AP Bio Unit 1
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
electronegativity
measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons
chemical bonds
attraction between 2 atoms resulting from the sharing or transferring of valance electrons
covalent bond
when 2+ atoms share electrons (usually nonmetals)
ionic bond
electrons are transferred between 2 atoms
hydrogen bond
the partially positive H atom in one polar covalent molecule will be attracted to an electronegative atom in another polar covalent molecule
polarity
unequal sharing of electrons in H2O
cohesion
attraction of molecules to other molecules of the same kind (surface tension)
adhesion
clinging of water molecules to different molecules due to polarity (water going up stem)
capillary action
upward movement of water due to cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension (plants nutrition)
high specific heat
resists changes in temperature through H bonds (ocean doesn’t freeze)
evaporative cooling
molecules with the highest kinetic energy leave as gas (stabilizes water temps, sweating)
lower density as solid than liquid
as water solidifies, it expands and becomes less dense due to H bonds
universal solvent
water as dissolving agent in a solution (its polar molecules are attracted to other polar molecules to form H bonds)
carbon
-can form single double or triple covalent bonds via valance electrons
-this can link them into a chain
hydrocarbon
organic molecule only consisting of C and H
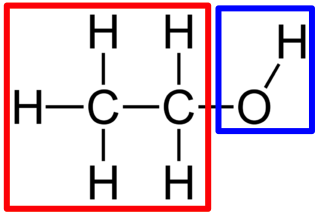
hydroxyl group
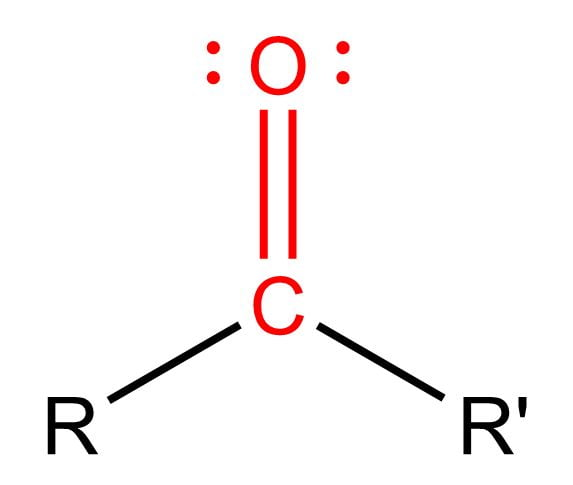
carbonyl group
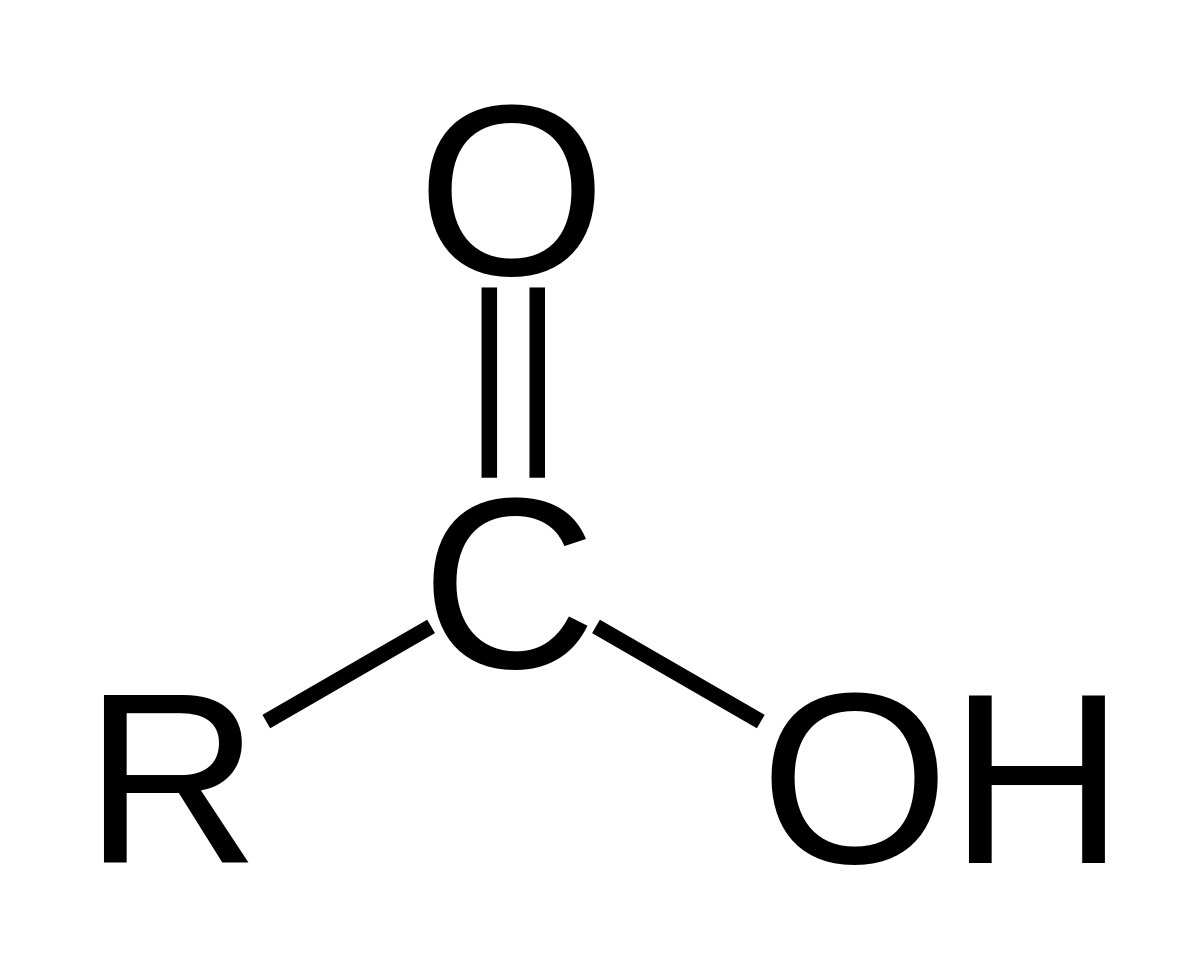
carboxyl group
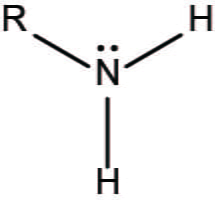
amino group
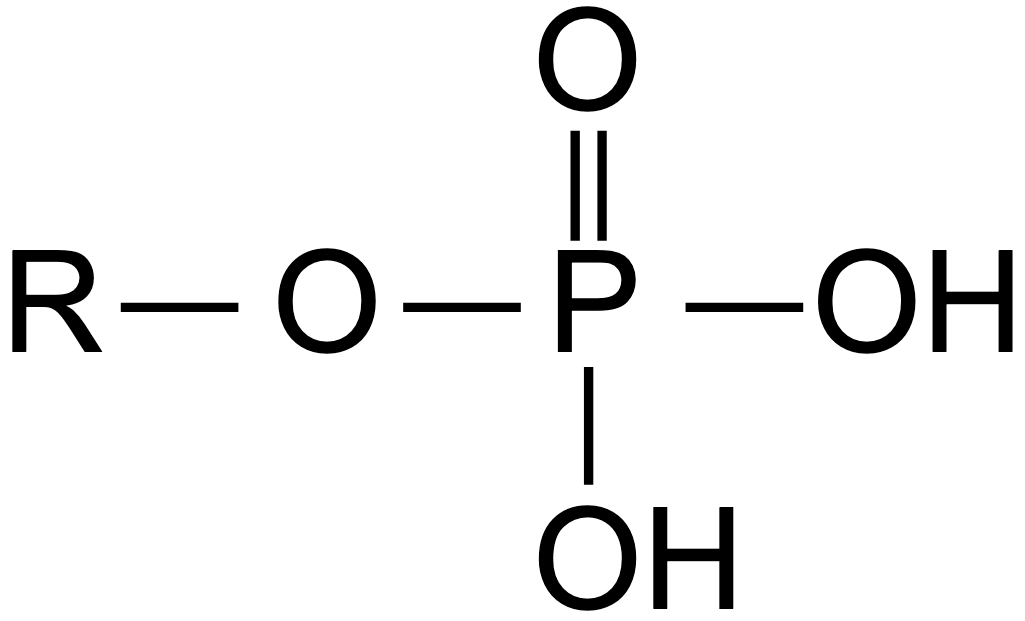
phosphate group
dehydration reaction
bonds 2 monomers with the loss of H2O
A + B —> AB + H2O
hydrolysis
breaks the bonds in a polymer by adding H2O
AB + H2O —> A + B
carbohydrates
CHO
-energy storage and structure
-monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
- hydroxyl and carbonyl groups
monosaccharides
simple sugars, can serve as building blocks for amino acids or monomers
polysaccharides
polymer with many sugars joined via dehydration ractions
-storage (starch for plants, glycogen for animals)
-structural (cellulose for plants, chitin for animals)
proteins
CHON(S)
-amino acids, peptides, polypeptides (3D folded polypeptides)
-shape determines function
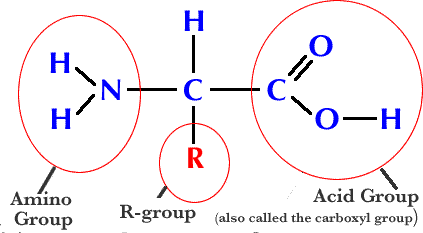
-amino + carboxyl + R group
amino acids
amino group + carboxyl group (20 different ones)
protein structure
nonpolar
hydrophobic
polar/charged/ionic
hydrophilic
polypeptides
many amino acids linked by peptide bonds (each has a unique amino acid sequence and unique ends with N terminus and C terminus)
primary protein structure
linear chain of amino acids, determined via genes, dictate other forms
secondary protein structure
coils and folds due to H bonding within the polypeptide backbone (B pleated bonding with amino acid and a helix with every 4th)
tertiary protein structure
3D folding due to interactions between the side chains of the amino acids, disulfide bridges
quaternary protein structure
arrangement and interaction of multiple folded polypeptide chains into a larger protein complex
nucleic acids
CHONP
-processes hereditary information
-forms are DNA and RNA
-nucleotides —> polynucleotides
-contains nitrogenous base, pentose, and phosphate group
nitrogenous base (pyrimidine)
one ring, 6 atoms, cytosine, thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA
nitrogenous base (purine)
2 rings (one 6 atoms, one 5 atoms), adenine and guanine
5C sugar/pentose
sugar bonded to the base (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA)
phosphate group
added to the pentose (which is attached to the base) to form a nucleotide
polynucleotide
phosphate groups link adjacent nucleotides through phosphodiester linkage
-directionality (one 5 to 3, one 3 to 5)
sequence of nucleotide bases
-unique for each gene
-dictates amino acid sequence
-dictates primary structure of a protein and 3D structure of a protein
DNA
consists of 2 polynucleotides, forms a double helix, antiparallel strands, held together by H bonds with bases, base pairing (A- T, C-G), OH and H
RNA
single stranded polynucleotide, variable in shape, base pairing (A - U, C- G), OH and OH
Adenine and thymine/adenine and uracil
2 H bonds
cytosine and guanine
3 H bonds
lipids
-CHOP
-glycerol and fatty acids —> no real polymer
-nonpolar hydrophobic
-glycerol (hydroxyl groups) + fatty acids (long C chains with carboxyl group at one end)
-3 fatty acids join to a glycerol via ester linkage
unsaturated fatty acid
contains one or more double bond, missing a H
saturated fatty acid
no double bonds, more H
phospholipids
-major component of cell membranes
-2 fatty acids attached to a glycerol and a phosphate
-assemble as a bilayer with hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads
steroids
lipids with 4 fused rings, unique groups attached to the ring determine the type