Photosynthesis and Light Reactions: Key Concepts and Processes in Biology
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What is photosynthesis
The process by which a cell converts light energy into chemical energy
Carotene or xanthophyll
these are word for pigments
What is the primary pigment in plants
chlorophyll
What coenzyme carries hydrogen in light reaction to dark reaction
NADP
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food
Heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food.
Photon
a particle of light/ energy
What is the relationship between photosynthesis and Cellular respiration
The products of one are the reactants of the other
What is purpose of photosynthesis
to make glucose
What are the three molecules that light reactions produce?
Carbon and NADP which is needed for the dark reaction. The product is oxygen.
What does the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll demonstrate
It tells us that green is not used in photo synthesis
Why is light reaction essential for dark reactions
Its products provide energy for the second reaction
what is a chemoautotroph
an organism that derives energy from the oxidation of inorganic compounds/ chemicals
Photoautotrophs
Organisms that use light as a source of energy to synthesize organic substances.
Six parts of chloroplast
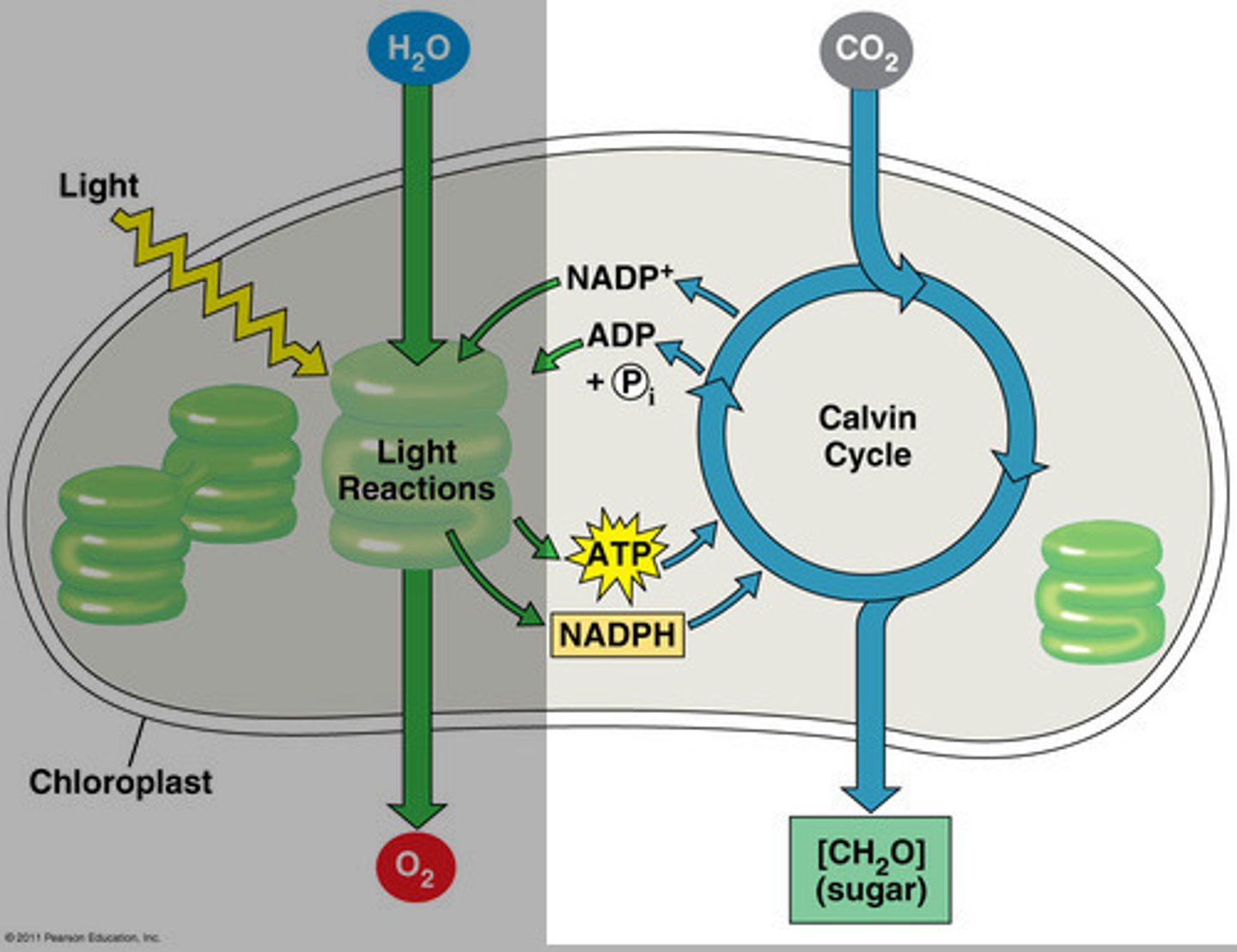
What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis
H20+CO2 ----light O2+H2O+ glucose
What are the two main differences between light and dark reactions
One happens in the thylakoids and one happens the stroma
Where does the light reaction take place
thylakoid
Where does the dark reaction take place
stroma
What is oxidized in light reaction
Water (H2O)
Reduced in Calvin cycle
carbon dioxide (CO2)
What is another word for Calvin cycle
Dark reaction
carries H and electrons from the light reactions to the Calvin cycle
NADP+
What food is produced in photosynthesis
glucose c6 h12 o6
What is the molecular formula for photosynthesis
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
What is the ultimate purpose of the light reaction
To create NADPH and ATP
How many PGAL molecules are needed to make a glucose molecule
2
What is carbonfixaction
its when you take an inorganic carbon and add an organic molecule
What reaction center is responsible for making oxygen
p680/ Photosystem 2
what is the difference between P680 and P700
P680: Drives the light-dependent reactions from water to the plastoquinone pool.
P700: Drives final electron transfer to NADP⁺.
How many ATP's are needed for a Dark Reaction?
18
What is RuBP
A 5-carbon sugar in the Calvin cycle that combines with CO₂ (with the help of Rubisco) to start carbon fixation; it is regenerated so the cycle can continue.
it is also a coenzyme
How many molecules of pgal and how many ATPs are needed to make RuBP
10 PGAL 6 ATP
Source of H and electrons in glucose
NADPH
Source of O atoms in glucose
carbon dioxide
where O atoms from water end up
Oxygen
Oxidized in Calvin Cycle
NADPH
Reduced in light reactions
NADP+
Supplies energy for Calvin Cycle
ATP NADPH
where C and O atoms in carbon dioxide end up
glucose
Recycled form Calvin cycle to make ATP
ADP+P
Supplies energy to light reactions
light/photons
Gas produced by the reactions in the thylakoids
Oxygen (O2)
Gas consumed by the reactions in the stroma
carbon dioxide (CO2)
Source of carbon for carbon fixation
carbon dioxide (CO2)
source of H for the Calvin cycle
NADPH
Picks up energized electrons from reactions in the thylakoids
NADP+