Amines (6D)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is a chiral carbon
A carbon with 4 different groups or chains
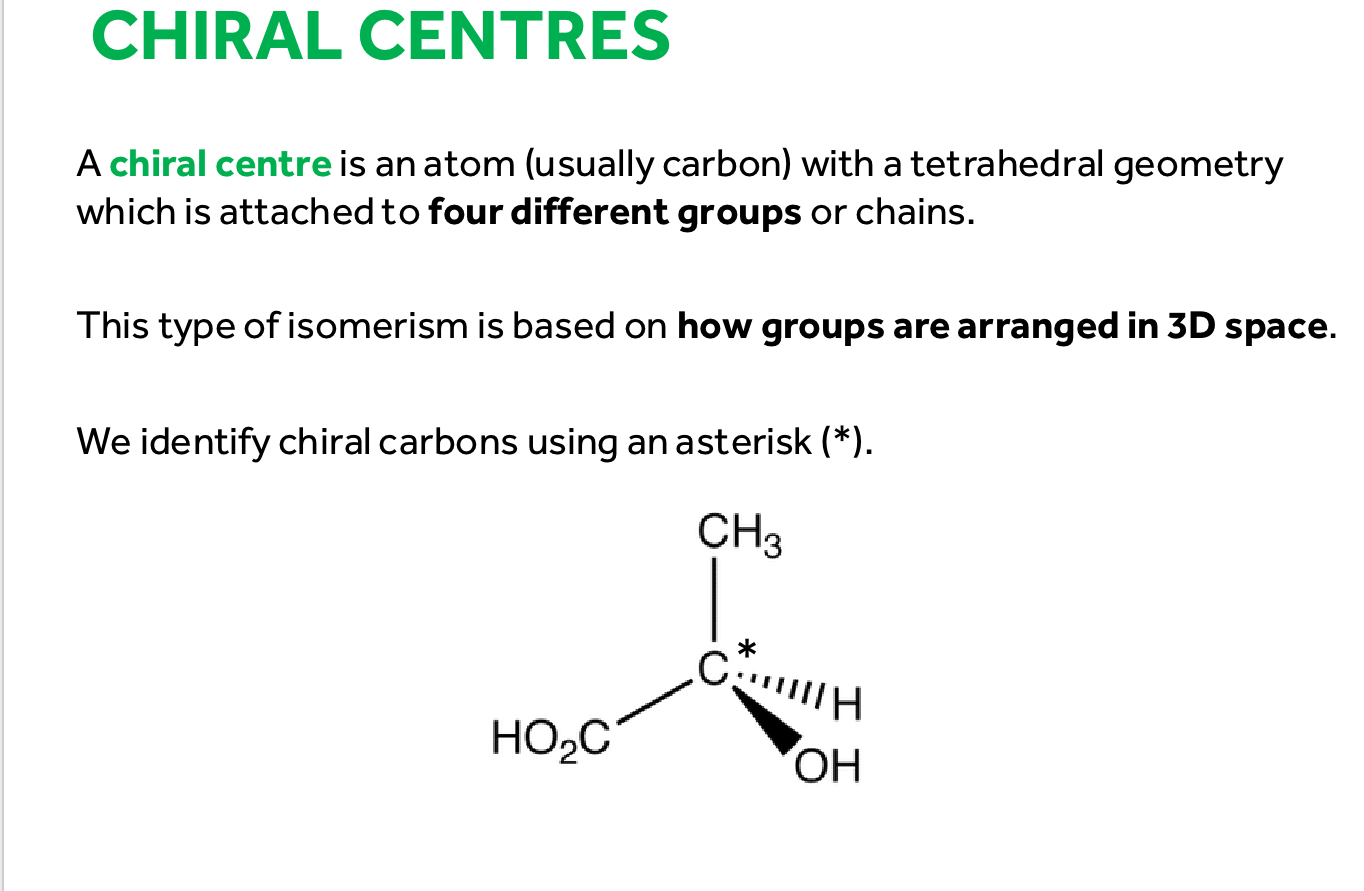
what are Enantiomers (optical isomers)
A molecule with a chiral carbon in the centre that mirror images of each other
Uses of amines
Painkillers
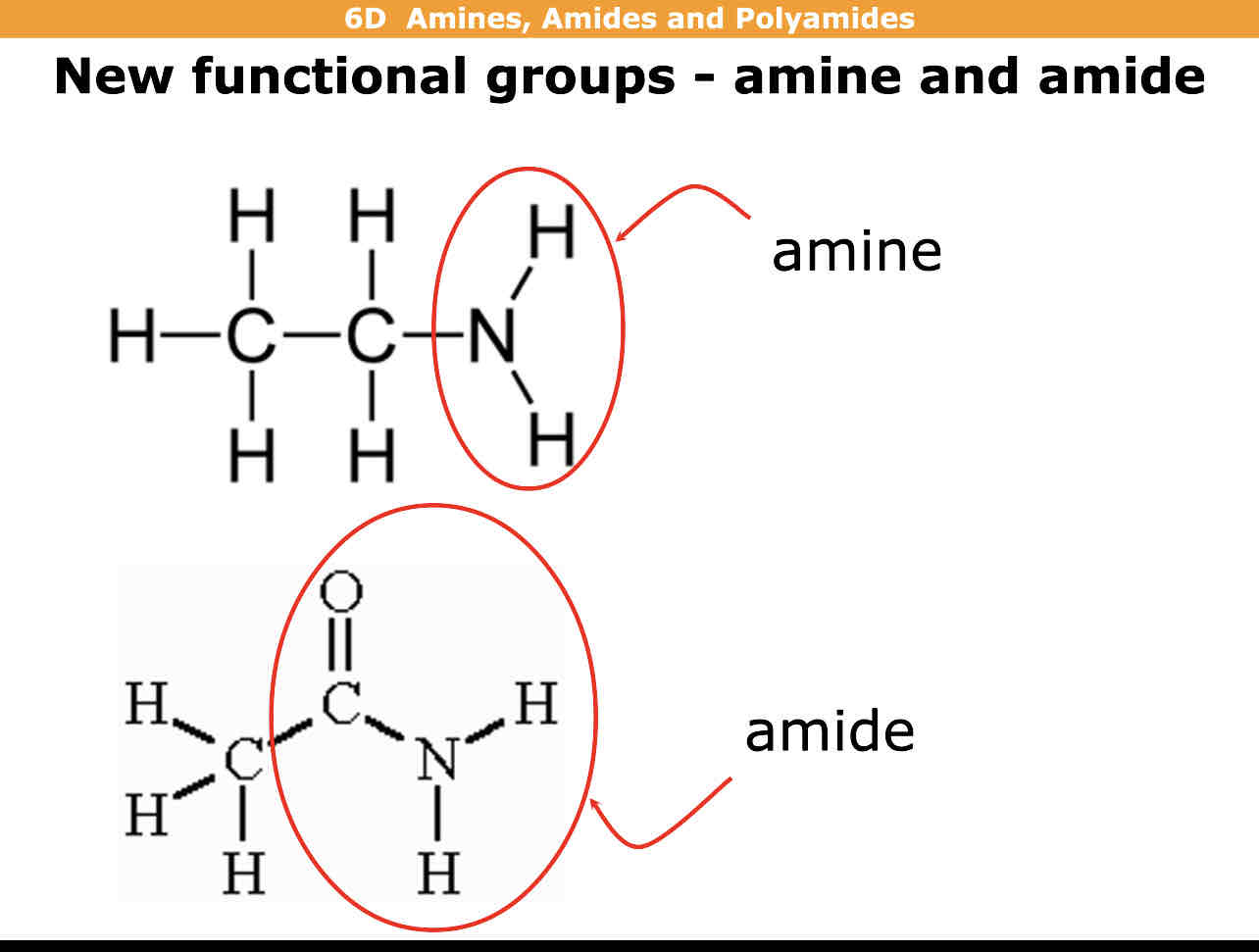
What is an amine?
What is an amide?
Amine is N bonded to 2 hydrogens
Amide is N bonded to 2 Hydrogen atoms also with C=O
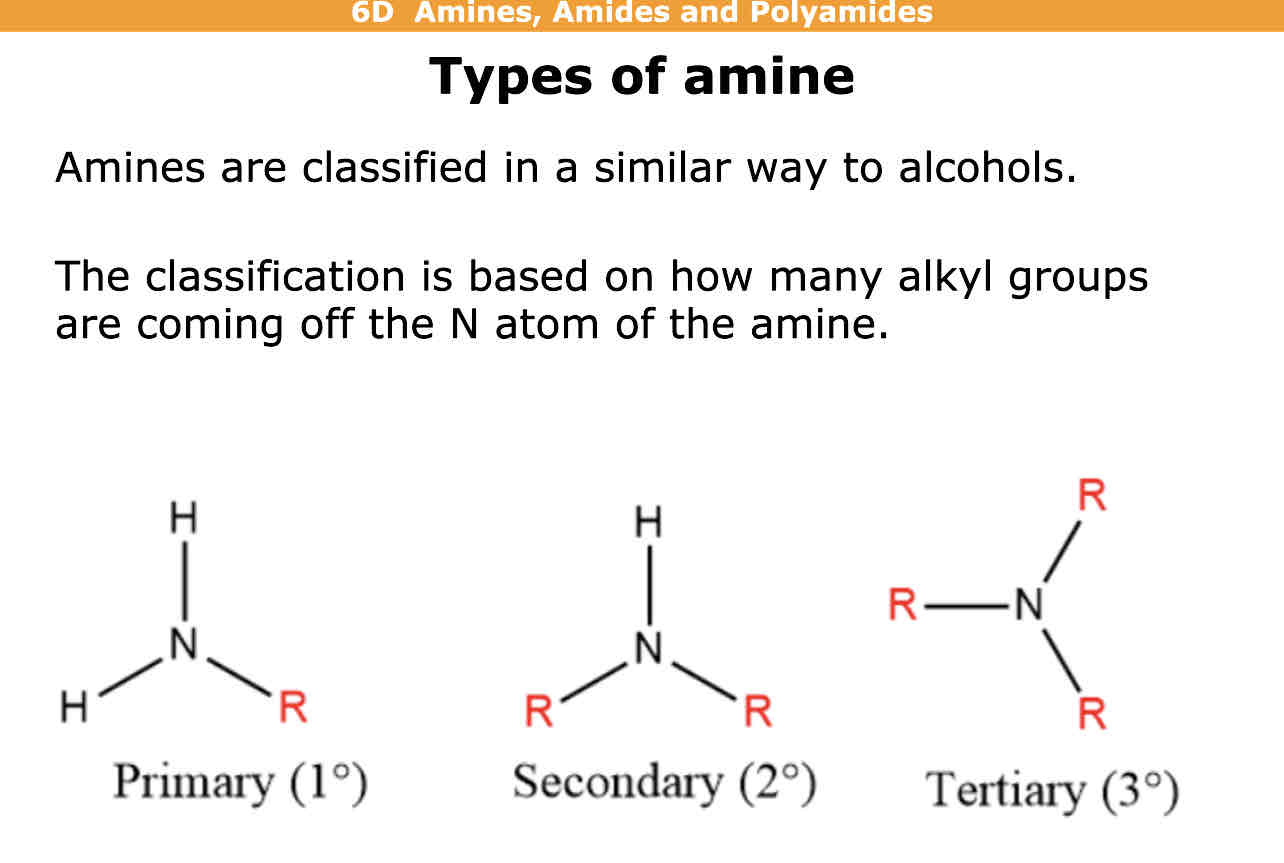
What is a primary amine
What is a secondary amine
What is a tiertiary amine
Primary amine has 1 group coming off N( not including hydrogen) bonded to 2 hydrogens and 1 r group
Secondary amine has 2 groups coming off N( not including hydrogen) bonded to 1 hydrogen and 2 r groups
Tiertiary has 3 groups coming of N
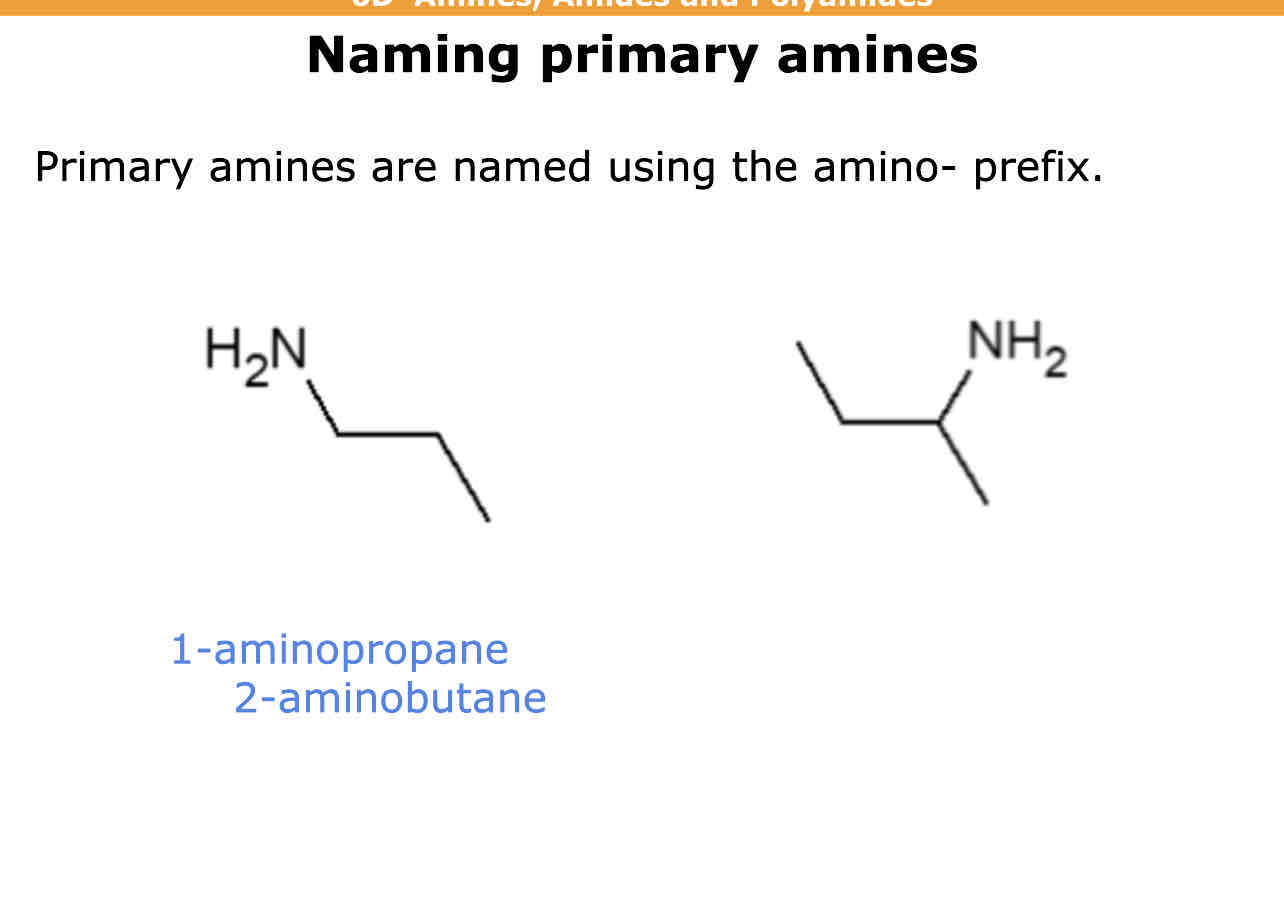
Primary amines are named using what prefix
Amino
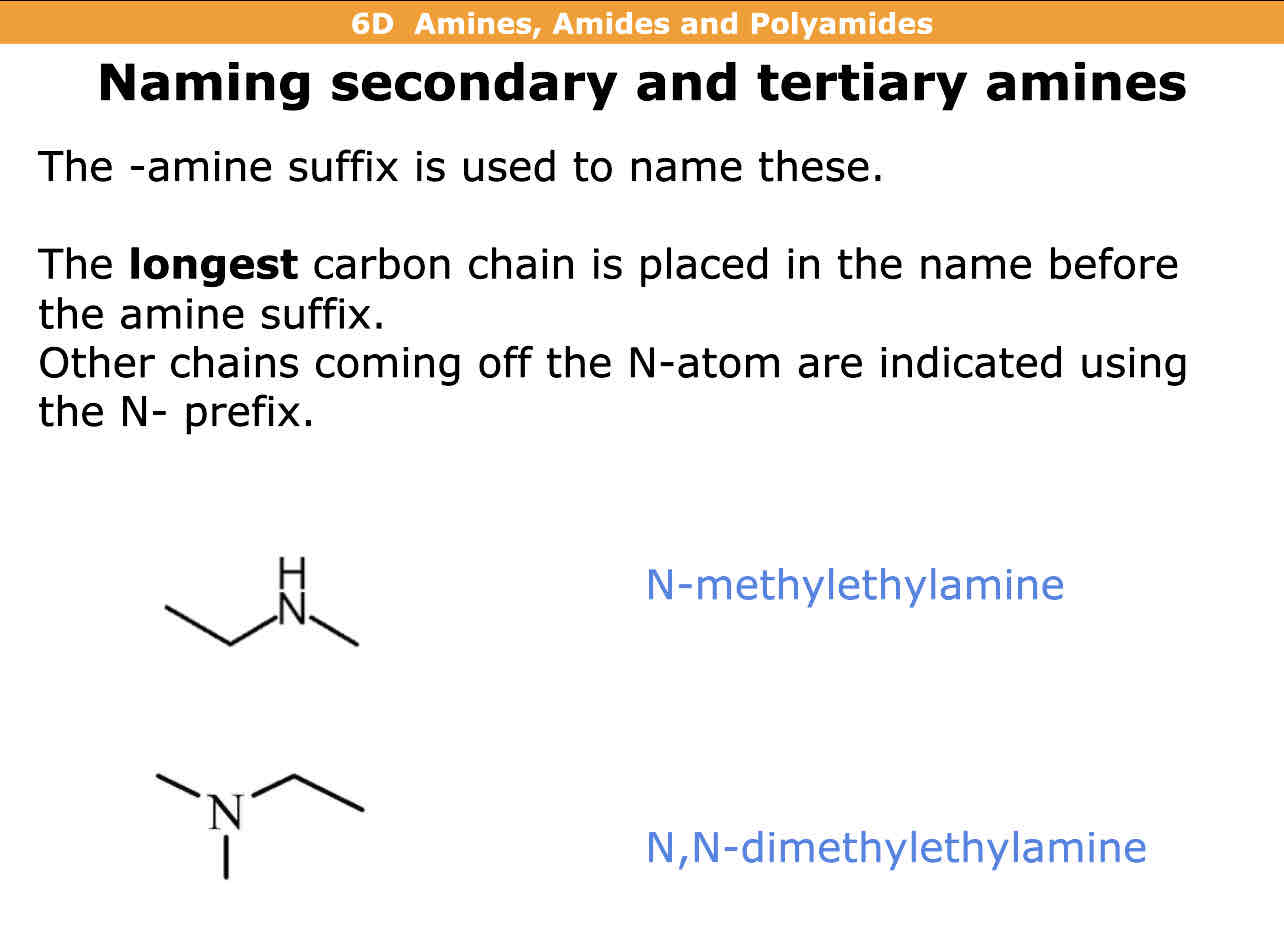
How do you name secondary and tiertiary amines
Amine suffix is used
Longest carbon chain is placed in the name before amine suffix
Other chains coming off N atom you use N- prefix
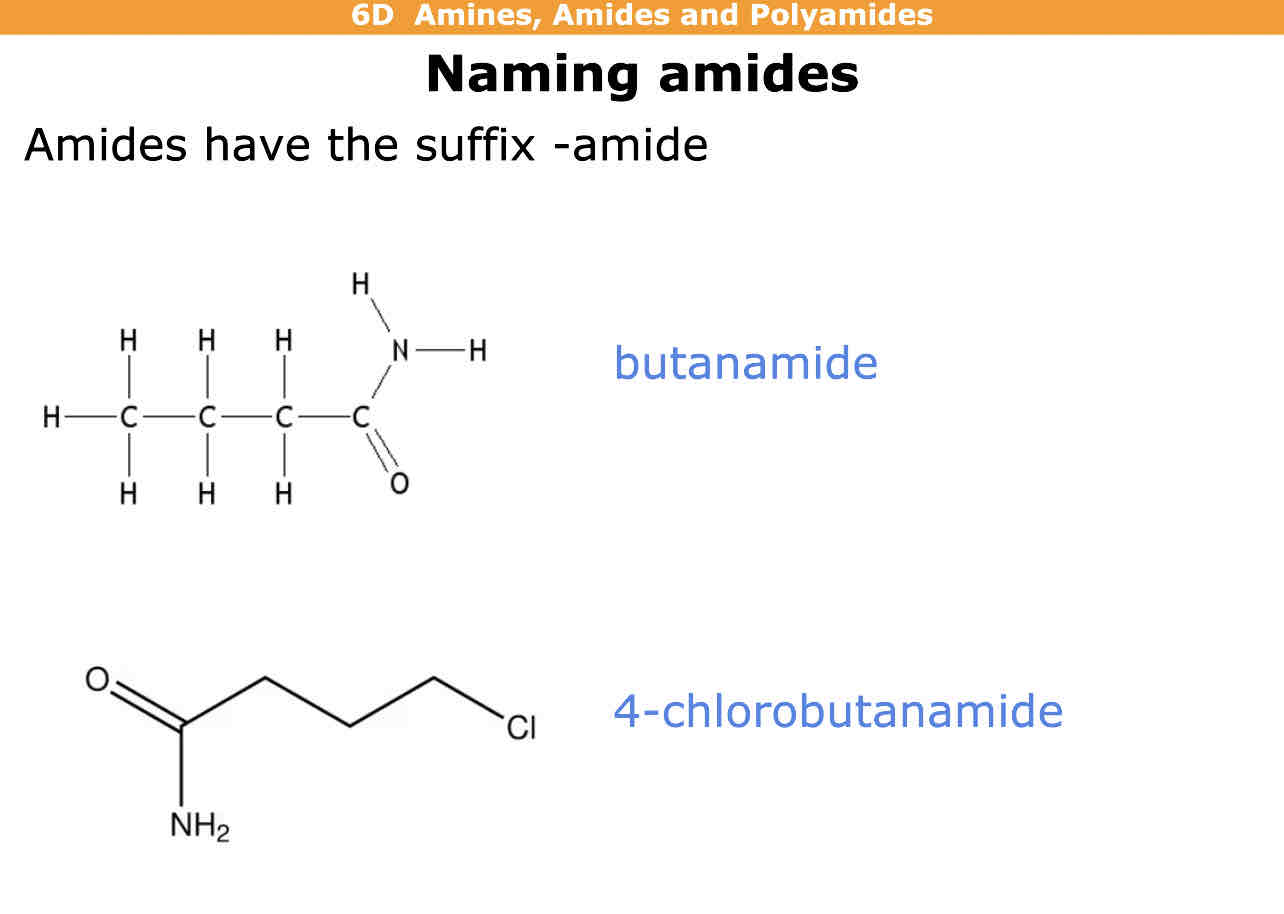
How do you name amides
Suffix - amide
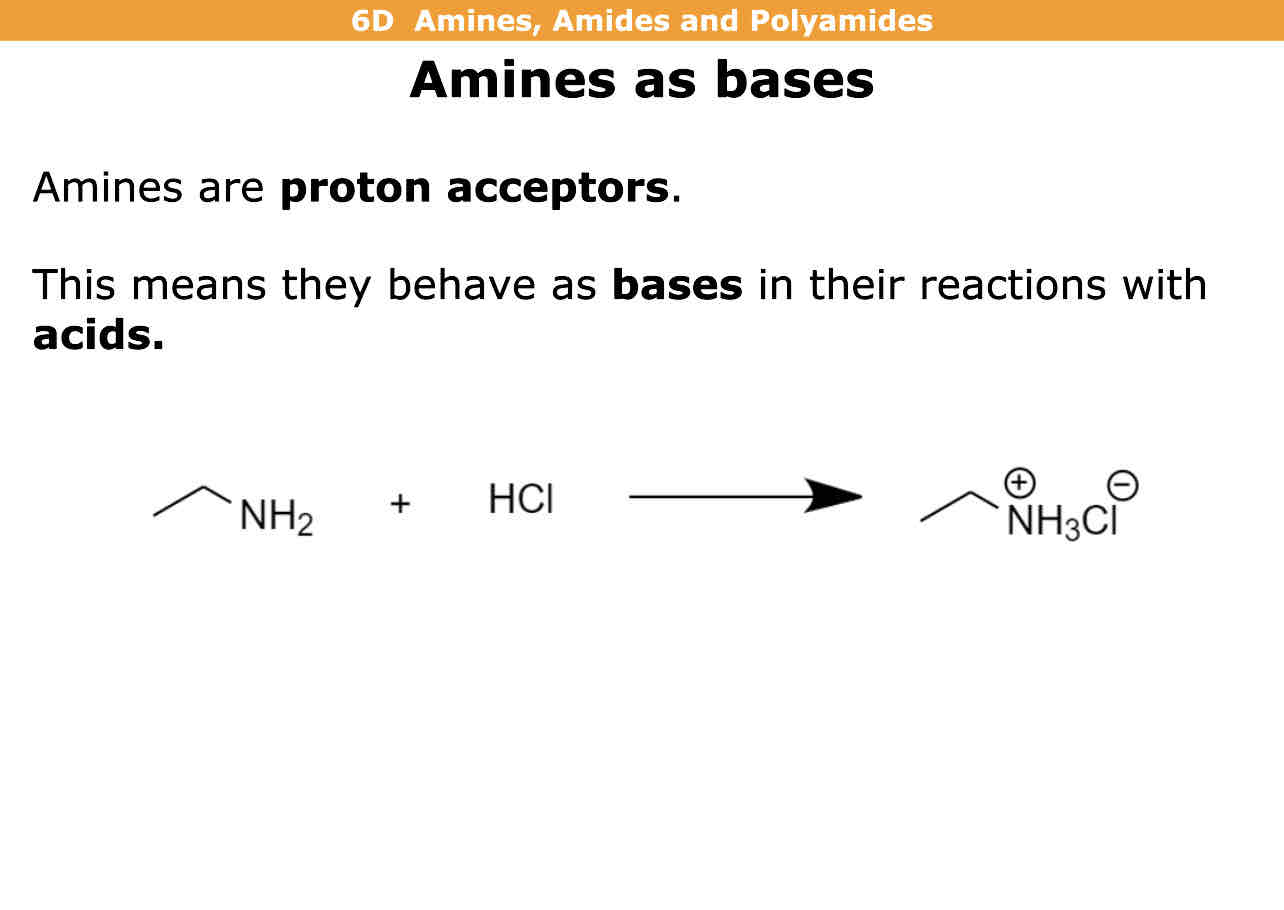
Amines can act as bases meaning their what
Proton acceptors
Reaction of amine with an acid
NH2 gains hydrogen to form NH3 with + charge
And negative ion is formed too
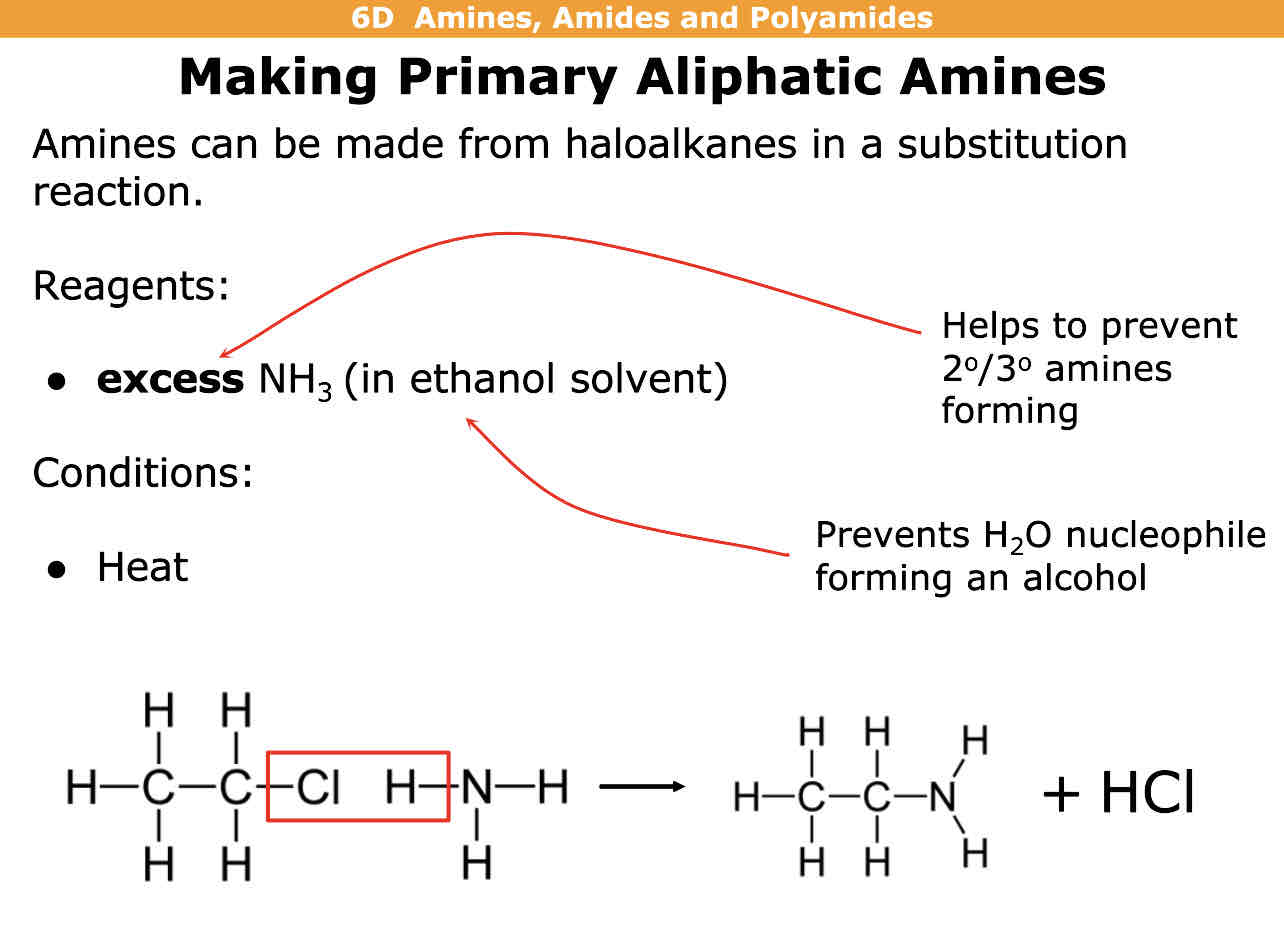
How to make primary aliphatic (doesnt contain a benzene ring) amines
What are the reagents?
What are the conditions?
Haloalkane + NH3 —> primary aminr + hydrogen halide
Reagents =excess NH3 (in ethanol solvent)
Conditions = Heat
How would you make secondary and tiertiary aliphatic amine
Secondary = primary amine + more haloalkane —> secondary amine + Hydrogen halide
Tiertiary = secondary amine + more haloalkane —> tiertiary amine + hydrogen halide
How do you make aromatic amines
What are the conditions
From nitrobenzene and forms amine + water
Use [H] as reducing agent
Conditions = Sn(tin) , conc HCl, reflux
Add NaOH (aq)
![<p>From nitrobenzene and forms amine + water</p><p>Use [H] as reducing agent</p><p>Conditions = Sn(tin) , conc HCl, reflux</p><p>Add NaOH (aq)</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/935ad75d-490f-4a5e-bea1-5375af235390.jpg)
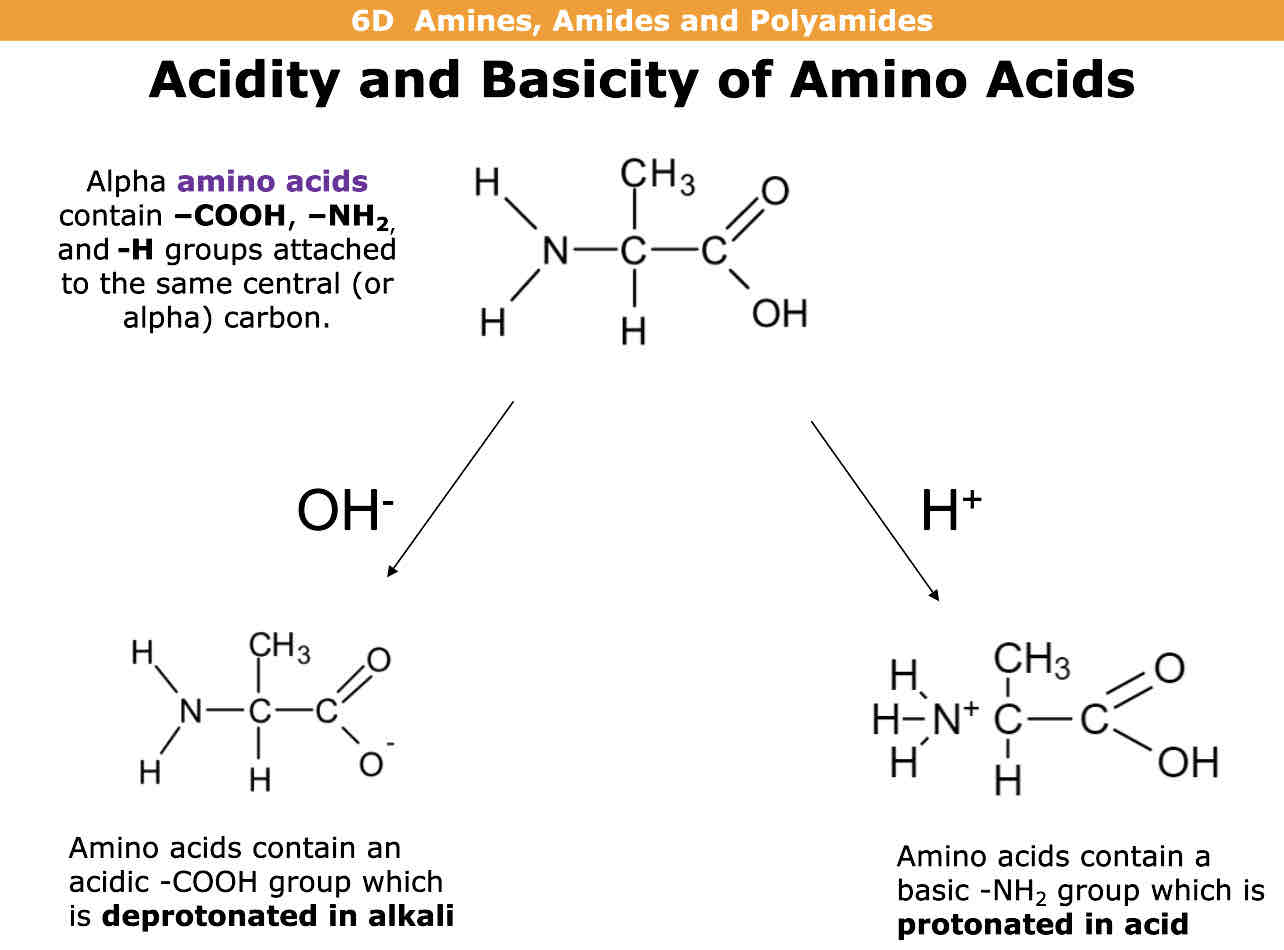
What are alpha amino acids
Amino acids containing COOH, NH2 and H attached to central carbon atom
How do alpha amino acids react to OH-(hydroxide ion)?
How do alpha amino acids react to H+ (hydrogen ion)?
OH= The COOH group is deprotonated (loses hydrogen ion and forms negative charge)
H+ = The NH2 group gains a hydrogen and gets protonated and forms a positive charge
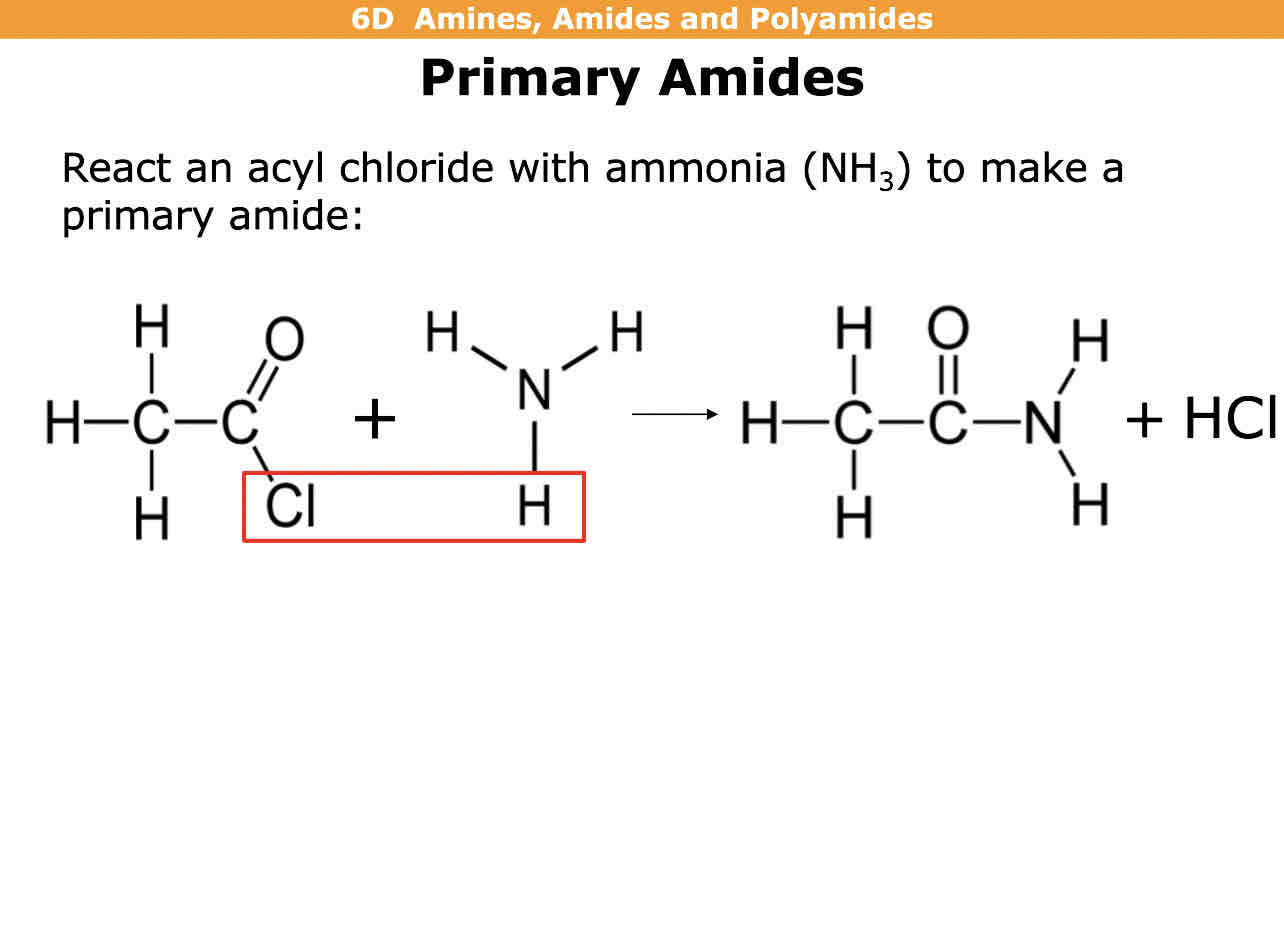
How do you make primary amides
Acyl chloride + ammonia (NH3) —> primary amide + HCl
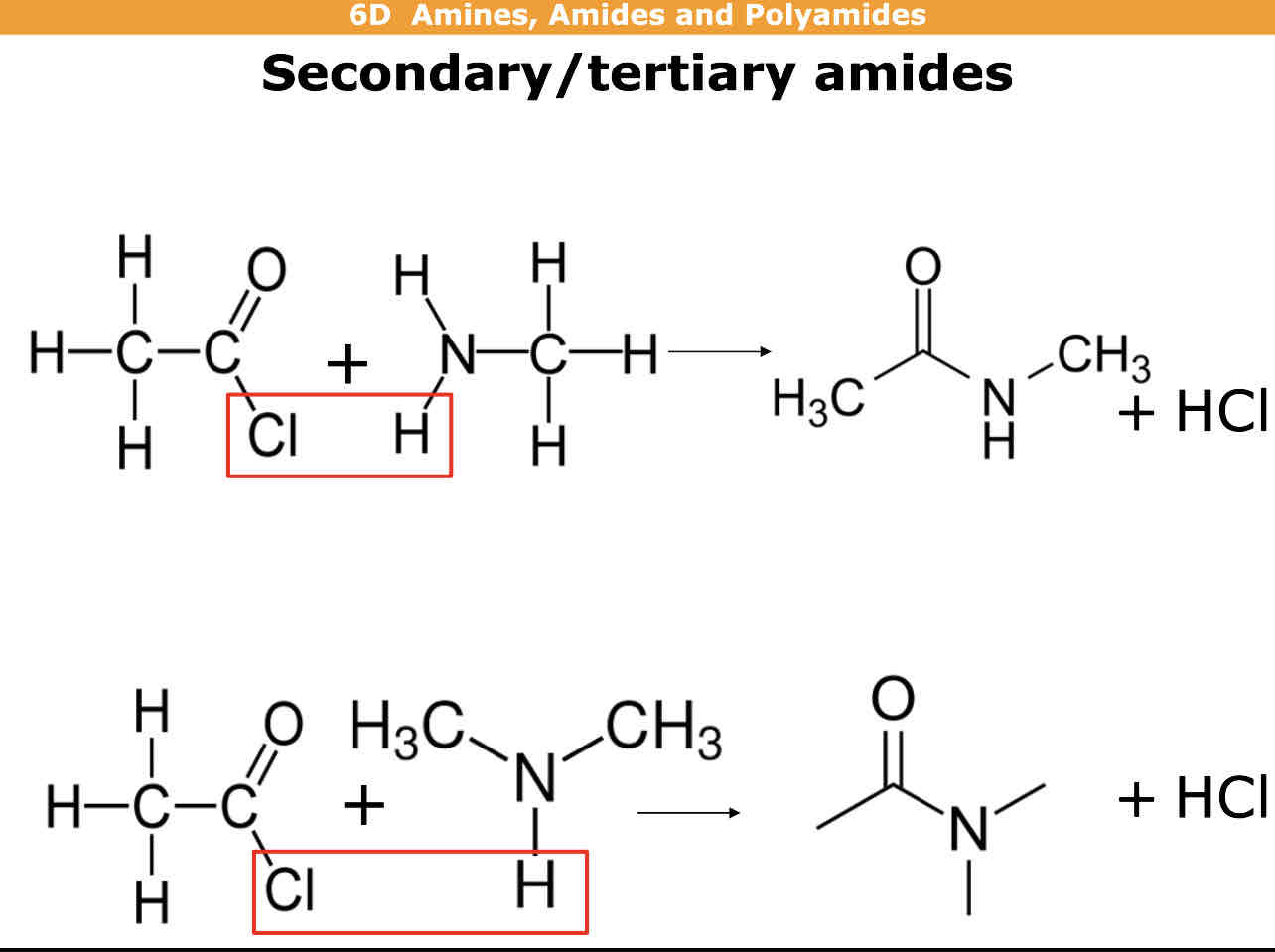
How do you make secondary/tiertiary amides
Secondary = Acyl chloride + primary amine —> secondary amide + HCl
Tiertiary = Acyl chloride + secondary amine —> tiertiary amide + HCl
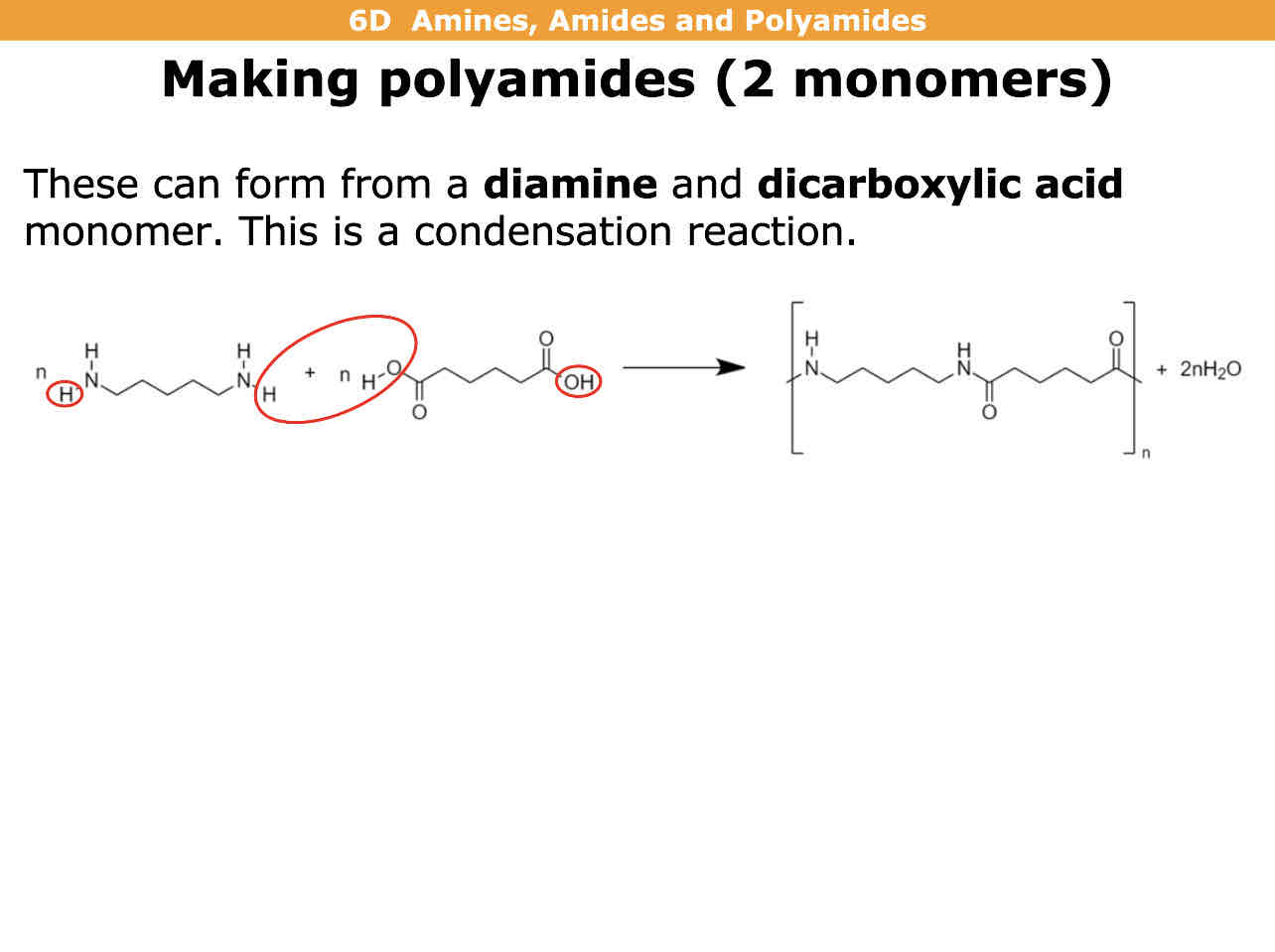
How do you make a polyamide with 2 monomers
Condensation reaction of diamine and dicarboxylic acid to form polyamide and water (2 molecules of water is formed)
How do you make a polyamide with one monomer
The single monomer must have carboxylic acid or Acyl chloride group and must have an amine group and h20 is a product
In polyamide hydrolysis what happens
The carboxylic acid and the amine is split up
With HCL the amine is protonated and carboxylic acid remains the same
With OH the amine remains the same and the carboxylic acid is deprotonated