Lecture 1-3 Astrobio notes
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What is Astrobiology?
A scientific field of study focused on understanding the origins, evolution, and distribution, of life in the universe.
What does Astrobiology consider?
The question of whether extraterrestrial life exists and if it does, how humans can detect it.
How many protons does Carbon have?
6
(T/F) “All life on earth made of chemistry of carbon”
True
What are the complex carbon molecules?
Lipids, Carbohydrates, Nucleic Acids, and Proteins
Why Carbon?
Carbon has many different oxidation states, forms chemical bonds with many other elements, forms large complex molecules, and is water soluble.
What do all cells possess?
A plasma membrane ( an outer covering), Chromosomal DNA (the genetic blueprints of life), proteins (machines of life), ribosomes (protein factories)
What does the sequence of nucleotide bases do?
Store genetic information
Characteristics of DNA?
All living things have DNA, it’s double helix structure, two molecular strands coil about eachother.
What is Amino Acid?
An organic molecule that contains a carboxyl (-COOH) and an amino group (-NH²)
How do amino acids chemically bond?
They bond together by reaction of the carboxylic acid group of one molecule with the amine group of another
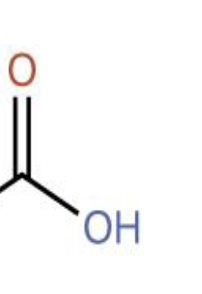
What part of the amino acid is this?
Carboxyl group
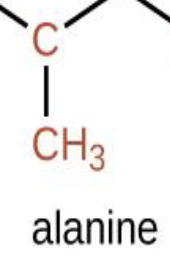
What part of the amino acid is this?
Chain
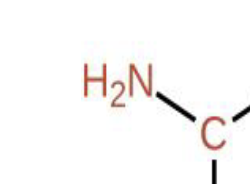
What part of the amino acid is this?
Amine

Characteristics/Definition of Hydrothermal Vents?
Located at tectonic plate boundaries; The black smokers emit fluids with very fine-grained particles that are often iron-sulfide minerals. The Mineralization forms chimney-like structures.
What type of tectonic plate boundary has spreading centers?
Divergent boundary
What type of tectonic plate boundary has subduction zones?
Convergent plate boundary
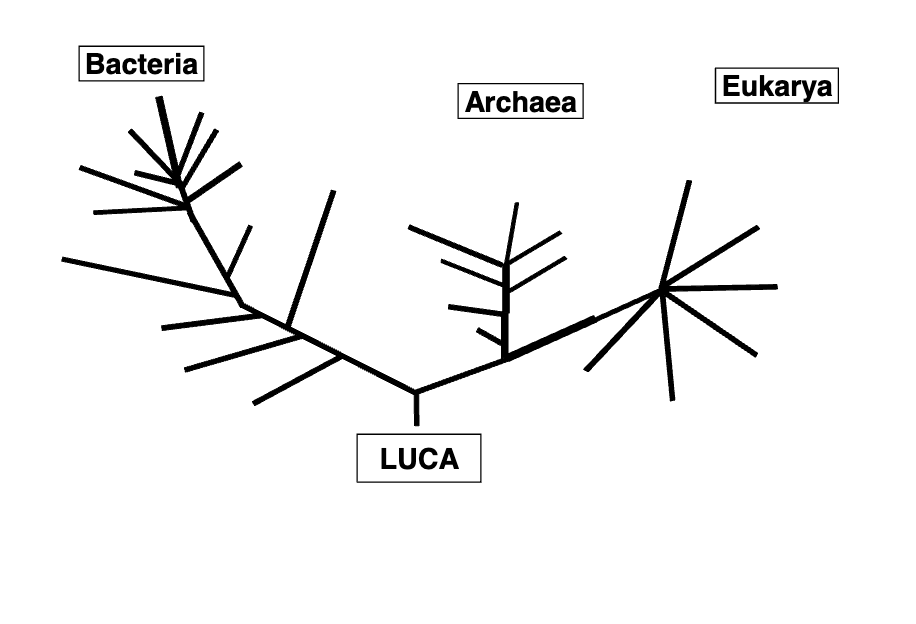
What is LUCA?
last universal common ancestor
When chemical fossils are preserved in rocks, what is the mark for it to be one of the oldest lipid biomarkers?
Greater than 1 billion years
Characteristics/ Definition of the James Webb Space telescope?
Largest, most powerful and complex space telescope ever built and launched into space. It is a orbiting infrared observatory. Helps us understand the universe.
What are the 4 most abundant elements in living matter that have low atomic numbers and are light elements that can form strong bonds with other atoms to produce molecules?
C,N,O and H
Macronutrients
Account for about 99% of dry weight of cells. Examples are CNOHPS
Micronutrients
Are required by some cells in very small amounts and are called micronutrients or trace elements. Examples are sodium (Na), potassium (K)
Organic molecules contain ____; inorganic compounds do not
Carbon
Where is most of the carbon found in organic molecules orginating from?
Inorganic carbon sources
Organic Molecules
Larger and more complex, use covalent molecules, form the cells of an organism and perform the chemical reactions that facilitate life.
Why are all these molecules called biomolecules?
They are part of living matter and contain carbon which is the building block of life.
Most abundant biomolecule
Carbohydrates
Why are carbohydrates “hydrated”?
Water molecules attach to each carbon atom
Carbohydrates are often called saccharides meaning
sugar
_____ “simple sugars” are the building blocks (monomers) for the synthesis of polymers or complex carbohydrates.
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are claffied by the number of carbons in the molecule, what is triose?
3 carbons
_______ are large polymers composed of hundreds of monosaccharide monomers.
Polysaccharides
_____ are lipids that contain long-chain hydrocarbons terminated with a carboxylic acid functional group (—COOH)
Fatty acids
Fatty Acids with hydrocarbon chains that contain only single bonds are called
Saturated fatty acids
Hydrocarbons containing at least one double bond are called _____ because they have fewer hydrogen atoms
Unsaturated fatty acids
Lipids containing saturated fatty acids are _____ at room temperature whereas lipids containing unsaturated fatty acids are ____.
Solid ; liquid
Why are Lipids significant?
They can be a source of nutrients, a storage form for carbon, energy-storage molecules, or structural components of membranes and hormones.
_______ is an organic molecule in which a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group (—COOH_ and an amino group (-NH²) are all bonded to the same carbon atom
Amino acid
How do amino acids chemically bond together?
By the reaction of the carboxylic acid group of one molecule with the amine group of another. This is called a peptide bond
Too many amino acids linked together or multiple polypeptides used as building subunits
Proteins
When there is 50+ amino acids linked together
Polypeptide
Like other macromolecules, nucleic acids are composed of monomers called ___ which are polymerized to form large strands.
Nucleotides
Contains the order within the strand
Base sequence
What is the base sequence of DNA responsible for carrying and retaining?
Hereditary information in a cell
Nucleotides that compose DNA are ________?
deoxyribonucleotides
What are the three components of deoxyribonucleotides?
A five carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.
Adenine goes with
Thymine
Cytosine goes with
Guanine
The base pairs are stabilized by
Hydrogen bonds
The two DNA strands are ___, such that the 3’ end of one strand faces the 5’ end of the other
antiparallel
These two form the backbone of the structure (of polymerized nucleotides)
Sugar and phosphate group
RNA is typically single stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by
phosphodiester bonds
What does a ribonucleotide in the RNA chain contain:?
Ribose (pentose sugar), one of the four nitrogenous bases (A, U, G and C) , and a phosphate group.
____ are units of matter that have the properties of a chemical element.
Atoms
What is the Atomic Number?
The unique number of protons in an element’s nucleaus
What does the number of protons define?
The chemical element and atomic number
What is the Oxidation state determined by?
Number of electrons
When is the oxidation state 0?
When the negatively charged electrons balance the positively charged protons, then oxidation state is zero
What is an ion?
Charged atom particles, reactions between different type of atoms
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons
How many protons and neutrons does C12. have ?
6 protons and 6 neutrons
What is the oxidation state of a H+ proton?
+1
What is the oxidation state of O?
-2
How is methane represented?
CH4 ; one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms
Rules for oxidation
Oxidation state of a pure element is 0
When oxygen is bonded to an element, its oxidation state is always -2
When hydrogen is bonded to an element, its oxidation is always +1
What do the verces represent in the skeleton formula?
Carbon
What are polymers?
Large molecules made up of a sequence of molecules called monomers
What are proteins and its characteristics?
Machines of life, polymers of amino acids (repeating subunits), perform a vast array of functions
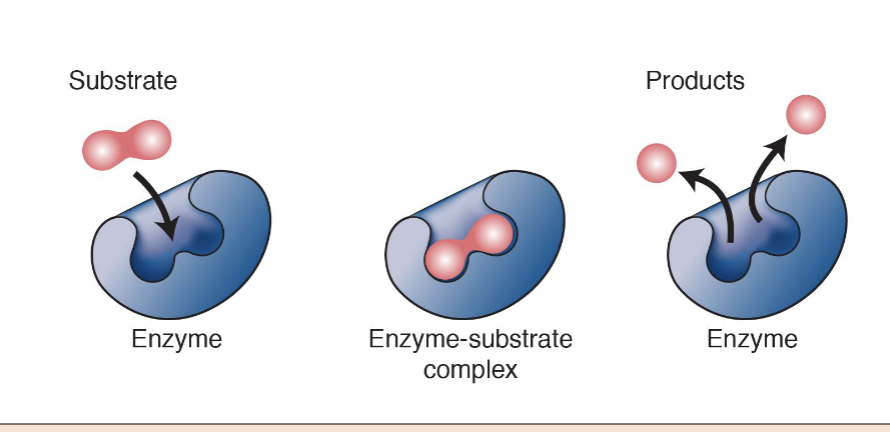
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions, but itself is not being consumed during the reaction.
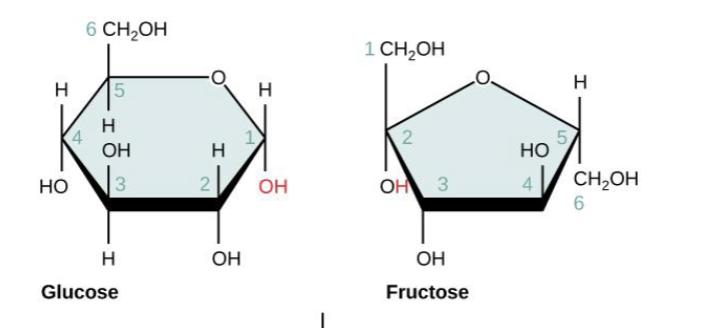
How does sucrose form?
Forms when a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer join together.
Difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA has one less ribose sugar, has hydrogen coming off whereas RNA has OH coming off, DNA is double stranded and RNA is single.
What is a phosphodiester bond?
Connects nucleic acids
How is the nucleotide base structure like?
Heterocyclic ring structure that contains nitrogen and carbon
This type of RNA carries information from the DNA.
Messenger RNA
What does the ribosomal RNA do?
Is the primary component of ribosomes
What does transfer RNA do?
Is small molecule involved in protein synthesis
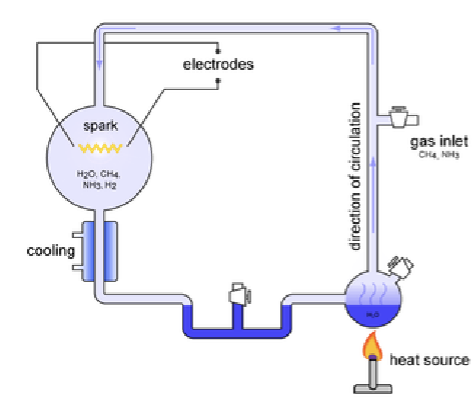
What happened in the Miller Urey Experiment?
Water vapor was mixed with methane, ammonia and hydrogen. Continuous electrical sparks were fired between the electrodes to simulate lightning. Amino acids were formed. Wanted to answer if amino acids are bioidentifiers?
What is the RNA World hypothesis?
That RNA contains hereditary information and can catalyze chemical reactions so int the RNA world, RNA served a genes and catalysts.
What is the process for DNA replication?
The double helix is unzipped and DNA strands are separate
A small piece of RNA(called a primer) binds onto the single stranded DNA
A protein called DNA polymerase binds to the DNA strand and then ‘walks’ along it, adding new complementary nucleotide bases (A, C, G, and T) to the strand of DNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction
What is the central dogma of biology?
DNA ( stores genetic information) —> RNA (active forms of genes)—> Protein(The machines that drive life processes)
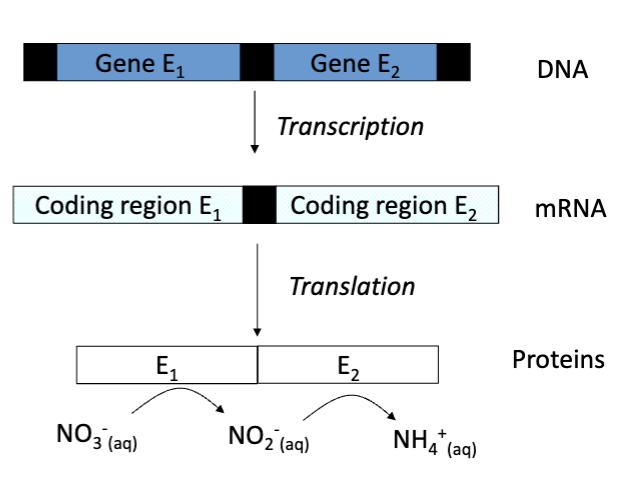
What is a gene?
A segment of DNA specifying a single protein, the information in the gene is present as the sequence of bases in the DNA.
What is messenger RNA ?
Contains the genetic information to encode proteins and carries genetic information from DNA to ribosome.
What is transcription in protein synthesis?
The biological process of making an mRNA copy of a DNA gene sequence
What is the process of Transcription?
Transcription of RNA from DNA involves the protein RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase attaches to the initiation site
RNA polymerase moves down the DNA chain, causing temporary opening of the double helix and transcription of one of the DNA strands
When a termination site is reached, chain growth stops. The mRNA and RNA polymerase protein are released
What happens in translation?
The sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA is “translated” into a sequence of amino acids. Translation occurs in the ribosome (“protein factory”)
What is a Codon?
Sequence of 3 nucleotides that encodes a specific amino acid.
What is the relation of genetic code and translation?
Translation of informatin encoded within genetic material into proteins.
What is the role of tRNA/transfer RNA in translation in the initiation phase?
In initiation, It carries amino acid to ribosome and recognizes and decodes an mRNA codon. It reads the mRNA 3 nucleotides at a time, and has the corresponding amino acid attached to its end.
What is the role of tRNA/transfer RNA in translation in the elongation phase?
In elongation, another tRNA containing an amino acid enters the ribosome and binds onto mRNA, they connect in peptide bond formation, then the ribosome continues to translate each codon in turn. Each corresponding amino acid is added to the growing chain and linked together.
What are the biological functions of proteins?
They catalyze chemical reactions, DNA replications, transport molecules, provide structure.
Q1: Ammonia is essential for life because of its role in the biosynthesis of amino acids. What is the chemical formula of Ammonia?
NH3
Q1. If a strand of DNA contains the sequence AGGTCT, what is the complementary nucleotide sequence?
TCCAGA
Q1. In proteins, amino acids are linked together by?
Peptide bonds
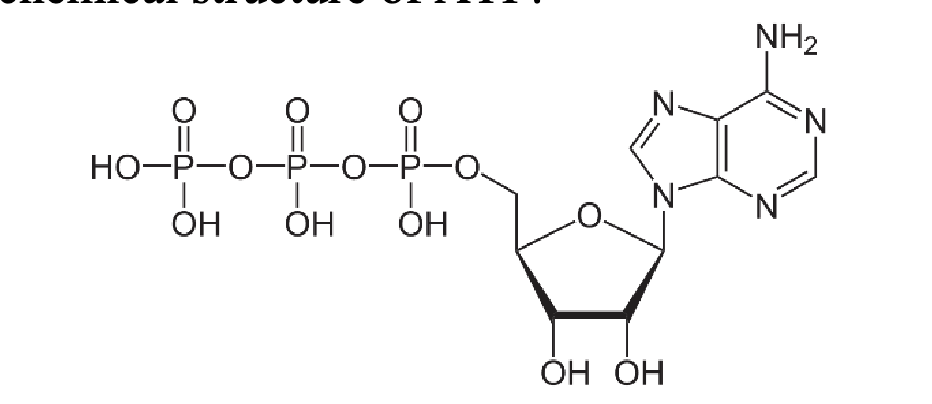
Q1. All living things use the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to store energy. Examine the chemical structure of ATP and list some true statements
ATP contains a heterocyclic nitrogenous base
ATP contains the sugar ribose
ATP contains phosphorus
ATP does not contain sulfur
Q1. Fatty acids are lipids that contain long-chain hydrocarbons terminated with a carboxylic acid functional group. Which one of these is a carboxyl functional group?
-COOH