Capacitence
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What does a capacitor consist of?
Two metallic plates separated from each other by an insulator, often known as a dielectric
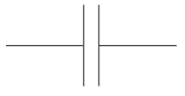
Hence the circuit symbol for a capacitor shows two lines separated by a gap
Examples of dielectrics are air, paper, ceramic and mica
What is a dielectric?
The insulating material placed between two conductors in a capacitor
What is capacitance?
The charge stored per unit potential difference across a capacitor
What is the defining equation of capacitance, with the meaning and unit of each term?
C = Q / V
C is the capacitance in farads (F)
Q is the charged stored in coulombs
V is the potential difference across the capacitor
Derive the bases unit of the Farad
C = Q/V
Q = It so Q → A s (Ampere seconds)
V = W/Q so C = Q/(W/Q) = Q2/W
W = Fx
F = ma so F → kg m s-2
Hence W → kg m2 s-2
C = Q2/W so C → (A s)2 / (kg m2 s-2) = A2 s4 kg-1 m-2
∴ Farad = A2s4kg-1m-2
What is the circuit symbol of a capacitor?
What can capacitors be used for in a circuit?
Can used for:
Storing charge
Storing energy
Providing timing (when combined with a resistance)
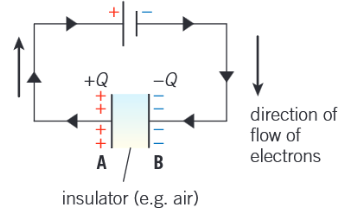
How does charge move when a capacitor is connected to a cell (include diagram in explanation)?
When the capacitor is connected to the cell, electrons flow from the cell for a very short time.
The electrons cannot travel between the plates because of the insulation.
The very brief current means electrons are removed from plate A of the capacitor and at the same time electrons are deposited onto the other plate B.
Plate A becomes deficient in electrons so acquires a positive charge. Plate B gains electrons and hence acquires a negative charge.
The current in the circuit must be the same at all points and charge must be conserved, so the two plates have an equal but opposite charge of magnitude Q.
Therefore there is a p.d. across the plates. The current in the circuit falls to zero when the p.d. across the plates is equal to the e.m.f. ɛ of the cell. The capacitor is then fully charged. The net charge on the capacitor plates is zero.
Does charge flow across the gap between the plates, and why?
No, because of the insulation
What causes the momentary current in a capacitor circuit?
The charging of the capacitor
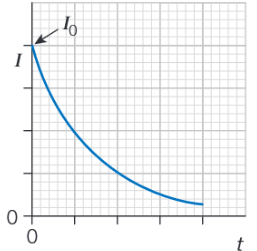
Draw a graphs to show how current varies with time during charging.
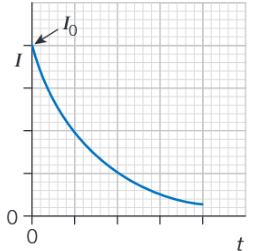
Draw a graphs to show how current varies with time during discharging.
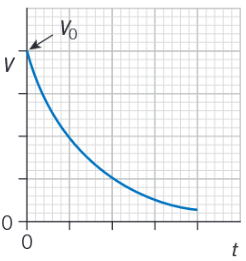
Draw a graphs to show how potential difference varies with time during charging.
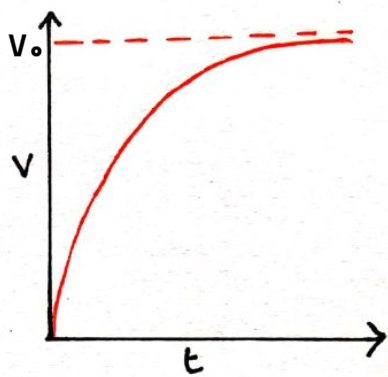
Draw a graphs to show how potential difference varies with time during discharging.
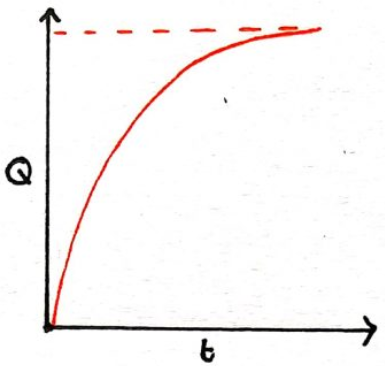
Draw a graphs to show how charge varies with time during charging.
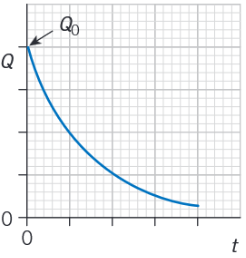
Draw a graphs to show how charge varies with time during discharging.
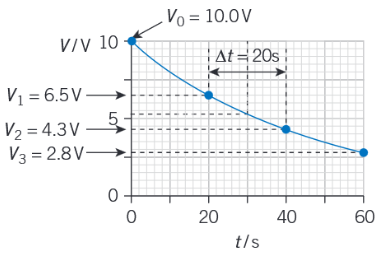
Describe the constant ratio property of exponential decay
For a time interval of 20s (or any interval), we see that ratios of the p.d.s will still be the same: V1 / V0 ≈ V2 / V1 ≈ V3 / V2
Define the time constant.
The time taken for current, p.d. or charge to decrease to 1/e of its initial value when a capacitor is discharged through a resistor
What is the equation relating time constant to capacitance and resistance, including the meaning and unit of each term?
τ = CR
τ is the time constant
C is the capacitance
R is the resistance
Define half life
Time taken for a quantity to halve
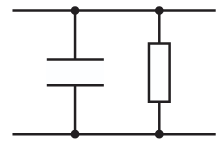
The time constant of the circuit shown is estimated to be about one minute. The capacitance and resistance values of the components are not known. Describe an experiment to determine the time constant of the circuit.
Connect the capacitor to a power supply / cell
Disconnect the power supply / cell
Measure the p.d. across the capacitor using a voltmeter and measure the time of discharge using a stopwatch
The time constant is the time taken for the p.d. to decreases to 1/e of its initial value.