Nasal Route
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Describe the anatomical and physiological challenges posed by the nasal routes of administration
Small and lipophilic drugs can pass olfactory only
If use the olfactory bulb too much for nasal route of drugs, the cells with create a defense mechanism (characterisation) and this route will not work anymore
If olfactory is abused, keratinization occurs as a defense mechanism
Medications used: analgesics, vaccines, hormones, opioid analgesics, insulin, glucagon
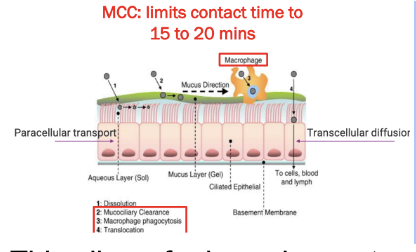
Respiratory region allows for the systemic
20 min contact time max in respiratory region because of the Mucociliary clearance that clears every 15-20 mins

Vascularization is higher in respiratory than vestibular
Enzymatic activity is lower than in the GI tract even though there are 4-5X CYP enzymes due to shorter residence times
Analyze the physiological characteristics needed for nasal drug delivery
Less than or equal to 300 Da - no other properties matter for absorption
Bioavailability decreases with increasing MW → 300-1000 Da
For molecular weight of 1000-6000 Da penetration enhancers will be needed
Partition coefficient → > 1 will have good bioavailability
Coefficient indicated small and lipophilic molecules
Solubility, pH, and pKa → drug needs to dissolve in 20 mins if prepared as suspension due to mucociliary clearance
If particles are too big they will be sneezed out
Gels and suspension preferred because they have a higher contact time
Other considerations: cyclic molecules are absorbed faster than linear molecules
Formulations
Nasal Drops
Solutions, Suspensions
Nasal Sprays
Solutions, Suspensions
Nasal Gels
Solutions, Suspensions
Nasal Powders
For drugs with poor stability and/or poor solubility
Characteristics formulations
pH: 4.5-6.5 (prevent infections)
Dose: Max 25 mg
Droplet size: 5-10 micrometers to deposit in respiratory region
Isotonic: decreases irritation; hypertonic solutions will decrease BA
Suspension must dissolve within 20 min to have enough absorption before MCC
Notes on Excipients and viscosity
Humectants: to prevent nasal irritation and drying out especially for gels
Penetration enhancers allow any drugs to go in and can cause infection
Advantages/Disadvantages

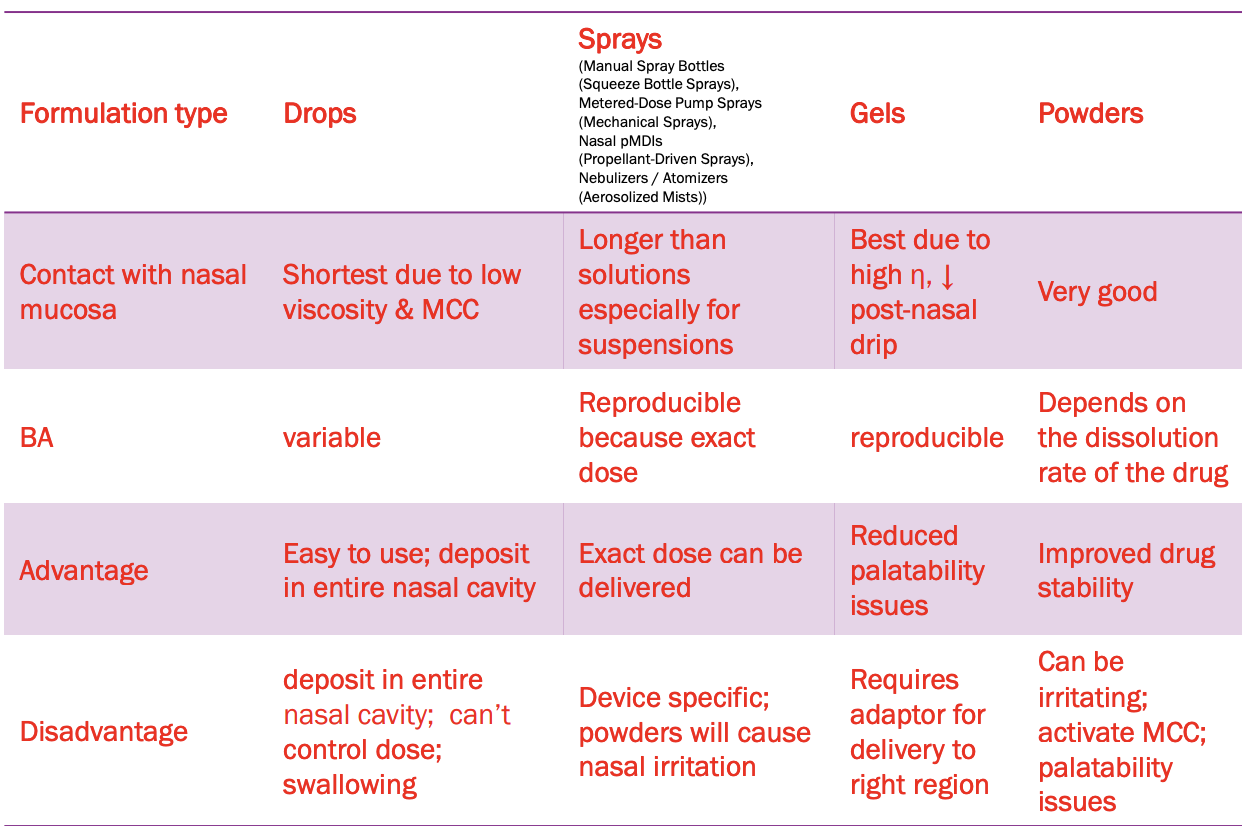
I would recomend sprays
excipients
Viscosity
increases n increasing retention time
over increase in n decreases diffusion
makes gel soothing
Solubilizers
Preservatives
Antioxidants
humectants: to prevent nasal irritation
penetration enhancers for large MW drugs
local action target
nasal cavity -congestion, allergies
systemic delivery possible - acute chronic condition
acute chronic condition got pain addiction
can target brain through olfactory region
for both local brain action or systemic action
Nasal drug delivery
as a route of administration utilizes the nasal cavity for drug absorption
Mucociliary Clearance (MCC)
is the physical unidirectional movement and removal of deposited particles and gases dissolved in the mucus from the respiratory tract.
First Pass Effect (1st Pass Effect)
is a phenomenon in which a drug gets metabolized at a specific location in the body that results in a reduced concentration of the active drug upon reaching its site of action or the systemic circulation. The first pass effect is often associated with the liver, as this is a major site of drug metabolism
nasal passes this