Public Policy Analysis and Administration - lecture 5
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Why does the state exists?
It regulates the way in which the economy works
Ir promotes social harmony and ensures the well being of its citizens
Karl Polanyi, the paradox of the state
The state is essential for ensuring the proper functioning of markets by establishing a legal framework and regulating economic activities. At the same time, it is necessary to mitigate the harmful effect of markets
What do neoliberals advocate for?
Free and regulated markets, claimed to be more efficient at allocating resources, stimulating economic growth and fostering innovation
What are the elements of neoliberalism?
Liberalisation: opening of national markets to global markets
Privatisation: public owned enterprises and services are transferred to the private sector
Deregulation: government regulations on businesses are reduced or eliminated
What is NPM?
New Public Management (NPM) has been one of the key initiatives that have reshaped public administration by integrating private-sector methods while è maintaining governmental oversight by introducing principles such as operational efficiency and accountability
What is public administration?
It is the organisational structure and civil servants who implement the policies and decisions made by political leaders.
It is responsible for the daily execution of government operations, the management of public resources and the delivery of public services to citizens.
What is political authority?
It is the power and influence held by elected political leaders who possess the poor to make political decisions formulated public policies and represent citizens within the government.
It derives from the legitimate mechanisms of appointment
What aer the characteristics of weberian bureaucracy?
Hierarchy and organised structure
Division of labor
Rules and defined procedure
Impersonality
Enormity-based pay system
Career logic
Specialisation and expertise
What is an administrative tradition?
It refers to the historical, cultural and institutional frameworks that shape how public administration operates in a specific country or region
What are the key features of administrative traditions?
Rooted in long-standing historical and legal foundations
Influences the structure, behaviour and decision-making processes of bureaucracies
Reflects the values, norms and priorities of the society it serves
Which are the main administrative traditions?
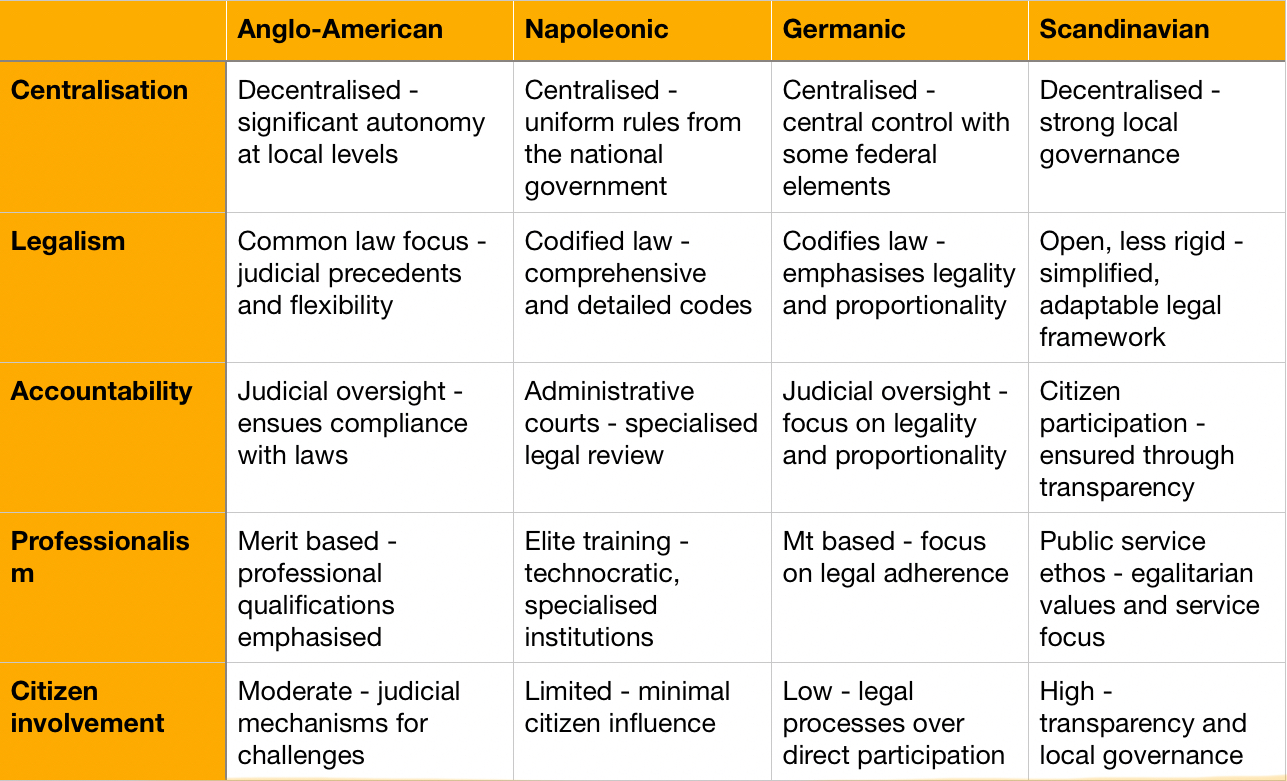
What is Public Choice Thery?
It is an economic approach that focuses on the role of the state and the political behaviour of various actors.
It argues that the government is composed of individuals, including civil servants, who seek to serve not only the public interest but also their personal interests
What are the main criticism towards bureaucracy?
Exponential growth
Ineffectiveness and slowness
Increasing demands for accountability
Impact of technology and globalisation
Economic challenges
Theoretical critiques
What are the main effects of NPM reforms?
Strengthening of the political over the administration
New relationship between control-oriented bureaucracies and professional groups
Introduction of market and competition mechanisms
Challenges to institutional protections and employment flexibility
What is the NPG?
The collaborative model of New Public Governance puts the state at the heart of solutions and strategies to build a more sustainable and equitable future
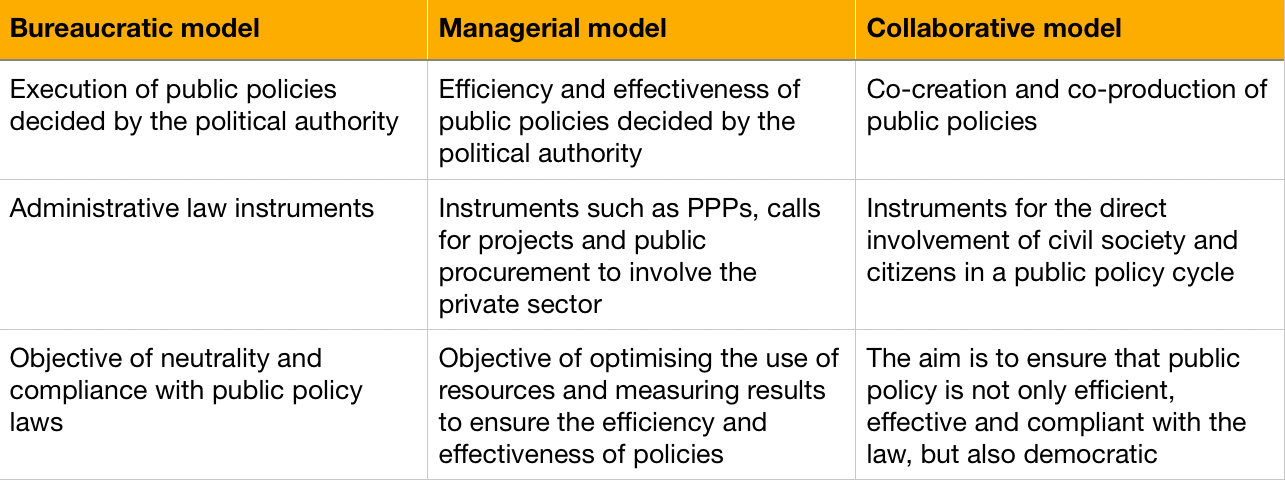
What are the main differences between the bureaucratic model, the managerial model and the collaborative model?
What are the features of the neo-weberian state?
Weberian principles retained: rule of law, professional bureaucracy, state authority
Modern adaptation: citizen engagement (NPG) and service oriented (NPM)
Strategic role of the state: combines long-term policy planning with the modernisation of institutions and leverages technology to improve efficiency and transparency
Balanced approach: rejects full market logic (NPG), balances state-driven governance with efficient service delivery (NPM) and emphasises democratic oversight, transparency and participatory governance (NPG)