WJEC AS Chemistry Unit 1.1 - Equations and Formulae
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Formula for Water
H2O
Formula for Carbon Dioxide
CO2
Formula for Sulfur Dioxide
SO2
Formula for Methane
CH4
Formula for Hydrochloric Acid
HCl
Formula for Sulfuric Acid
H2SO4
Formula for Nitric Acid
HNO3
Formula for Ethanoic Acid
CH3CO2H
Formula for Ammonia
NH3
Formula for Ammonium Chloride
NH4Cl
Formula for Sodium Hydroxide
NaOH
Formula for Sodium Chloride
NaCl
Formula for Sodium Carbonate
Na2CO3
Formula for Sodium Hydrogencarbonate
NaHCO3
Formula for Sodium Sulphate
Na2SO4
Formula for Copper (II) Oxide
CuO
Formula for Copper (II) Sulphate
CuSO4
Formula for Calcium Hydroxide
Ca(OH)2
Formula for Calcium Carbonate
CaCO3
Formula for Calcium Chloride
CaCl2
Formula for an Ammonium Ion
NH4+
Formula for a Hydrogen Ion
H+
Formula for a Lithium Ion
Li+
Formula for a Potassium Ion
K+
Formula for a Sodium Ion
Na+
Formula for a Silver Ion
Ag+
Formula for a Barium Ion
Ba2+
Formula for a Calcium Ion
Ca2+
Formula for a Magnesium Ion
Mg2+
Formula for a Copper (II) Ion
Cu2+
Formula for an Iron (II) Ion
Fe2+
Formula for an Iron (III) Ion
Fe3+
Formula for an Aluminium Ion
Al3+
Formula for a Bromide Ion
Br-
Formula for a Chloride Ion
Cl-
Formula for a Fluoride Ion
F-
Formula for an Iodide Ion
I-
Formula for a Hydrogencarbonate Ion
HCO3-
Formula for a Hydroxide Ion
OH-
Formula for a Nitrate Ion
NO3-
Formula for an Oxide Ion
O2-
Formula for a Sulfide Ion
S2-
Formula for a Carbonate Ion
CO32-
Formula for a Sulfate Ion
SO42-
Formula for a Phosphate Ion
PO43-
Writing the formula for ionic compounds
Write the symbols of the ions in the compound
Balance the ions so that the total of the positive ions and negative ions adds to zero (the compound itself must be neutral)
Write the formula without the charges and put the number of ions of each element as a small number following and below the element symbol
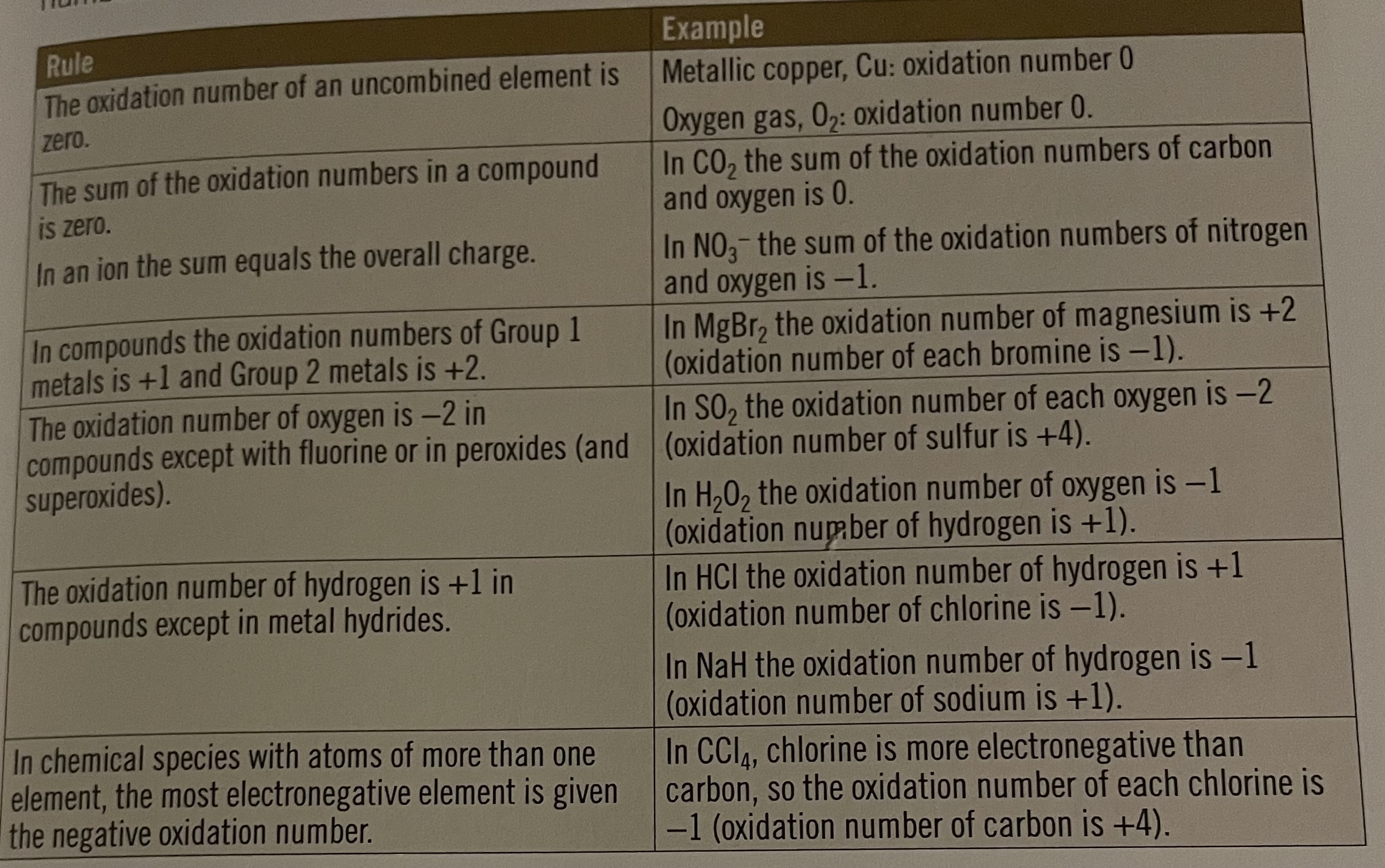
Oxidation numbers
the number of electrons that need to be added to (or taken away from) an element to make it neutral
Used in redox reactions to show which species is oxidised and which is reduced; increases = oxidised, decreases = reduced
Used to name compounds unambiguously
Writing balanced chemical equations
Write a word equation for the reaction (optional)
Write the symbols and formulae for the reactants and products (make sure that all formulae are correct)
Balance the equation by multiplying formulae if necessary (never change a formula)
Check to see if the equation is balanced
Add state symbols (if required)
(s) = solid
(g) = gas
(l) = liquid
(aq) = aqueous (solution in water)
Writing ionic equations
Frequently used for displacement and precipitation reactions
Write out the chemical equation
Write out the same chemical equation but using the ions
Write out the ionic equation using the ions that are changed, leave out the unchanged spectator ions

Stoichiometry
The molar relationship/ratio between the amounts of reactants and products in a chemical reaction