Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Unit
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
what kind of reaction is the process of harvesting chemical energy
catabolic
energy flows into ecosystem through ______ and leaves as _______
photosynthesis/heat
fermentation
partial degradation of sugars without oxygen present
REDOX reactions
combination of reduction and oxidation in reaction
cellular respiration
process where glucose is broken down to create ATP
reducing agent
substance losing electrons
oxidizing agent
substance recieving electrons
reduced means having _______ potential energy why?
greater/bc gaining gained electrons bring their energy with them
4 stages of aerobic cellular respiration
glycolysis
pyruvate oxidation
Kreb’s/citric acid cycle
oxidative phosphorylation, ETC, and chemiosmosis
substrate-level phosphorylation
enzyme trasnfers phosphate group from substrate molecule to ADP instead of inorganic phosphate
in cellular respiration what happens to carbons
released as CO2
where does substrate level phosphorylation happen
as pyruvate is broken down to CO2
oxidative phosphorylation
NADH and FADH2 relay electrons extracted from food to ETC
cytochromes
electron carrier proteins that deliver electrons from ubiquinone to oxygen ho’s iron atom accepts donated electron
chemiosmosis
energy stored in hydrogen ion concentration gradient is released as they travel through membrane allowing for ATP synthesis
where does aerobic cellular respiration occur in prokaryotic organisms
cytoplasm or cell membrane
purpose of fermentation
rejuvenates NAD+ supply for glycolysis
facultative anaerobe
organisms that generate ATP with fermentation or respiration
what macromolecule provides the most energy and why
lipids/fatty acids because they provide acetyl CoA directly feeding the citric acid cycle
_______ stimulates cellular respiration and ______ inhibits it why
ADP/ATP/bc surplus of product (ATP) inhibits production through feedback inhibition
carbon fixation
initial incorporation of carbon into organic compounds
2 parts of photosynthesis
light reactions
calvin cycle
absorption spectrum
3 curves show the wavelengths of light best absorbed by three types of chloroplast pigments
action spectra
effectiveness of different wavelengths at providing energy for photosynthesis
what happens to chlorophyll when hit by light
chlorophyll absorbs photon of light and electron gets excited and jumps to a higher orbital providing higher potential energy
photosystem
reaction enter with light-harvesting complexes
light-harvesting complex
pigment molecules bound to proteins
reaction center
protein complex two special chlorophyll a molecules and a primary electron acceptor molecule
primary electron acceptor
molecule that receives the electron from a chlorophyll starting ETC
cyclic electron flow
electrons take path via only PSI cycling back from Fd to cytochrome complex and to chlorophyll (no NADPH or O2 release but ATP generated)
calvin cycle
anabolic process building sugars from small molecules and storing energy in bonds
carbon fixation
incorporation of CO2 by attachment to five carbon sugars that become unstable 6 carbon sugars and split to 2, 3 carbon sugars
reduction
3 carbon sugars recieve phosphate group from ATP and reduced by 2 electrons from NADPH storing more potential energy
regeneration
3 ATP used to rearrange 5 G3P into 3 RuBP
photorespiration
when not enough CO2 enzyme Rubisco combines 5c RuBP with O2 making 4c OAA and CO2
CAM plants
plants that open their stomata at night and close during day to consrve water and prevent the entrance of CO2/at night take up CO2 and incorporate into molecules
noncyclic electron flow in photosynthesis steps (8)
photon strikes chlorophyll exciting electron (PSII)
electron taken by primary electron acceptor
H2O broken via enzyme during photolysis releasing 2 electrons (replacing lost electrons in chlorophyll molecules) and O that combines with another O releasing O2
excited electron passes through PSII and PSI via ETC
electron fall produces energy from ATP synthesis
photon strikes chlorophyll exciting electron (PSI) and passing it on creating a hole that is filled by de-energized electrons that reach the end of first ETC
exciting electrons passed down second ETC through protein Fd
NADP+ reductase transfers electrons from Fd to NADP+ reducing to NADPH with 2 electrons
where does glycolysis occur
cytosol
what initial investment does glycolysis need
2 ATP
glycolysis flow chart
6c glucose → 2, 3c PGAL → 2, 3c pyruvate
net gain of ATP during glycolysis
2 ATP
pyruvate decarboxylation definition and flow chart as well as byproducts
process between glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle
3c pyruvate → 3c Acetyl + CoA → Acetyl CoA
CO2 and NAD+ → NADH
Kreb’s cycle/citric acid cycle location, flowchart, and byproducts
mitochondria matrix
2c Acetyl CoA + 4c oxaluacetic acid → 6c citric acid → 5c keto gluterate → 4c succinate → extra step → extra step → 4c oxaluacetic acid + →
CO2, NAD+ → NADH, ATP and FADH2
what happens to CoA
enzyme reused
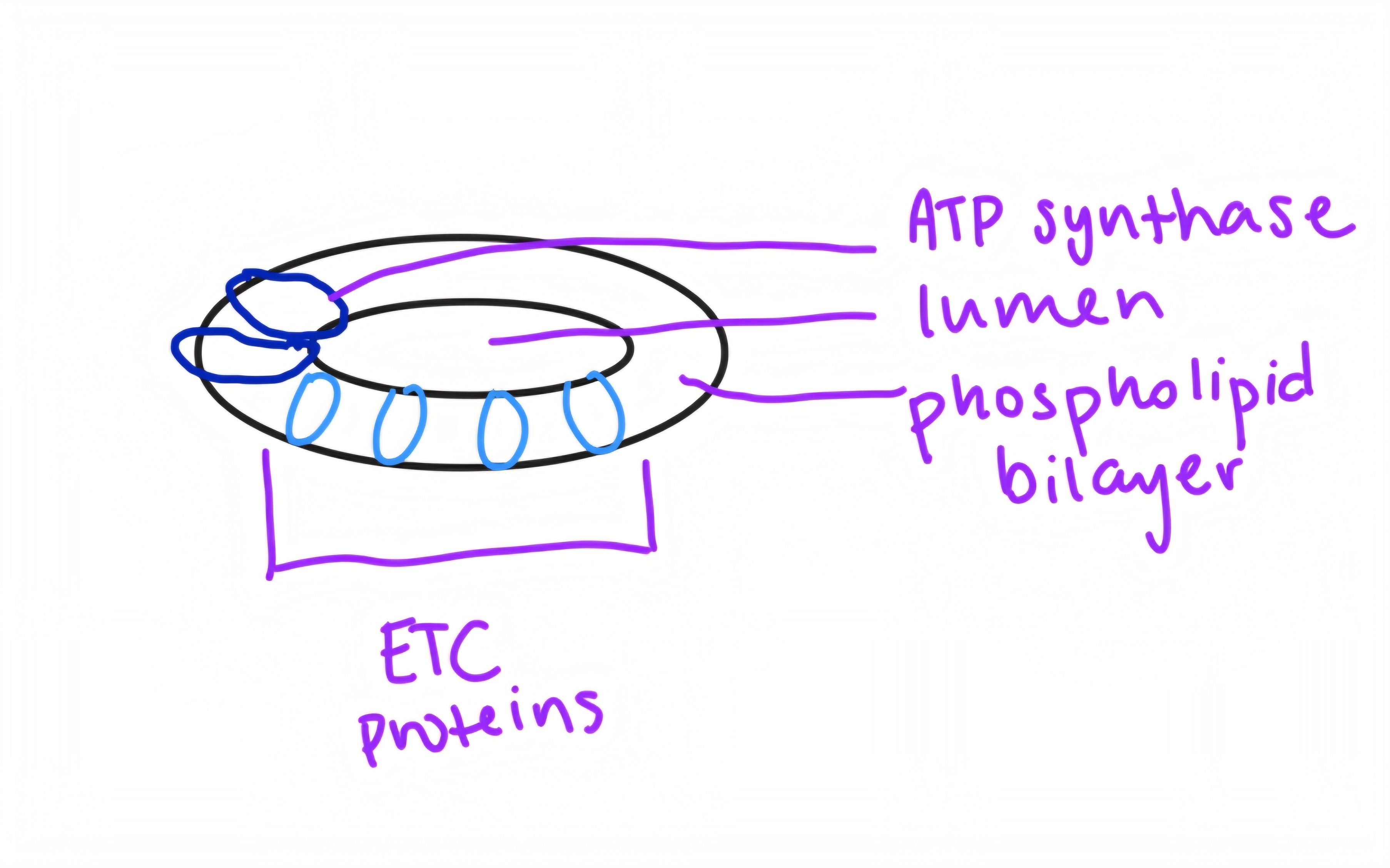
location of Electron Transport System
inner mitochondrial membrane
oxylated phosphorylation
ADP+P→ATP
fermentation flowchart and byproducts
glycolysis → pyruvate → 2c acetyldehyde (or just 2 lactate) → reduced to ethanol
| _________________/
NADH → NAD+ + electron/
CO2, ADP→ATP
photosynthesis equation and where it is taken up or released
6CO2+6H2O→C6H12O6+6O2
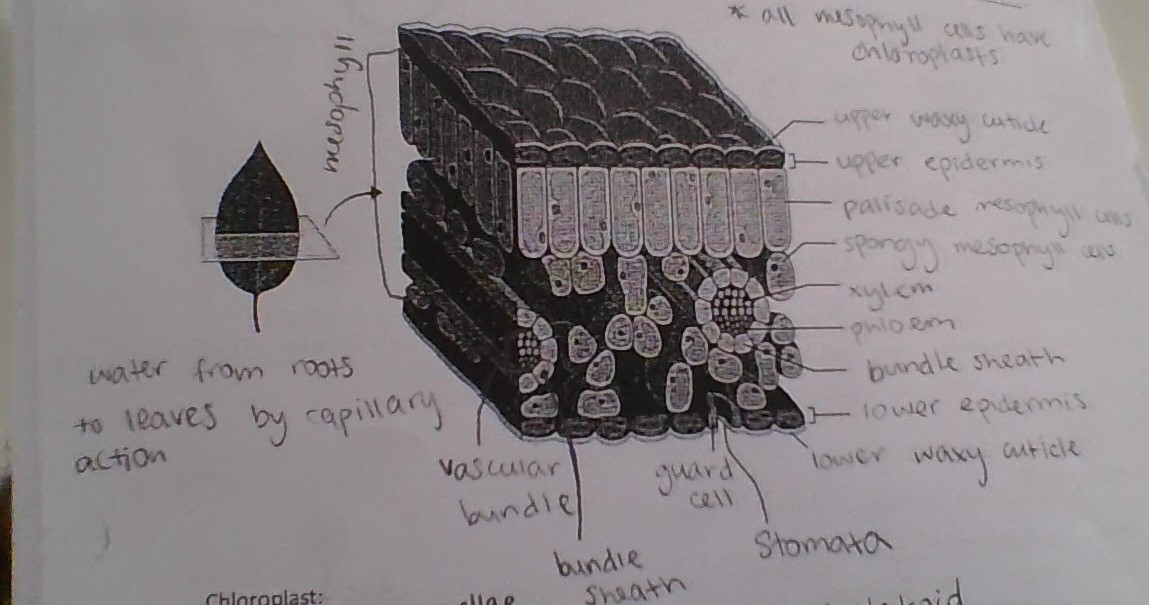
CO2 through stomata to leaves
H2O through roots through xylem tissue
C6H12O6 moved by phloem tissue
O2 released through stomata
central atom in chlorophyll
Magnesium (Mg)
primary pigment
chlorophyll a
accessory pigments
absorb different light and transfer energy to chlorophyll a
examples of accessory pigments
chlorphyll b
carotenoids
phycobilins
xanthophyll
2 photosynthesis steps
light dependent reaction and light independent reaction (Calvin Cycle)
light dependent reaction
converts light energy to ATP and NADH
Calvin Cycle/Light Independent Reaction
energy from ATP and NADPH to PGAL and NADH
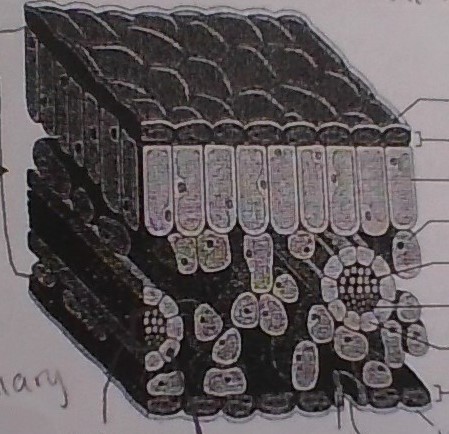
label
non-cyclic phosphorylation
normal photosynthesis with 2 PS
PSII→ETC(Qui,Cyt,Pc)→PSI→ETC(Fd, FNR)→NADPH
cyclic phosphorylation
when NADPH not produced due to lack of NADP+ electrons at the end of ETCI get sent back through maintaining H+ ion gradient and continuing ATP synthesis
PSI→ETC(Qui, Cyt, Pc)→PSII
label chloroplast
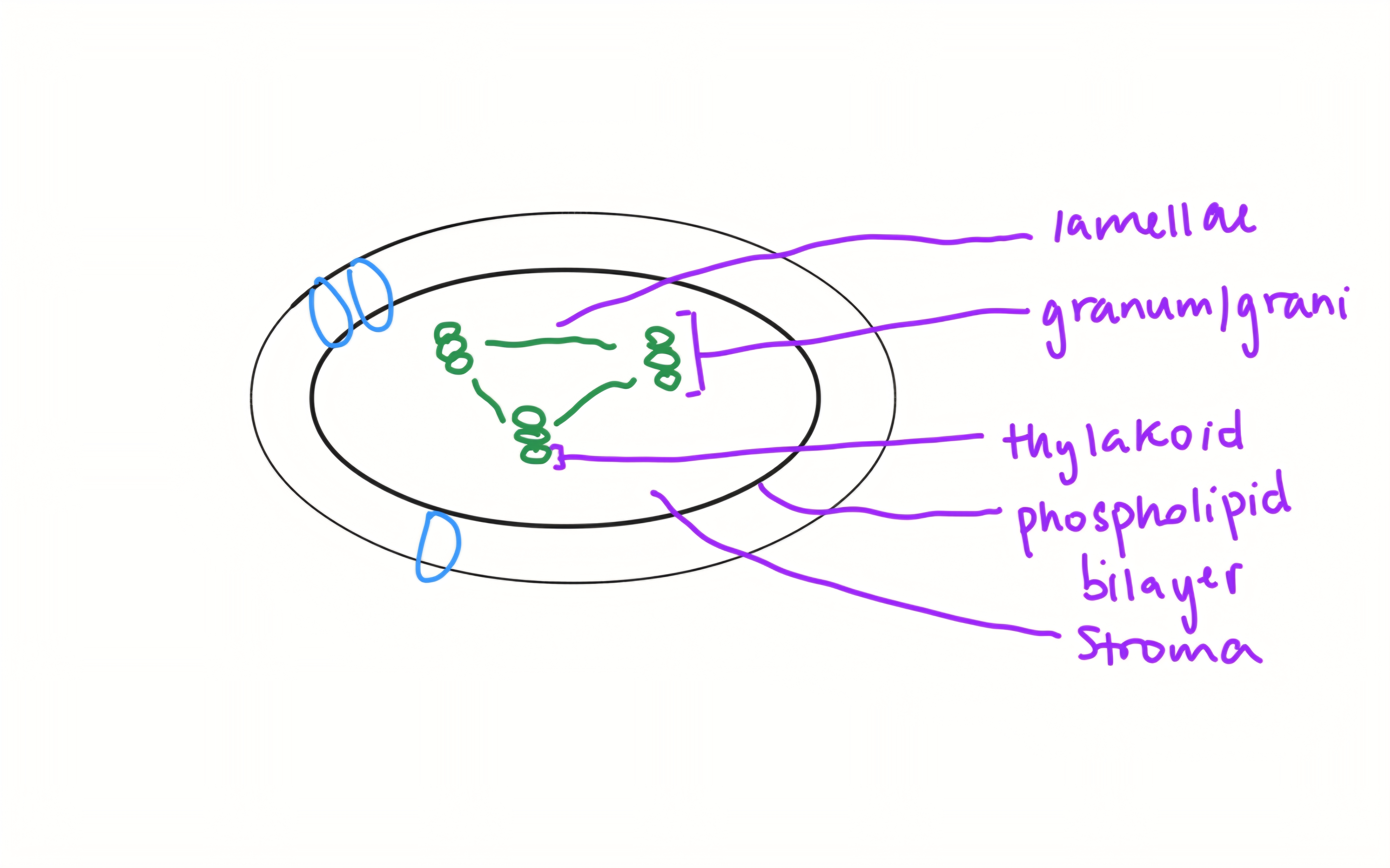
label thylakoid
photosystem
proteins that have chlorophyll embedded to allow for light absorption
enzyme complex
enzyme on PSII that uses light energy to split H2O into 2H+ 2electrons and O
H+ increases concentration
2electron go into PSII to replace excited electrons
O combined with O and released as O2
photolysis
light energy used to split H2O
photosynthesis steps (6)
PSII chlorophyll absorbs light and electrons in lipid head get excited and jump to protein in ETC 1 that pulls H+ into lumen
electron jumps to next protein pulling H+ into lumen
electron loses enery as it jumps
at PSI light absorbed and electrons excited and jump into ETC 2
electron reaches FnR (ferredoxin NADP reductase) which combines NADP with the electrons and to balance out takes up H+ making NADPH
electrons that travel down ETC 2 replaced with low energy electrons from PSII traveling down ETC 1
chemiosmosis
H+ ion concentration gradient causes H+ move down ATP synthase allowing for ADP+P→ATP
photophosphorylation
light energy used to add phosphate group to ADP making ATP
why do ETC proteins pull in H+
electrons from photosystems make proteins slightly negatively charged attracting positively charged H+ when electrons move one the H+ is released on the opposite side of the protein
which electrons replace electrons in PSI
low charge electrons from ETC 1
ETC 2 components
ferredoxin and ferredoxin NADP reductase
calvin cycle/light independent reaction
process occurs in stroma using CO2, ATP, and NADPH producing PGAL and then glucose
3 steps of calvin cycle
carbon fixation, reduction, regeneration
carbon fixation flow chart
5c molecule RuBP + 3 Rubisco carboxylase + 3 1c CO2 → 3 6c unstable intermediate → 6 3c PGA
reduction flow chart
6 3c PGA → 6 3c PGAL
NADPH → NADP+
regeneration
6 3c PGAL → 5 3c PGAL → ATP and 3 5c RuBP
1 3c PGAL → glucose
C3 plants
usual carbon fixation
C4 plants
additional step PEPcarboxylation in addition to usual carbon fixation
PEPcarboxylation and flow chart
done by pepcarboxylase
3c PEP + CO2 → 4c OAA → 4c malate
where is PEPcarboxylation done
in mesophyl cells
CAM plants
make crassulacean acid and break down for CO2
temporal separation of carbon fixation
stomata open during night
chemiosynthesis
H2S and H2O is broken down (alternate pathway to make organic molecules)
aerobe
needs O2
Anaerobe
no need for O2
facultative
can survive for shrot period of exposure
obligate
need to exposed at all time
what kind of molecule is pyruvate
acid
cellular respiration step by step (14)
in cytosol 6c glucose is broken down to 2 3c PGAL with the help of 2 ATP molecules
as 3c PGAL is oxidized to 3c pyruvate NAD+ picks up the electron and makes NADH and 2 ATP are produced with the excess energy from the oxidation (glycolysis)
3c pyruvate moved to mitochondria matrix
enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase complex removes a carbon from 3c pyruvate and it is released as CO2 and NAD+ is reduced to NADH
the 2c Acetyl product is combined with Coenzyme A creating Acetyl CoA (pyruvate decarboxylation)
2c Acetyl CoA is combined with 4c OAA making 6c Citric Acid
CoA leaves to be reused with Acetyl in pyruvate decarboxylation
6c Citric Acid oxidized to 5c ketoglutarate with 1 carbon released as CO2 and NAD+ reduced to NADH
5c ketogluterate oxdized to 4c succinate with 1 carbon released as CO2 and NAD+ reduced to NADH
4c succinate is oxidized to make 4c OAA which is used again combining with 2c acetyl reducing FAD to FADH2 and phosphorylating ADP to ATP (Kreb’s cycle)
electrons from FADH2 and NADH travel down ETC in the inner mitochondrial membrane
FAD and NAD+ go back to Kreb’s cycle
as electrons travel H+ pumped into intermembrane space (ETC)
due to gradient H+ pass through ATP synthase generating ATP (chemiosmosis)