cob 300c - test 1 study guide (ch. 1-7)
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Service
Intangible
Can not be stored
Quality corrections may not be possible
Higher customer contact (experience matters)
Process may affect customer
Less uniformity in outputs
Supply Chain
a sequence of activities and organizations involved in producing and delivering a good/service
Suppliers → producer → distributor → customers
Process
one or more actions that transform inputs into outputs
Two factors that tend to have universal strategic operations importance.
Quality and time
Operations Function
set of activities in business that generate value by transforming inputs into outputs using efficient processes
Ex. Input = doctor → process = surgery
output = healthy patient
Product
Tangible
Can be stored
Quality corrections possible
Less customer contact
Process may not affect customer
Higher uniformity in outputs
Systems Design
Typically strategic decisions that require long-term commitment of resources and determines parameters of system operation
Ex. capacity, facility location & layout, product/service planning
Systems Operations
- Generally tactical and operational decisions
- Ex. scheduling employments, managing quality control and projects
- Where operations managers spend most of their time
Mass Production
Utilizes interchangeable parts and division of labor
Lean Production
- Get inventory just in time, simply when it is needed.
- More efficient, reduce waste
Mass customization
catering to high demand, but customers can put their specified request
Ex. dell computers, nike shoes
Order Loser
product/service characteristics that repel customers
Order qualifiers
basic characteristics of product/service for customers to consider
Order Winners
characteristics of product/service is perceived as better than competition
Ex. mcdonalds give free toys to kids
Cost Leadership
- Price lower than competitors (max value)
- Ex. walmart
Differentiation
- Distinguish organization (value add)
- Ex. apple
focus
Target specific segment of market
Upper management processes
govern the operation of entire organization
Operational processes
core processes that make up value stream
Supporting processes
support core processes
Supply > Demand
Too much investment, not a lot of return
- Wasteful + costly
Supply < Demand
Cannot cater to demand, losing potential to earn revenue
- Opportunity loss + customer dissatisfaction
Supply = Demand
ideal
Systems Approach
Emphasizes interrelationships among subsystems (the whole is greater than the sum of its parts)
Strategy
action plan for how an organization expects to achieve its missions/goals
Organizational strategies
Higher level, org as a whole
Functional level strategies
- Slightly different focuses
- More detailed/specific
organizations implement strategies through:
- tactics : the "how to" part
- operating procedures : the actual "doing" part
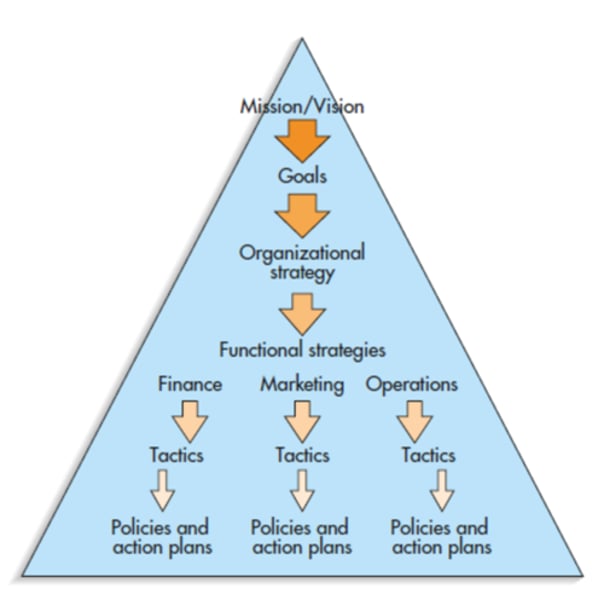
Strategic Hierarchy
Mission -> Organizational goals-> organizational strategies ->
functional strategies -> operations strategies -> tactics -> operating procedures
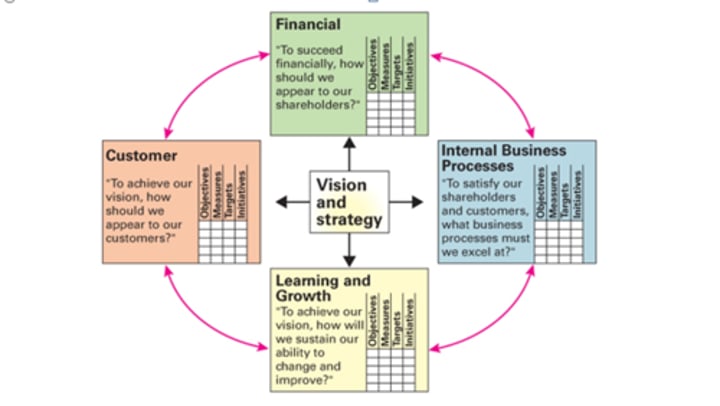
Balanced Scorecard
A top-down management system used to clarify vision/strategy and transform them into action
Productivity
- A measure of the effective use of resources
- Usually expressed as the ratio of output to input
- Operations Manager's responsibility is to increase productivity
Single-factor productivity
= output/(single input)
Multifactor productivity
=output/(multiple inputs)

Life cycle and its implications
- Selling something at maturity phase, relatively stable (Efficiency)
- Growth phase, focus on speed
The six phases of the generic development process are:
Phase 0: Planning
Phase 1: Concept development
Phase 2: System-level design
Phase 3: Design detail
Phase 4: Testing and refinement
Phase 5: Production ramp-up
In which variant of the generic product development process, does concept development assume a proven technology?
Platform products
Variants of product development
- technology push products
- platform products
- process-intensive products
- customized products
- quick-build products
- complex systems
- generic (market pull products)
- High-risk Products
technology push products
firm begins with new technology and looks for a market
ex. tyvex envelopes, gore-tex rainwear
platform products
built around a preexisting technological subsystem
-EX: consumer electronics, computers, printers
process-intensive products
-production process has an impact on the properties of the product
-Product design cannot be separated from process design
- characteristics are highly constrained by the production process
-ex. snack foods, breakfast cereals, chemicals
customized products
new products are slight variations of existing configurations
- highly structured development process
- ex. motors, switches, batteries, containers
quick-build products
rapid modeling and prototyping enables many design-build-test cycles
- testing phases are repeated
- ex. software, cellular phones
complex systems
systems must be decomposed into several subsystems and many components
- system integration and validation
- airplanes, jet engines, automobiles
generic (market pull products)
The team begins with a market opportunity and selects appropriate technologies to meet customer needs
- distinct planning, process design, etc.
- sporting goods, furniture, tools
High-risk Products
Technical or market uncertainties create high risks of failure
- ex. pharmaceuticals, space systems
sequential approach
stakeholders getting involved in stages, one at a time
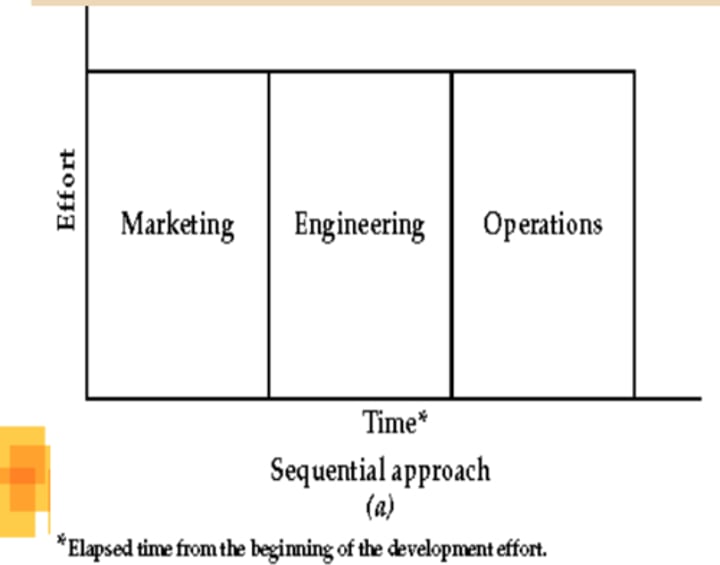
concurrent approach
stakeholders getting involved around the same times
- More agreement on services, faster and less mistakes
- Bring product faster to the market
House of Quality
a matrix that helps translate customer requirements into concrete operating or engineering goals. However, the most important benefit of the house of quality is that it helps focus on building a product that satisfies customers.
- Customer requirements + design requirements meet at the middle in relationships
Which of the following is primarily used to help design products that will connect product attributes with customer desires?
The house of quality matrix
Value analysis / value engineering
used to simplify products with the goal of achieving better performance at a lower cost.
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA)
Oriented toward the engineering of the product with an emphasis on reducing production cost
- simplification of the product by reducing the number of separate parts.
Cycle Time
the average time between completion of successive units
Utilization
the ratio of the time that a resource is actually used/activated relative to the time that it is available for use
Process Flowcharting
use of a diagram to present the major elements of a process
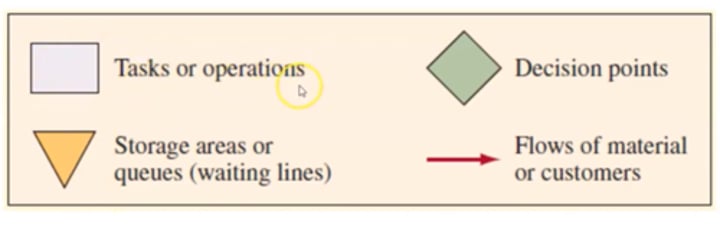
flowchart symbols
tasks/operations : rectangle
decision points : diamond
storage areas/queues(waiting lines) : triangle
flows of material/customers : arrow
Stage
used to indicate that multiple activities have been pulled together for analysis purposes
- Single-stage process
- Multi-stage process
Buffering
a storage area between stages where the output of a stage is placed prior to being used in a downstream stage
Blocking
occurs when the activities in a stage must stop because there is no place to deposit the item
Starving
occurs when the activities in a stage must stop because there is no work
Bottleneck
stage that limits the capacity of the process
Make to Stock (MTS)
process activated to meet expected or forecast demand
- Serve customers from finished goods inventory
Make to Order (MTO)
process activated in response to an actual order
- Make the customer's product from raw materials, parts, and components
Assemble to Order (ATO) / Hybrid
quicker response than MTO and more flexible than MTS
- Combine a number of preassembled modules to meet a customer's specifications
engineer to order
Firm will work with the customer to design the product , and then make it from purchased materials, parts, and components
Total average value of inventory
The total average investment in raw material, work-in-process, and finished goods inventory
Inventory turns
cost of goods sold divided by the average inventory value
Days-of-supply
inverse of inventory turns scaled to days
Little's Law
inventory = throughput rate x flow time
Efficiency
A ratio of the actual output of a process relative to some standard
actual output/standard output
Operation Time
The sum of the setup time and the run time for a batch of parts that are run on a machine
set up time + run time
Flow Time
The average time that it takes to move through an entire system
Throughput Rate
The output rate that the process is expected to produce over a period of time
1/ cycle time
Process Velocity (Throughput Ratio)
Ratio of value added time to flow time;
value added time/flow time
Value-added Time
The time in which useful work is actually being done on the unit
Run time
The time required to produce a batch of parts.
Calculated by multiplying the time required to produce each unit by the batch size.
Lead Time
The time needed to respond to a customers order
Customer Order Decoupling Point
Where inventory is positioned in the supply chain to allow processes or entities in the supply chain to operate independently
Product-Process Matrix
a model that describes the alignment of process choice with the characteristics of the manufactured good
Project Layout
For large or massive products produced in a specific location, labor, material, and equipment are moved to the product rather than vice versa
- Ex. airplane
Workcenter (Job Shop)
A process with great flexibility to produce a variety of products, typically at lover volume levels
Batch
a process in which goods or services are produced in groups (batches) and not in a continuous stream
Assembly Line
An item is produced through a fixed sequence of workstations, designed to achieve a specific production rate
Continuous Process
A process that converts raw materials into finished product in one contiguous process
Service Package
A bundle of goods and services that is provided in some environment
Bundles consist of five features:
1. Supporting facility
2. Facilitating goods
3. Information
4. Explicit Services
5. Implicit Services
High Degree of Customer Contact
More difficult to control and more difficult to rationalize than low degree of customer contact
Service System Design Matrix
1. Mail contact
2. Internet and on-site technology
3. Phone contact
4. Face-to-face tight specs
5. Face-to-face loose specs
6. Face-to-face total customization
Service System Design Matrix characteristics
high contact reduces efficiency, but has high sales potential
Production line approach
service delivery is treated much like manufacturing (McDonald's)
Self-Service Approach
customer takes a greater role in the production of the service (ATM machines)
Personal Attention Approach
Ritz-Carlton Hotel Company
Service Blueprint
The flowchart of a service process, emphasizing what is visible and what is not visible to customers
Poka-yokes
Procedures that prevent mistakes from becoming defects. They are commonly found in manufacturing but also can be used in service processes
How should services accommodate the variation introduced by the customer?
more accommodation → more cost
less accommodation → less satisfaction
Five Types of Variability
1. arrival variability
2. request variability
3. capability variability
4. effort variability
5. subjective preference variability
arrival variability
customers arrive at times when there are not enough service providers
request variability
travelers requesting a room with a view
capability variability
A patient being unable to explain symptoms to doctor
effort variability
shoppers not putting back their carts
subjective preference variability
interpreting service action differently
strategies for managing customer-introduced variability
- classic accommodation (employees on hand)
- low cost accommodation (low-cost labor, outsource, self service)
- classic reduction (require reservations)
- uncompromised reduction (target customers)