NPB101: Neurophysiology Part 4
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Detecting Stimuli
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
DISCLAIMER: Receptor is used here in this Part 4 in regards to a sensory system is that it cangrab onto the stimulus whether its light waves, sound waves, chemicals, becaus ethey are the cell types that can do transduction
In PREVIOUS parts its used as: bind to a neurotransmitter and they are little proteins that are on the cell & bind to specific chemical
Receptors
NS
transduces and filters things out
Transduction
converting a stimuli into an electrical signal
T/F: even if you don’t have a receptor you can still detect stimulus and transduce the stimulus
False, you need a receptor to detect stimulus and transduce the stimulus
When the neuron has a ____ receptor, it detects the receptor and ___ the ____ potential
special, changes, membrane
T/F: it has to be a neuron that has a special receptor to detect the receptor and have membrane potential
False, it can also be a sensory cell not a neuron
Membrane potential change (Receptor Potential)
when stimulus is detected it changes the membrane potential and when we have a change in the membrane potential that change is from rest & is called a graded potential well specifically a receptor potential
Receptor Potential
if its a neuron it can cause a neuron to fire an AP
Majority of our sensory systems
when we get a receptor potential most of them cause the cell to depolarize & fire off an AP w/exception of our eyes & brain to hyperpolarize
T/F: Our Sensory Systems can only depolarize
False, our sensory systems can depolarize & hyperpolarize
Which of the following statements about detecting stimuli and/or sensory systems is TRUE?
A. Sensory receptors cells always depolarize in response to stimuli
B. Stimuli are always consciously perceived before a
response is elicited
C. In receptor neurons, strong stimuli causes large APs,
while small stimuli induce small APs
D. Sensory receptors must convert the“form” of a stimulus
into a change in membrane potential.
E. ALL of the above are TRUE statements.
A: no it also hyperpolarizes
B: No you cant feel all the stimuli inside your body
C: No because AP are stereotyped & an AP will set off as long as it passes threshold
D. it has to transduce so YES
Components of Sensory Systems
Receptor Cells
Pathways
Nervous Tissue
Receptor Cells
“capture” / detect the stimulus & some can be neurons or cells
Pathways (Afferent)
Carry the info to a central processor (spinal cord or even brainstem)
Nervous Tissue
filter (thalamus filters) & process the sensory input (exception: taste & olfactory) (can be processes in different spots)
Receptor neuron
receive the stimulus
T/F: In some instances the neuron will fire AP (depolarize)
False, the neuron will fire AP in MOST instances which is our main focus
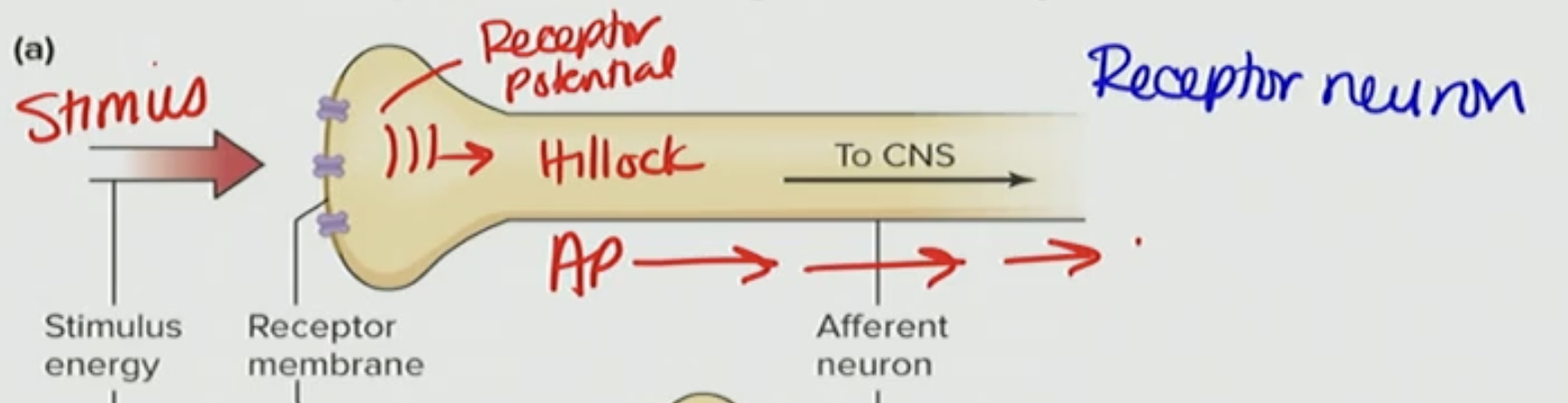
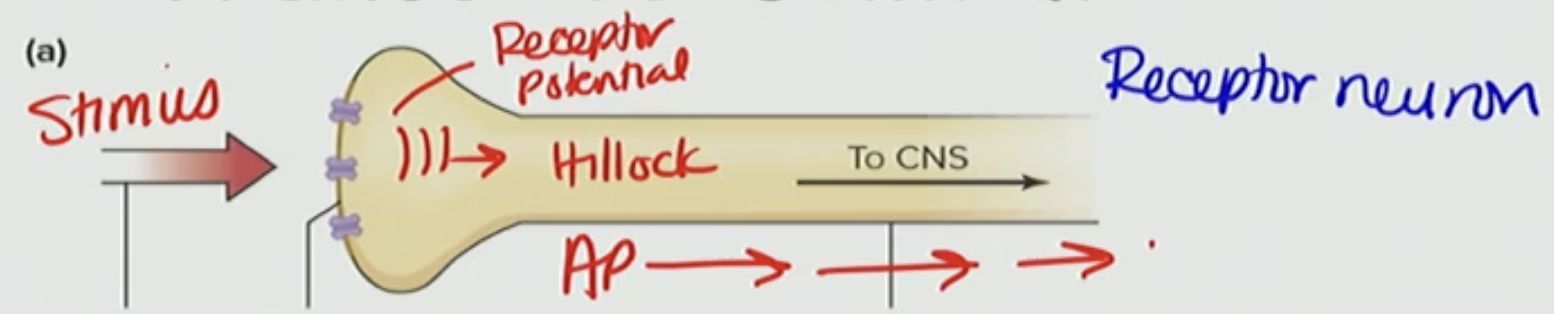
Explain what is occurring here
receptor potential occurring on the axon and spreads to the axon hillock that creates and AP and then it regenerates
Neuron
carrying the info and fire the AP
Receptor Cell
Receptor cell receive stimulus and the cell changes membrane potential like depolarizing and it affects the release of neurotransmitter
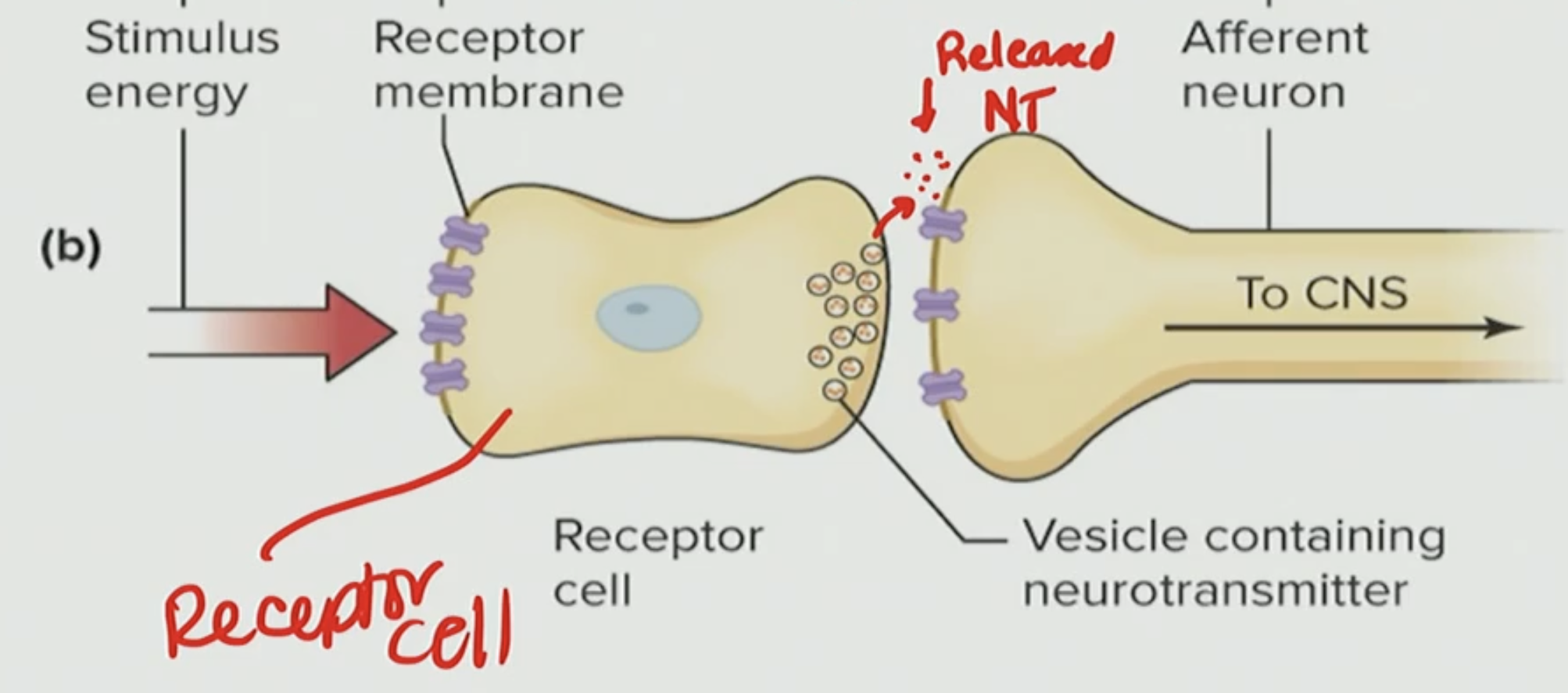
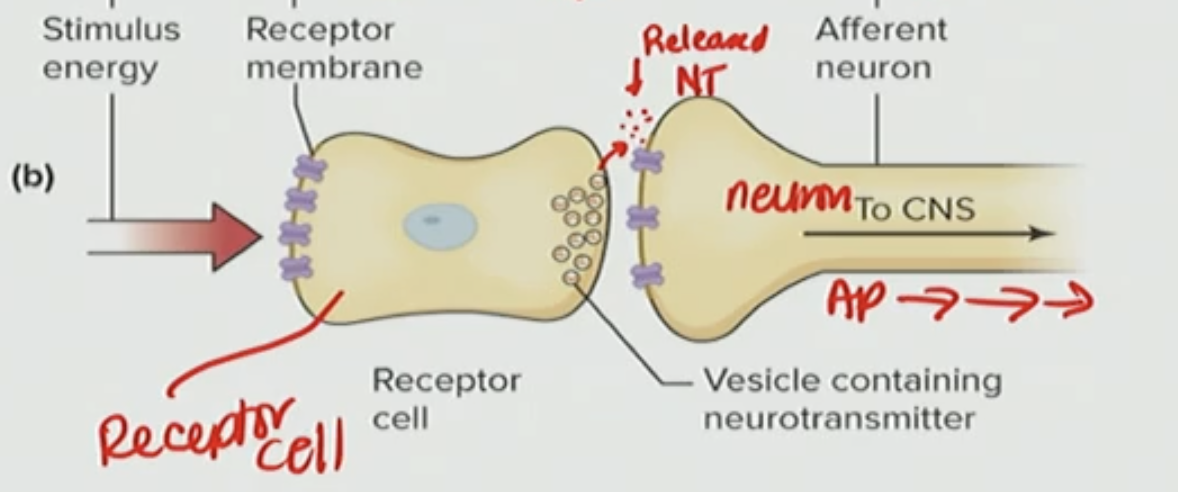
What is the neuron doing here
the neuron is firing the AP
Stimuli that are transduced by Non-receptor cells
Pancreatic B-cells
GI endocrine
The B-cell is in the ____ & produces ____
pancreas, insulin
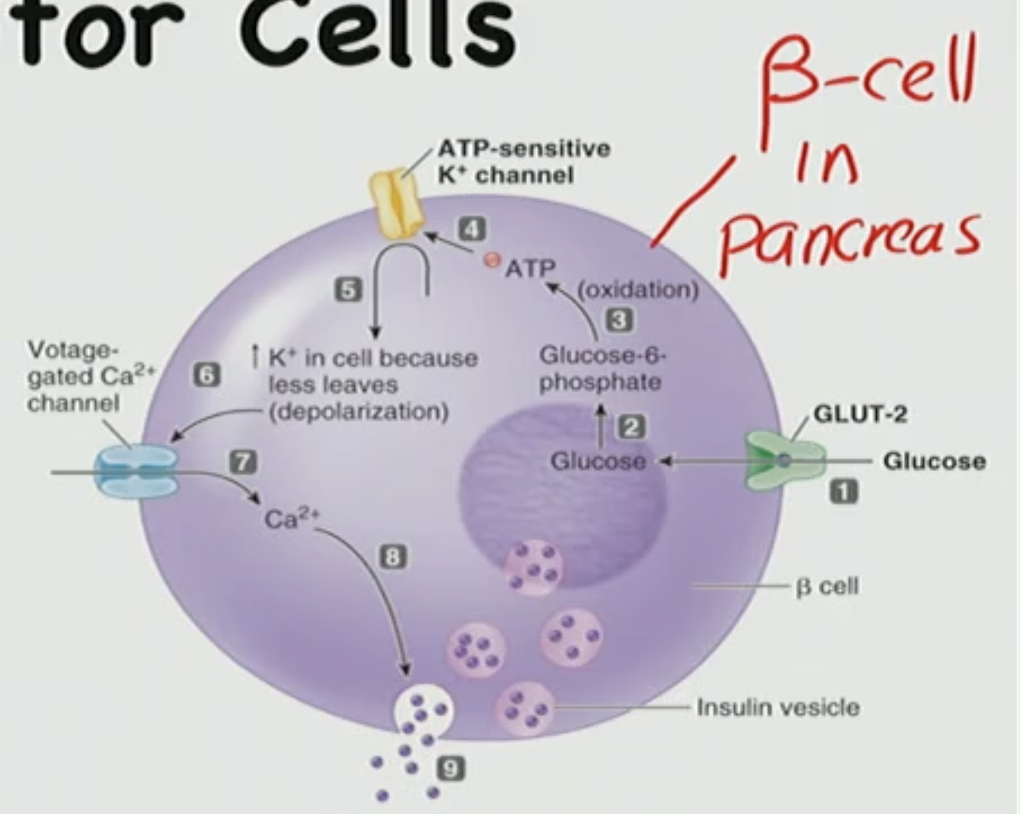
What is happening here
The beta cell is sitting in the pancreas & blood flows to it and the pancreas will grab glucose out of the bloodstream & the beta cell detects the glucose coming into it & changes the amount of insulin it secretes