PDHPE CORE 1
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
Role of Epidemiology
Identify patterns, analyze usage, allocate resources
Mortality
Number of deaths within a specified time period
Mortality examples
Cancer surpassed CVD as leading cause of death in 2013
Infant Mortality
Measures number of infant deaths within first year of life per 1000 babies
Post Natal
death in remaining first year
Neonatal
death in first 28 days
Infant Mortality example
2022 Australian rate was steady at 3.2
Morbidity
Patterns of illness, disease and injury not resulting in death
morbidity example
2021-22, around 47% of Australians had one or more chronic conditions
Life Expectancy
Length of time a person is expected to live based on current death rates in a population, typically calculated at birth
Life expectancy example
2022, life expectancy at birth was 81.2 years for males and 85.3 years for females
Why is epidemiology limited in describing health status?
It focuses on statistics (mortality, morbidity) but overlooks quality of life, mental health, and social determinants.
Why might epidemiology not accurately show health differences between groups?
Data collection issues can underrepresent groups like Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples.
What does epidemiology often fail to capture after a diagnosis?
Pain, emotional distress, and daily life impact beyond just disease rates.
Why is mental health underrepresented in epidemiology?
Stigma, underreporting, and lack of diagnosis make conditions like anxiety and depression hard to measure.
Why doesn’t epidemiology fully explain health inequalities?
It shows disparities but not underlying causes like income, education, and healthcare access.
What key factors are often ignored in epidemiology?
Social, economic, and environmental factors that impact health outcomes.
Factors determining disease burden
Social justice priorities, priority population group, costs to individuals/community, relevance of conditions, potential of prevention
Social justice: Equity in Health
resources and funding is distributed fairly
Social justice: Diversity in Health
Planning and making decisions about health whilst recognizing the cultural and societal differences
Social justice: Supportive environments in Health
refers to the physical and social aspects of our surroundings, resources for living and opportunities for employment.
Social justice in health example
Provision of equal access to resources, health services, education and information may reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes in the indigenous population
Priority groups in Australia
Indigenous Australians, Socio-economically disadvantages, Rural and remote residents, Veterans, Prisoners and Overseas-born.
What is prevalence in health?
refers to the current number of cases of an illness or condition. Higher prevalence indicates a greater issue
How does prevalence relate to the burden of disease?
The greater the prevalence, the more significant the burden of disease
Why is cardiovascular disease a major concern in Australia?
has been a priority health issue for a long time and is expected to continue impacting
What is the trend of cancer prevalence in Australia?
Cancer is a growing priority, but reduced smoking rates are helping lower some cancer rates.
Who is most affected by dementia and Alzheimer’s disease?
primarily affect the elderly, making them a significant health concern in Australia.
Why is diabetes a priority health issue in Australia?
highly prevalent but also has an increasing incidence
How is cerebrovascular disease related to cardiovascular disease?
similar underlying causes and remains a major health issue in Australia.
Early Intervention
Can also decrease disease burden by enabling effective treatment and recovery
Early Intervention example
Successful cervical cancer screening and HPV immunizations programs.
Direct costs of ill health
Prevention (health campaigns, vacx programs), Diagnosis (testing, screening, consultations), treatment (hospitals, rehab, pharamacy)
Indirect Costs of Illhealth
Quality of life (reduced wellbeing), Relationships (strain and potential breakdown), Productivity (loss of work hours and economic output)
ATSI: Life Expectancy gap
overall improvement, ASTI still approximately 10 years lower than the general population
ASTI: adult morality
Aged 35-44 face have a 4 times higher mortality rate
ATSI: infant mortality
twice more likely die to early life challenges, nutrition and healthcare access
ATSI: Prevalence of Chronic diseases
Circulatory, Endocrine, Metabolic Disorders, Mental health, Substance Abuse, Digestive conditions
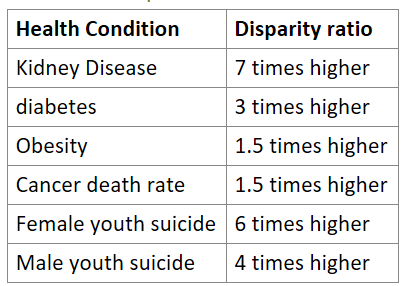
ATSI: Sociocultural determinants of Health
Family structure, Education, Cultural, Community disempowerment
ATSI: Socioeconomic and Environmental Determinants of Health
Income disparity, housing conditions, geographical location, Environmental hazards
ATSI: Addressing health inequities
Culturally appropriate Healthcare, Community lead initiatives, addressing social determinants, Continued research and monitoring.
Low SES: Health outcomes
Poorer Health due to limited resources, and healthy living activities/education
Low SES: Smoking Rates
23% compared to 10% in high SES
Low SES: Physical Inactivity
66% compared to 48% in high SES
Low SES: Risky Alcohol
22% compared to 17%
Low SES: Obesty outcomes
33% in women, 66% higher in children
Low SES: Chronic illness
Circulatory, Endocrine, Metabolic Disorders, Mental health, Substance Abuse, Digestive conditions
Low SES: Socio-cultural determinants
Limited Access to Healthcare, Education, Environmental, Poor living conditions, lifestyle, economic instability, nutrition, family influence, media, peer pressure
Low SES: socio-cultural example family influence
drinking to heavy levels is acceptable, children are more likely to drink at early ages e.g. 12 years old in the home, promoting unhealthy relationship with alcohol
Low SES: Socioeconomic and Environmental Determinants
Education, employment, income, living conditions
Low SES: addressing inequities: Individual
Need to focus on education, making healthy choices and personal responsibility
Low SES: addressing inequities: Community
Programs like PCYC and 'Youth of the Streets' provide crucial services
Low SES: addressing inequities: Government
Medicare, PBS, and social welfare programs aim to reduce inequities
Cardiovascular Disease
All diseases of the circulatory system (heart and blood vessels)
CVD Types
Coronary Heart disease, stroke (Cerebrovascular disease), Myocardial arrhythmia, Heart Failure
CVD: Coronary Heart Disease
arteries of the heart cannot deliver enough oxygen-rich blood to the heart, usually because of Atherosclerosis.
CVD: Stroke (cerebrovascular disease)
Damage to the brain from interruption either of its blood supply, because blockages or sudden bleeding in the brain
CVD: Myocardial arrhythmia
Improper beating of the heart, electrical impulses in the heart don't work properly
CVD: Heart Failure
heart doesn't pump blood as well
CVD: Arteriosclerosis
Hardening or narrowing of arteries.
CVD:Atherosclerosis
buildup of fat and plaque inside the arteries, blocking blood vessels
CVD: Trends
1 in 5 Australian's suffer. Second leading cause of death. Downward trend. Strokes incident decreasing, prevalence increasing
CVD: Risk Factors
Hypertension (high blood pressure), Physical inactivity, Obesity, Smoking
CVD: Protective Factors"
Regular physical activity regular health checks, and eating a balanced diet low in saturated fats
CVD: Socio-cultural
Influenced by Family (provides foods and influence activity), peers(pressure ie starting to smoke), media, religion and culture. Genetics can play a role
CVD: Socioeconomic
employment, income and education. CVD is higher in blue collar
CVD: Environmental
Geographical isolation can limit health/services access which results in high death rates because of lagged time between stroke or heart attack and treatment.
CVD: Groups at Risk
ATSI, LSES, Rural/remote, Elderly, Smokers, Men, Genetic history
Cancer
When cells become abnormal and begins to multiply rapidly and cannot be controlled by the body
Cancer: Tumour
where cancer is located/originated from
Cancer: Benign Tumour
Non-cancerous tumour
Cancer: Malignant Tumour
Cancerous, can invade surrounding tissue
Cancer: Metastasis
When a malignant tumour moves away from its primary site
Cancer: Most Common
Prostate, Bowel, Breast, Skin and Lung
Cancer: Trends
Leading case of death, rates declining. Increased incidence. Lung cancer declining for men, increase for women. Bowel cancer and Melanoma decreasing. Breast increasing
Cancer: Lung Cancer Death Rates
Decreasing in men. Increasing smoking rates, only slightly decreasing amongst women. Incidence for women is not expected to decline.
Cancer: Lung Cancer, Risk Factor Smoking
Increases Incident by 10, increases through amount and length of smoking
Cancer: Lung Cancer, Risk Factor Smoking, Highest risk group
Children/Adolescents: lung tissue is easily damaged.
Cancer: Lung Cancer, Risk Factor Environmental/Occupational
No-smokers are less than 10% lung cancer cases. Contributing factors, nonsmoking -> Occupational hazards, air pollution, other environmental factors
Cancer: Lung Cancer, Protective Factors
Smoking cessation, public education, work place and environmental safety regulations
Cancer: Breast Cancer, Incidents
Second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women. 1 in 8 women in Australia will be affected. Risk increases with age.
Cancer: Breast Cancer, Risk Factors
Age, Family History, lifestyle, Reproductive history
Cancer: Breast Cancer, Early Detection
Increases survival rates: Self-examination and Mammograms
Cancer: Breast, Prevention/awareness
Regular checks and mammograms are vital. Awareness campaigns and public health programs Lifestyle changes -> Healthy diet, Maintain a healthy weight.
Cancer: Skin Cancer, Types
Non-Melanoma and Malignant Melanoma
Cancer: Skin Cancer, Non-Melanoma
Basal cell carcinoma & Squamous cell carcinoma, common, rarely fatal
Cancer: Skin Cancer, Melanoma
Most dangerous, can spread around the body
Cancer: Skin Cancer Trends
Over 2 000 Australians die each year. Deaths can be prevented; early detection and skin protection
Cancer: Skin Cancer, Prevention/Awareness
Skin Checks, Sunscreen, Sun Safety Campaigns
Cancer: Socio-cultural
Influenced by Family history , ATSI , Family practices
Cancer: Socio-economic/environ
Influenced by occupation, Lower SES, Lower Education
Cancer: Environmental
Rural Living → less access
Cancer: Groups at risk
ATSI, LSES, Remote/Rural, Elderly, Smoker’s, Genetic History, Women with no children
Diabetes
Effects the body's ability to take glucose from the blood stream and use it for energy.
Diabetes: Type 1
Genetic: Caused by issues in the pancreas with insulin production and management of glucose
Diabetes: Type 2
Pancreas produces insulin but it is insufficient or ineffective. Managed through diet, exercise and medication. Caused by obesity and high fat diets
Diabetes: Gestational
Occurs during pregnancy and increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life
Diabetes: Trends
Risen, upward trend, 7th highest cause of death in Australia
Type 2 Diabetes: Risk Factors
Family history, Age, high blood pressure, obesity, PCOS, overweight, Aboriginal, Torres Strait Islander, Pacific Islander, Indian, or Chinese background, High-fat and high sugar diet, physical inactivity
Type 2 Diabetes: Protective Factors:
Maintaining healthy body weight, Regular physical activity, Balanced diet, Limiting alcohol intake, Regular health checks