Chemistry Regents Review: Kinetics/Equilibrium Notes & Unit 4.4/5.1 (week #6)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Collision Theory
reaction is most likely to occur if reactant particles collide with the proper energy and orientation
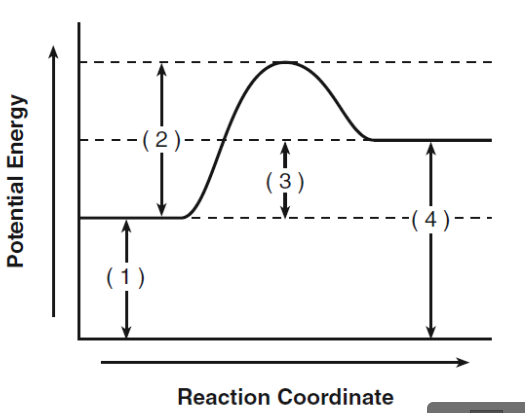
What does 1 represent?
activation energy for reactants
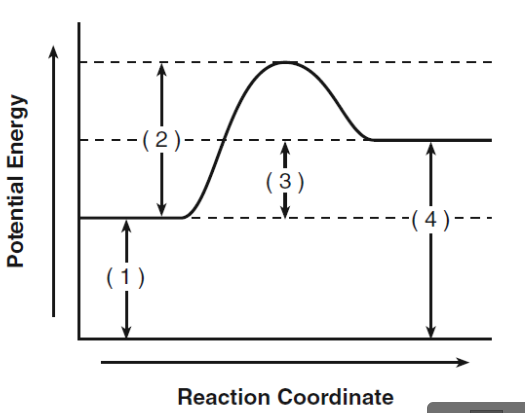
What does 2 represent?
activation energy for activated complex
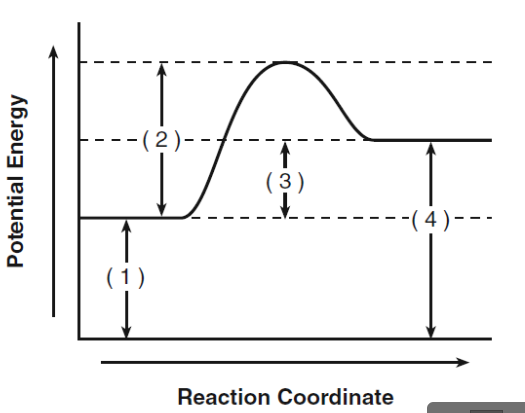
What does 3 represent?
heat of the reaction
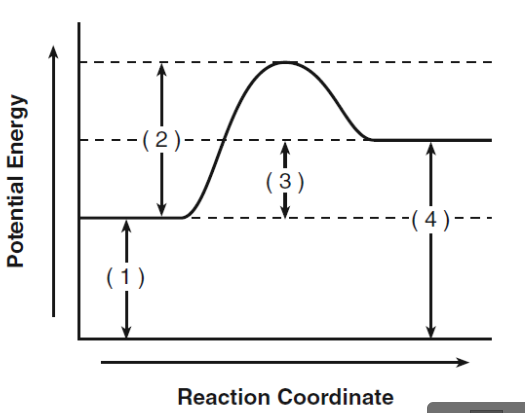
What does 4 represent?
activation energy for products
First 6 equations on Table I are all…
combustion
4 factors effecting reaction rates
increasing temp
increasing concentration
increasing surface area
catalyst
Increasing temperature…
faster moving particles →increased frequency of effective collisions
Increasing concentration…
more particles → closer tgth → more collisions
Increasing surface area….
breaking up bonds (powdered) → particle release & increased frequency of effective collisions
Catalyst
provides an alternative reaction pathway and lowers activation energy
Why doesn’t a catalyst shift the reaction?
it increases the rate of foward and reverse equally
Combustion
hydrocarbon + O2 → H2O + CO2 + energy (heat)
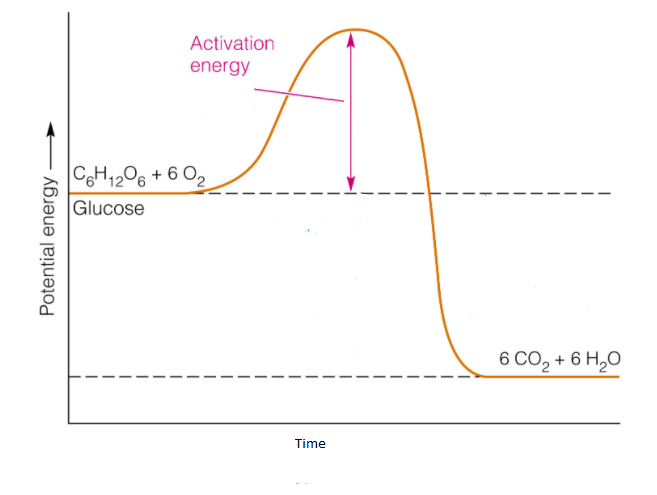
Heat of Reaction
PE products - PE reactants
Negative sign means exothermic so….
heat released from system to surroundings (air temp increases)
Exothermic Potential Energy Diagram
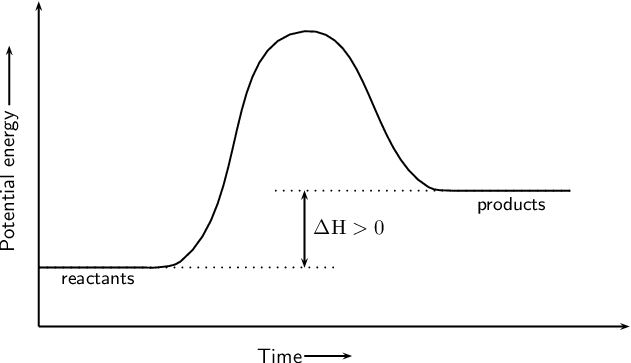
Endothermic Potential Energy Diagram
Equilibrium
rate of foward and reverse reactions is equal and concentrations of reactants and products is constant
Phase Equilibrium
occurs during phase changes
melting
freezing
boiling
Le Chatelier’s Principle
if a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the equilbirium will shift to relieve that stress
3 ways to stress Equilibrium
concentration
pressure
temperature
Concentration and Temperature Acronym
Add Away
Take Towards
Pressure Increases and Decreases shifts
increases - less moles of gas
decreases - more moles of gas
Synthesis Chemical Reaction
A + B → AB
Decomposition Chemical Reaction
AB → A +
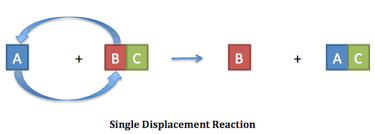
Single Replacment
Dynamic Equilibrium
rate of dissolving = rate of recrystalization
Static Equilibrium
solution at rest and all external forces on it are balanced so there is no motion
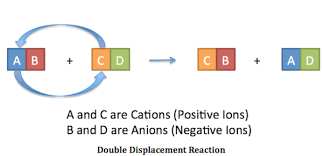
Double Replacment
Vaporization
amount of energy it takes to vaporize a substance
liquid to gas
Fusion
amount of energy required to melt
solid to liquid
Low boiling points have a high vapor pressure because
its easier to overcome atmospheric pressure
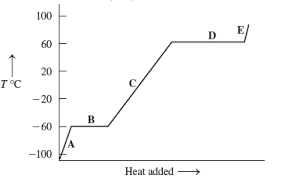
A, C, and E
temperature increases while PE is constant
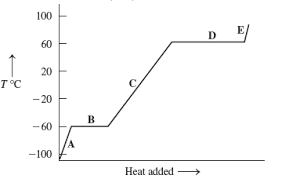
B and D
PE increases because changing phase while temperature is constant
In heat of fusion, the melting and refreezing energy amounts…
are the same
Specific Heat Capacity, delta T is
T final - T initial