Regression Methods Exam 1 Chapter 3
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the form of multiple regression model?
y = B0 + B1×1 + B2×2 + … + Bnxn+ e
Is this a valid equation for multiple regression? y = B0 + b1x + b2x² + B3x² + e
Yes, we can say x1 = x, x2 = x², x3 = x³
Is this a valid equation for multiple regression? y = B0 + b1×1 + b2×2 + B12×1×2 + e
Yes, we can have interaction effects
If we have a model with k = 100 features and choose to have interactions (2 per term). How many two-factor interactions?
100 C 2
True or False? Any regression model that is linear in parameters is a linear regression model, regardless of the shape of the surface that it generates.
True
What is the expected value and variance of the error in multiple regression?
E(e) = 0, Var(e) = sigma²
In the regressor matrix, what is each column vs each row?
The columns are different features. The rows are observations. A cell is the value of the feature in a certain observation
What is OLS estimating in multiple linear regression?
B0, B1, … Bk parameters that minimize S (error across all n)
Explain this formula: y = XB + e
Matrix notation of Least Squares where X is an n x p matrix (n rows, p cols)
y is an n x 1 matrix (n rows, 1 col)
B is (k + 1) x 1 = p x 1 matrix
epsilon (e) = n x 1
(p x 1)(n x p) = (n x 1) matrix
What is formula for B(^)?
(X’X)^-1X’y
What is Hat matrix?
X(X’X)^-1X’
What is special about Hat matrix?
H² = H Idempotent
What is the desired case for columns? (X1, X2)
X1’X2 = 0 or in other words, X1 orthog to X2
What is the estimated variance of (bhat) known as?
Mean squared error
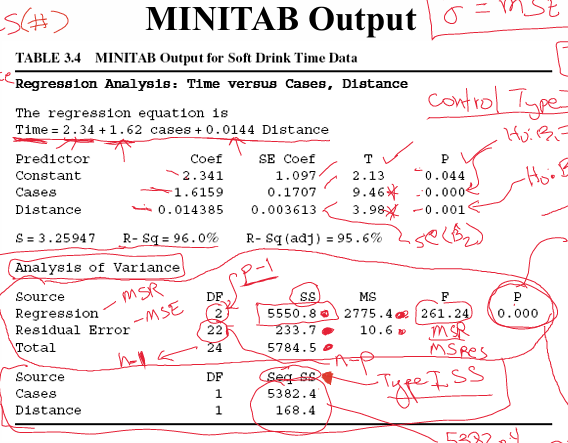
In this minitab output? What are the type 1 p-values? What are these testing?
0.044, 0.000, 0.001
They’re testing H0, B1 = 0, B1 ≠ 0; B2 = 0,, B2 ≠ 0
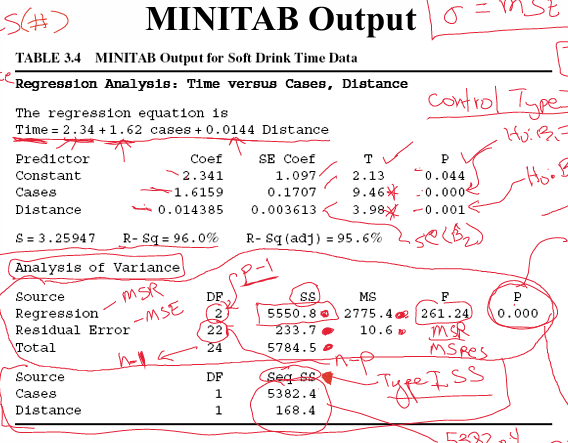
In this minitab output, what is the result of the global F-Test p-value? What does this mean?
p = 0.000; this means that there is at least 1 parameter that ≠ 0. At least one contributes to explaining the variance H0: B1 = B2 = 0; Ha: at least one Bi ≠ 0
What is true about least squares estimators in terms of properties?
E(B(hat) = B => B(hat) is unbiased estimator of B
Cov(B(hat)) = sigma² (X’X)^-1
What is true about estimator of sigma²?
This is model dependant estimator — changing model will change estimate of sigma² (Why? —> depends on SSres/(n - p))
What is true about scatter diagrams in multiple regression?
Little value in multiple regression because plots are misleading; may be interdependency b/w regressors that masks relationship b/w xi and y
What questions do we need to ask when we estimate parameters in the model?
What is overall adequacy of the model?
What specific regressors seem important?
What is the Test for Significance of Regression?
This is the Global F-Test
We’re testing H0: B1 = B2 = … = Bk = 0
Ha: Bj ≠ 0 for at least one j
What are the degrees of freedom for ANOVA for Multiple Regression?
Regression DF = k
Residual DF = n - k - 1
Total = n -1
Interpret F0 = MSr/MSres intuitively
Signal/Noise. Is Signal > Noise by a significant amount? Yes —> more likely to reject
Is R² different for multiple regression?
No! It’s still 1 - SSRes/SStotal or SSReg/SStotal
What is true about adjusted R²?
R² but penalizes for added terms that aren’t significant:
1 - SSres/(n - p)/SSt/(n - 1), penalizes for large p!
Should use this as a metric for comparing models
What is a Type 3 test for Individual Regressors?
Contribution of Xj given other Xs are already included in the model
H0: Bj = 0
Ha: Bj ≠ 0
What is the Extra Sums of Squares method?
Method for testing hypotheses on individual model parameters or group of parameters
“Partial F Test”
What is the reduced model?
Consists of response and Xs not set = to 0 by H0. Model w/o the Xs we’re testing
Model under H0 (these Xs that w'e’re testing are not significant)
What is the full model?
Model that contains B0 and all k regressors
What do we calculate in extra sums of squares?
SSR(Full | Reduced) = Regression sums of squared of full given reduced = SSR(full) - SSR(Reduced)
How much SSR did we gain by adding back the Xs we’re testing?
What is true if columns in X are orthogonal? X1 orth X2
The sums of squares due to B2 is free of any dependence on regressors in X1
If we want to remove a regressor, we DONT have to refit the model, we can just remove it
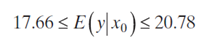
Interpret this Confidence Interval estimation of the mean response
95% confident that the the interval contains the true delivery time
What is true about the CI on mean response in measuring quality of regression model?
Can be used to compare competing models: If the width of CI with 2 regressors X1 and X2 is less than the width of CI with only X1 => Adding X2 improved our model because we’re more precise with 95% confidence.
Change in the length of interval depends on location of point in the x space
Further the point is from centroid of the x space, the greater the difference will be in lengths of the two CIs (more variance further from centroid)
What is the point of the simultaneous CIs?
Have joint confidence across all parameters
What is true about standardizing regression coefficients?
These standardized regression coeffs are dimensionless
common method = unit normal scaling
They help when Xs are in different units
Scaled regressors and scaled response have sample mean = 0 and sample var = 1
What is true about multicollinearity?
Near-Linear dependence among Xs (regressors)
=> Singular X’X, non invertible (no solution for B1)
Correlation among Xs
What is special about diagonal elements of inverse of X’X in correlation form?
These diagonal values are Variance Inflation Factors (VIFs)
What is true about VIF?
VIFj = 1/ (1-Rj²)
High Rj => High VIF => xj is highly correlated with another regressor
Why might regression coeffs have wrong sign?
Range of some regressors is too small
Important regressors missed
Multicollinearity! (There’s a chance that B1(hat) will be < 0 )
What is difficult about multiple testing?
With so many regressors, it’s very likely that 1 will have a low p-value just by chance even though it’s not truly low (type 1 error)
What is Family-Wise Error Rate?
Probability of making >= 1 Type 1 Error when conducting m hypothesis tests
What is bouferroni’s alpha* (FWER)?
original alpha / m hypothesis tests
What is true about bouferroni vs holme’s method of FWER?
bouferroni is more conservative (leads to less rejections)
Holme’s leads to more rejections
Holm is a better choice
What is the benefit of FDR (False Discovery Rate)?
It is better when we have a lot of m’s => lots of ms make other methods of adjusting alpha very conservative!
Controls fraction of candidates in set that are really false rejections (number of false rejections/total number of rejections)