Coastal Landscapes & Change Vocabulary List
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:38 PM on 3/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
1
New cards
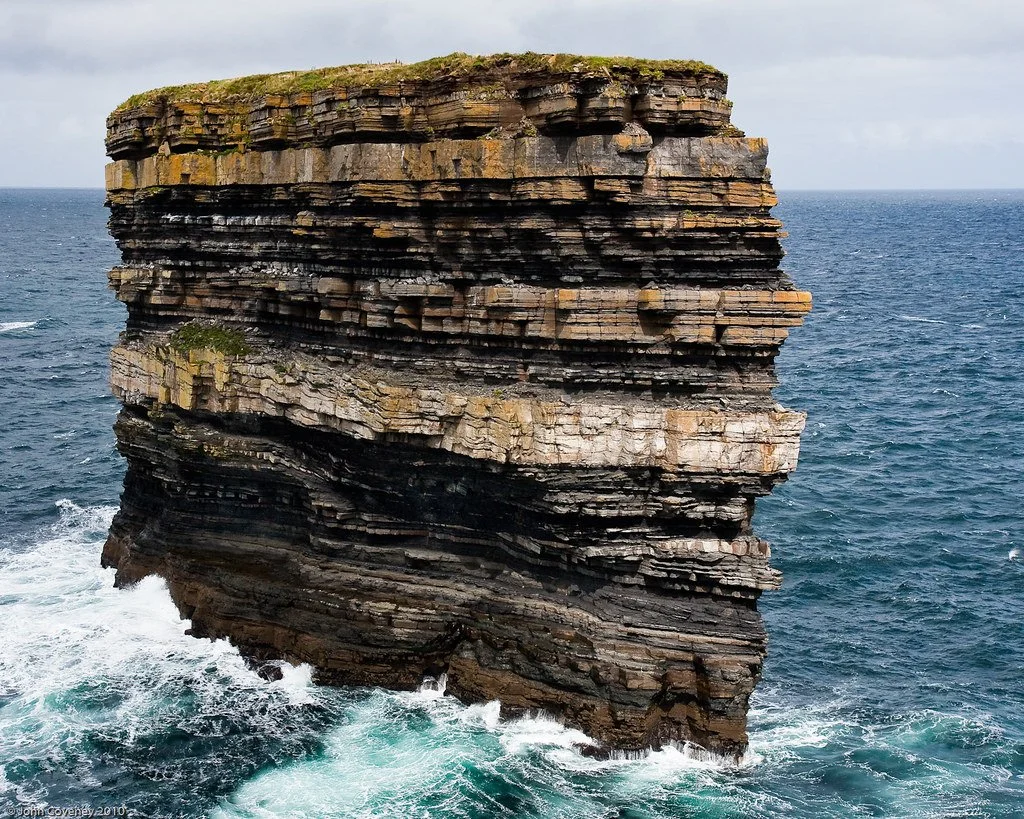
Littoral zone
The area of shoreline where land is subject to wave action
2
New cards
Offshore
The area of deeper water beyond the point at which waves begin to break
3
New cards
Nearshore
The area of shallow water beyond the low tide mark
4
New cards
Foreshore
The area between the high tide and the low tide mark
5
New cards
Backshore
The area above the high tide mark
6
New cards
Rocky coastline
Areas of high relief varying from a few metres to hundreds of metres in height, with resistant geology & high energy
7
New cards
Sandy coastline
Areas of low relief with sand dunes and beaches, that are much flatter, with less resistant geology & high energy
8
New cards
Estuarine coastline
Areas of low relief with salt marshes and mudflats, at river mouths in a low energy environment
9
New cards
Eroding coastline
Where erosion exceeds deposition: there is a net loss of sediment and the coastline retreats
10
New cards
Outbuilding coastline
Where deposition exceeds erosion there is a net gain of sediment and the coastline advances
11
New cards
Lithology
Physical properties of a rock (rock type)
12
New cards
Weathering
The breakdown of rock *in situ*
13
New cards
Erosion
The breakdown of rock and its immediate transport by the eroding agent
14
New cards
Mass movement
The downslope movement of material due to the force of gravity
15
New cards
Coastal accretion
Where continuous net deposition causes the coastline to extend seawards
16
New cards
Concordant coastline
Coasts that form where rock strata run parallel to the coast
17
New cards
Discordant coastline
Coasts that form where rock strata are aligned at an angle to the coastline
18
New cards
Geological structure
The characteristics and arrangement of rock units
19
New cards
Strata
Different layers (or beds) of rock
20
New cards
Bedding plane
The interface between two sedimentary strata

21
New cards
Deformation
The degree of tilting of folding of rock
22
New cards
Dip
The angle of inclination of titled strata
23
New cards
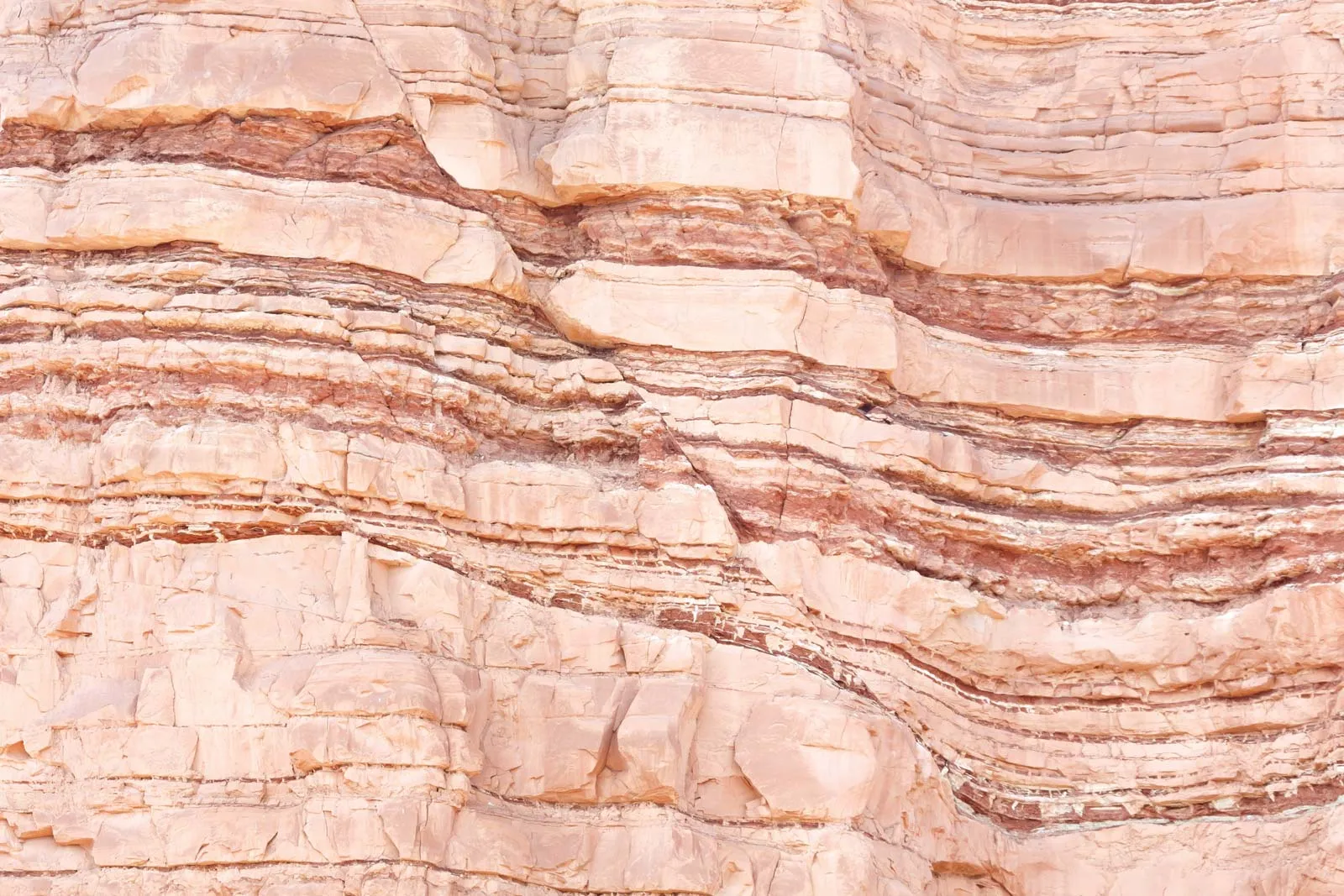
Faulting
The fracturing of rock with movement from its original position

24
New cards
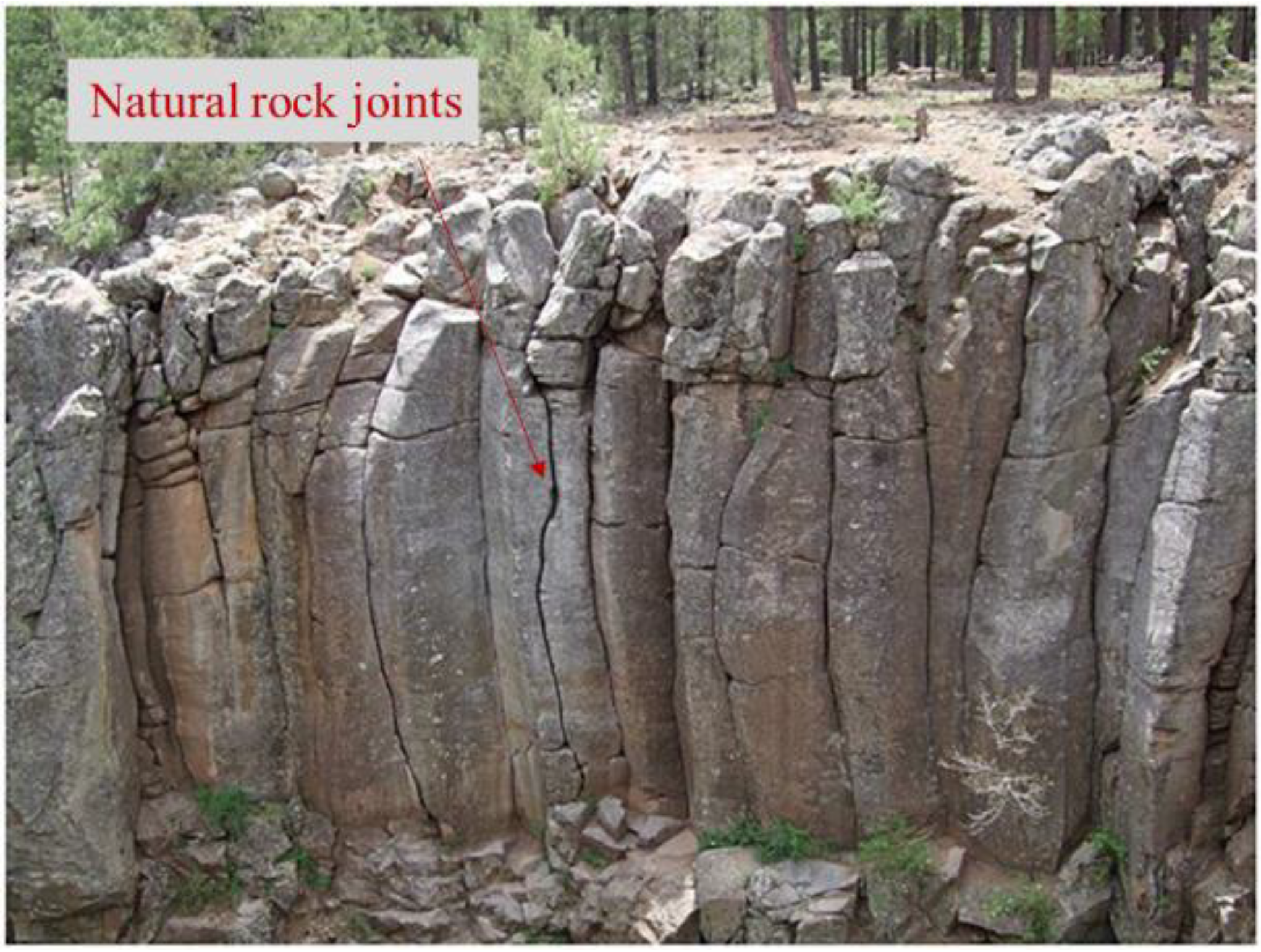
Joint
A fracture of rock without movement from the original position

25
New cards
Morphology
The shape of landscape features, influenced by geological structure
26
New cards
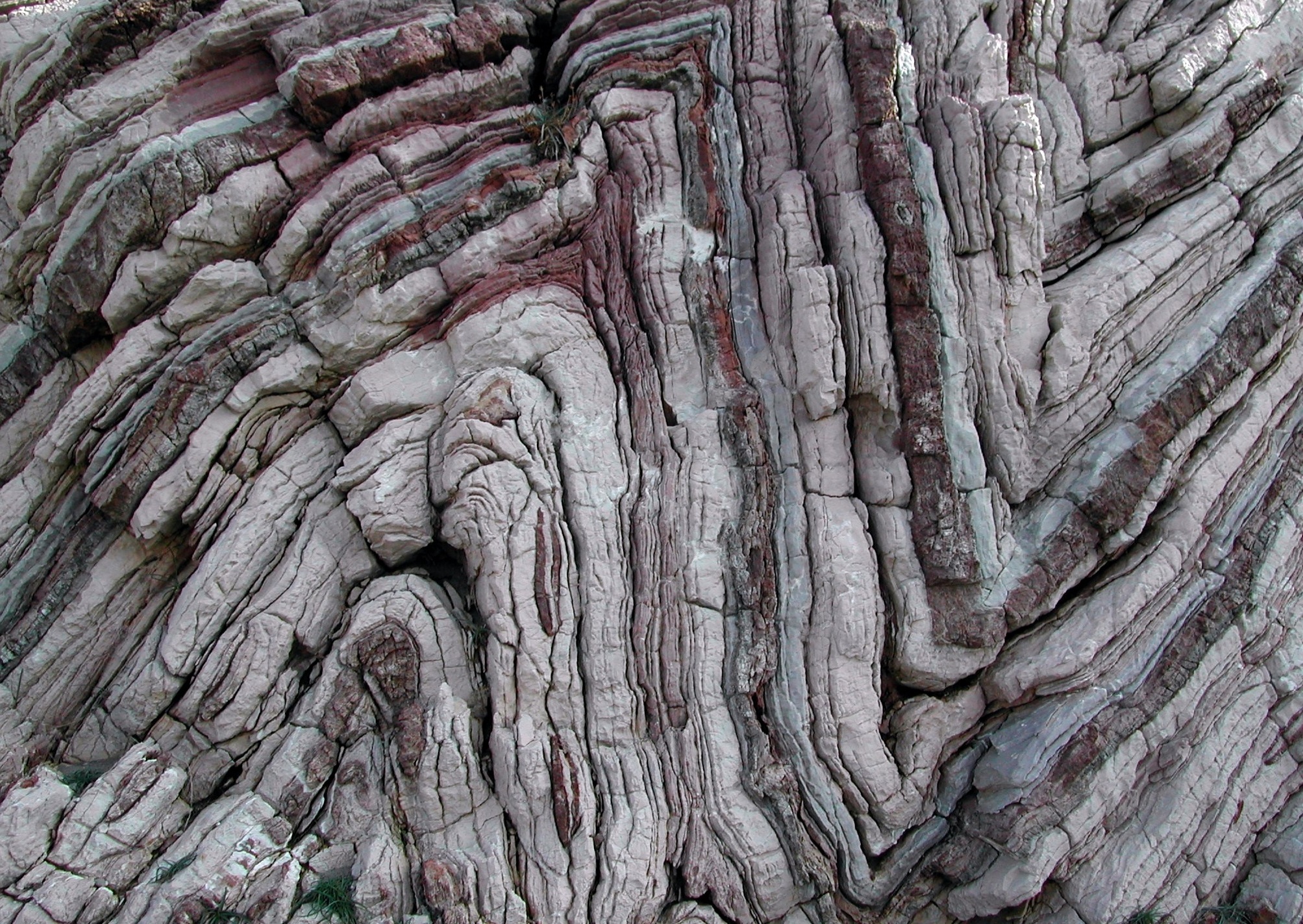
Folds
Bends in rocks produced by sedimentary rock layers being squeezed by tectonic forces

27
New cards
Cliff profile
The height and angle of a cliff face, plus its features such as wave-cut notches or changes in slope angle
28
New cards
Micro-features
Small-scale coastal features such as caves and wave-cut notches which form part of a cliff profile
29
New cards
Rate of recession
The speed at which the coastline is moving inland
30
New cards
Clastic rocks
Rocks made of sediment particles cemented together
31
New cards
Crystalline rocks
Rocks made of interlocking mineral crystals
32
New cards
Igneous rocks
Rocks formed from solidified lava or magma
33
New cards
Metamorphic rocks
Rocks formed by the recrystallisation of sedimentary and igneous rocks through heat and pressure
34
New cards
Sedimentary rocks
Rocks formed by the compaction and cementation of deposited material, or sediment
35
New cards
Unconsolidated sediment
Sediment that has not yet been cemented to form solid rock
36
New cards
Drift geology
Recently deposited unconsolidated sediment that usually overlies the solid geology of the bedrock
37
New cards
Permeable rocks
Those that allow water to flow through them, due to being porous or having numerous joints
38
New cards
Pioneer plants
The first plants to colonise freshly deposited sediment
39
New cards
Plant succession
The changing structure of a plant community over time as an area of initially bare sediment is colonised
40
New cards
Climax community
The end result of a plant succession
41
New cards
Xerophytic plants
Plants that are specially adapted to dry conditions to colonise bare sand
42
New cards
Psammosere
Plant succession on sand
43
New cards
Embryo dunes
Form when seaweed, driftwood or litter provides a barrier or shelter to trap sand
44
New cards
Yellow dunes
Form when marram grass colonise sand, have a sandy surface
45
New cards
Grey dunes
Form when marram grass & sedge grass dries, adding hummus to the sand; are fixed
46
New cards
Halophytic plants
Plants that are specially adapted to saline conditions to colonise mud
47
New cards
Halosere
Plant succession in salty water
48
New cards
Flocculation
When clay particles stick together and sink
49
New cards
Dune blowouts
Gaps created when storm events erode sections of the yellow dune through wind or wave action

50
New cards
Wave
The transfer of energy from one water particle to its neighbour with individual water particles moving in a circular orbit
51
New cards
Wave height
Vertical distance from peak to trough
52
New cards
Wavelength
The horizontal distance from crest to crest
53
New cards
Wave frequency
The number of waves passing a particular point over a given period of time
54
New cards
Fetch
The uninterrupted distance across water over which the wind blows
55
New cards
Constructive waves
Low energy waves with a strong swash, depositing sediment
56
New cards
Destructive waves
High energy waves with a strong backwash, eroding sediment
57
New cards
Swash
The name given to the waves that rush up the beach after a wave has broken
58
New cards
Backwash
The name given to the water that runs down the beach after the swash
59
New cards
Beach morphology
The shape of the beach
60
New cards
Sediment profile
The pattern of distribution of different sized or shaped deposited material
61
New cards
Berm
A ridge of material across the beach

62
New cards
Shingle
Pebble-sized sediment
63
New cards
Hydraulic action
Where the force of water breaks up rocks by infiltrating cracks, through the direct impact of the water or through the compression of air
64
New cards
Abrasion
Where a wave picks up sediment and throws these load items against a rock; the repeated impact chips away at the rock face until small fragments break away
65
New cards
Corrosion
Where acidic water in waves dissolves rock minerals, which are carried away in solution
66
New cards
Attrition
Where material transported by a wave is eroded through collision with other load items
67
New cards
Wave cut notches
A curved indentation of about 1-2 m high extending along the base of a cliff

68
New cards
Wave cut platform
A flat rock surface exposed at low tide, extending out to sea from the base of a cliff.
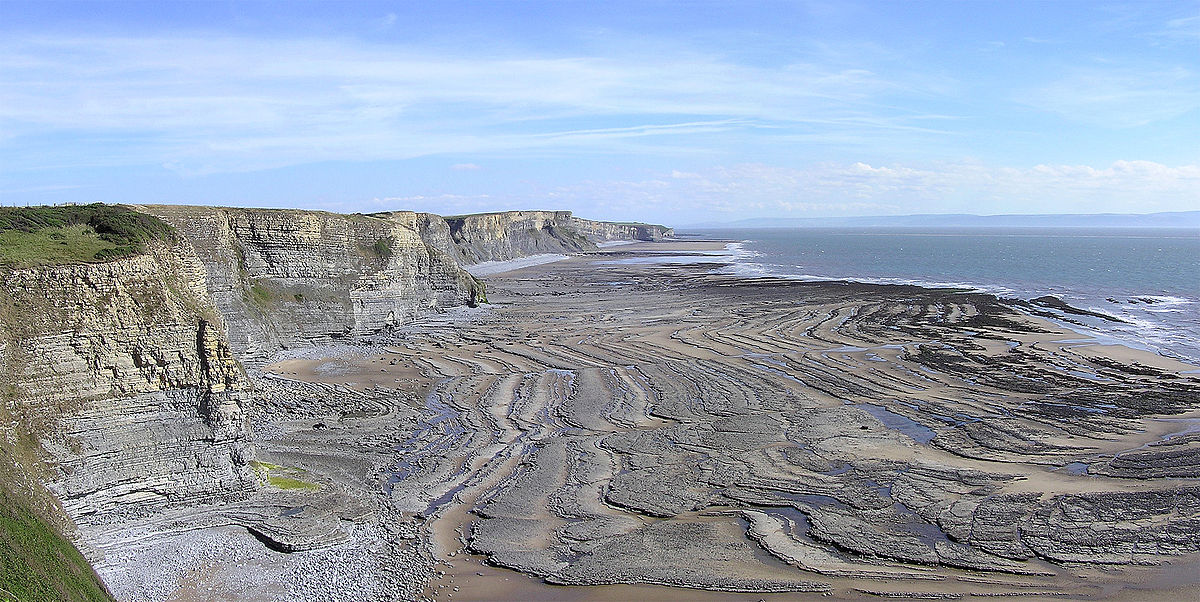

69
New cards
Cliffs
Steep slopes that are usually unvegetated
70
New cards
Traction
Where large, heavy load items are rolled along the sea bed
71
New cards
Saltation
Where lighter sediment bounces along the sea bed
72
New cards
Suspension
Where very light sediment is carried aloft within a body of water or air
73
New cards
Solution
Where sediment is carried dissolved within the water
74
New cards
Longshore drift
The net lateral transport of material along the coastline when waves approach the coast at an angle
75
New cards
Current
The flow of water in a particular direction
76
New cards
Tides
The flow of water in a particular direction, and they can transport sediment in the nearshore and offshore zone
77
New cards
Prevailing wind
Most common wind direction
78
New cards
Dominant wind
Strongest wind direction
79
New cards
Tidal range
The distance between high tide and low tide
80
New cards
Beaches
Accumulations of sand and/or shingle found in the foreshore and backshore zones
81
New cards
Bayhead beaches
Curved beaches found at the back of a bay

82
New cards
Spits
Linear ridges of sand or shingle beach stretching into the sea beyond a turn in the coastline but connected to the land at one end
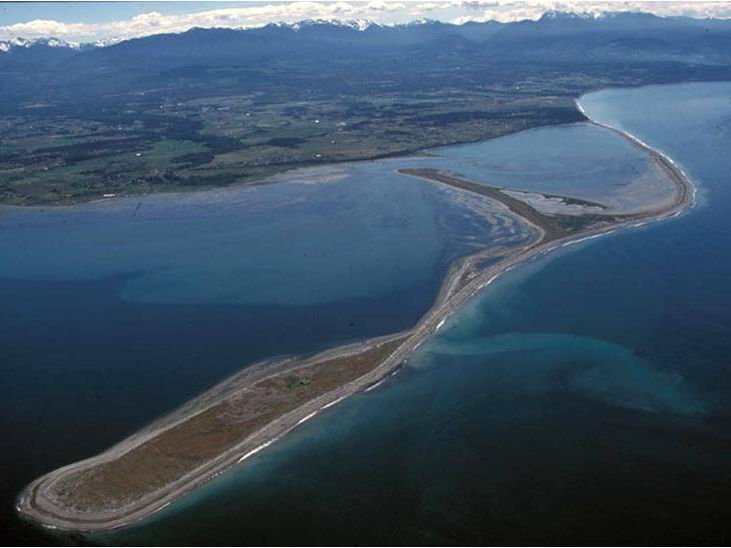

83
New cards
Hooked/recurved spit
A spit whose end is curved landwards, into a bay or inlet
84
New cards
Double spit
Where two spits extend out in opposite directions from both sides of the bay, towards the middle
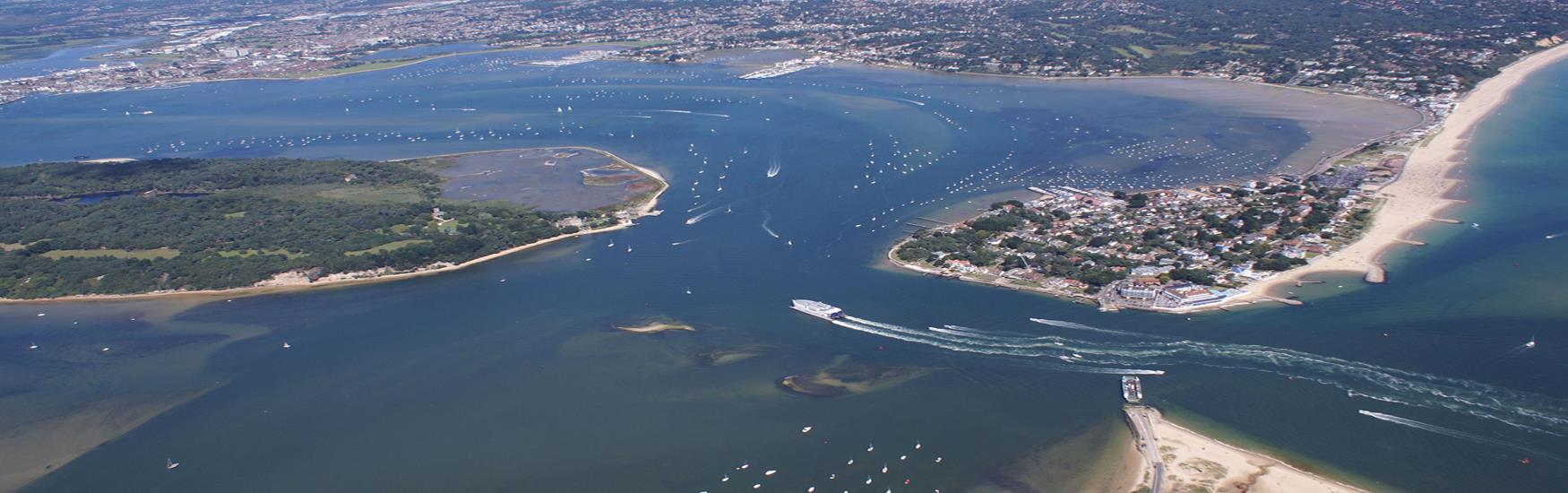

85
New cards
Offshore/breakpoint bars
Ridges of sand or shingle running parallel to the coast in an offshore zone
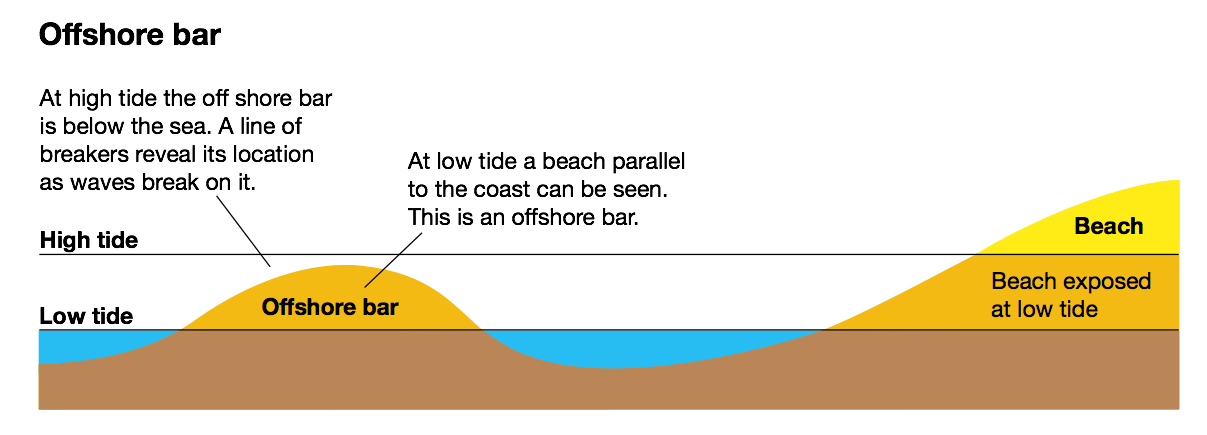
86
New cards
Bars/barrier beach
Linear ridges of sand/shingle extending across a bay and are connected to land on both sides
87
New cards
Tombolos
Linear ridges of sand and shingle connecting an offshore island to the coastline of the mainland
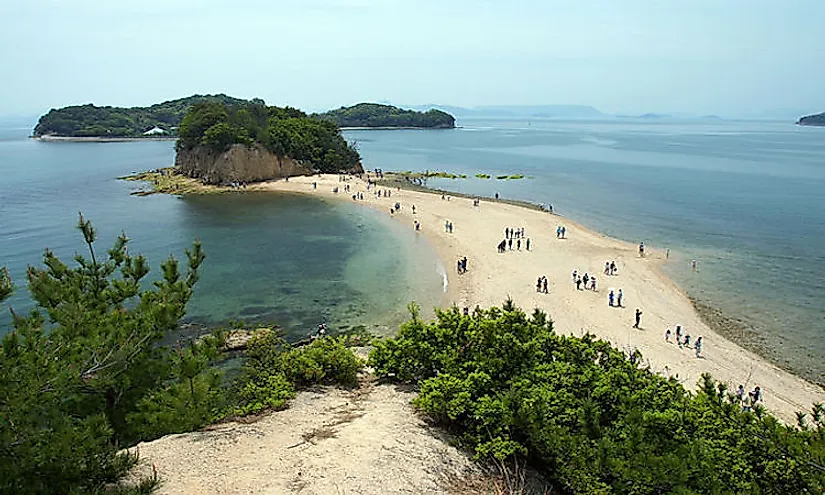

88
New cards
Cuspate foreland
Low lying triangular shaped headlands, extending out from a shoreline, formed from deposited sediment when longshore drift currents from opposing directions converge
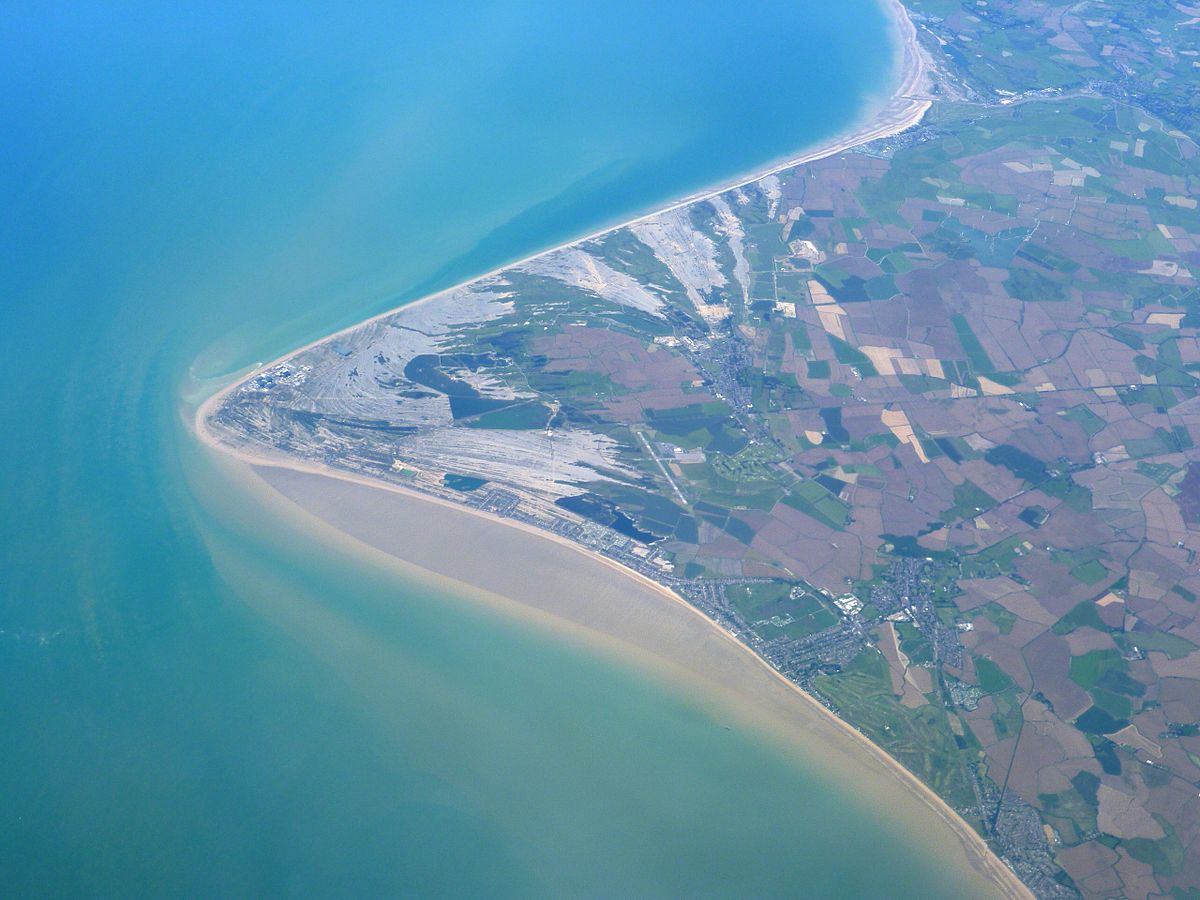

89
New cards
Sediment cell/Littoral cell
A linked system of sources, transfers and sinks of sediment along a section of coastline
90
New cards
Inputs/sources
Places where sediment is generated
91
New cards
Transfers
Places where sediment is moving alongshore through longshore drift and offshore currents
92
New cards
Outputs/sinks
Locations where the dominant process is deposition and depositional landforms are created
93
New cards
Physical/mechanical weathering
The application of force to physically fragment rock into smaller pieces called clasts
94
New cards
Freeze-thaw weathering
When water seeps into cracks in rocks & freezes, expanding in volume by 9% and fracturing rock
95
New cards
Salt crystal growth
When repeated tidal cycles lead to salt crystal growth in rock cracks, exerting tensional pressure
96
New cards
Wetting & drying
When rocks containing clay minerals are soaked with sea water & expand, then dry & shrink; repetition of this eventually causes rock to fragment & crumble
97
New cards
Chemical weathering
Where chemical reactions attack individual minerals in the rock, breaking bonds and producing new chemical compounds
98
New cards
Carbonation
When carbonic acid rain mixes with calcium carbonate in rocks to dissolve the minerals
99
New cards
Hydrolysis
The breakdown of minerals to form new clay minerals, plus materials in solution, due to the effect of water and dissolved carbon dioxide
100
New cards
Oxidation
The addition of oxygen to minerals, especially iron compounds, which produces iron oxides and increases volume, contributing to mechanical breakdown