2.23 Developmental Abnormalities of Tendons
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What are examples of congenital flexural deformities?
Flexural laxity
Hyperflexion
Rupture/elongation of the common digital extensor tendon
What are examples of acquired flexural deformities?
Club foot
Flexural deformity in metatarso/carpophalangeal joint
What is the cause of flexural laxity?
Quite frequent problem in premature foals. Intrauterine infection, mother infection.
In older horses, previous injuries or diseases, nutritional deficiencies, lack of exercise, or normal ageing.
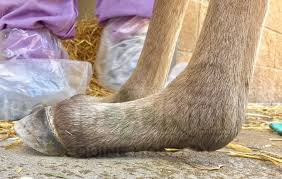
What is the diagnosis of flexural laxity?
X-ray: Check skeletal maturity – shows insufficient mineralization and delayed long bone development.
When is euthanasia indicated for flexural laxity?
Severe insufficient mineralisation.
How can flexural laxity be prevented?
Prevent premature delivery of foal by proper care of the mare. Premature foals should not be allowed to stand up.
With older horses, prompt attention to tendon injuries, good nutrition, and sufficient exercise will help prevent development of weak or lax flexor tendons.
Flexion of the carpal (preying mantis) or fetlock joints (knuckling), with an inability to stand or nurse.
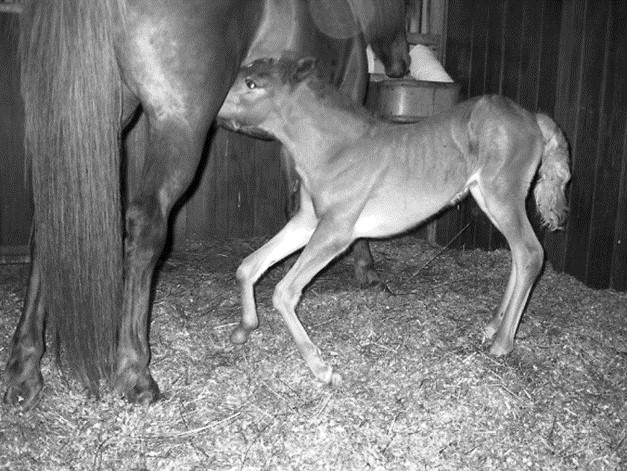

How is hyperflexion diagnosed?
CS, x-ray.
Reshaping, moderate exercise, NSAIDs, oxytetracycline, and surgery to cut flexor tendons (flexor carpi ulnaris/ulnaris lateralis).
What is the effect of oxytetracycline in the tendons?
Binds calcium and causes lengthening.
What is the diagnosis for rupture or elongation of the common digital extensor tendon?
CS, USG. Free ends of tendon palpated.
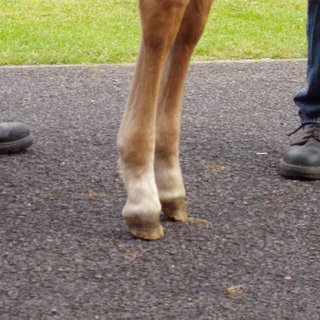
Overfeeding, mineral imbalances, sudden nutritional changes, hyperparathyroidism, exercise, or trauma.
How can overfeeding lead to club foot?
High energy and protein diet → bone grows faster than tendon.
What are the stages of club foot?
Stage I: hoof wall <90°; Stage II: >90° - bad prognosis.
Hoof correction, shoeing (e.g., Dallmer shoe), and surgery such as desmotomy of ALDDFT or elongation of the DDFT.
How is club foot prevented?
Take off pasture, reduce energy/protein consumption. Keep on hard ground, hoof trimming.
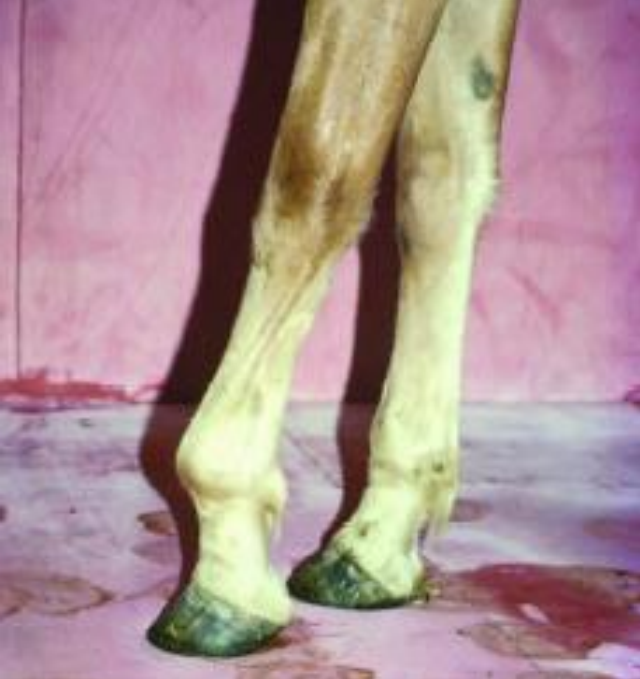
What are the clinical signs of flexural deformity in MTCP?
Hoof has normal appearance, but straight, upright appearance of pastern → over knuckling

How is flexural deformity in MTCP diagnosed?
CS.
Heel support with a wedge
Transecting accessory ligaments of the DDFT and SDFT.
Lateral digital extensor tendon.
For flexural laxity, which bones do you look at on x-ray for mineralisation?
Cuboidal bones.
What type of support bandage can you use?
Robert-Jones.
What is the problem with bandaging?
Pressure necrosis, so have to change regularly.