Lesson 5: Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is a macromolecule?
large biological molecules that are comprised of smaller subunits
Monomers
smaller subunits
Polymers
larger molecules made up of a chain of monomers
Large biological molecules
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
Which macromolecule is not a polymer?
Lipids
Dehydration/Condensation Reactions
linking two monomers, attach a monomer to a growing chain, water molecules is produced, new bond is formed
Hydrolysis Reactions
break polymers (break bonds)
Carbohydrates are ___
sugars
What is a monosaccharide?
sugar monomer
What is a disaccharide?
double sugar, two monosaccharides with a covalent bond
What is a polysaccharide?
many sugars
Monosaccharide structure
attached hydroxyl groups, one carbonyl group, monomers from which carbohydrates are built, 3-7 carbons
Aldose
Carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain
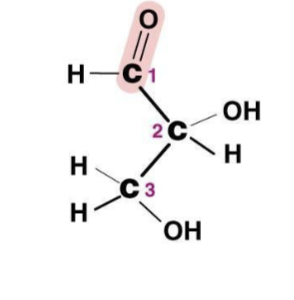
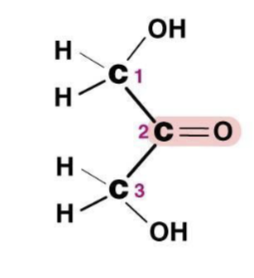
Ketose
Carbonyl group in the middle of a carbon chain
Ribose is a ___ Carbon ____saccharide (____ sugar)
5,mono,aldose
Glucose&Galactose is a ___ Carbon ____saccharide (____ sugar)
6,mono,aldose
Fructose is a ___ Carbon ____saccharide (____ sugar)
6, mono, ketose
3 Common Disaccharides
Maltose
Sucrose
Lactose
Energy stores
Glycogen (animals) and Starch (plants)
Structural Material
Cellulose (plant cells walls), Chitin (exoskeletons)
Glycogen (animals)
highly branched polymer of glucose, in liver and skeletal muscles of humans
Starch (plants)
polymers of glucose monomers, use amylose and amylopectin
Different forms of glucose:
(alpha) and (beta)
Starch contains only …
alpha glucose monomers
Cellulose contains only….
beta glucose monomers
Alpha glucose OH- facing ___
downward
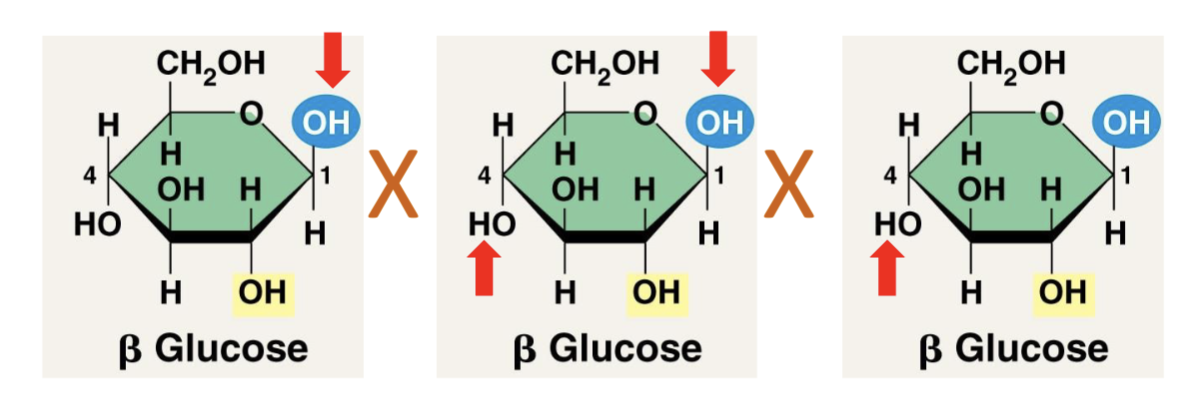
Beta glucose OH- facing ___
up and downward
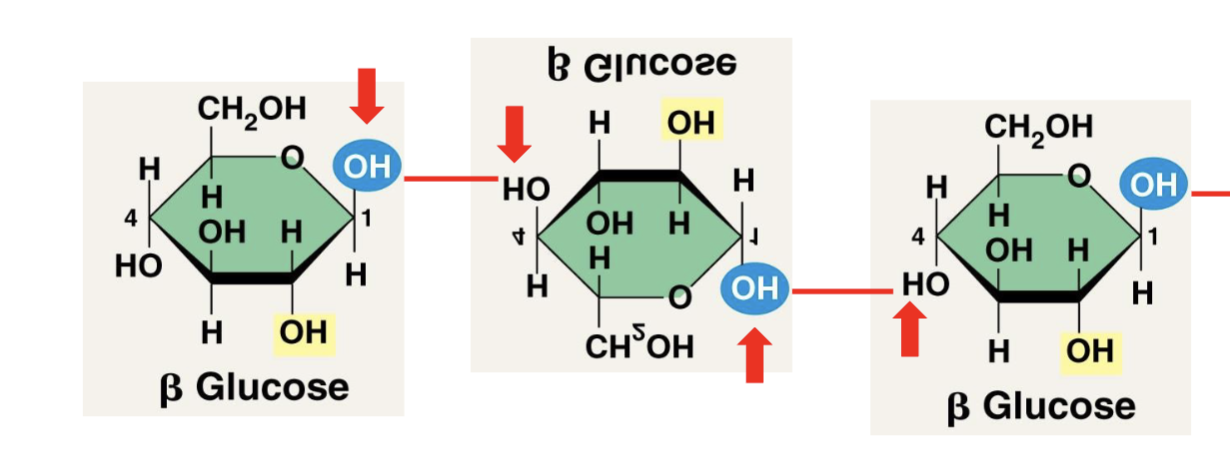
2 forms of starch
amylose - unbranched & helical
amylopectin - branched & helical