my finaly study shesh
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
237 Terms
Mitosis
The process of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells.
Meiosis
A type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, producing gametes.
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter cells.
Hyphae
The long filaments that make up the body of a fungus.
Mycelium
A mass of hyphae, which is the vegetative part of a fungus.
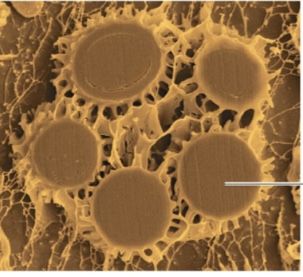
Ascospores
Sexual spores produced in an ascus by Ascomycota.
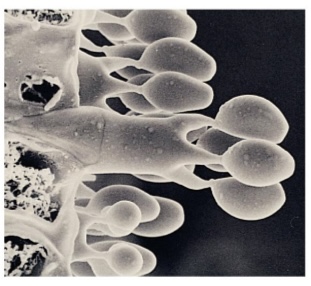
Basidiospores
Sexual spores produced on a basidium by Basidiomycota.
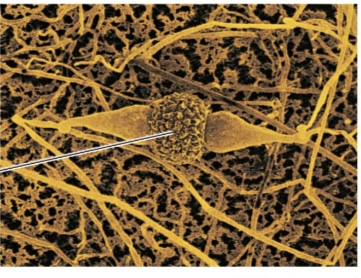
Zygospores
The thick-walled resting spores formed from the fusion of haploid cells.
Zygomycota (d)
Fungal division known as conjugation fungi that reproduce sexually via zygospores.(rhizopus)

Ascomycota
Fungal division known as sac fungi; reproduce sexually via ascospores.

Basidiomycota
Fungal division known as club fungi; reproduce sexually via basidiospores.(coprinus, amanita)

Deuteromycetes
Fungi with no known sexual reproduction phase.
Plasmogamy
The fusion of cytoplasm from two parent fungi during sexual reproduction.
Karyogamy
The fusion of two nuclei from different fungal cells during sexual reproduction.
Schizogony
A method of asexual reproduction in which organisms divide multiple times before separating.
Pseudohyphae
An incomplete budding structure seen in some yeasts.

Rhizopus
A genus of fungi commonly known as black bread mold.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
A species of yeast used in baking, brewing, and winemaking.
Entomophaga
A genus of fungi used for biocontrol of insect pests.
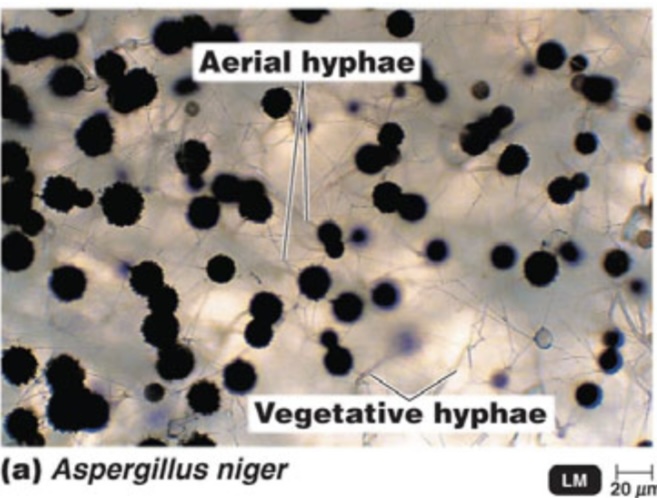
Aspergillus niger
A species of fungus known for causing spoilage in food and producing mycotoxins.
Mucor
A genus of fungi commonly found in soil and decaying organic matter.
Helminths
Multicellular parasites that belong to two main groups: flatworms and roundworms.
Cestodes
Tapeworms, which are flat, segmented helminths.
Trematodes
Flukes, a class of flatworms that are often parasitic.
Nematodes
Roundworms, characterized by a body covered with a flexible cuticle.
Definitive Host
The host in which the sexual reproduction of a parasite takes place.
Trichoderma
Fungi used in producing enzymes.
Taxomyces
A genus of fungi known for producing Taxol, an anticancer drug.
Significance of fungi
Decompose dead organisms, produce antibiotics, important research tools
Thallus
The body of the mold or fleshy fungus (vegetative)
Yeast
Unicellular fungi
Fission yeast
Divide symmetrically, binary fission
Budding yeast
Divide asymmetrically, budding
Filamentous fungi
Produce lightweight spores that disperse over large distances
What are the 3 phases of sexual reproduction
Plasmogamy, karyogamy, meiosis
What are the 4 fungal divisions?
Zygomycota, ascomycota, basidiomycota, deuteromycetes
paecilomyces
Kills termites
Economic effects of fungi
Taxomyces, paecilomyces, trichoderma, entimophaga
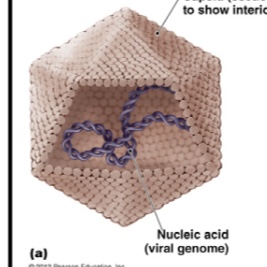
Virion
Complete, fully developed infectious viral particle.
Capsid
Protective protein coat surrounding the viral nucleic acid.
Nucleic acid
The genetic material of the virus, which can be DNA or RNA.
Host range
The specific types of cells or organisms that a virus can infect.
Generalists
Viruses that can infect many types of cells across different hosts.
Bacteriophage
A virus that specifically infects bacteria.
Capsomeres
The protein subunits that make up the capsid.
Envelope
A lipid, protein, and/or carbohydrate layer around some capsids.
Spikes
Protein-carbohydrate complexes used for attachment to host cells.
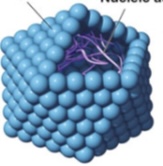
Polyhedral viruses
Viruses with many sides, with the icosahedron being the most common form.
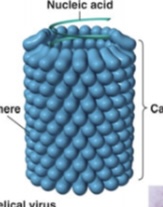
Helical viruses
Viruses that are shaped like long rods or cylinders.
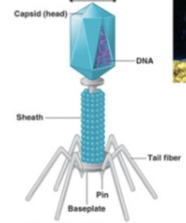
Complex viruses
Viruses with complicated structures that exhibit both helical and polyhedral characteristics.
Lytic cycle
A phase in viral replication where infected cells are lysed and destroyed.
Lysogenic cycle
A phase in viral replication where the phage DNA incorporates into the host genome and remains dormant.
Prophage
The dormant form of a phage when it integrates into the host chromosome.
Transduction
The process by which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus.
Endocytosis
The process by which viruses enter host cells by engulfing them.
Budding
The process by which enveloped viruses are released from host cells.
Exocytosis
The process by which naked viruses are released from host cells.
Latent viral infections
Infections where the virus remains dormant in the host cell for long periods.
Cytopathic effects
Observable changes in host cells caused by viral infections.
Serological tests
Tests that detect antibodies against viruses in a patient.
RFLPs
Restriction fragment length polymorphisms, a method for analyzing DNA.
PCR
Polymerase chain reaction, a technique used to amplify DNA sequences.
Cultivation of viruses
The process of growing viruses in living cells
different techniques are required to grow and maintain viruses
techniques used depend on the normal host of the virus.
Animal viruses
Viruses that infect animal cells, often requiring different techniques for cultivation.
Embryonated eggs
Eggs used as a medium for growing animal viruses.
Cell culture
A method for growing viruses in isolated cells from an organism.
Taxonomy of viruses
The classification of viruses based on nucleic acid type, replication strategy, and morphology.
Viridae
The suffix used for naming virus families.
Virus genus
The category in virus classification that groups viruses with similar characteristics.
Prions
Infectious protein particles that cause neurological diseases.
Protein is an altered normal cellular protein
Inherited and transmitted by ingestion, transplant, and surgical instruments.
Spongiform encephalopathies
A group of neurodegenerative disorders associated with prions.
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
A human prion disease characterized by rapid neurodegeneration.
Mink encephalopathy
A prion disease affecting minks.
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy
A prion disease in cattle, also known as mad cow disease.
Fatal Familial Insomnia
A prion disease characterized by severe sleep disturbances.
Gertrudam-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome
A rare genetic prion disease characterized by ataxia.
Kuru
A prion disease observed in humans, historically linked to cannibalism.
Alpers Syndrome
A prion disease that affects infants, causing neurological dysfunction.
Oncogenic viruses
Viruses that can cause cancer in the host organism.
Zoonotic viruses
Viruses that are transmitted from animals to humans.
Immunoglobulin
Antibodies produced by the immune system to identify and neutralize pathogens.
Viral hemagglutination
A test that determines the ability of viruses to agglutinate red blood cells.
Cultivation of bacteriophages
Grown in either liquid cultures of bacteria, or in bacterial cultures on solid medium
Viruses can be detected by the formation of plaques
Cultivation of Animal Viruses
Animal viruses may be grown in living animals, embryonated eggs, or in cell culture
Observers see cytopathic effect-cell deterioration due to virus activity
Viral replication in the lytic cycle
Virus comes into cell, makes all viral products it needs, puts all viral products back together, then releases through host cell
Lysogenic cycle Viral replication
Replicates viral DNA but doesn’t cause cells to be destroyed, incorporated into genetic material and causes infection in lytic cycle
Replication of animal viruses process
Viruses attach to cell membrane, penetration by fusion, uncoats itself, makes viral products, puts them back together, then released and destroys host cells
Requirements for Replication of animal viruses
Requires different strategy depending on its nucleic acid
DNA viruses assemble in nucleus and RNA viruses develop solely in cytoplasm
Number of viruses depend on on type of virus and size and initial health of host cell
Enveloped viruses cause persistent infections
Naked viruses are released by exocytosis or lysis
3 ways animal viruses come in body
Endocytosis, membrane fusion, direct penetration which is the rarest
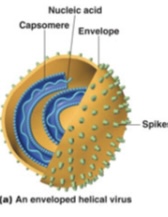
Enveloped viruses
Surrounded by an envelope roughly spherical
Can be helical or polyhedral
Viral species
A group of viruses sharing the same genetic information and ecological host.
Black piedra
Spores on hair shaft
In central and South America and Asia
Treat-shave or oral terbinafine
malassezia furfur
Fungus interferes with melanin production
Treat-topical or oral ketoconazole
Dermatophytosis, trichophyton, microsporum, epidermophyton
Ring worm and athletes food, jock itch
Affects skin hair and nails
Treat-topical or oral terbinafine
Sporothrix schenckii
Rose gardener fever, grows on thorn of roses
Found in Mexico Latin America and Africa
Treat-topical or oral terbinafine
Cladophialophora
Disease-Chromblastomycosis
Causes dry wart like scales
Treat by removing skin
Acremonium
Disease-Mycetoma
Puss filled tumors, skin, fascia, bones of hand and feet
Treatment is removing tissue or limb
Aspergillus Niger
Grows on food items, might causes problems if allergic
Stachybotrys chartarum
black mold, heavy mold spore
Grow in air condition vents colonizing in lung tissue
Cryptoccus neoformans
Meningitis
Capsul
Found in soil, bird poop, airborn
Treat-Iv amphotericin B