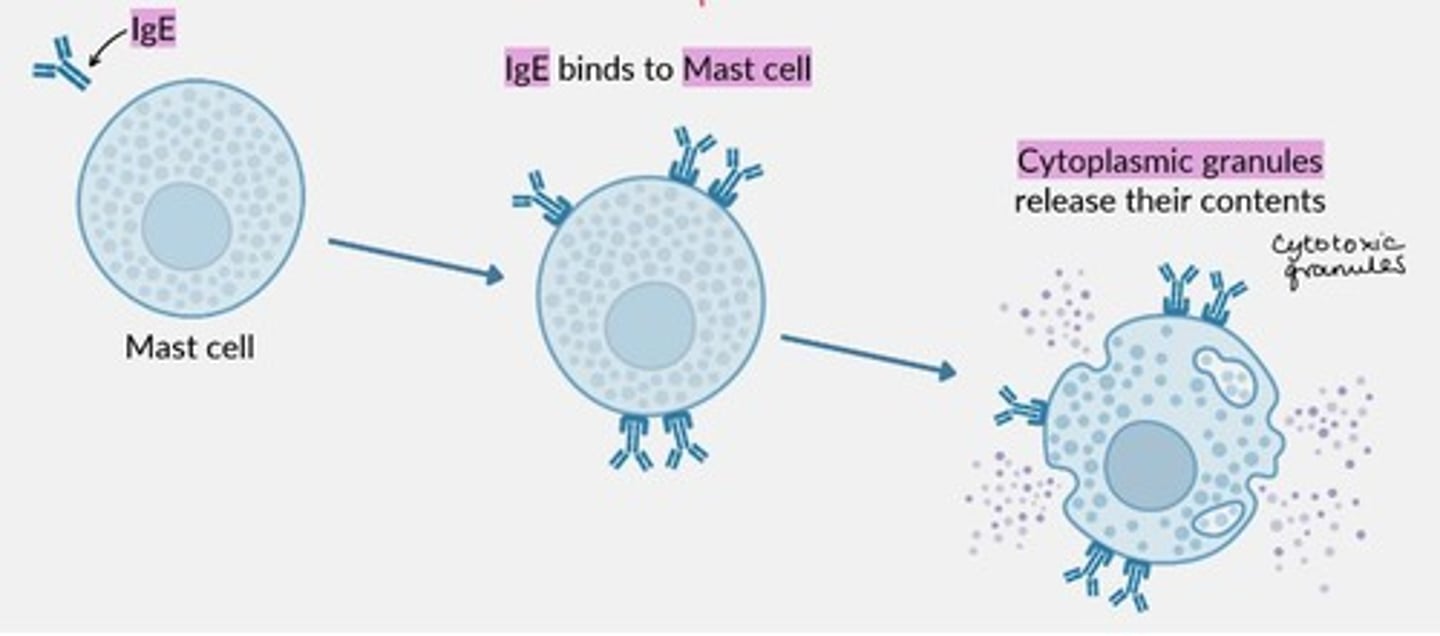
Histamine function
Increase vascular permeability
Causes smooth muscle contraction
Mast cell activation products
Degranulation of Histamine
- Increases vascular permeability
- Smooth muscle contraction
Cytokine secretion
- IL-4 = Th2 differentiation
- IL-13 = promotes IgE production
- TNF-a = promotes tissue inflammation
Lipid mediators = Leukotrienes & Prostaglandins
- Increases vascular permeability
- Smooth muscle contraction
- Mucus secretion
- Chemoattractant for T cells, eosinophils, mast cells, basophils
Degranulation of mast cells is triggered by cytokines.
Mast cells have a high affinity for ___ in particular.
IgE
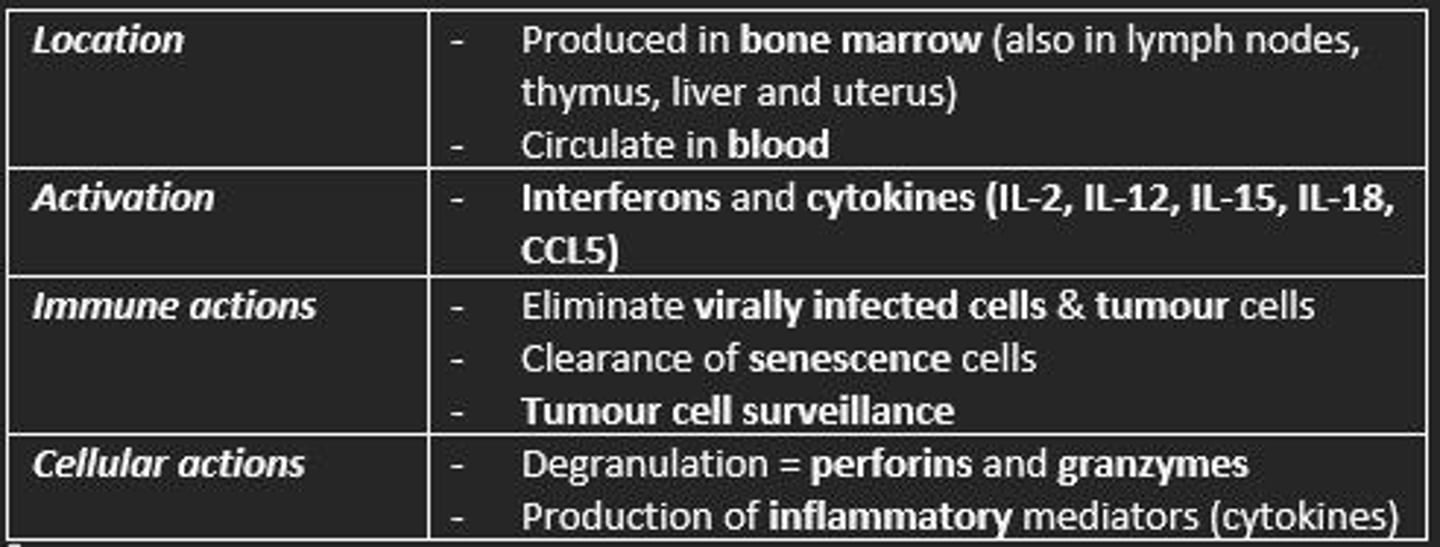
Natural Killer cells
Location, activation, immune actions, cellular actions
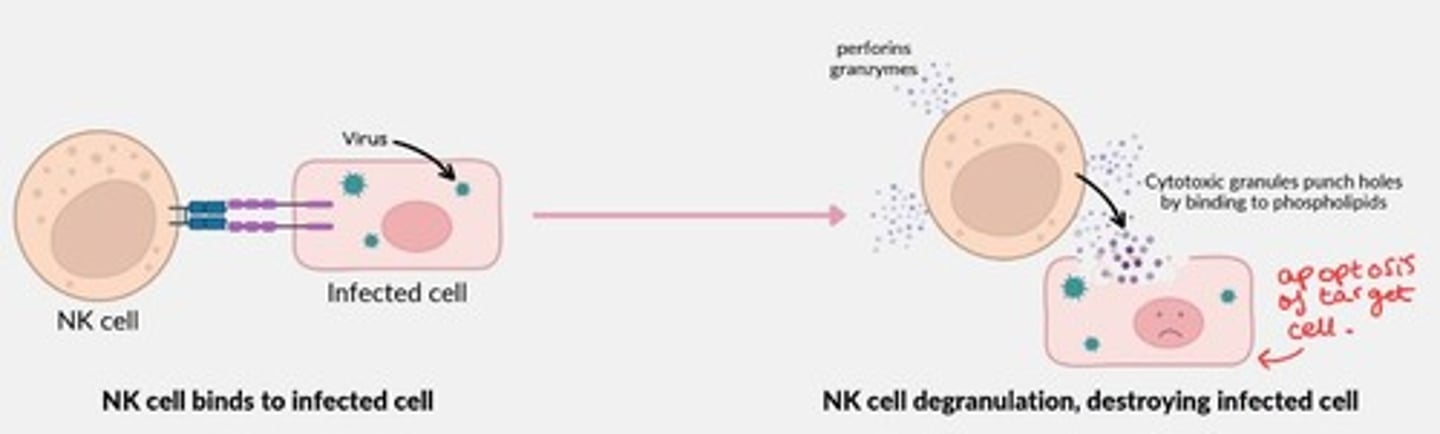
Natural Killer cells mechanism of action
Bind onto virally infected cells
Degranulate to release cytotoxic substances such as Perforin, Granzyme B which punch holes into cell membrane of target cell - destroying the infected cell (apoptosis of target cell).
Lymphocytes arise form ___ progenitor cell
Lymphoid
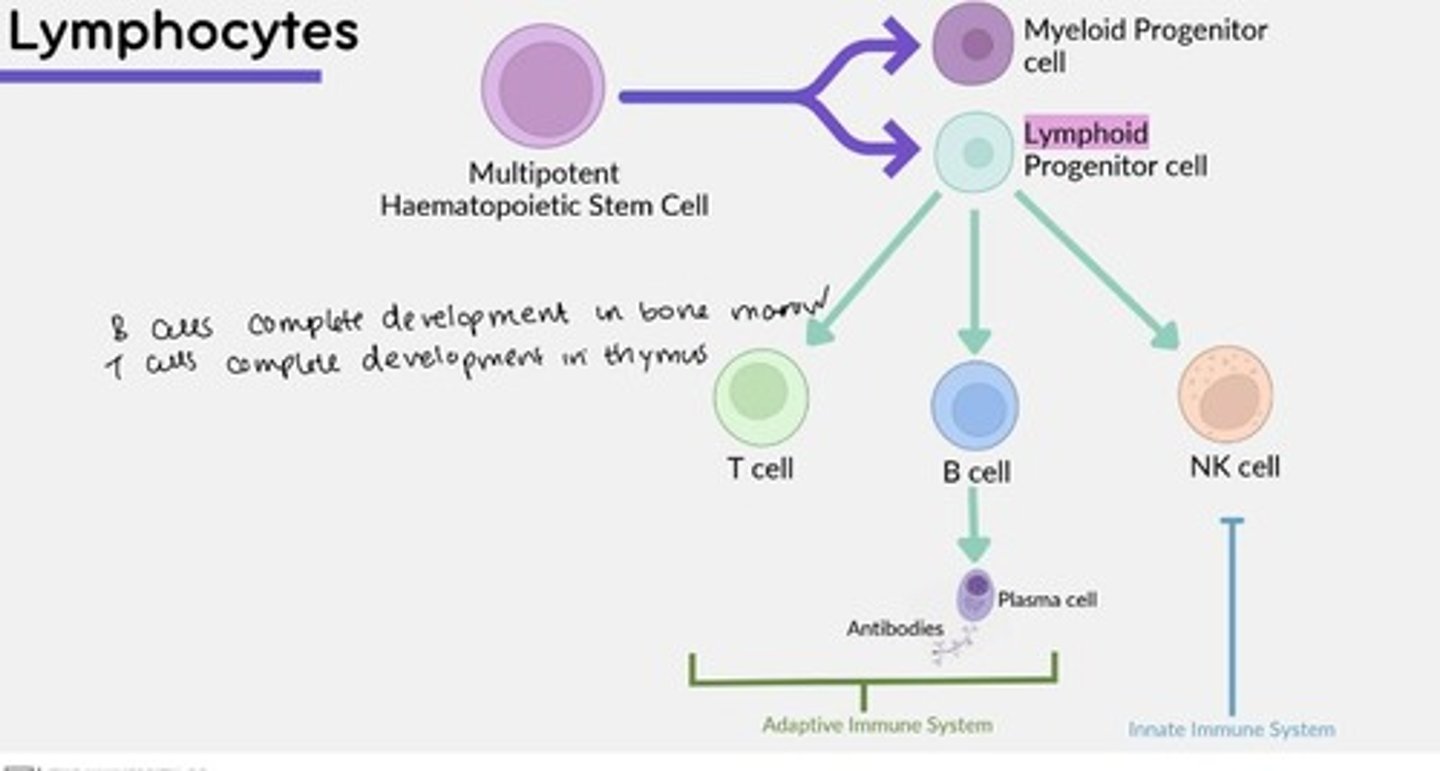
B-cells complete development (mature) in the...
Bone marrow
T-cells complete development (mature) in the...
Thymus
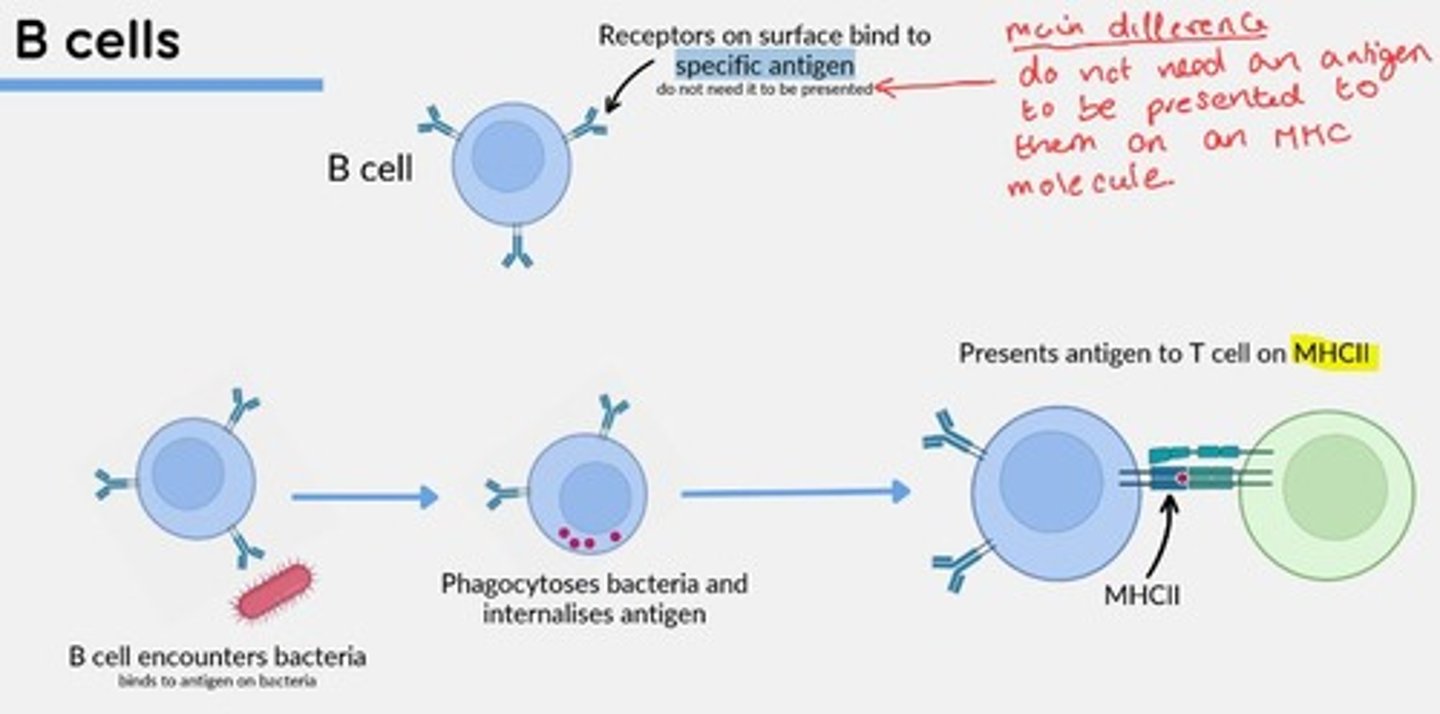
B-cells function
Humoral Immunity
Mediate production of antigen-specific immunoglobulins (antibodies).
Mature cells circulate between secondary lymphoid organs in search of antigens.
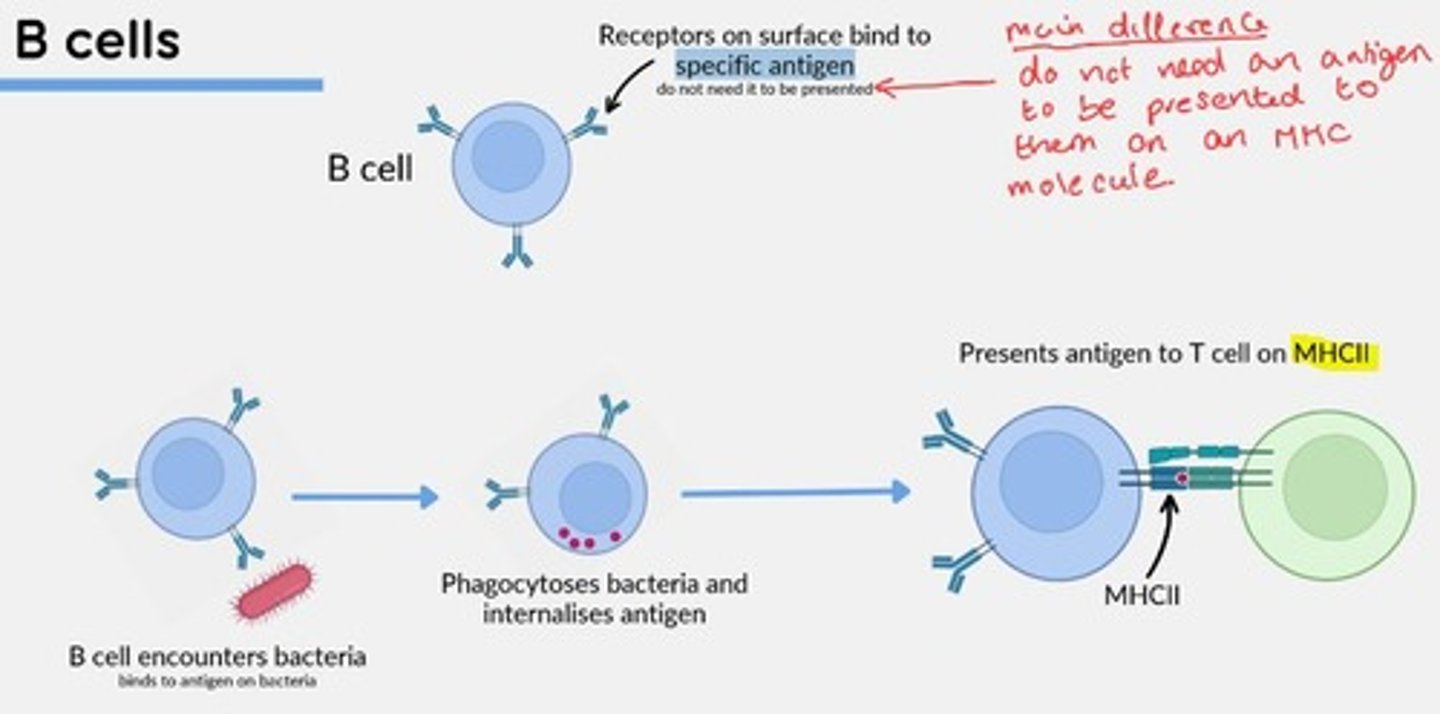
B-cells present antigens to T cells on ___
MHCII
T-cells function
Cell-Mediated Immunity
Help macrophages kill intracellular microparasites by releasing macrophage activating factors (IFN-y)
Identify and kill virally infected cells before viral replication occurs.
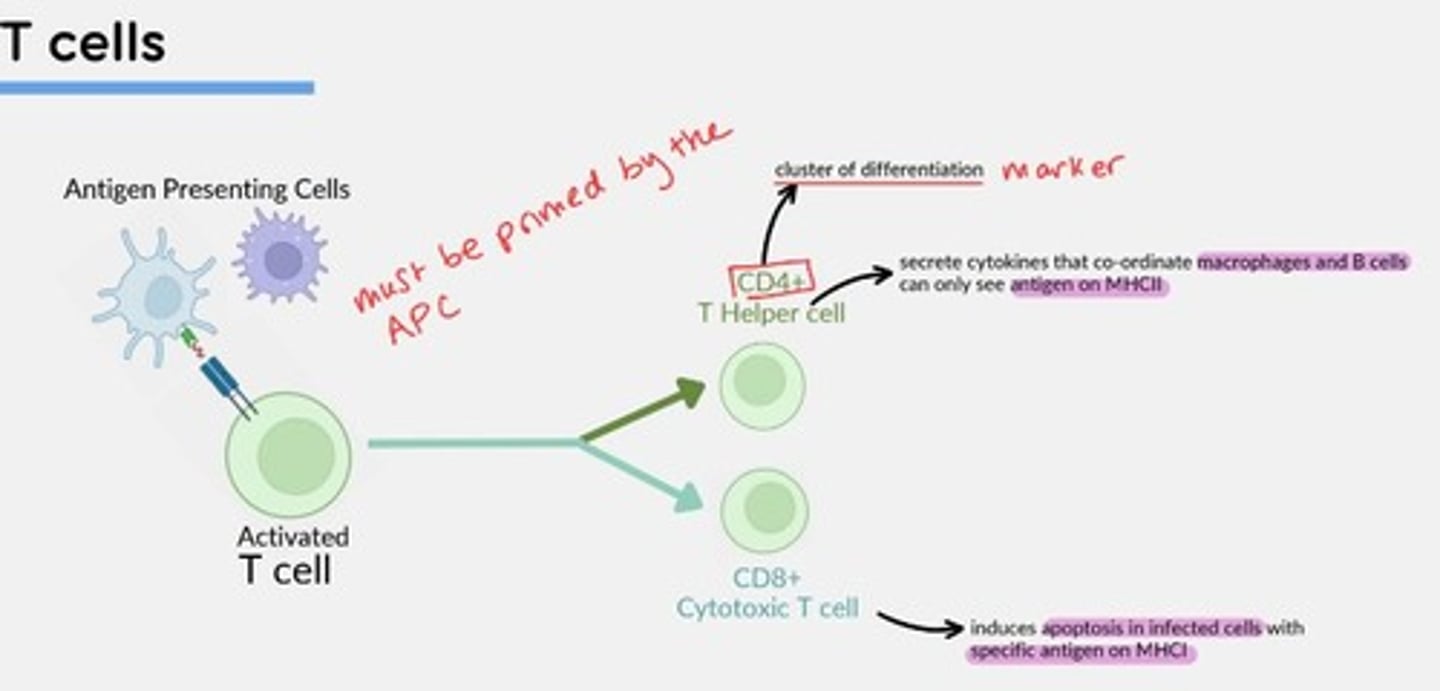
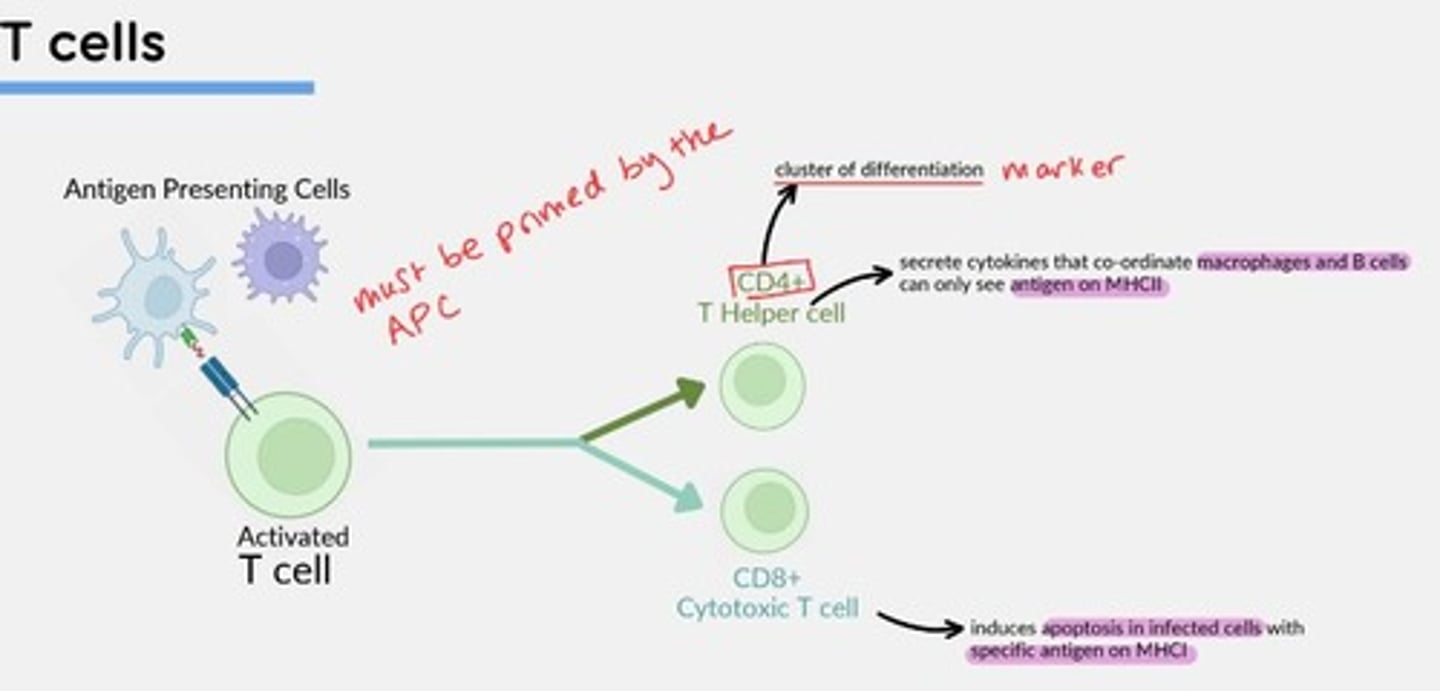
CD4+ T-helper cells
Secrete cytokines that coordinate macrophages and B-cells - can only see antigens on MHCII
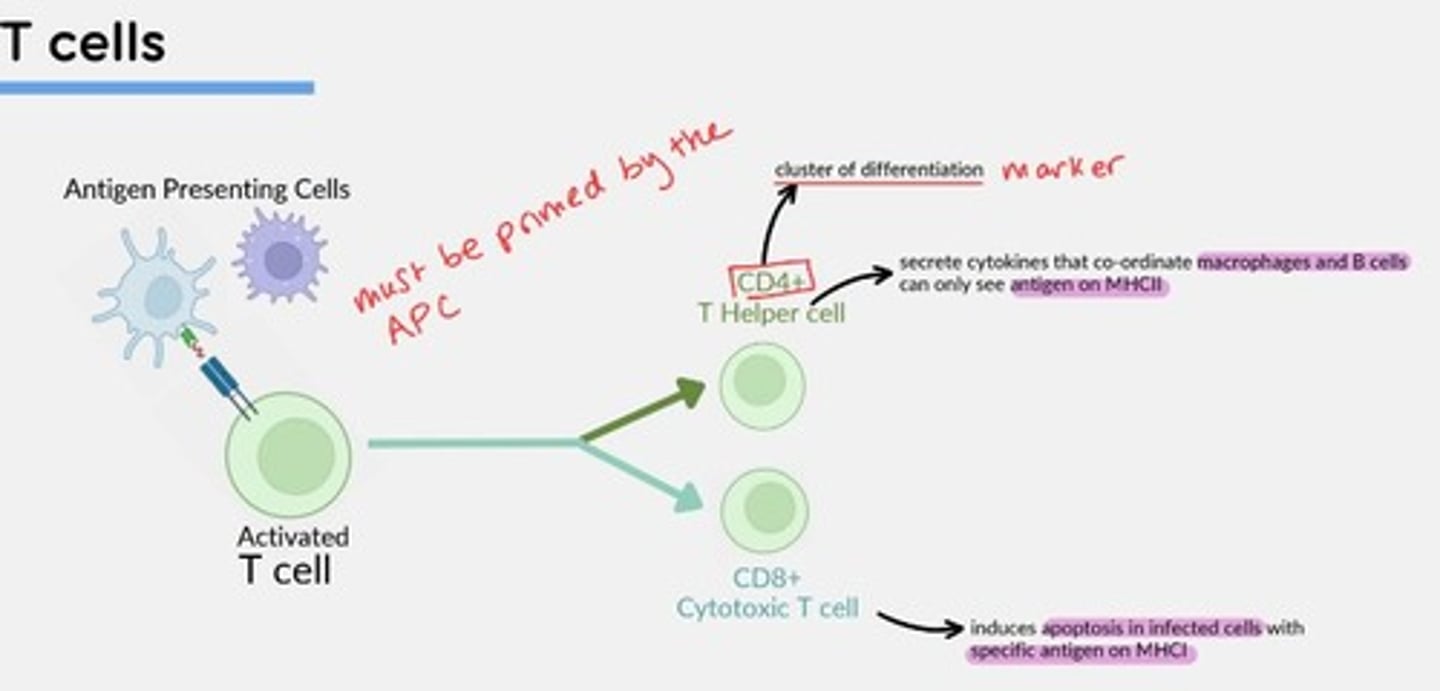
CD8+ Cytotoxic T-cells
Induce apoptosis in infected cells with specific antigen on MHCI
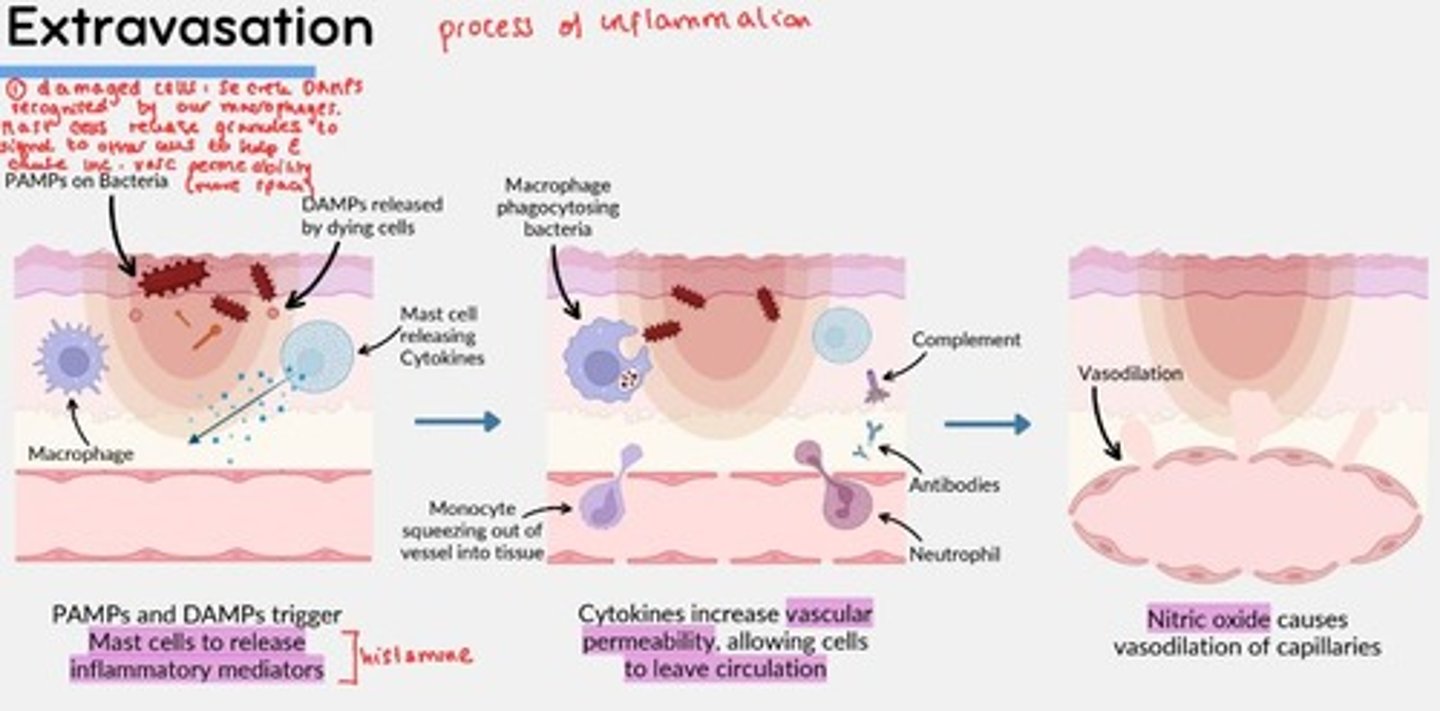
Extravasation
1) PAMPs and DAMPs trigger mast cells to degranulate and release inflammatory mediators (e.g., histamine)
2) Histamine released increase vascular permeability, allowing cells to leave circulation
3) Nitric oxide (NO) causes vasodilation of capillaries
Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction examples
Asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, anaphylactic shock, urticaria, angioedema
Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction
- Alveolar macrophages phagocytose pollen particles, travel to lymph nodes and present pollen antigen (& co-stimulatory molecules) to T-helper cells
- Primed T-helper cell secretes IL-4 which acts on B-cells to produce specific antibodies which are specific to the pollen antigen - B-cells produce IgE specific to the pollen antigen.
- Primed T-helper cells also secrete IL-5 which stimulates Eosinophils to degranulate
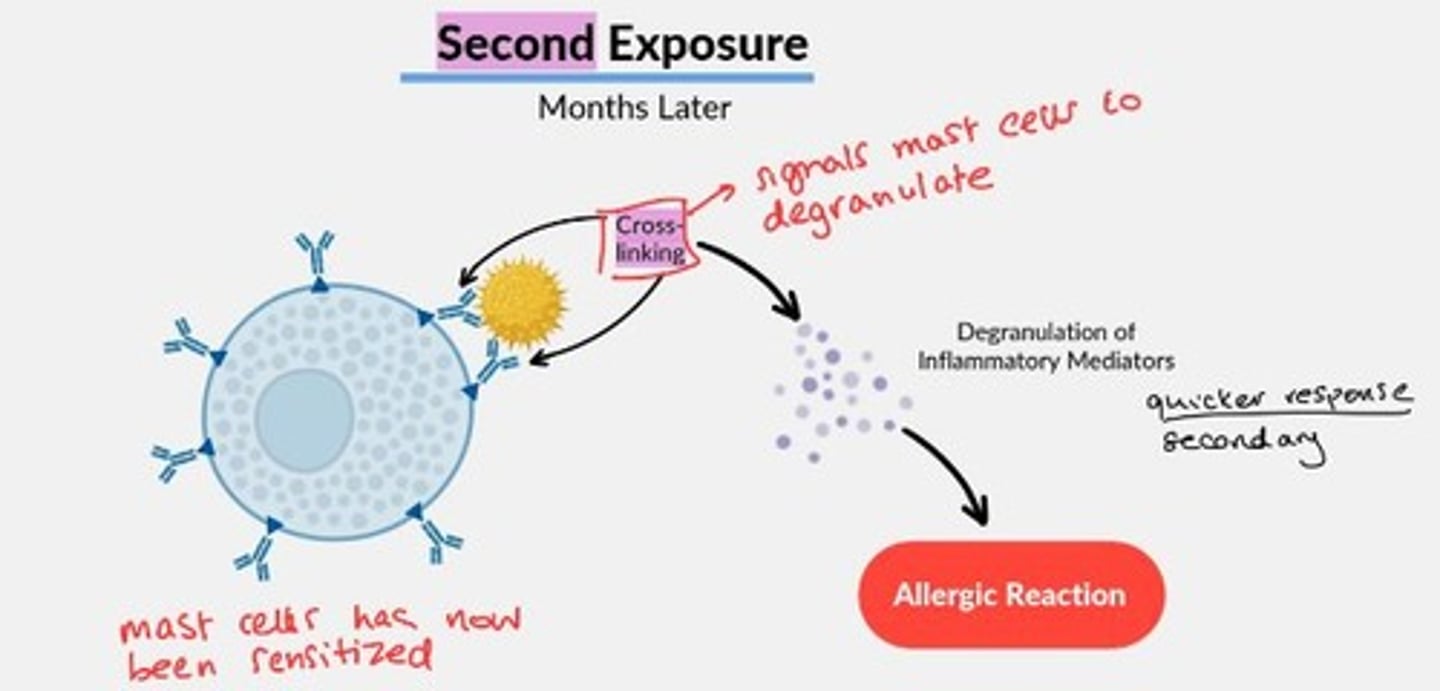
Mast cell sensitization
1st exposure to antigen causes plasma cell to produce specific IgE antibodies, which attach to the surface of tissue mast cells.
2nd exposure, months later = signal mast cells to degranulate rapidly.
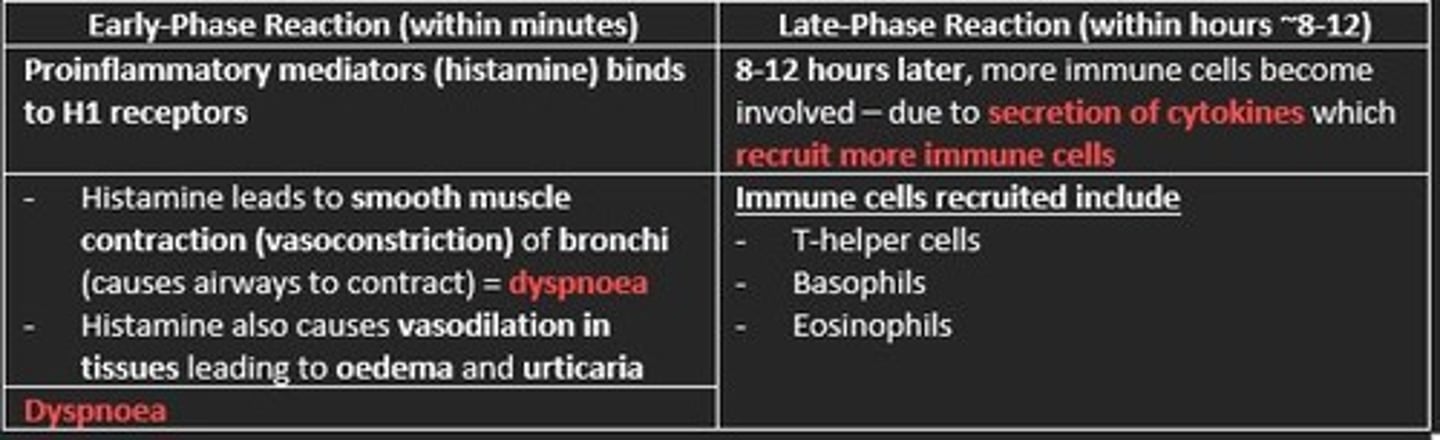
Type-1 hypersensitivity early and late-phase reactions
Early-phase reaction (minutes)
- Histamine binds to H1 receptors
- Smooth muscle contraction of bronchi = dyspnoea
- Vasodilation of tissues = oedema & urticaria
Late-phase reaction (8-12 hours later)
- More immune cells recruited due to secreted cytokines
- T-helper cells, Basophils, Eosinophils
Which stage of the infection cycle do symptoms first present, although vague?
a) Incubation
b) Prodromal
c) Illness
d) Convalescence
b) Prodromal
Which type of antibody is commonly produced in response to bacterial infections?
a) IgA
b) IgE
c) IgG
d) IgM
e) IgD
IgG
What is the primary mechanism of the immune system to detect bacterial pathogens?
a) Phagocytosis
b) Antibody production
c) Complement activation
d) Cytokine release
e) Neutrophil diapedesis
b) Antibody production
The inflammasome is a multiprotein complex that is involved in which of the following processes?
a) Immune cell migration to site of infection
b) Detection of bacterial pathogens by immune cells
c) Activation of complement system
d) Phagocytosis of pathogens by immune cells
e) Production of cytokines and chemokines
e) Production of cytokines and chemokines
Inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha and IL-1 are primarily produced by which type of cells in response to bacterial infection?
a) T cells
b) B cells
c) Macrophages
d) Neutrophils
e) Mast cells
c) Macrophages
Neutrophils are primarily responsible for which activity during the innate immune response to bacterial infection?
a) Phagocytosis of bacteria
b) Production of cytokines and chemokines
c) Activation of complement
d) Recognition of PAMPs
e) Secretion of IgE
a) Phagocytosis of bacteria
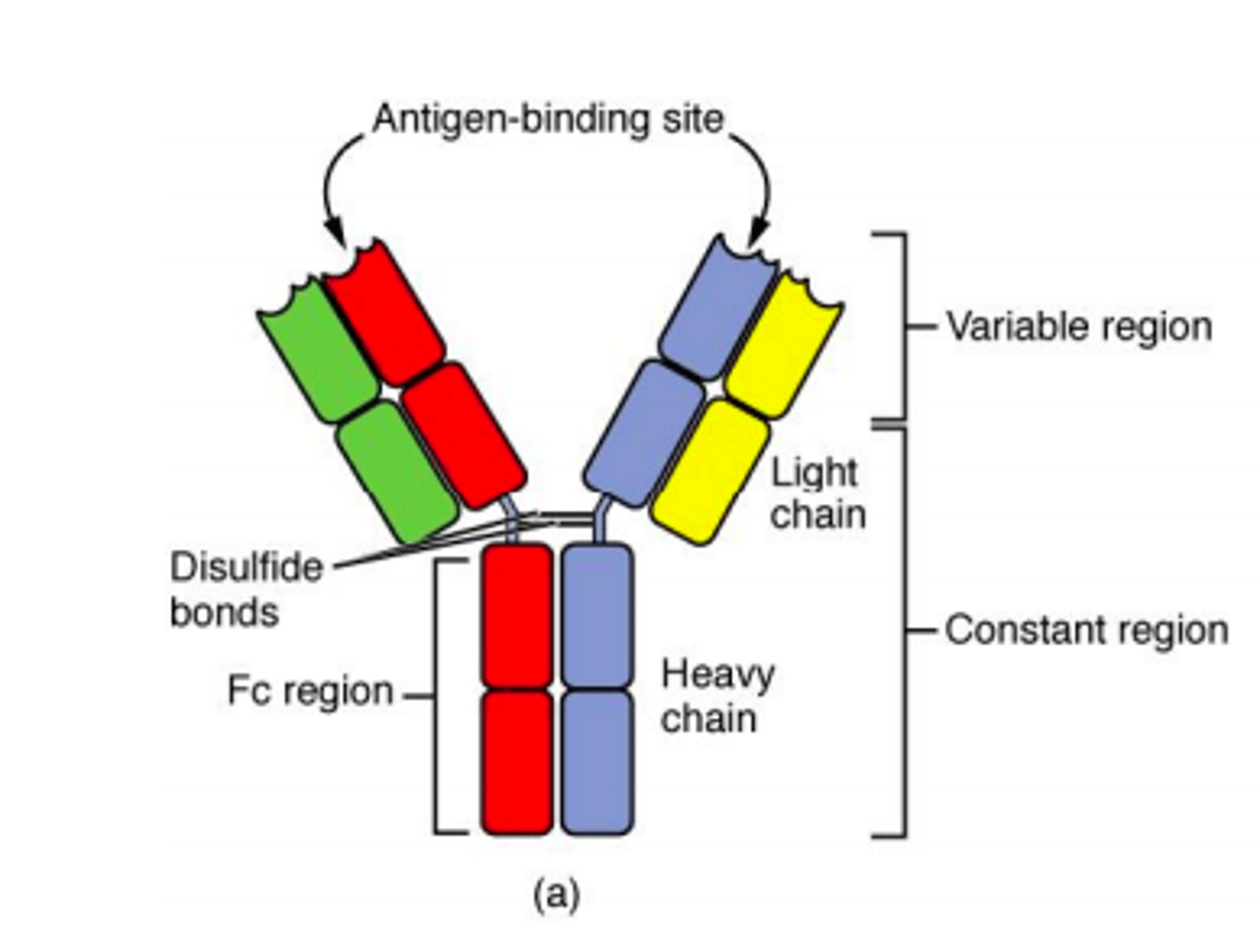
Antibody
Antibodies are glycoproteins that are essential in the immune system. They are synthesized by the B-lymphocytes. Antibodies will bind with high affinity to an invasive molecule.
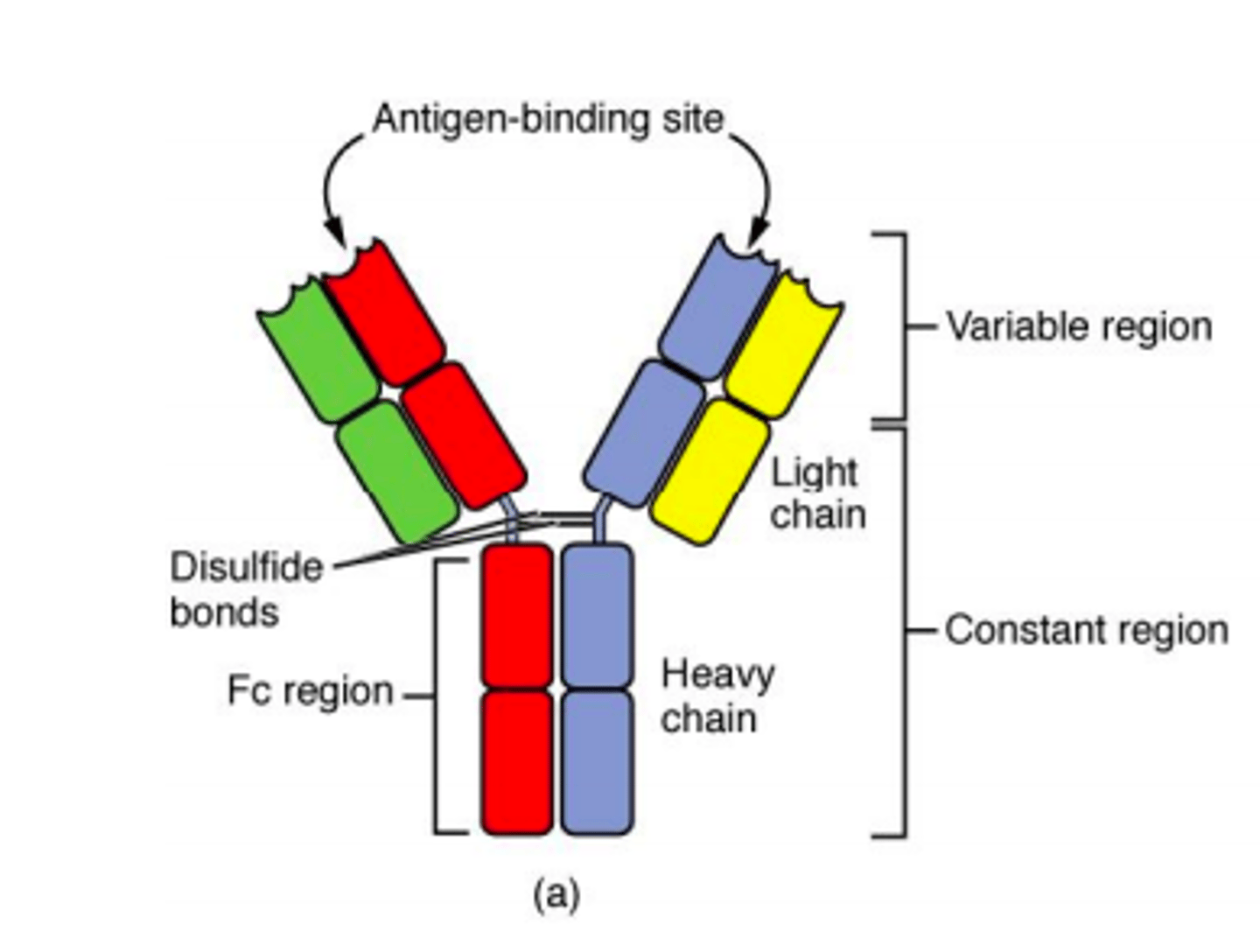
Five major classes of antibody
MAGED
IgM
IgA
IgG
IgE
IgD
T cells originate in the bone marrow and mature in the thymus.
In the thymus, T cells multiply and differentiate into...
1) Helper T-cells
2) Regulatory T-cells
3) Cytotoxic T-cells

Fever
Fever is a common symptom of infectious and inflammatory disease.
It is well-established that prostaglandin E2 is the final mediator of fever, which by binding to its receptor subtype in the preoptic hypothalamus initiates thermogenesis
Cytokines
Large, diverse family of small proteins or glycoproteins that regulates cell differentiation, proliferation, and gene expression to affect immune responses.
The binding of PRRs with PAMPs triggers the release of ___
Cytokines
Interleukin (IL)
Mediates interactions between leukocytes
Interferons (IFNs)
Released by infected cells as a warning to nearby uninfected cells.
Inhibit viral replication, making them particularly effective against viruses.