crisis management, stress and defense mechanisms, anxiety, and violence - quiz 4
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
crisis
limited and acute
4-6 weeks
triggers a coping response that cannot be managed with pts normal coping mechanisms
crisis risk factors
unresolved loss
life stressors
mental and physical health issues
excess fatigue or pain
age and developmental status
unresolved loss
an unexpected loss
protective factors for crisis
prior personal experience
types of crisis
situational/external
maturational/internal
adventitious
situational/external crisis
unanticipated
ex: kid fell into a pool
maturational/internal crisis
new developmental stages
adaptive: graduating, getting married, having kids, retirement
adventitious crisis
natural disasters
national disasters
ex. fire burning down house, hurricane Katrina
what is our goal as nurses for managing crisis
safety
what is our numeber 1 task for crisis
address pt immediately
strategies to decrease anxiety
offering self, remain with pt
listen and observe
eye contact
ask questions relevant to the event
communicate clearly
avoid false assurances
help pt to develop action plan
primary theraputic interventions for crisis
identify potential problems
- what is causing this crisis?
secondary theraputic interventions for crisis
identify interventions
- what can I do to help this pt through this crisis?
tertiary theraputic interventions for crisis
provide support during recovery from severe crisis
- ex. outpt rehab centers, crisis sstabilization centers, workshops
- debreif what exercises can help pt through this hard situation
fight or flight
increased HR, RR, BP
slowed GI
increased metabolism
pupils dilate
good stress
ex. traveling, new job, exercising at gym
bad stress
ex. school, money
are physiological responses the same for good and bad stress?
yes
can cause anxiety and dysfunctional behavior
stress can lead to
decreased attention span from fatigue
weaker immune system
what do people do with stress
develop adaptive or maladaptive defense mechanisms
acute stress
apprehention
unhappiness
sorrow
decreased appetite
increased HR, RR, BP
increased metabolism
depressed immune system
chronic stress
chronic anxiety or panic attacks
depression
chronic pain
sleep disturbances
wt fluctuations
increased risk for MI, stroke
poor disease management
increased risk for infection
adaptive defense mechanisms
altruism
sublimation
altruism
dealing with anxiety by reaching out to others
ex. you call your mom when you are sad
ATI ex. a nurse who lost a family member in a fire is a volunteer firefighter
sublimation
dealing with unacceptable feelings or impulses by unconsiously substituting acceptable forms
adaptive: going to the gym when you are angry and want to punch someone
adaptive and maladaptive defense mechanisms
suppresion
repression
regression
displacement
reaction formation
undoing
rationalization
dissociation
denile
compensation
identification
intellectualization
suppression
voluntarily denying unpleasant thoughts and feelings
adaptive: student puts off thinking about a fight they had with friend so they can focus on test
maladaptive: someone who lost their job says they will worry about paying bills next week
repression
unconsciously putting unacceptable ideas, thoughts, and emotions out of awareness
adaptive: someone preparing to give a speech unconsciously forgets about the time they were young and kids laughed at them while on stage
maladaptive: someone with a fear of the dentist forgets to go to their dental appointments frequently
regression
sudden use of childlike primative behaviors that dont correlate with the person's current developmental level
adaptive: young child temporarily wets the bed when they learn that their pet died
maladaptive: person who has disagreement with a co workers begins throwing things in their office
displacement
shifting feelings related to an object, person, or situation to another less threating object, person, or situation
adaptive: adolescent angirly punches bad after losing game
maladaptive: person who is angry about losing job destroys their child's favorite toy
reaction formation
unnacceptable feelings or behaviors are controlled or kept out of awareness by overcompensating or demonstrating the opposite behavior of what is felt
adaptive: someone trying to quit smoking repeatedly talks to adolescents the dangers of nicotine
maladaptive: someone who resents having to care for an aging parent becomes overprotective and restricts their freedom
undoing
performing an act to make up for prior behavior (usually seen in children)
adaptive: child completes chores without being prompted to after an argument with their parent
maladaptive: someone buys their girlfriend flowers and gifts after abusing them
rationalization
creating reasonable and acceptable explanations for unacceptable behavior
adaptive: someone says "they must already have a boyfriend" when they get rejected
maladaptive: someone says they have to drive home drunk because they have to feed their dog
dissociation
disruption in consciousness, memory, identity or perception of the environment that results in compartmentalization of uncomfortable or unpleasant aspects to oneself
adaptive: parent blocks out distracting noise in order to focus while driving
maladaptive: someone forgets who they are after a sexual assult
denile
pretending the truth is not reality to manage unpleasant anxiety-causing thoughts or feelings
adaptive: someone initially says "no that can't be true" when told they have cancer
maladaptive: parent who is told their child was killed in combat tells everyone a month later their child is coming home for the holidays
compensation
emphasizing strengths to make up for weakness
adaptive: someone who is unable to play contact sports excels in academic competitions
maladaptive: someone who is shy learns computer skills to avoid socialization
identification
conscious or unconscious assumption of characteristics of another individual or group
adaptive: child who has a chronic illness pretends to be a nurse for their dolls
maladaptive: child who observes their parents abuse and becomes a school bully
intellectualization
separation of emotions and logical facts when analyzing or coping with a situation or event
adaptive: a law enforcement officer blocks out the emotional aspect of a crime so they can objectively focus on the investigation
maladaptive: someone who learns they have a terminal illness focuses on creating a will and financial matters rather than acknowledging their grief
maladaptive defence mechanisms
conversion
splitting
projection
conversion
responding to stress through the unconscious development of physical manifestations not caused by a physical illness
maladaptive: someone experiences deafness after their partner tells them they want a divorce
splitting
demonstrating an inability to reconcile negative and positive attributes of self or others in a cohesive image
maladaptive: pt tells nurse that the nurse is the only one who cares about them but the next day the pt refuses to talk to the nurse
projection
attributing one's unacceptable thoughts and feelings to another who does not have them
maladaptive: a married client who is attracted to another person accuses their partner of having an affiar
nursing care for stress
cognitive reframing
journal writing
cognitive reframing
helps pt look at irrational thoughts in a more realistic light
restructure the thought in a more positive way
ex. "im a bad father" to "ive made some mistakes as a parent but ive learned from them and improved my parenting skills"
journal writing
helps ease anxiety
increases confidence and hope
relxation techniques
meditation
guided imagery
breathing exercise
progressive muscle relaxation
physical exercise
guided imagery
close eyes and imagine a calming place
breathing exercises
goal is to increase O2 to brain
- helps pt calm down and increases their ability to think and recall things
progressive muscle relaxation
tighten muscle groups then relax them
physical exercise
NON weight lifting exercises to ease anxiety
levels of anxiety
mild
moderate
severe
pani
mild anxiety
every day living
headache
mild discomfort
mild restlessness/irritability
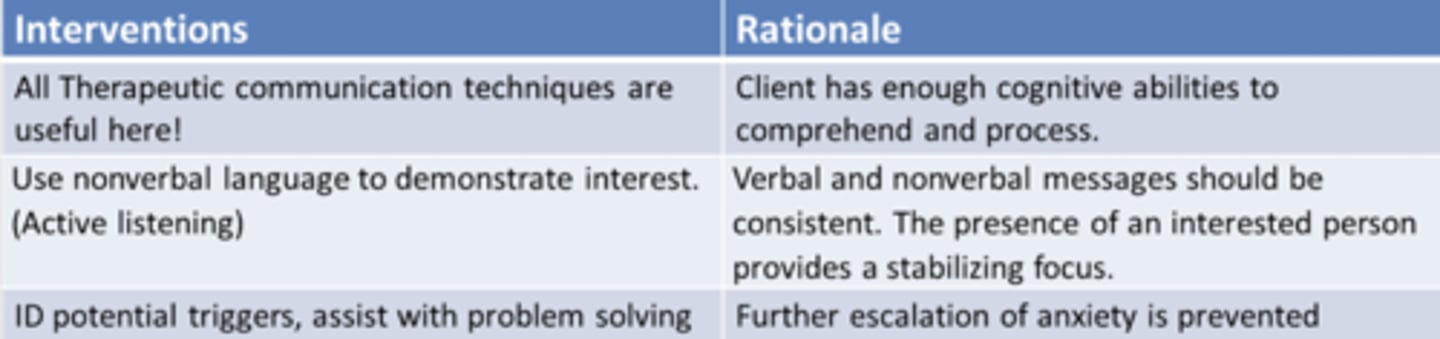
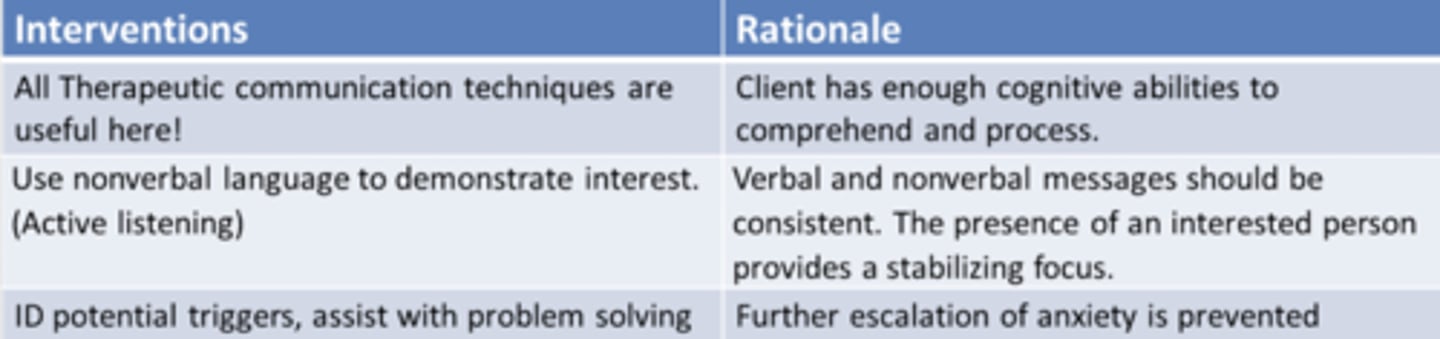
moderate anxiety
DO NOT leave pt at this point
decreased ability to think and problem solve
insomnia
pacing
voice tremors
increased vital signs
keep directions brief
problem-solving and learning can still occur at this stage
severe anxiety
field of view greatly reduced
learning and problem solving does not occcur
function is effective and behaviors are automatic
increased HR, RR, BP
confusion
impending doom
keep direction simple
usually unable to take directions from others
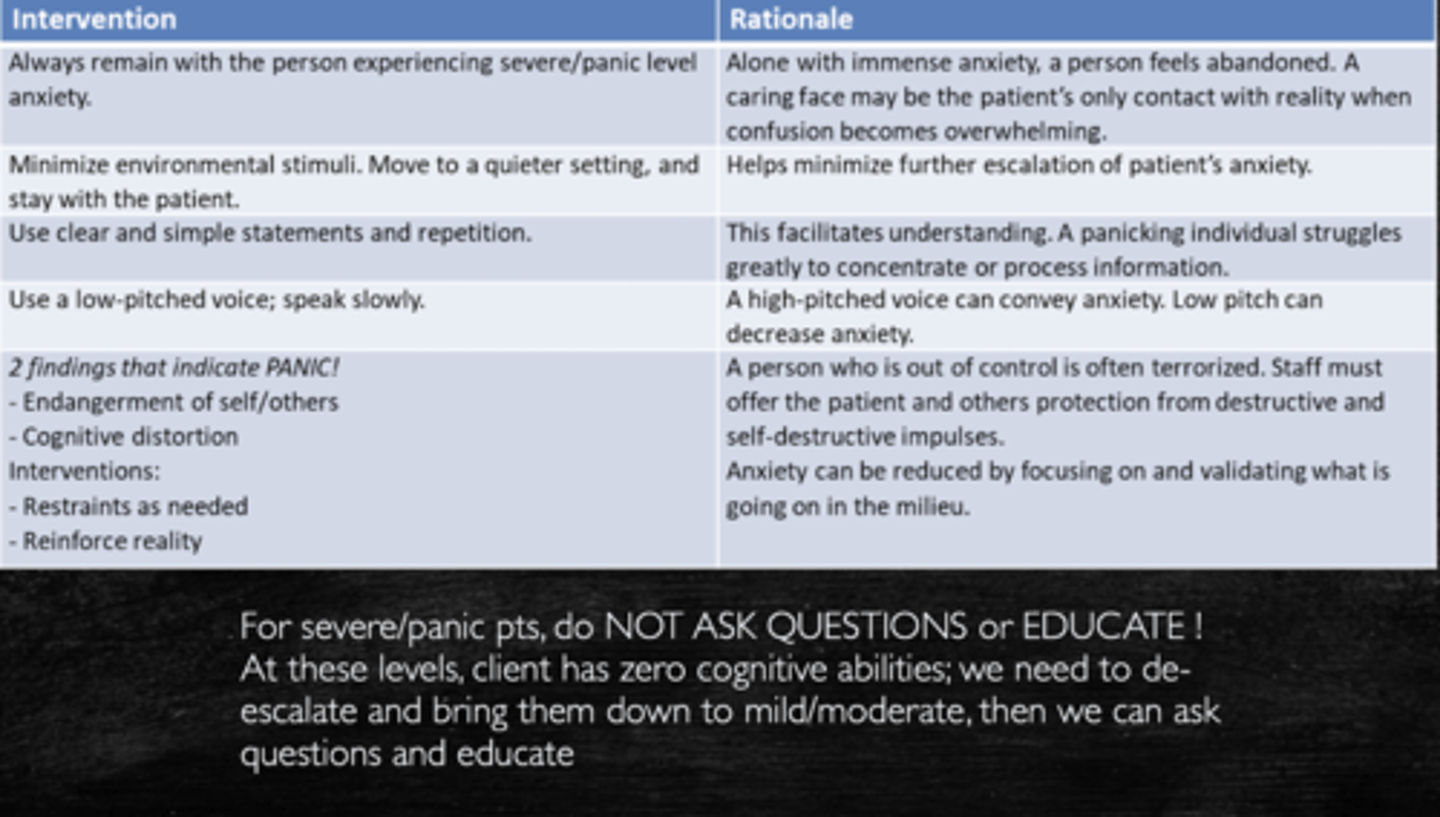
panic
pt not able to process things
lost touch with reality
extreme fright and horror
hyperactivity or immobility
hallucinations
dilated pupils
dysfunction in speech
who is at higher risk for anxiety
females
environment for anxiety
must keep the physical safety of the pt
quiet and low stimulation
when would we need to put them in restraints
if they get violent
use therapeutic communication first
anxiety nursing considerations
encourage exercise
- stress relief
set limits, talk slow and low
what levels of anxiety is theraputic communication useful for
mild and moderate ONLY
* severe anxiety and panicing pts do not have the cognitive abilities for theraputic communications or questions/education to be helpful, you must bring them down to mild/moderate anxiety in order to start asking questions and educate them
anxiety disorders
anxiety
OCD
anxiety
separation anxiety
specific phobias
agoraphobia
social anxiety
panic disorder
generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
OCD
obsessive compulsive disorder
- obsessive: hyper-focused on ONE thing
- compulsive: has to perform some action or else their anxiety will increase
- compulsion will decrease anxiety
hoarding
body dysmorphia
1st line med for OCD and anxiety
SSRI: sertaline (zoloft)
benzodiazepines for OCD and anxiety
lorazepam (ativan)
diazepam (valium)
benzodiazepines for anxiety and OCD considerations
not long term meds or first line because they are very adictive
causes respiratory depression and sedation
cannot take with ETOH
may cause paradoxical response
paradoxical reponse
opposite response than what is expected
- insomnia, anxiery, restless, agitation
atypical anxiolytic meds for OCD and anxiety
buspirone
buspirone considerations
cant have
- st johns wort
- grapefruit
- erythromycin
- ketoconazole
these will increase buspirone in the body
non benzo meds for OCD and anxiety
betablockers: propanolol
antihistamines
antiepileptic: lamotrigine, valproic acid (VPA)
* these are used for those with a history of drug use/addiction
antihistamines for OCD and anxiety considerations
causes anticholinergic effects
also affects antipsychotic use (it is the antidote for EPS symptoms)
- cant use antihistamines with antipsychotics
beta blockers for OCD and anxiety considerations
decreases BP
take BP before giving
cognitive behavioral therapy for OCD and anxiety
relaxation training
modeling
systematic desensitization
flooding
response prevention
thought stopping
systematic desensitization
progressive exposure to someone's fear
ex. showing them a picture of a spider, then having them hold a spinder stuffed animal, then having them hold a real spider
flooding
putting them in an environment filled with their fear
ex. putting them in a room with a bunch of spiders
relaxation training
a treatment procedure that teaches pt to relax at will so they can calm themselves in stressful situations
modeling
learning by imitating others; copying behavior
response prevention
focuses on preventing the pt from performing a compulsive behavior with the intent that anxiety will diminish
thought stopping
teaches pt to say "stop" when negative thoughts or compulsive behaviors begin, and substitute a positive thought
the goal of therapy is that with time, the client uses the command silently
cycle of violence
tension building stage
acute battering stage
honeymoon stage
tension bulding stage
minor episodes of anger
- verbal and some minor physical violence ex. pushing, shoving
- victim is usually tense during this stage and accepts blame
acute battering stage
serious abuse takes place
- victum may provoke perp due to unbearable tension
- victim will try to hide bruises
- shortest stage
honeymoon stage
they fall in love again and perp tells victim they will not hurt them again
perp love bombs victim
how to as suspected victim of violence about bruising/injuries
"how did you get these buises/injuries?"
types of violence
physical
emotional (mental/verbal)
sexual
financial
neglect
most common type of violence
emotional
perpetrator common characteristics
poor impulse control
poor coping skills
lacking knowledge in role
low self esteem
likely to have experienced violence as a kid
possible history of substance abuse
victim common characteristics
low self esteem
helpless, hopeless, powerless, guilt, shame
may consider the abuse as warranted
suspicious injuries in children that may indicate abuse
spiral fracture
bruising inconsistent with age
- ex. bruises on knees when they no longer crawl
patterned burn marks
what to do when you encounter suspected child abuse
report it to the non emergency hot line
- do not go to charge nurse or anyone else before doing this
how much proof is needed to report suspected abuse
none, just a suspicion
elder abuse findings
malnutrition
clothing not matching weather
bad hygiene
financial abuse: no water/utilities/gas/electricity in home
the child's perpetrators are most often who
their parents
unwanted sexual advances and sexual harassment
stranger rape
marital rape
date rape
drug facilitated sexual assault
incest
human sex trafficking
* all perps are usually acquaintances of the victim
who are the main victims of rape
anyone can be a victim of rape
main reason perpetrators commit rape
so they can have control
rape-trauma syndrome
PTSD like
- flashbacks, nightmares, hyperarousal, avoidance, emotional instability, may appear detached or confused
pt may develop a depressive or anxiety disorder