The Roman Republic (509 - 27 BC)
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from the expulsion of the last king to when Octavian receives title of Augustus
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
consul
chief magistrate with civic, military, and religious duties; 2 elected each year
senate
former magistrates (consuls); council of elders; advisory board to the consuls; not a representative delegation
Important background…advent of the Republic
509 BC: Kings expelled, last king overthrown by Lucius Iunius Brutus
New system - res public (Republic) = literally the “public thing”
2 Magistrates elected every year to lead the government
Former magistrates form the Senate
Republican Rome Monuments
No major public building until 4th century BC
390 BC: Rome sacked by the Gauls
Major rebuilding follows the sack of Rome; WALLS
Buildings tied to Republican forms of government and spurred by individual competition
Little remains because Republican Rome has been built over by later structures
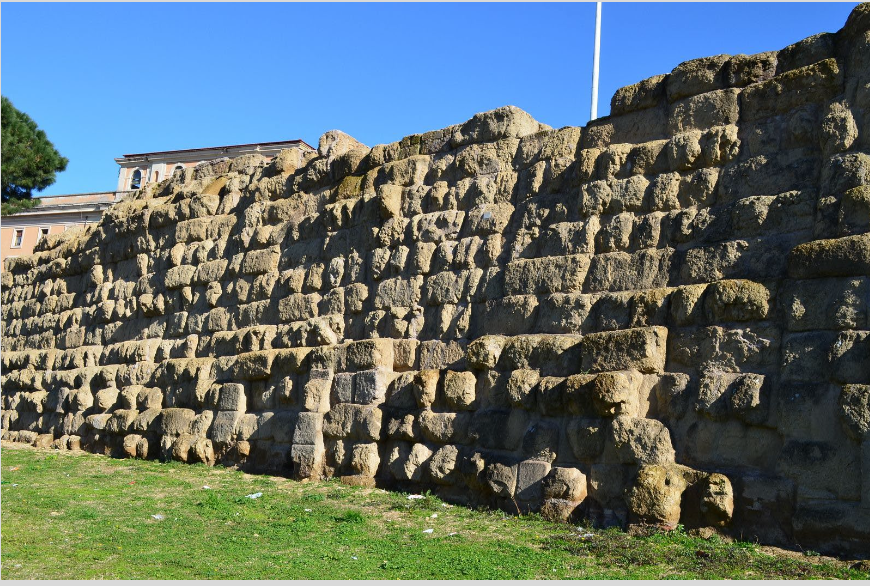

Servian Wall (380 BC)
misnomer (not actually built by Servius)
defense until Rome expands
tufo rock
Name three functions of Roman Republic roads…
military function —> efficiency
political function —> names / legacy
economic function —> trade
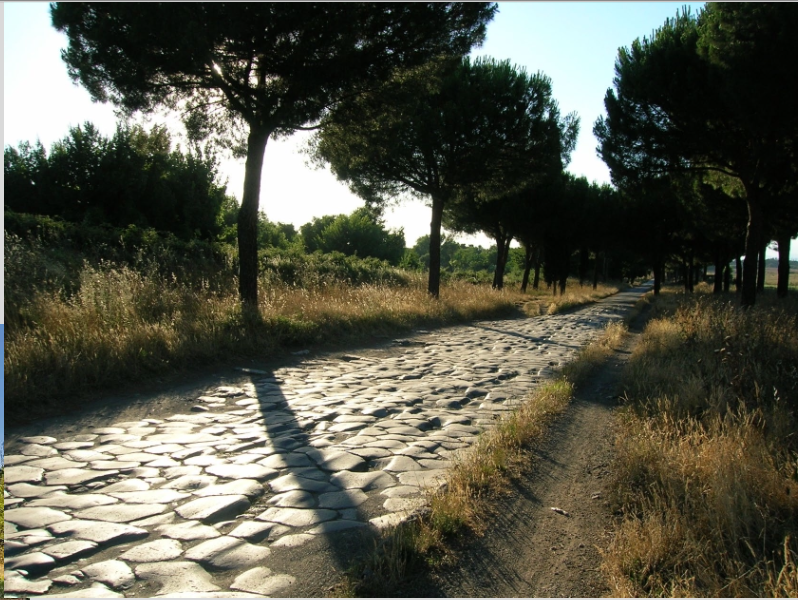

Roman Republic Road: VIA APPIA (312 BC)
still survives
leads all the way way to Rome (still the fastest)
patron: Appius Claudius

Roman Aqueducts
take water from springs in the mountains and take it down to city to be drinking water
still used today
arches = less brick used
Example = PONT DU GUARD, FRANCE (50 AD)
Pompeii (79 AD Volcanic ash layers)
has a lot of republican remains
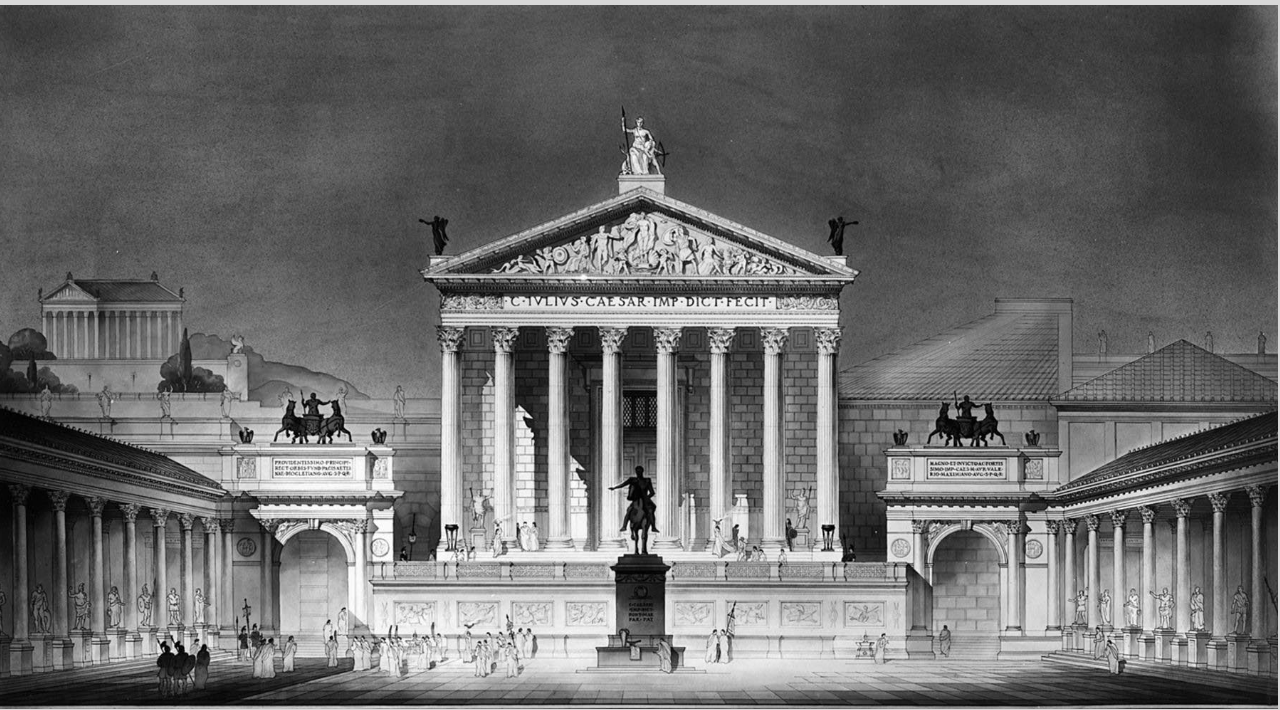
Forum of Pompeii
Basilica (c. 80 BC) - used for trials and other activities
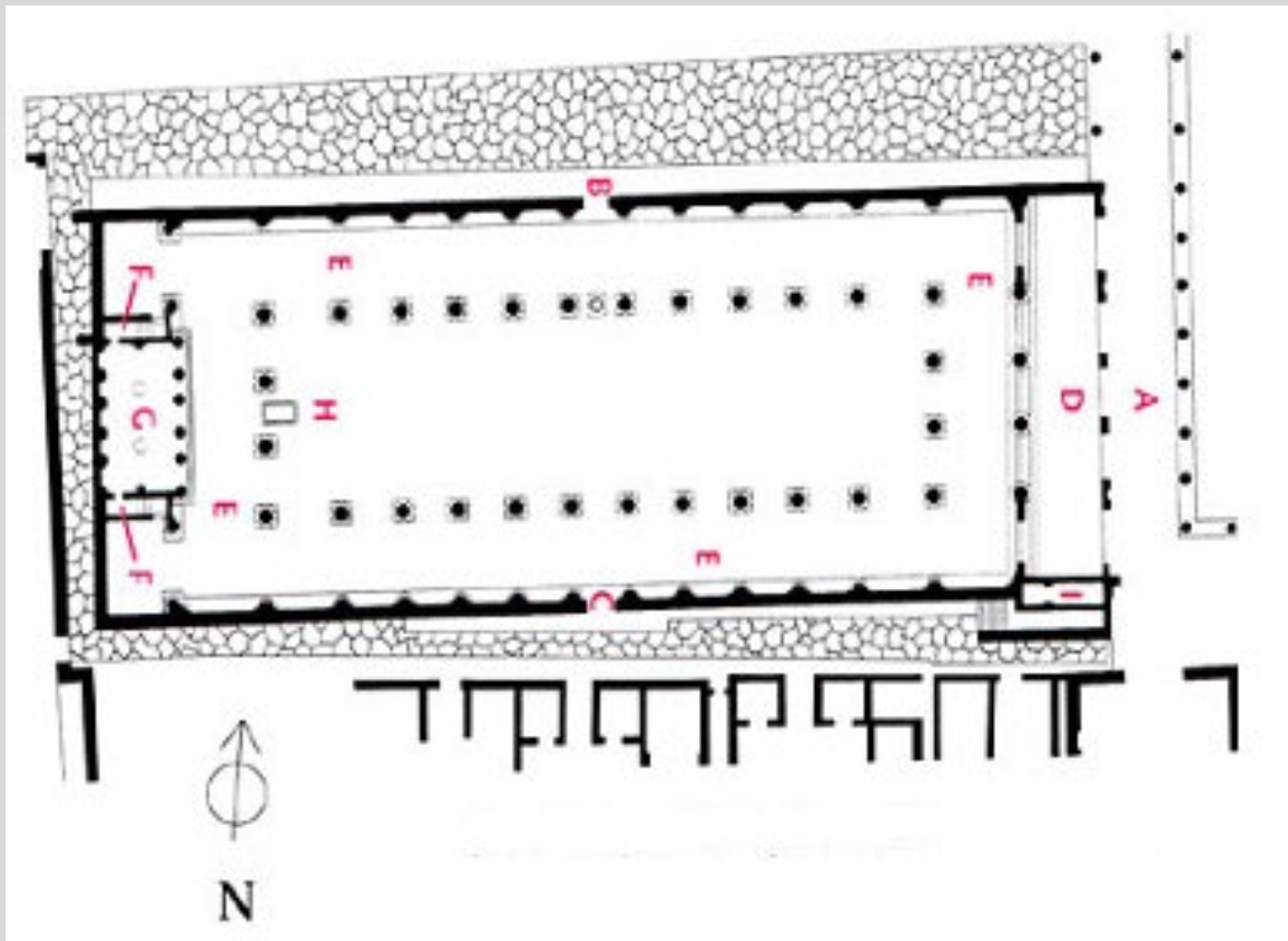
basilica (Roman basilica)
a public building for legal and other civic proceedings; rectangular in plan with an entrance usually on the long side
Basilica (c. 80 BC) - used for trials and other activities
tribunal—>judge’s box
nave
aisles
ionic & corinthian columns (greek influence)
nave
central area of basilica demarcated from aisles by piers or columns
aisle
portion of a basilica flanking the nave and separated from it by a row of piers or columns
Name and describe the four styles of Pompeii (20 BC - 55 AD)
1st / Masonry Style - model stucco to look like fancy marble
2nd / Allusionistic Style - looking through wall ( used fake columns); realistic; allusion of open/bigger room
3rd / Decorative Style - fancy and decorative; no longer realistic
4th / Mixed Style - mixture of 3 previous styles
Roman Forum
curia - senate house reconstructed around 300 AD
comitium - an open-air public square used for political assemblies
rostra - speaker’s platform located within the comitium
Basilica Aemilia
religious architecture
Temple of Saturn
Temple of Castor and Pollux
Lacus Iuturnae - pool built by Romans near a spring or well
chronology of the Late Republic
106-47 BC: Pompey the Great
100-44 BC: Julius Caesar
31 BC: Octavian defeats Mark Antony
27 BC: End of Republic
Julius Caesar (100-44 BC)
49 BC - crossing of the Rubicon / outbreak of civil war
44 BC - assassination of Julius Caesar
Describe the atmosphere of the late Republic
106-31 BC: Civil wars and powerful rulers
Civic institutions developed for governing city-state were overextended in attempt to run the Empire
military now dependent on generals rather than state for rewards and their maintenance
Name 2 important monuments of the Late Republic (hint: they have to do with Pompey and Julius Caesar)
55 BC - Theater of Pompey
51 BC - Forum of Julius Caesar
Describe the introduction of concrete into architecture (around 150-125 BC)
made of lime mortar, volcanic sand, water, and small stones
places emphasis on carpentry rather than stone carving
requires less sophisticated labor force than stone construction
permits buildings with curvilinear designs
allows construction of larger open spaces
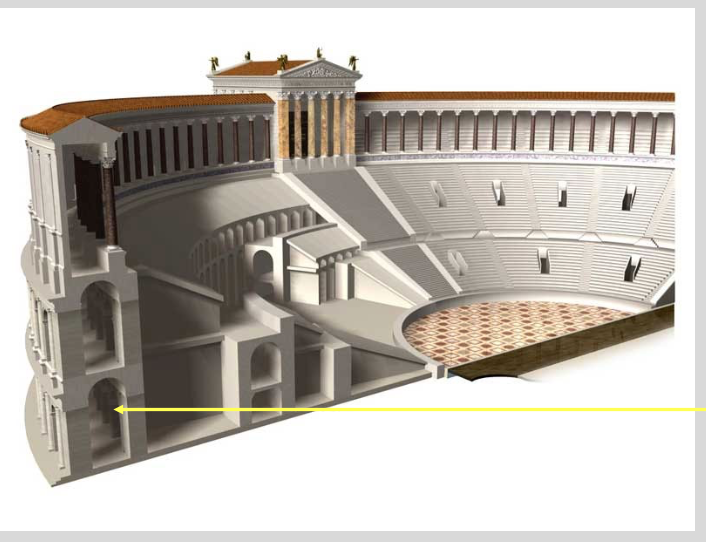
Theater of Pompey (55 BC)
example of barrel vault
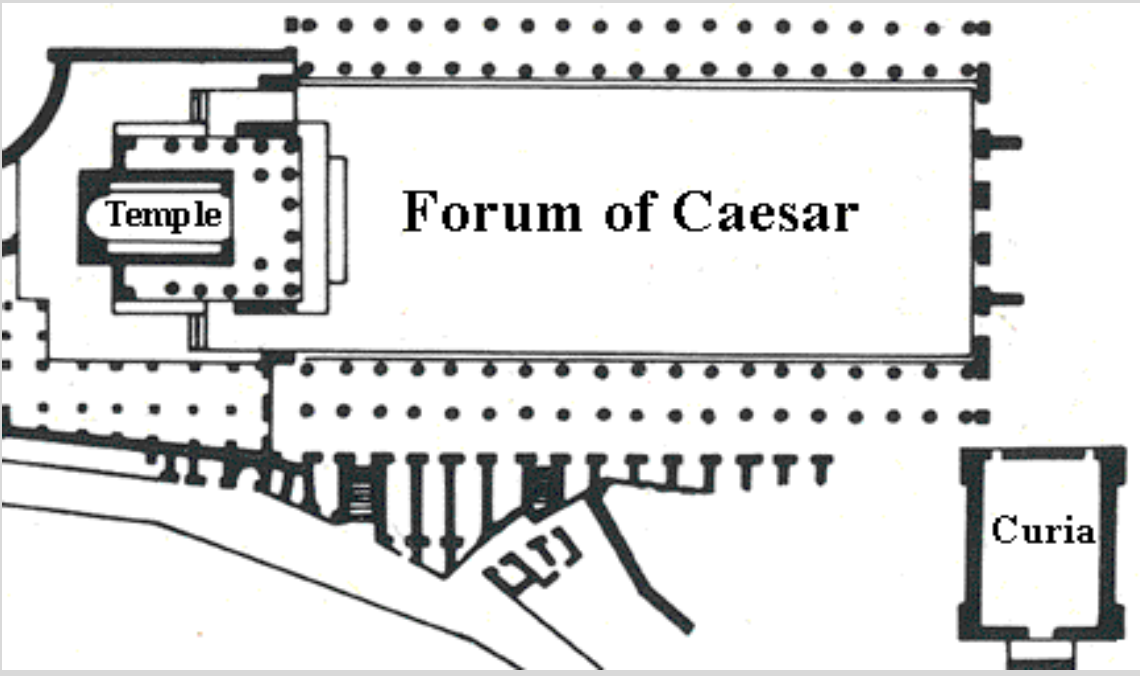
Forum of Julius Caesar / Caesaris Forum (51 BC)
made for himself!
open area surrounded by colonnades with shops
temple on one end to Venus Genetrix —> connection to his family
curia on other end