Systems: digestive system process + organs
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U (Secours) - rest of digestive system hyperdoc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
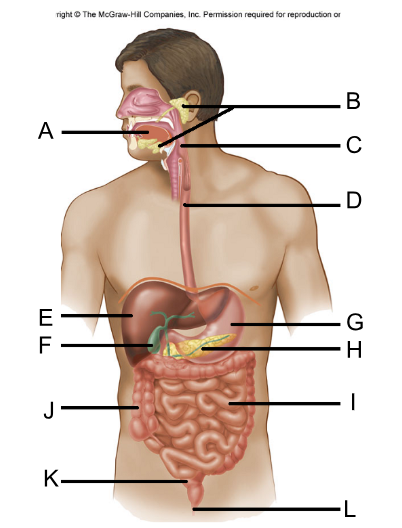
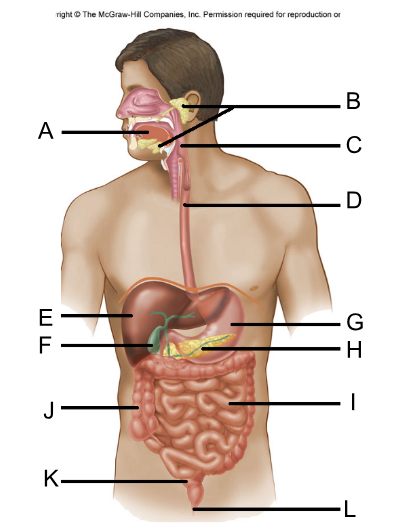
Label the digestive system
A. Tongue
B. Salivary Glands (3)
C. Pharynx
D. Esophagus
E. Liver
F. Gallbladder
G. Stomach
H. Pancreas
I. Small Intestine
J. Colon/Large Intestine
K. Rectum
L. Anus
Accessory organs
organs that are used in digestion but through which food does NOT pass
5 Accessory Organs
Tongue
Salivary Glands
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
4 Stages of food digestion
Ingestion: introduction of food into body
Digestion: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into molecules that are small enough to pass through the cell membrane
Absorption: transport of digestion products from the digestive → circulatory system (which distributes to body)
Elimination: excretion of undigested solids
Digestion begins in the ______
mouth
Role of the teeth (and tongue)
help with mechanical digestion; break the food down into smaller pieces = greater surface area for chemical digestion
Enzyme (+ its role)
a protein that acts as a catalyst; it speeds up the chemical reaction
✄ acts like metabolic scissors to break bonds
3 roles of saliva
Lubricates food
Salivary amylase helps digest starches
Dissolves water-soluble food particles
Salivary amylase
an enzyme in the saliva, produced by salivary glands; it breaks down starches only
The esophagus moves food along through wave-like ________ called _________
contractions, peristalsis
The _________ sphincter separates the esophagus and the stomach, while the ________ sphincter separates the stomach and the _________.
gastroesophageal, pyloric, duodenum
When the gastroesophageal sphincter relaxes at the wrong time, this causes ____ _____
Acid Reflux (heart burn)
4 Layers of the Stomach
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscular (composed of 3 layers)
Serosa (outermost layer)
the 3 muscular layers of the stomach are unique because?
they go in different directions - allows for better movement
Types of digestion that occur in the stomach
Both mechanical digestion(contraction of muscles - churning) and the chemical digestion of proteins (pepsin)
Pepsin
An enzyme present in gastric juices that digests proteins
The mucus of the stomach (mucosa layer) _______ the walls of the stomach from its ______ environment
protects, acidic
Hydrochloric Acid
the acid that breaks food into smaller pieces in the stomach
⇨ HCl only breaks down protein
HCl acid is regulated by the ___________ ________
Gastrin Hormone

Nothing is absorbed by the stomach EXCEPT _________
alcohol
The small intestine digests ____ and ________, along with any remaining undigested ______
lipids, carbohydrates, proteins
In addition to digestion, the small intestine must _______ these subunits so that they enter the __________.
ABSORB, bloodstream
Structural features of the small intestine (4)
Length (longest part of the digestive system!)
Interior is folded
Folds are covered in villi
Villi are covered in microvilli
The structure of the small intestine is linked to its function in that it ________ _________ _____
increases surface area
3 parts of the small intestine
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
The ________ is connected to the pancreas and liver (ie. they empty out into it)
Duodenum
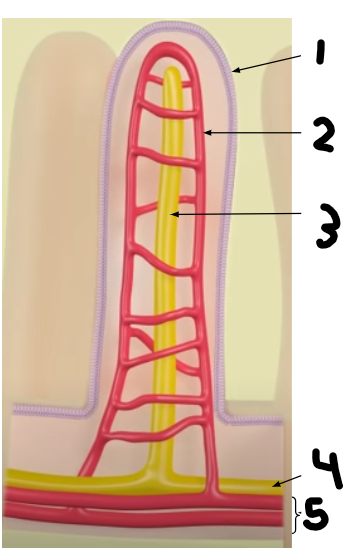
label this villus
Endothelial Cell
Capillary
Lacteal Vessel
Lymphatic Vessels
Blood Vessels
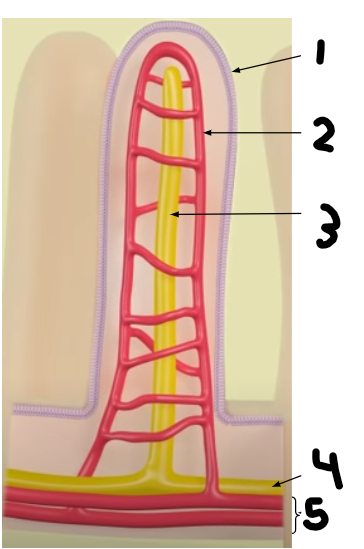
The lacteal vessels, which are connected to the _______ system, absorb primarily the subunits ________+____ _____
lymphatic, glycerol, fatty acids
The capillaries, which are connected to the __________ system, absorb primarily the subunits ________, ______ ______.
circulatory, monosaccharides (glucose), amino acids
Bolus vs Chyme
Bolus: food + saliva
Chyme: food + stomach juice
The pancreas produces _________ _____, which contains _________ and ____________.
pancreatic juice, enzymes, bicarbonate
3 enzymes produced by the pancreas + what they break down
Pancreatic Amylase: starch
Trypsin: undigested proteins
Lipase: lipids
☆ these enzymes are used by the small intestine
Bicarbonate function
neutralizes acid from the chyme
Function of the Liver
Produces bile, which emulsifies large fat globules into small fat droplets that can be chemically digested by the enzymes produced by the pancreas
⇨ also filters blood
Gallbladder function
attached to the liver, it stores bile and releases it when fatty food enters the duodenum
The small intestine’s 3 main absorption methods
Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Active Transport
Diffusion in the small intestine
movement of particles from high concentration (inside) → lower concentration (the villi)
Facilitated Diffusion in the small intestine
type of diffusion that requires specialized membrane-embedded proteins to bind to and transport molecules across the membrane
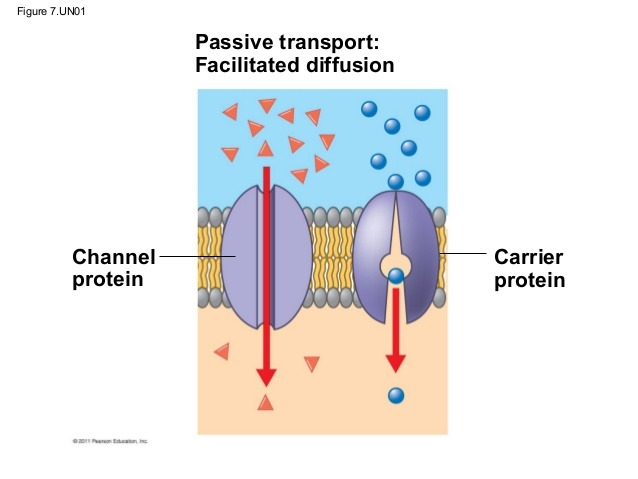
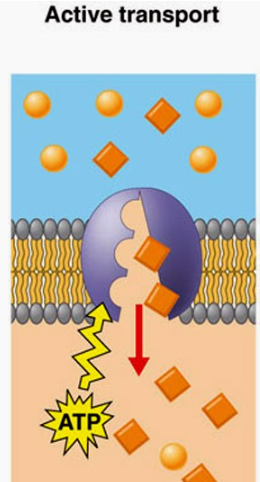
Active Diffusion in the small intestine
type of diffusion that requires energy to transport the material across the membrane
The colon/large intestine are part of the ___________ and ___________ stages of food digestion
absorption, elimination
The large intestine ______ digest food. However, it can continue to absorb _______.
CANNOT, water
The remaining undigested material (feces) is made up of:
water (75%)
bacterial biomass
proteins
carbohydrates or undigested plant matter (fiber)
fats (2-15%)
Bacteria in the colon produces _________ ___ and __, but can also cause flatulence by __________ ___.
vitamins, A, K, releasing gas
Rectum
fecal matter storage
Anus
eliminates waste by excreting it through the internal (involuntary) and external (voluntary) anal sphincters