Algae
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Cyanobacteria
Which of the following is technically not algae but is often called “blue-green algae”?
They perform photosynthesis and live in aquatic environments
Why are cyanobacteria often mistaken for algae?
False
Seaweeds (macroalgae) are true plants.
Seaweed (macroalgae)
Which of the following is a plant-like protist that is not a true plant?
They are multicellular, grow underwater, and look like algae
Why are simple aquatic plants like Chara sometimes mistaken for algae?
They are prokaryotes and lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Why are cyanobacteria not considered true algae?
They have plant-like structures such as fronds and holdfasts
Why are seaweeds often mistaken for plants?
Algae are eukaryotes with a nucleus, while cyanobacteria are prokaryotes
Which feature distinguishes true algae from cyanobacteria?
Provide oxygen through photosynthesis
Cyanobacteria are important in aquatic ecosystems because they:
They are plant-like protists that absorb nutrients directly from water
Which of the following statements about macroalgae (seaweeds) is TRUE?
It is a simple aquatic plant (embryophyte)
Chara is not considered algae because:
They provide food for tiny aquatic animals
Cyanobacteria are important in the food chain because:
Nitrogen fixation
Which ability of some cyanobacteria helps plants grow better?
Pollution or excess nutrients (algal bloom)
Too many cyanobacteria in water can indicate:
Produce oxygen, provide food in water, fix nitrogen
Which of the following lists all the main benefits of cyanobacteria?
prokaryotic
Cyanobacteria is;
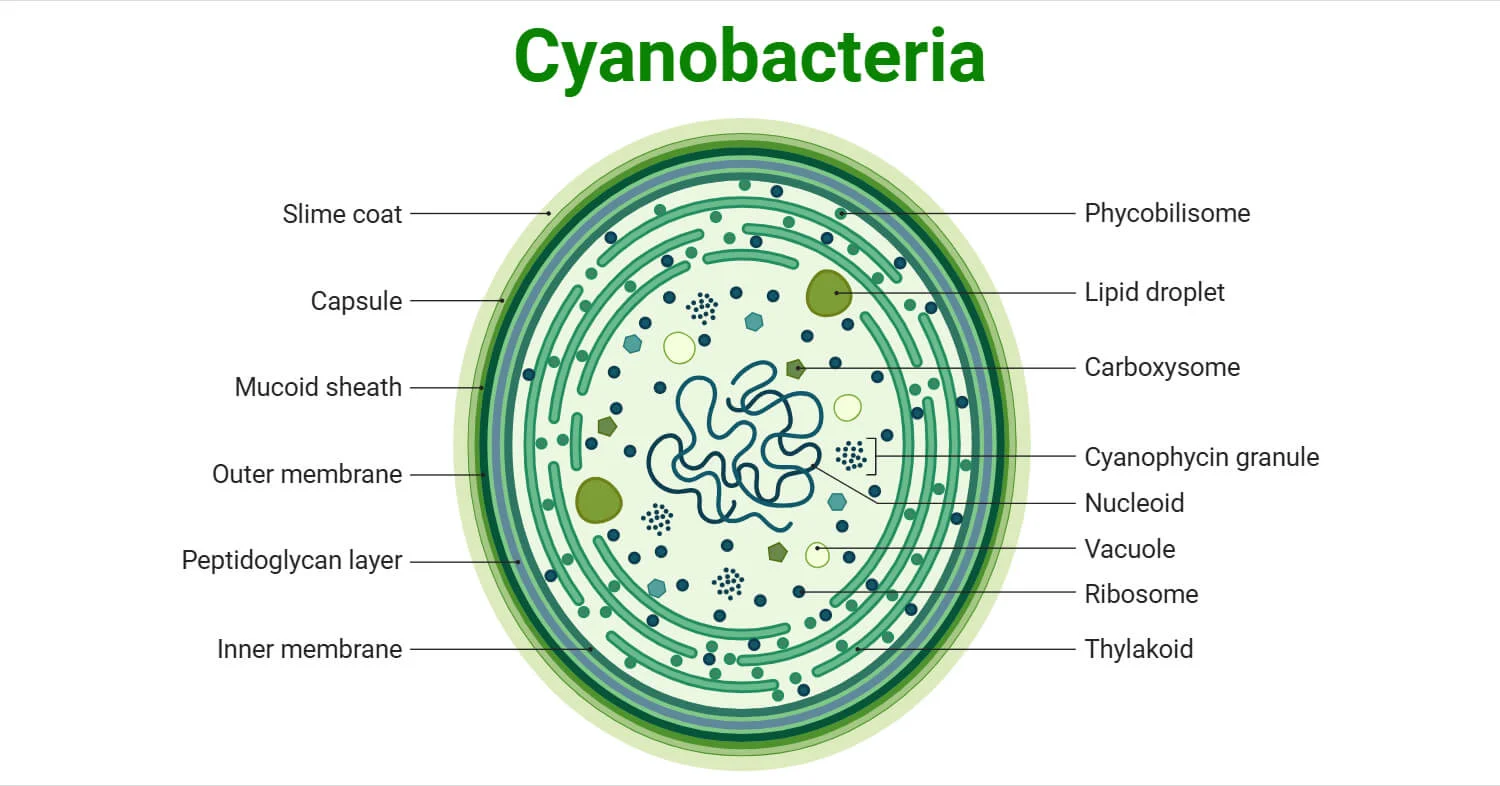
Green algae
Which algae are considered the closest relatives of land plants?
Red algae
Which type of algae is used to produce agar and carrageenan for food and lab purposes?
Brown algae
Which algae includes large seaweeds like kelp and is important for marine habitats and human food additives?
Diatoms
Which algae are major photosynthesizers in oceans and have silica shells used in filters and soil additives?
Cyanobacteria, Green algae, Red algae, Brown algae, Diatoms
Which of the following lists only significant algae important for oxygen production, food chains, and human use?
Produce oxygen and serve as food for aquatic animals
Green algae are important because they:
Produce agar and carrageenan for food and laboratory uses
Red algae are mainly used by humans to:
Provide habitat for marine life and are used in food additives
Brown algae, such as kelp, are important because they:
Produce oxygen, form the base of aquatic food chains, and have silica shells used in filters
Diatoms are significant because they:
Produce oxygen, support aquatic food chains, provide human food and industrial uses
Which of the following correctly lists the main purposes or benefits of algae?
Fucoxanthin
Which pigment gives Phaeophyta (brown algae) their characteristic color?
Brown algae
Phaeophyta is a scientific name for:
Chlorophyta
Which is the scientific name for green algae?
Rhodophyta
Which algae is also called red algae?
Phaeophyta
Which algae is commonly called brown algae or brown seaweeds?
Bacillariophyta
Diatoms are scientifically called:
(Dinophyta)
Dinoflagellates
Tiny, mostly microscopic, photosynthetic organisms in water
What are phytoplankton?
Diatoms and dinoflagellates
Which of the following are types of phytoplankton?
They produce a lot of oxygen and form the base of aquatic food chains
Why are phytoplankton important?
Oceans, rivers, and lakes
Phytoplankton live mostly in:
Produce oxygen / grow excessively and produce toxins
Algae are beneficial because they __________ and harmful when they __________.
Reduce oxygen in water, causing fish to die
Which of the following is a harmful effect of excessive algae?
Producing food additives like agar and carrageenan
Which of the following is a human use of algae?
They produce oxygen and form the base of the food chain
Why are algae beneficial to aquatic ecosystems?
By producing food (sugars) and oxygen through photosynthesis
How do zooxanthellae help their host animals?