Start of Orgo II, yikes...
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Gamma Rays cause?
Ionization
UV’s cause?
Electron Transitions
Infrared causes?
Molecular Vibrations
Microwaves cause?
Rotational Motion
Radio causes?
Nuclear Spin Transitions
IR spectroscopy determines?
Functional Groups
NMR is for determining what?
Arrangements of carbon and hydrogens, uses radio waves
UV-VIS Spectroscopy is for what
Determining pi conjugated systems
Different kinds of molecular vibrations IR causes
Stretching and bending
What determines IR spec intensity?
Strength of bond dipole movement
What determines IR spec WAVENUMBER, not intensity?
Strength of bond and mass

Remember this order
Vaporize, Ionize, Accelerate, Separate, Detect
M/Z in a mass spectroscopy uses what?
Mass/Charge ratio
Electron Impact
How Mass spectrometers ionize molecules
Base Peak vs Molecular/Parent Ion
Base peak is most abundant, Molecular/Parent ion is the molar mass
Bromine M and M+2 are
50/50
Chlorine M and M+2 are
3:1
Amines (NH2, no carbonyl) and OH typically undergo?
Alpha cleavage
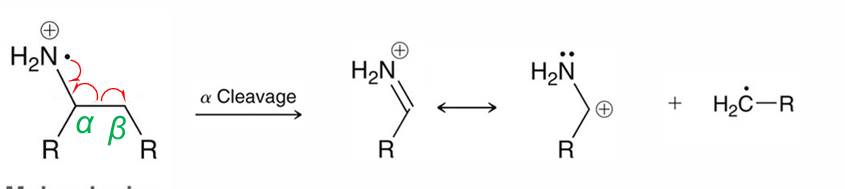
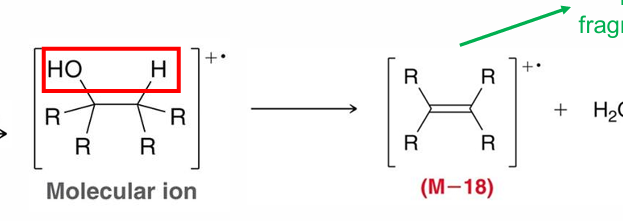
OH can also undergo?
Dehydration
Ketones may fragment how?
Lose an R group, leading to carbonyl doing resonance
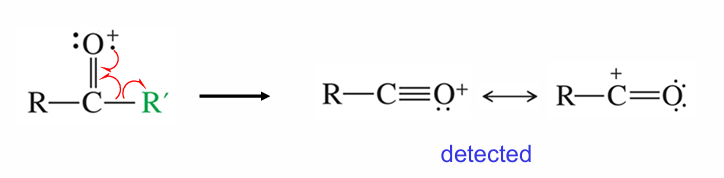
Aldehydes may fragment how?
Same as ketones, but with an H group to do resonance
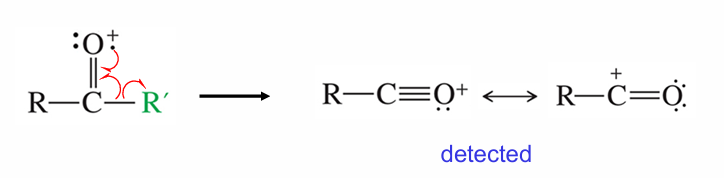
Number of HNMR signals?
Number of different TYPES of hydrogens
Chemical Shift (Location of the HNMR signal?)
Tells about its environment
Integration (area under the HNMR signal)
Indicates relative number of hydrogens in the signal
Multiplicity (signal splitting)
Indicates number of hydrogens on adjacent atoms
Look out for what sneaky hydrogens?
2 hydrogens on a carbon, look for homotopic/enantiotopic/diasteroptopic
More shielded = more electron density = appear where?
Low numbers (right), since it is harder to move them so they chemically shift less.
Chemical shifts are measured in?
parts per million (ppm)
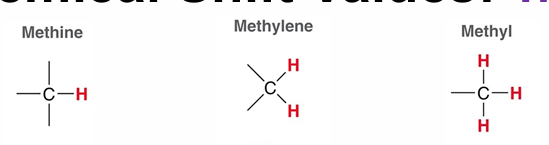
The more methylated a carbon?
The more shielded the hydrogens = lower PPM
Hydrogens near stronger electronegativities have what happen?
They get deshielded from electron stealers, and gain PPM
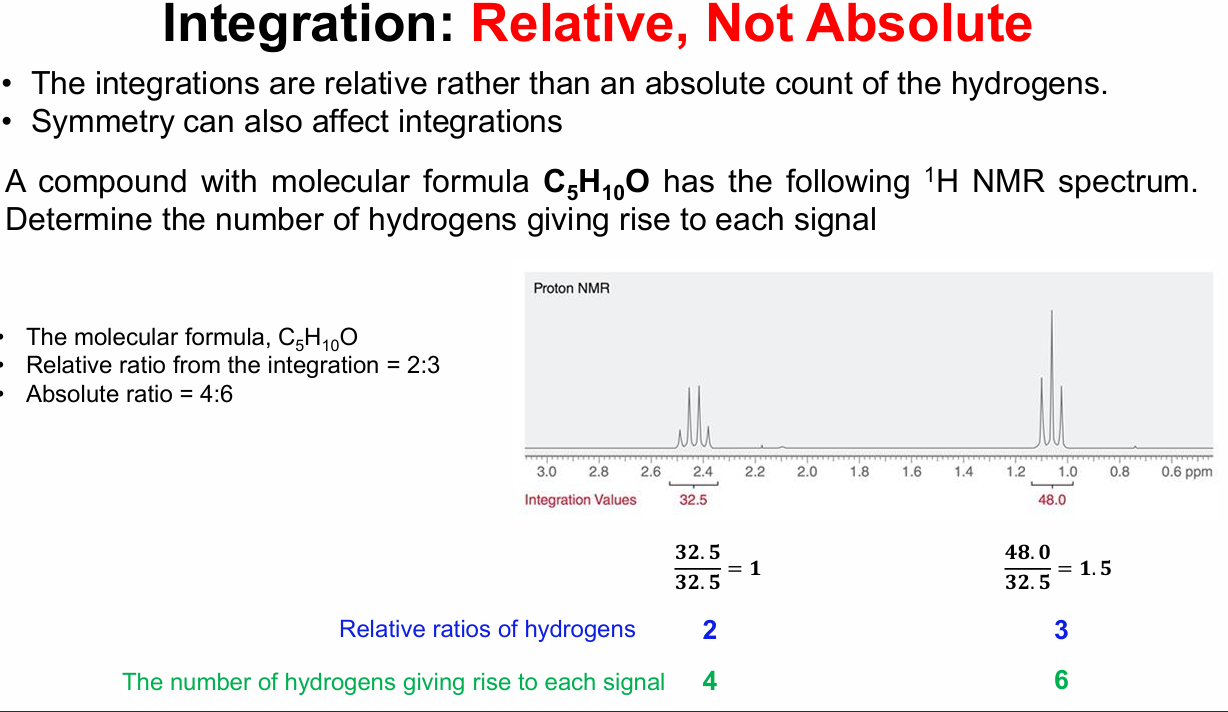
Important slide, memorize this concept that integration values (number given) corresponds to RATIO of hydrogens
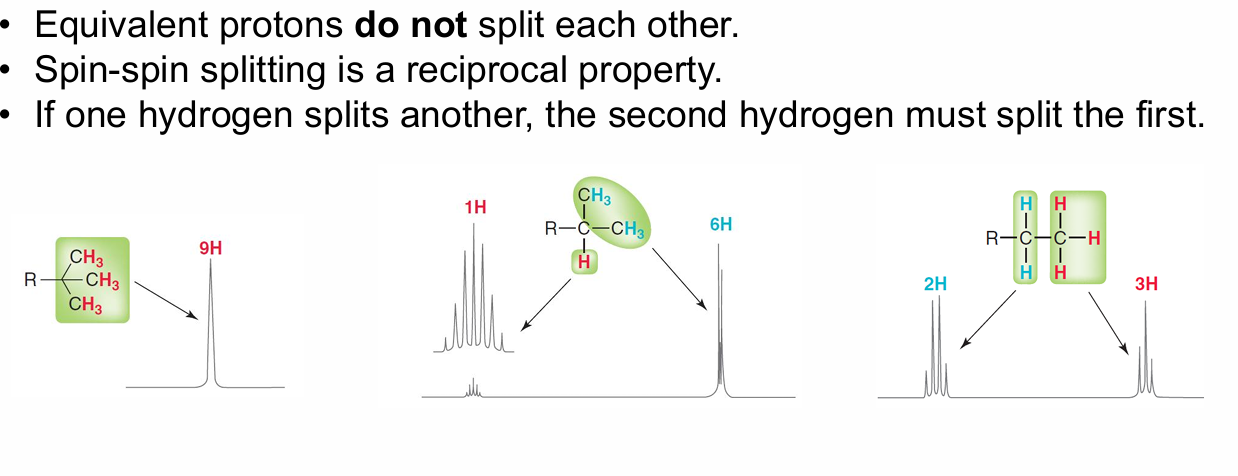
Nice slide on splitting
7 HZ
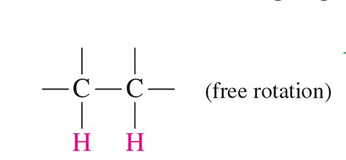
Free rotation HNMR
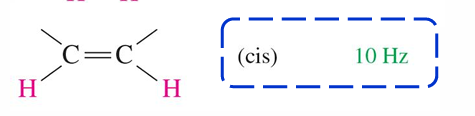
10 Hz
Cis HNMR of alkene
15 Hz
Trans HNMR of alkene
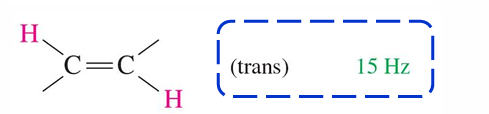
2 Hz
Diastereotopic alkene

6 Hz
Allylic hydrogen of alkene
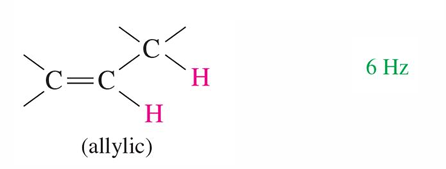
What functional group is sneaky and always appears as a singlet?
Aldehyde
Do axial and equatorial hydrogens on chair conformations give 1 or 2 signals?
1 at regular temps, 2 at -80 C
What 2 functional groups are NOT split by OTHER hydrogens?
OH and NH/NH2, identifiable by D2O by making their signals disappear
What types of solvents for HNMR must be used?
Solvents without hydrogens, so mostly deuterated solvents (D instead of H)
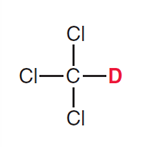
Chlorofoam-d
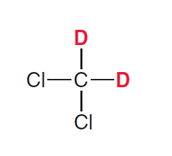
Methylene chloride-d2
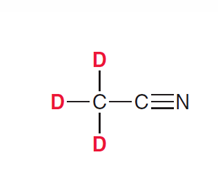
Acetonitrile-d3
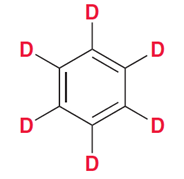
Benzene-d6
Deuterium oxide