CMB1004-L22: acids, bases and buffers
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the dissociation equation for water?
2H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + OH⁻
Water dissociates into hydronium (H₃O⁺) and hydroxide (OH⁻) ions.
how is a buffer prepared
can be prepared in 2 ways:
mixing a large volume of a weak acid with its conjugate base - eg acetic acid and acetate ion
making a large volume of weak base with its conjugate acid- eg ammonia and ammonium ion
Why is the concentration of water treated as a constant in aqueous solutions?
Water is present in large excess in almost all solutions, so its concentration ([H₂O]) does not change significantly during reactions.
What is the water dissociation constant (Kw)?
Kw = [H⁺][OH⁻] = 1 × 10⁻¹⁴ at 25°C
This constant represents the equilibrium between water dissociation into hydronium and hydroxide ions.
What is the definition of an acid and a base?
Acid: A proton (H⁺) donor.
Base: A proton (H⁺) acceptor or hydroxide (OH⁻) donor.
How is pH calculated?
pH = -log₁₀[H⁺]
pH measures the acidity of a solution, based on the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺).
What is a buffer?
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
Formed by mixing a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
How do buffers work when a strong base is added?
The weak acid in the buffer reacts with OH⁻ (from the strong base), consuming the hydroxide and only slightly changing the pH.
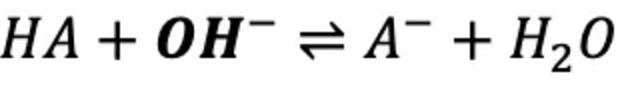
How do buffers work when a strong acid is added?
The conjugate base in the buffer reacts with H⁺ (from the strong acid), consuming the hydronium ion and only slightly changing the pH.
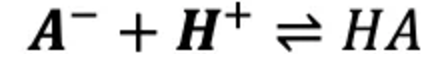
What is Ka and what does it represent?
Ka is the acid dissociation constant, representing the equilibrium between a weak acid (HA) and its conjugate base (A⁻).
Ka = [H⁺][A⁻] / [HA]
A higher Ka indicates a stronger acid.
What is pKa and how is it related to Ka?
pKa = -log₁₀Ka
pKa expresses the strength of an acid; lower pKa means a stronger acid.
What does pKa tell us about an acid?
If pKa < 3, the acid is strong.
If 3 < pKa < 7, the acid is weak.
If pKa > 7, the substance is a weak base.
How is pKa used in the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is used to calculate the pH of a buffer solution.
pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA])
pKa helps predict the pH based on the ratio of the conjugate base ([A⁻]) to the weak acid ([HA]).
What is the carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffer system?
The system involves the equilibrium:
H₂CO₃ ⇌ H⁺ + HCO₃⁻It stabilizes pH by absorbing excess H⁺ or OH⁻, using Le Chatelier’s principle to shift the equilibrium as needed.