Week 2: Stress Psychophysiology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Last updated 6:28 PM on 2/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
Biomedical Model
* a traditional model of health
* health is primarily a product of **biological factors**
* health and illness are **dichotomous** (either-or)
* Either healthy or ill
* health is primarily a product of **biological factors**
* health and illness are **dichotomous** (either-or)
* Either healthy or ill
2
New cards
Biopsychosocial Model
* a more recent model of health
* health is a product of __biological, psychological, and social influences__
* health and illness are on a *continuum*
* a more accurate and comprehensive description of illness
* health is a product of __biological, psychological, and social influences__
* health and illness are on a *continuum*
* a more accurate and comprehensive description of illness
3
New cards
Has a **linear model of illness**; cause of illness is **physical**
Biomedical Model
4
New cards
an **interactive model** of illness; the causes of illness are **physical, social, psychological**
Biopsychosocial Model
5
New cards
The Biopsychosocial model includes:
* behavioral pathogens
* behavioral immunogens
* psychosocial stress
* poor coping behaviors
* behavioral immunogens
* psychosocial stress
* poor coping behaviors
6
New cards
Behavioral pathogens
risk-increasing behaviors (smoking, drinking excessive amounts of alcohol)
7
New cards
behavioral immunogens
health-enhancing behaviors (such as not smoking, eating healthy, exercising)
8
New cards
* considers the relationship between mind and body as **separate entities** (treatment is focused on the body)
* treatment approaches are **physical**: medications, surgery because the illness is __purely physical__
* treatment approaches are **physical**: medications, surgery because the illness is __purely physical__
Biomedical Model
9
New cards
* considers the relationship between mind and body as **integrated entities and interact** with each other in a holistic manner (treatment focused on both)
* treatment approaches may be physical, behavioral, and/or psychological
* treatment approaches may be physical, behavioral, and/or psychological
Biopsychosocial Model
10
New cards
* individuals are __passive victims of illness;__ have no responsibility
* a linear model of health illness
* illness causes psychological consequences, and not the reverse
* a linear model of health illness
* illness causes psychological consequences, and not the reverse
Biomedical Model
11
New cards
* individuals are **not** **passive victims**; have a responsibility and contribute to the illness
* behavior and lifestyle play a role
* an interactive model of illness (continuum)
* psychological factors can **both** *affect* illness and also be *consequences* of illness
* behavior and lifestyle play a role
* an interactive model of illness (continuum)
* psychological factors can **both** *affect* illness and also be *consequences* of illness
Biopsychosocial Model
12
New cards
The value of psychology in health: biopsychosocial model of health
biological, social, and psychological factors interact in an interdependent way in maintaining health (or causing illness)
13
New cards
Psychological Factors play a **key role** in health and illness as well (T/F)
True
14
New cards
Our lifestyles are **indirectly** related to health and illness (T/F)
False; directly
15
New cards
When under (dis)stress, we tend to engage in behavioral -----, which affect our ----, and hence our health
pathogens; lifestyles
16
New cards
Health Psychology
__a specialty area of psychology__ which uses the __knowledge based on the discipline__ of psychology **to promote maintain health and treat illness**
17
New cards
Stressors can produce ---, ----, ----, ---- changes which may be detrimental to health
cognitive, emotional, physiological, behavioral
18
New cards
Negative stressors (and distress) have an impact on ----
life expectancy
19
New cards
Explain why Stress is a **2-way street?**
* it is a cycle of stress **contributing** to poor health and poor health **contributing** to stress
* interdependence between health and stress
* interdependence between health and stress
20
New cards
What is the most effective way to manage stress is to ----
* **live a healthy lifestyle**
* examples: drinking in moderation, not smoking, eating healthy
* examples: drinking in moderation, not smoking, eating healthy
21
New cards
Goal of stress management is to stay in an **------** of functioning & life satisfaction through the use of health-promoting strategies
**optimal zone**
22
New cards
What is the **Yerkes-Dodson Curve/Law?**
* identifies a relationship between **physiological** **arousal** and **performance**
* identifies optimal performance
* identifies optimal performance
23
New cards
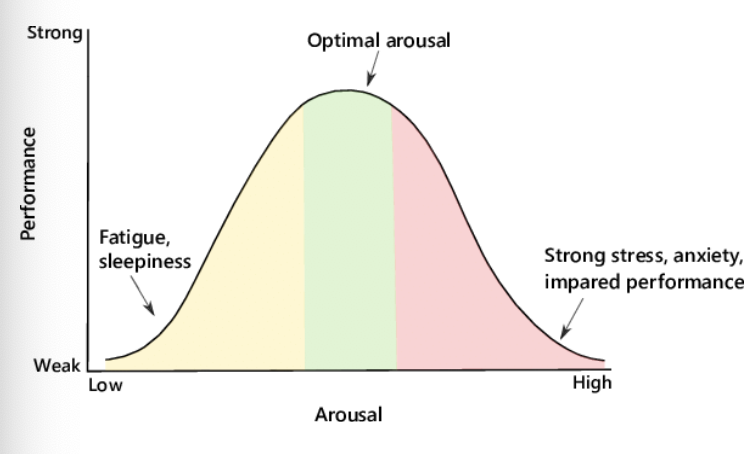
What is Optimal Performance
* occurs when we are **midlevel** of physiological arousal
* neither overstimulated or understimulated for a period of time
* neither overstimulated or understimulated for a period of time
24
New cards
What law is accepted as the basis for the __physiological explanation__ for anxiety
Yerkes-Dodson Curve/Law
25
New cards
High levels of anxiety will impair performance, while low levels of anxiety (co-exists with low levels of motivation) **doesn’t** impair performance (True or False)
False; both high and low levels of impair performance
26
New cards
Are optimal levels stable or not stable? Why or Why not?
* **It’s not stable** because it __changes and adapts__ based on *prolonged changes in the* __*external environment*__
* Sometimes we adapt → habituation
* Sometimes we adapt → habituation
27
New cards
How does **Habituation** occur?
When a new stimulus __elicits increase in physiological arousa__l (fight-or-flight response) → *repeated exposure* results in __no observable response__ due to having adjusted to it
28
New cards
The CNS **monitors** *bodily functions* by picking up *signals* that indicate when any part of the body deviates from ----
**Homeostatic Stability**
29
New cards
What does the brain do to counteract this deviation to return to homeostasis?
* The brain initiates a response.
* This response can be in terms of an **autonomic/endocrine mechanisms**
* or **behavioral responses**
\
* This response can be in terms of an **autonomic/endocrine mechanisms**
* or **behavioral responses**
\
30
New cards
What can autonomic/endocrine mechanisms do
* alter physiological processes within the body (such as sweating to cool down and return to homeostasis)
\
\
31
New cards
**Behavioral response** to counteract deviation from homeostasis
alters the external environment (i.e., open a window to cool doen and return to homeostasis)
32
New cards
What axes are activated during the fight-or-flight response?
SAM and HPA axes
33
New cards
What part of the PNS innervates the voluntary or skeletal muscles (i.e., striated muscles such as biceps), skin and sense organs
Somatic
34
New cards
What part of the PNS innervates the organ systems of the body (viscera)
Autonomic
35
New cards
Sympathetic Branch is associated with
the **fight-or-flight** reaction (i.e., **physiological response** to a potential threat)
36
New cards
Parasympathetic Branch is associated with
the **relaxation and restoration** responses (i.e., activated to shut down fight-or-flight response and decrease arousal once we realize there is no threat)
37
New cards
•Sympathetic & parasympathetic branches __________ one another
•As one becomes more __________, the other is ___________
•As one becomes more __________, the other is ___________
opposite; activated; suppressed
38
New cards
What is the outermost layer of the brain
Cerebral Cortex/ Gray Matter
39
New cards
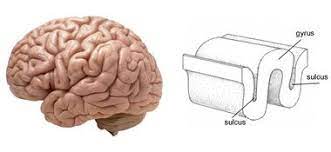
What are the folds and grooves of the brain called?
Fold: Gyrus/Gyri
Groove: Sulcus/Sulci
Groove: Sulcus/Sulci
40
New cards
Proof that folds on the brain are not random
* Every healthy human brain has similar folds and grooves on the cortex
* Locations and functions are stable across the typical brain
* Degree to how much each part of the cortex is folded is important → psychological disorders
* Locations and functions are stable across the typical brain
* Degree to how much each part of the cortex is folded is important → psychological disorders
41
New cards
The Brain analyzes
**sensory information** *&* **higher-order brain functions** (i.e., reasoning, problem-solving, language, etc.)
42
New cards
How many hemispheres are in the brain?
2: Right and Left
43
New cards
What are the terms for the front, back, right, left of the brain?
Front: Anterior
Back: Posterior
Right: Lateral
Left: Medial
Back: Posterior
Right: Lateral
Left: Medial
44
New cards
White Matter
* consists of fibers that connect different regions of gray matter together, allowing them to communicate with one another
* inside of the brain
* connection: axons
* inside of the brain
* connection: axons
45
New cards
Corpus Callosum
Large bundles of fibers connecting the 2 cerebral hemispheres (part of white matter)
46
New cards
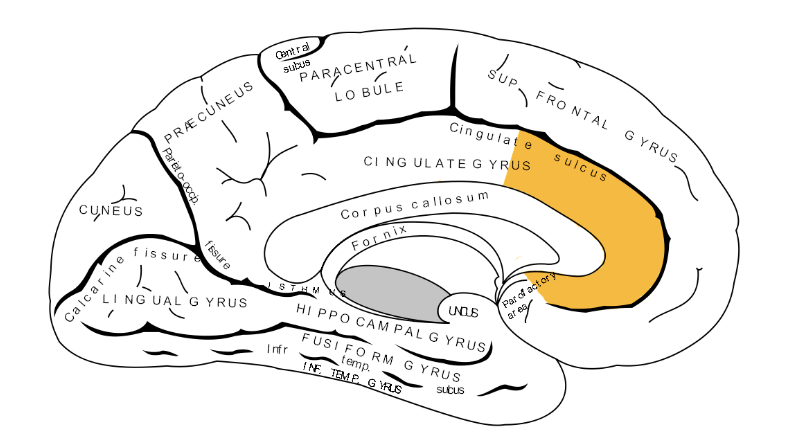
Anterior Cingulate Gyrus/Cortex (ACC)
* __part of the limbic system__
* processing **emotional information**
* extinguishing **conditioned fear**
* regulating **emotional responses**
* processing **emotional information**
* extinguishing **conditioned fear**
* regulating **emotional responses**
47
New cards
Lateralization
* cognitive functions that **rely more on one hemisphere** than the other
* The brain produces a **crossing over** for movement
* Right H controls Left part of body
* Left H controls Right part of body
* The brain produces a **crossing over** for movement
* Right H controls Left part of body
* Left H controls Right part of body
48
New cards
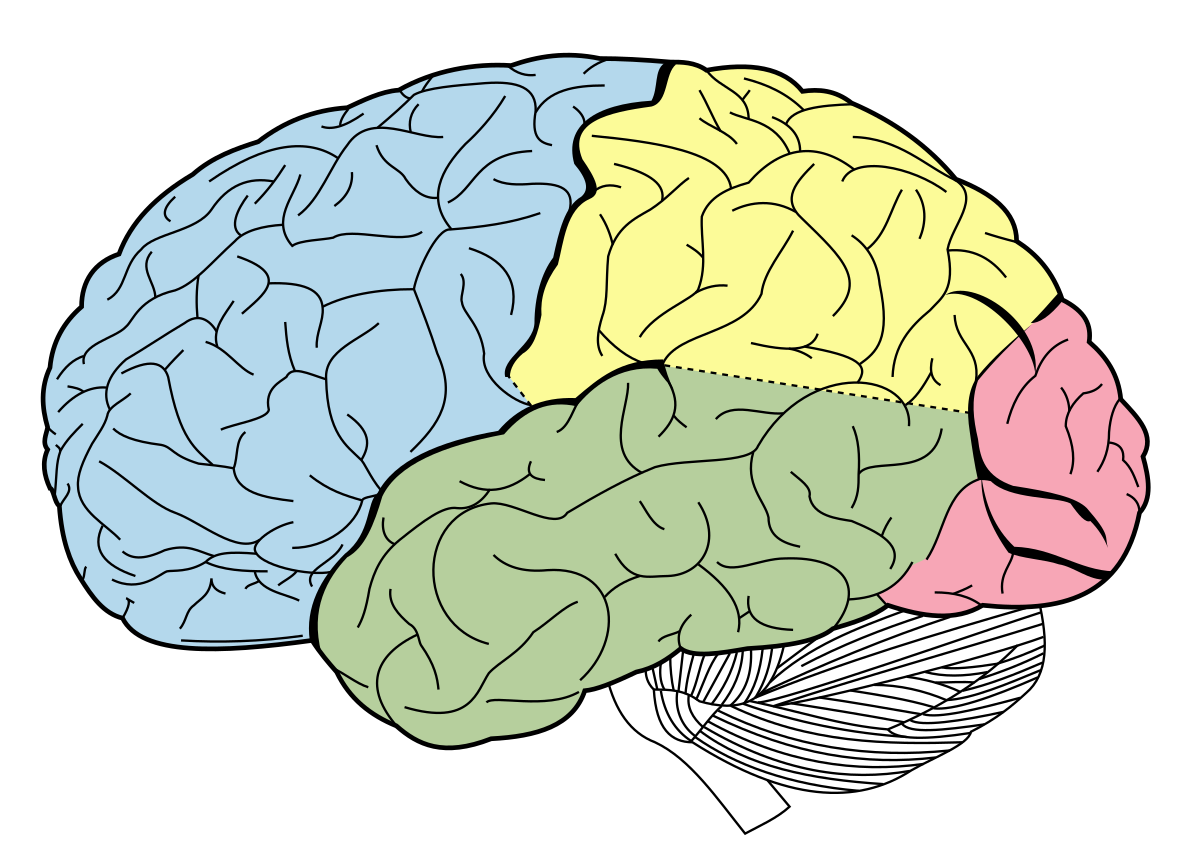
What are the 4 lobes of the Cerebral Cortex?
1. Frontal lobe
2. Parietal Lobe
3. Occiptal Lobe
4. Temporal Lobe
49
New cards
What are Subcortical Areas?
* areas that are located deep inside the brain
* i.e., amygdala, hypothalamus, etc.
* i.e., amygdala, hypothalamus, etc.
50
New cards
Brainstem
* responsible for the **basic bodily functions** of the body that help keep us alive (i.e., heartbeat, respiration, etc.)
51
New cards
The Brainstem consists of 3 parts:
1. midbrain
2. pons
3. medulla
52
New cards
Medulla
* controls (and regulates) **autonomic processes** (i.e., heartbeat, blood pressure, respiration)
* responsible for physiological responses (i.e., heartbeat) during fight-or-flight
* responsible for physiological responses (i.e., heartbeat) during fight-or-flight
53
New cards
Pons
* Latin for ‘bridge’
* **connects** the *cerebral cortex* to the *cerebellum*
* **connects** the *cerebral cortex* to the *cerebellum*
54
New cards
Midbrain
* controls and coordinates **sensory and motor activities**
* plays an important role in __voluntary motor movement__
* controls the tracking of **visual stimuli and reflexes** that are *triggered by sound* (i.e., causes us to jump when hearing a loud sound)
* plays an important role in __voluntary motor movement__
* controls the tracking of **visual stimuli and reflexes** that are *triggered by sound* (i.e., causes us to jump when hearing a loud sound)
55
New cards
The Thalamus is a subcortical structure that’s part of the mesencephalon (T/F)
False, it’s part of the diencephalon
56
New cards
The Thalamus contains:
1. The Sensory Relay Station
2. The Sensory Projection System
57
New cards
Sensory Relay Station
* **all sensory information** *pass through* the **thalamus** first for the *initial process*, then are sent to the **cortex** for *further processing*
* each sensory system has a specific endpoint in the cortex
\
* each sensory system has a specific endpoint in the cortex
\
58
New cards
Sensory Projection System
* circuit from a sense organ, moving through the thalamus to its **specific region in the cortex**
59
New cards
The Thalamus has a --- nucleus for each sense organ
distinct
60
New cards
The Hypothalamus is part of the Diencephalon (T/F)
True
61
New cards
The Hypothalamus is responsible for r**egulating internal bodily states** by
* overseeing hormone release through connections with **pituitary gland**
* being involved in **normal homeostatic regulation** of the __autonomic nervous system__
* being involved in **normal homeostatic regulation** of the __autonomic nervous system__
62
New cards
The hypothalamus has both direct and indirect control over the **fight-or-flight** **activities** *during stress*. What does it directly control?
**directly controls** the hypothalamus through influencing the brain stem to __activate__ the **sympathetic responses** of the viscera, like stimulating the endocrine system
63
New cards
The hypothalamus has both direct and indirect control over the **fight-or-flight** **activities** *during stress*. What does it indirectly control?
**indirectly controls** the hypothalamus through connection to the **pituitary gland** to stimulate the *endocrine system*
64
New cards
What part of the diencephalon/subcortical structure of the brain plays an important role in **motivation behavior** and **controls homeostatic regulation of our body’s temperature**
The Hypothalamus
65
New cards
Amygdala
* subcortical area
* Greek for ‘almond’
* Part of the __limbic system__
* Involved in **mediating emotional responses** (especially fear & anxiety)
* Involved in **emotional memory formation** & assessing threat stimuli
* Plays a key role in **fear conditioning**
* Greek for ‘almond’
* Part of the __limbic system__
* Involved in **mediating emotional responses** (especially fear & anxiety)
* Involved in **emotional memory formation** & assessing threat stimuli
* Plays a key role in **fear conditioning**
66
New cards
Fear Conditioning
predicting when something fearful is about to occur
67
New cards
Hippocampus
* subcortical area
* Greek for ‘seahorse’
* Part of the limbic system
* Involved in **encoding long-term memories** of **declarative memories**
* Also plays a role in fear-conditioning
* Greek for ‘seahorse’
* Part of the limbic system
* Involved in **encoding long-term memories** of **declarative memories**
* Also plays a role in fear-conditioning
68
New cards
declarative memories
conscious memories of events
69
New cards
* Hippocampus encodes the ________
* Amygdala adds in the ________
* Amygdala adds in the ________
* Hippocampus encodes the context
* Amygdala adds in the emotion
* Amygdala adds in the emotion
70
New cards
Limbic System
* __**“Emotional center”**__ of the brain
* Includes:
1. __**hippocampus,**__
2. __**thalamus,**__
3. __**hypothalamus,**__
4. __**amygdala,**__
5. **cingulate gyrus (ACC)**,
6. __parts of the cerebral cortex (i.e., prefrontal cortex)__
7. __and other structures__
* Plays an important role in **fear response to potentially dangerous stimuli**
\
* Includes:
1. __**hippocampus,**__
2. __**thalamus,**__
3. __**hypothalamus,**__
4. __**amygdala,**__
5. **cingulate gyrus (ACC)**,
6. __parts of the cerebral cortex (i.e., prefrontal cortex)__
7. __and other structures__
* Plays an important role in **fear response to potentially dangerous stimuli**
\
71
New cards
PNS: somatic nervous system
* fuels the voluntary and skeletal system
* consists of the efferent and afferent neural pathways
* consists of the efferent and afferent neural pathways
72
New cards
Efferent and Afferent pathways are examples of
bidirectional neural networks
73
New cards
Efferent
* neural pathways that send (motor) signals from the brain to the periphery
* brain → periphery
* brain → periphery
74
New cards
Afferent
* neural pathways that send signals from the periphery to the brain
* periphery → brain
* periphery → brain
75
New cards
During the fight-or-flight response: Brain sends messages through the --- pathway
efferent, to tense muscles and prepare for fight or flight
76
New cards
Why are there health problems when the fight-or-flight response is constantly stimulated?
chronic stimulation of the somatic nervous system may lead to:
* Muscle tension
* Headaches
* Teeth grinding
(physiological effects)
* Muscle tension
* Headaches
* Teeth grinding
(physiological effects)
77
New cards
PNS: Autonomic nervous system
* Innervates the body’s __**viscera (internal organ systems of the body)**__
* consists of the **sympathetic and parasympathetic** branches
* consists of the **sympathetic and parasympathetic** branches
78
New cards
Sympathetic branch
* responsible for activating the **fight-or-flight response**
* Increases heartbeats or blood pressure
* Increases dilation of lungs for more oxygen in blood stream
* Increases heartbeats or blood pressure
* Increases dilation of lungs for more oxygen in blood stream
79
New cards
Parasympathetic branch
* associated with the **state of relaxation**; activation serves to decrease the fight-or-flight response
* Restoration
* Calm down the fight or flight response
* Decrease arousal when we realize that the stressor in the environment is not dangerous
* Restoration
* Calm down the fight or flight response
* Decrease arousal when we realize that the stressor in the environment is not dangerous
80
New cards
Endocrine System
A system of organs & glands that __secrete hormones__ into our bloodstream which *act as biochemical messengers* to their __target cells & organs__
81
New cards
The **primary command centre** of the endocrine’s stress response is in the
hypothalamus (paraventricular nucleus)
82
New cards
one of the primary target organs in the endocrine’s stress response is in
adrenal gland
83
New cards
Adrenals
* glands sitting atop the kidneys
* contains adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla
* contains adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla
84
New cards
Adrenal Cortex
**outer covering** of the adrenal glands, responsible for **secreting glucocorticoids**
85
New cards
Adrenal Medulla
**inner cor**e of the adrenal glands, responsible for **secreting the catecholamines epinephrine & norepinephrine**
86
New cards
Sympathetic-Adrenal-Medulla Axis (SAM Axis)
* Forms one of the primary systems of the fight-or-flight response
87
New cards
Describe the process of the Sympathetic Adrenal Medulla (SAM) Axis
1. signals from **brainstem → to paraventricular**
2. **pv** → **sympathetic nervous system**
3. **sympathetic nervous system** → **adrenal medulla**
4. **adrenal medulla** secretes __catecholamine and epinephrine__
88
New cards
Norepinephrine and Epinephrine
keep the body __vigilant & able__ to deal with stress by prompting **alertness & increasing blood flow** to the *skeletal muscles*, to ensure they are ready to act
89
New cards
Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
* Affects the cardiovascular system → **increase in heart rate & constriction & dilation of blood vessels** to shunt blood away from the outer periphery & digestive systems, and into the brain & large skeletal muscles
* Dilates lungs
* stimulates the release of glucose into the bloodstream
* increases metabolic rate
* Generally, has the __same effect__ as the s**ympathetic nervous system** on its target organs
* Dilates lungs
* stimulates the release of glucose into the bloodstream
* increases metabolic rate
* Generally, has the __same effect__ as the s**ympathetic nervous system** on its target organs
90
New cards
Norepinephrine
* has much of the same effects as epinephrine
* Physical stressors
* Anger
* Physical stressors
* Anger
91
New cards
Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal (HPA)
* A primary system of the fight-or-flight response
* slower involving the release of many hormones → immune suppression
* slower involving the release of many hormones → immune suppression
92
New cards
in the HPA axis the __**The paraventricular nucleus**__ of the __**hypothalamus**__ recognizes the
homeostatic imbalance
93
New cards
in the HPA axis the __**Hypothalamus**__ influences the **----** by secreting **CRH** into the **----**
**pituitary gland** ; **anterior pituarity**
94
New cards
pituitary gland
gland at the **base of the brain** consisting of an __anterior and posterior region__
95
New cards
**CRH** stimulate the anterior pituitary to secrete __**----**__ into the bloodstream
__**ACTH & beta-endorphins**__
96
New cards
beta-endorphine
* **a natural opiate** that has a **strong pain-relieving effect**
* Adapt to not feel anything to fight off danger
* Adapt to not feel anything to fight off danger
97
New cards
__**ACTH**__ stimulates the __**adrenal cortex**__ to __**release ----**__
glucocorticoids: play an important role in the fight-or-flight response
98
New cards
Cortisol
* **raises glucose levels in the bloodstream**, prepares stress responses by increasing catecholamine synthesis → aimed to restore homeostasis
* Short term → homeostasis is restored
* Short term → homeostasis is restored
99
New cards
Psychological & physical stressors __increase cortisol__ levels (T/F)
True
100
New cards
Cortisol is the *body’s primary glucocorticoid* secreted by the __**pituarity gland**__ during the fight-or-flight response (T/F)
False; Adrenal cortex