Government and Fiscal Policy
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Government Purchases (G):
government expenditures on currently produced goods and services and capital goods. (Government Investment are around 1/6 of G in the US
Transfer Payments (TR):
Payments made to individuals for which the government does not receive current goods or services in exchange (Social Security, military and civil service pensions, unemployment insurance, Medicare
Net Interest Payment
Interest Paid to the holders of government bonds less
the interest received by the government
The Government revenues come from _____
TAXES.
Personal Taxes:
Tax increases: Biggest jump during World War II, Clinton in deficit-reconstruction effort
Tax cuts: Kennedy Johnson 1964, Reagan 1981, Bush early 2000s
Contributions for Social Insurance
usually are levied as fixed percentage of a worker’s salary
up to a ceiling (increases both in the contribution rate and in the ceiling)
Taxes on production and imports
Sales taxes declined in WWII and then stable
Corporate taxes (on profits)
High during WWII and Korean war
Fiscal Policy is the use of
government spending G and taxes T
The objective of Fiscal Policy is to
stabilize the economy
Governments can have:
Output targets, Price Targets, Unemployment Targets
Stabilizing the economy means
moving the economy towards targets
Fiscal policy would be the
manipulation of G and T to move the economy towards
Y*. (Assumes government knows where Y* is - we will discuss other drawbacks to fiscal policy later in the course).
Government Budget Deficits
the actual budget deficit in the current period
Deficit =
outlays - tax revenues = G (Government Purchases) + Tr(Transfer Payments) Interest - T (Transfer)
Primary Government Budget Deficits
excludes net interests from gov outlays
Primary Deficit =
(outlays – interest) – tax revenues = G (Government Purchases) + Tr (Transfer Payments) - T (Transfer)
Transfer Revenues =
T^0 + TnY

Transfers =
= Tr^0 - gY
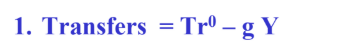
When Y ______, Taxes ______(more earnings in economy)
increases, increases
When Y______, Transfers _____
increases, fall (less people on welfare)
Actual Government Deficits

T^0 =
Tr^0 = Interest = 0
Automatic stabilizers:
fiscal policies that work without government action to stabilize economic cycles.
Side Effect of automatic stabilizers is
government budget deficits tend to increase in recessions!
Structural Budget Deficits
G - (Tn + g)Y*
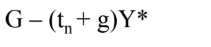
Cyclical Deficits:
Actual Deficits - Structural Deficits
Deficits are countercyclical!
(They rise when Y(income) falls and fall
when Y(income) rises)
What dampens the effects of consumption over the business cycle
Welfare Payments, Unemployment Insurance, and Tax System
T does what when times are good
it goes up
G/Tr does what when times are bad
goes down (welfare payments)
Given Automatic Stabilizers (and potentially proactive governmental fiscal
policies), cyclical deficits
seem to be an inherent part of our economy.
Government Debt (B)
the total value of government bonds outstanding
at any particular time.
government deficit is a
flow variable
government debt is a
stock variable
A given year deficit = new borrowing that the government must do
= change in the debt that year
Should Governments Try to Prevent Deficits.
it may be bad to have policies requiring governments to eliminate all deficits,
but there may be some benefits from eliminating structural deficits.
Consumption G
Governments can provide services that may be inefficiently provided in private sector
(i.e., police protection, parks, post office, etc).
Investment G: Physical Capital
Governments can provide investment that is used as an input into other production
(i.e., highway and transportation infrastructure, bridges, enforce property rights).
Investment G: Training and Education
Governments can train the work force
(i e student loan programs public education state colleges etc) (i.e., student loan programs, public education, state colleges, etc).
Infrastructure G
is government purchases of capital goods whose benefits arrive after the year of purchase.
Education G
includes public schools and public grants to students at private schools.
Argument that Public Debt will be a burden for Future generations

Argument that Public Debt will not be a burden for Future generations

Ricardian Equivalence:
Theory that states that consumers behavior is equivalent
regardless if the government finances G through increased taxes or through
increased debt.
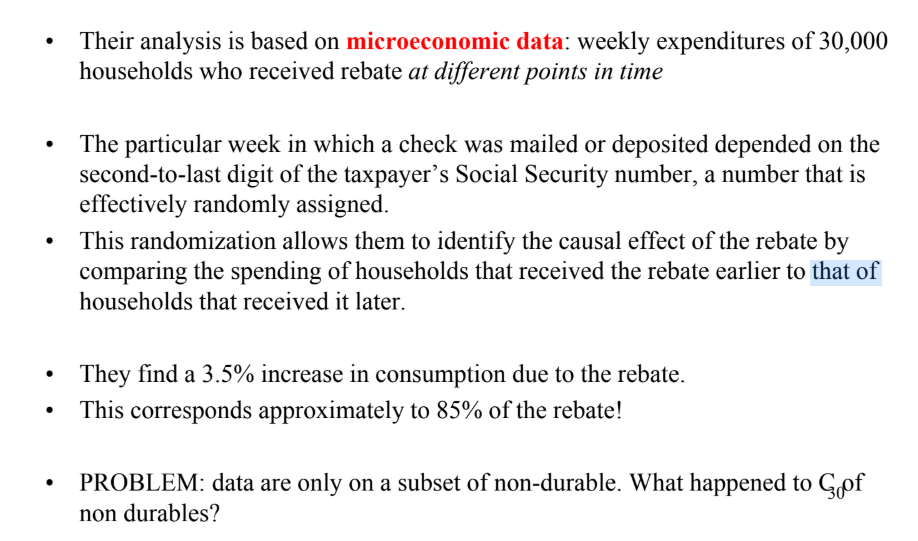
Martin Feldstein claims
that the tax rebate was a flop!

Christian Broda and Johnatan Parker claim
that the tax rebate was successful!
US Social Security is largely pay-as-you-go system
most of the payroll taxes
that workers and employers pay go directly to retirees and other beneficiaries
Average tax rate
total amount of taxes paid by a person divided by the
person’s before-tax income
Marginal tax rate
fraction of an additional dollar of income that must be paid in taxes