Melting Point and Acid-Base Indicator
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHEM 14BL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
acid-base indicator does not provide
pH readings
end point
an indicator changes color in an acid-base reaction
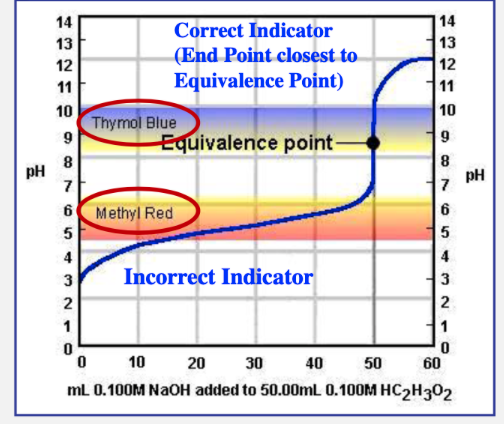
how to correctly choose an acid-base indicator for an acid-base reaction
the indicator should change color (the end point) very close to the equivalence point pH
equivalence point
moles of acidic protons = moles of hydrozide
at the end point (with correct indicator), we can assume
MaVa = MbVb
volumetric buret contains what in a titration?
titrant, base
equivalence point does not equal
end point
equivalence point
intermolecular forces
molecules of crystals are aligned in a conformation that are held together by these
to break molecule conformations
an input of energy is needed
melting point
one way to find the identity and purity of an experimental product
use of melting point in an experiment to find identity
melting point does not always confirm the identity of any given compound by itself (many organic compounds have similar melting points)
use of melting point in an experiment to find purity
“sharpness” of melting point range indicates purity of compounds, pure compounds melt at a narrow temperature range but an impure compound melts over a wide temperature range
melting point range for a pure substance
very sharp melting point, 2 degrees celsius or less in range
melting point range equation
Tf - Ti (Tf = temperature where melting completed, Ti = first sign of melting)
if something has dipole-dipole forces
then they also have london forces
effects of soluble impurities on experimental melting point
melting point depression (the lower end of the melting point range (Ti) occurs below the literature melting point value
melting point range increases - usually 2-4 degrees celsius for small amounts of impurity (more than 5 degrees celsius if highly impure)