Carbon based fuels
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
A fuel
a substance that stores chemical energy that can be released for use relatively easily
Renewable energy
energy sources are those that are continually being replaced by natural processes and can be replaced in a relatively short time
Sustainable energy
sources of energy are not expected to be depleted within the lifetime of the human race and use of these sources causes no long-term damage to the environment.
non sustainable sources of energy
fossil fuels( coal, natural gas and crude oil)
coal
is a very complex material with a variable composition.
· It is mainly composed of rings of six carbon atoms.
· It may also contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur in various compounds.
· Water and small amounts of minerals are also present.
Energy efficiency
is a measure of the percentage of energy from a source that is transformed into a useful form of energy
Petrol
Crude oil is a mixture of many hydrocarbons, mostly alkanes, and is the source of most transport fuels. These need to be separated before they can be used.
· The basis for their separation is their different molar masses and hence their different boiling points.
· Mixtures of molecules with a similar boiling point are separated from the crude oil and collected.
· These fractions are potentially used as a fuel or may be treated further to produce specific chemicals.
· One such fraction is petrol that consists mainly of octane (C8H18) together with other alkanes with a similar boiling point.
Natural Gas
Natural gas consists largely of methane together with small amounts of other small alkane molecules. Water, carbon dioxide, sulfur and nitrogen may also be present.
· Natural gas may be found trapped in deposits under rock or trapped as a layer above crude oil deposits.
· It can also be found in the form of coal seam gas (CSG) where the gas is adsorbed on to the surface of coal due to the pressure of water on the coal.
Liquid petroleum gas (LPG)
LPG consists largely of propane and butane that has been obtained through the fractional distillation of crude oil and of natural gas.
Whilst propane and butane would be gases under normal conditions of temperature and pressure, they become liquefied under high/low pressure and can be stored effectively in metal bottles.
· Liquid petroleum gas is used as a fuel in appropriately modified cars although relatively few cars capable of using LPG are produced, so they are much less common than cars running on petrol engines.
LPG is also used in some homes for heating and cooking with this being the primary fuel for barbeques
Liquid natural gas (LNG
Since 2018 Australia has become the biggest exporter of natural gas with many million tonnes of natural gas being exported each year.
· The gas is first pressurised to convert it to a /liquid before transport thus forming liquid natural gas (LNG).
Liquifying the fuel increases the energy density of the fuel although the process is costly/expensive
Electricity from natural gas
Since coal-fired power stations are slow to respond to fluctuation in energy demands, and because natural gas reserves are available, there are several power stations across Australia that burn natural gas rather than coal. These are called gas-fired power stations.
Other advantages of burning natural gas rather than coal include:
· The ability to adjust the energy provided by the plant quickly as demands change.
· A higher efficiency in the conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy.
· Significantly reduced greenhouse gas emissions
· Much less ash/smoke produced.
Biofuels
) are fuels that have been produced from plants or other organic material. The plant materials commonly used include:
· grains (e.g. wheat, maize & barley)
· sugar cane
· vegetable waste
· vegetable oil
Advantage of biofuels over fossil fuels.

Carbon neutral fuels make no net contribution of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
The amount of carbon dioxide released during combustion was earlier absorbed during photosynthesis when the plant material was grown.
It is a theoretical ideal, but not achievable in practice.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process in plants by which carbon dioxide and water is converted to glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen. Light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of glucose.
Biogas
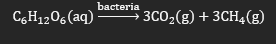
Biogas refers to the gas produced through the anaerobic (limited oxygen) digestion of organic material by bacteria.
· The bacteria break down large molecules into smaller molecules such as methane and carbon dioxide.
· The exact composition of the biogas is dependent on the nature of the material being broken down, but methane is consistently the most abundant component.
A reaction describing this process using glucose would be:
Electricity from biogas
Farms can particularly benefit from this process with the biogas obtained being suitable for heating and power production on a small scale while the waste from the biogas generator acts as an excellent fertiliser.
Electricity can be generated and is largely dependent on the combustion of methane in the biogas. It tends to occur at the site where the biogas is produced.
As the percentage of methane is lower in biogas than in natural gas, the energy released per gram of biogas is somewhat lower than per gram of natural gas.
Biodiesel
Biodiesel refers to the diesel fuel produced from the esterification reaction between vegetable oils or animal fats and an alcohol (usually methanol or ethanol) in the presence of a catalyst, commonly concentrated potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
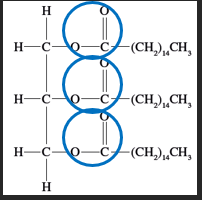
The vegetable oil is frequently obtained through crops of soyabean, canola or palm oil and sometimes recycled vegetable oils and animal fats can be used. Fats and oils are classified as triglycerides, as shown in figure 7. They consist of: · three hydrocarbon chains · attached by an ester functional group to · a backbone of three carbons. The three hydrocarbon chains may be the same as each other or different, and the type of biodiesel formed will vary depending on the source of the original triglycerides. Biodiesel is suitable to be combusted in diesel engines and generators. | Figure 7 A triglyceride (palm oil)
 |
Bioethanol
Most ethanol is produced using glucose that has been obtained from biomass (organic matter largely used for fuel). The raw materials include sugars (sugar cane, sugar beet and molasses) and starch (corn, wheat, and grains). In Australia, ethanol is made from waste products such as those left over after the processing of sugar cane. As such, this means ethanol production in Australia does not interfere with food production.
· Ethanol produced through the fermentation of glucose sourced from renewable sources such as these is classified as bioethanol.
· Synthetic ethanol can also be produced from non-renewable sources like coal and gas.
Energy from carbohydrates
Carbohydrates, such as glucose (C6H12O6), contain the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Their name is derived from their empirical formula CH2O, which shows that the hydrogen and oxygen is present in the same ratio as in water.
The original source of carbohydrates in the food chain is the combination of carbon dioxide and water by the photosynthesis in green plants in the presence of sunlight.
Photosynthesis is an endothermic process:
The plant usually converts the original glucose into more complex carbohydrates such as cellulose for structural material or starch for energy storage.
Glucose is present in all living things and is the most common source of energy. Energy is released from glucose via cellular respiration. The main type of respiration is called aerobic respiration and requires molecular oxygen (O2).
Energy from proteins
Proteins are present in every cell and are the structural basis of cells and tissues. They contain the elements of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and some have sulfur.
Many types of protein exist, all of which have specific functions, but they are rarely used as an energy source unless there is a severe depletion of glucose.
Energy from fats and oils
Fats and oils are a part of a group of compounds called lipids. They are a group of non-polar, insoluble biomolecules.
Fats and oils are a major energy source, providing more than double the energy per gram than carbohydrates.
The main distinction between these compounds is based on their state at room temperature.
· Fats: soft waxy solids at room temperature and tend to be sourced from animals.
· Oils: liquids at room temperature and tend to be sourced from plants.
Fats and oils are made up of large non-polar molecules called triglycerides that contain 3 ester functional groups. The products of digestion of these triglycerides include fatty acids that are carboxylic acids with a long hydrocarbon chain.
Energy values of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
The energy content of biomolecules varies widely. Foods are a mixture of biomolecule types, so the molar mass is not known. As such, the energy content is often expressed in kJ g-1, kJ/100 g, or for pure substances kJ mol-1.