Tendon Transfers
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
General Principles for Tendon Tranfers
Prognosis decline > age 30
Prioritize distal and similar muscles to be more effective
Ex: using a radial nerve ext based muscle for EIP to EPL - similar synergistic movements
the more distal the muscles, the more effective the transfer
Clarity on locations donor muscle motor point; ask dr “where is that motor point location for that muscle?”
MMT >4 (4+ or 5) to be useful as donor tendon; donor tendons lose 1 MMT following transfer
Expendable donor (i.e EIP, palmarus longus)
Treatment Principles
Tx as a laceration repair - splint as if laceration
Immobilize 0- 3 weeks
Early short arc 3+ weeks
3-6 weeks work on light mobility, AROM, soft tissue work to affected area
4 weeks avoid composite movements
6+ weeks: neuromotor retraining and reeducation
NMES, biofeedback, mirror therapy
“training old muscle to do new muscle job”
8+ weeks: strengthening and weaning out of orthosis
12+ weeks: return to work
High Median Nerve Presentation
Everything distal to this area involved
Hand of Benediction:
FCR
FPB/FPL
Th intrinsics: APB, FPB, OP
Lumbricals of IF/LF
FA DBS Splint indicated
Low Median Nerve Presentation
Muscles affected, resulting in loss of opposition and pinch:
Thenar intrinsics
IF, LF lumbricals (1st and 2ns lumbricals)
Hand based DBS splint
APB is primary muscle of thumb opposition
Median Nerve Transfers
Bunnel Transfer: FDS of RF to APB for TH retropusion for low injury
EIP to ABP for TH retropulsion for high injury
Camitz Transfer: PL to APB for Th opposition for low injury - augments palmer abd, but flex and pronation of Th are lost - indicated for severe CTS
Huber Transfer: ADM to APB for Th opposition - indicated for congenital conditions such as TH hypoplasia
ECRL or Brachioradialis to FPL - TH IP flex - can also be transferred to FDP for IP flex
FDP side-to-side: For DIP flexion to IF, LF and full flexion of digits for high nerve injuries
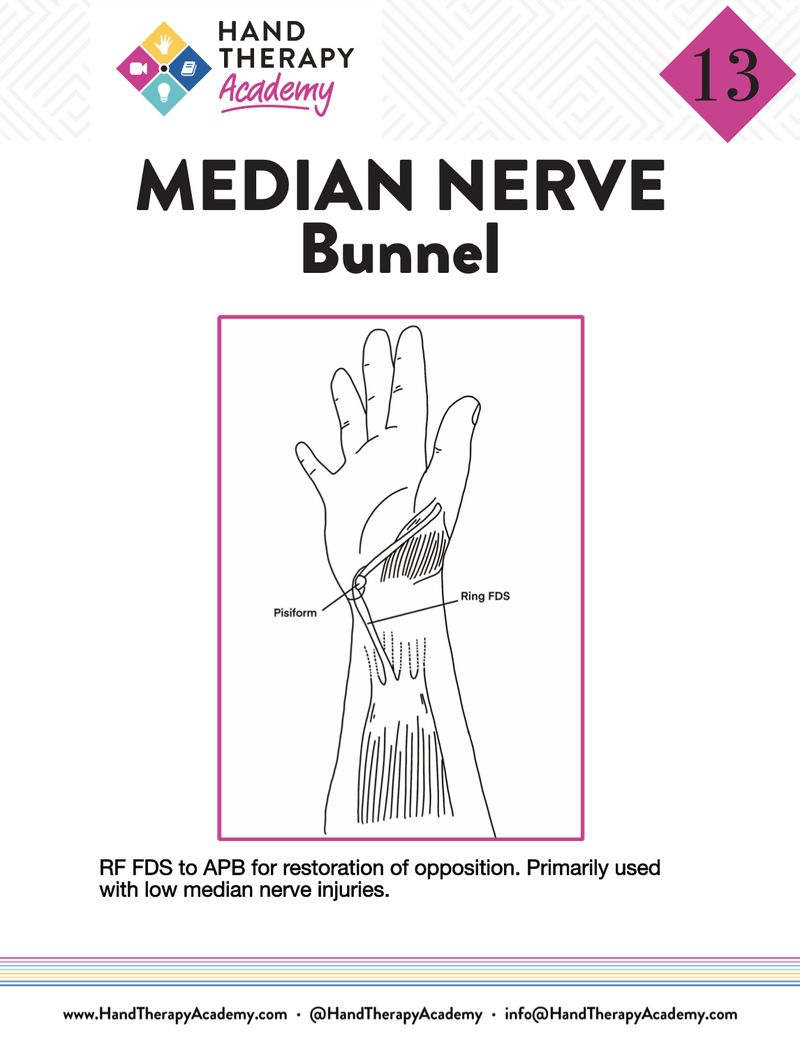
Bunnel Transfer
Median Nerve Tendon transfer for low median nerve palsy
FDS of RF to APB
for Th opposition
FDS of RF is taken and split - then re-routed via carpal tunnel and then redirected distally via tendon sheath and inserted into TH
EIP to APB Transfer
high median nerve injury transfer; where FDS is not available
non synergistic and harder to train, but easy to transfer
restores TH opposition
tunneled under ulnar aspect of wrist and routed across palm to level of pisiform and inserted to abductor pollicis brevis
Camitz Transfer
Median Nerve Tendon transfer
PL to APB
for Th opposition
Pronation and flexion component of TH lost with this transfer; purpose to augment palmar abduction in patients who have severe motor loss from severe CTS; only an option for low median nerve injuries
Huber Transfer
Median Nerve Tendon transfer for high median nerve injury
ADM to APB
for Th opposition OR EIP, EPL, EDM, ECU
ADM is released from its insertion point and then turned 180 degrees and inserted into APB
Used in congenital cases or with absence of thenar muscles
thumb hypoplasia or aplasia
ECRL or Brachialradialis to FPL
Median nerve transfer for high injury
ECRL and ECU can also be used to IF FDP
For TH IP flexion
FDP Side-to-Side
Median Nerve transfer for high nerve injuries
For DIP flexion to IF, LF and full flexion of digits
Radial Nerve
Innervates 3 heads of the triceps first
Brachioradialis
ECRL - high injury above here (above elbow)
ECRB - PIN starts here - low injury here, below elbow
Supinator
EDC
ECU
APL
EDM
EPB
EPL
Extensor indicis
MMT for these to determine tendon worth transferring
-wrist drop
-finger drop
-poor grip strength
-Min sensory issues
Goals:
restore MCP ext
restore TH ext
restore wrist ext
Orthotic position: Elbow flexion to 90 degrees and FA in pronation with slight wrist extension; TH abd and extended at MCPs and IPs free
4-6 weeks post: isolated movement; avoid composite
8+ weeks: strengthen
12 weeks: return to full activity
Radial Nerve Transfers
Boyes Transfer: FDS of RF to EDC for MCP ext
Paul Brand Transfer: FCR to EDC to MCP ext
PL to EPL: for TH ext and retropulsion
FDS of RF to EPL: for TH ext and retropulsion
PT to ECRB: for wrist ext
Bicep to Tricep: for elbow ext
Boyes Transfer
Radial nerve transfer
FDS of RF to EDC
for MCP extension
Paul Brand Transfer
Radial nerve transfer
FCR to EDC
for MCP extension
PL to EPL or FDS of RF to EPL
radial nerve transfer
for Th ext and retropulsion (abd)
PT to ECRB
radial nerve transfer for high radial nerve injuries
for wrist extension
most common to restore wrist extension; done while waiting on nerve to return
Bicep to Tricep
stores elbow extension in high radial nerve injuries
Ulnar Nerve Injuries
Presentation:
loss of key pinch, loss of power grasp, excessive IP flex
High injury: above elbow level (FCU and FDP RF/SF) - loss of grip strength
restore SF & RF DIP flex
improve functional grip strength
Low injury: below elbow level (deep branch intrinsics)
correct the clawing position
regain key pinch
restore balance to IP/MCP
TX:
Orthotic: DBS with wrist in flexion for claw; DBS on TH if included
no full ext of hand to avoid stretching transfer
mobilize 3-4 weeks
6+ weeks neuro reeducation
8+ weeks strenthen
12+ weeks return to work
Brand Transfer
Ulnar nerve transfer for low ulnar nerve injuries
ECRB to lumbricals
restores tenodesis
ECRB free graft through extensor retinaculum
ulnar nerve transfer for high ulnar nerve injury
muscle connected to EDC to restore tenodesis
decrease claw deformity
Stiles Bunnel Transfer
ulnar nerve transfer for low ulnar nerve injury
Each FDS split, Run along lumbricals or P2 of RF or SF
restores digit tenodesis
Zancolli Lasso Transfer
ulnar nerve transfer for low ulnar nerve injury
FDS loops around A1 pulley of RF/SF
Blocks MCP hyperextension and Claw deformity
Smith Transfer
Ulnar nerve transfer for low ulnar nerve injury
ECRB to AP; not synergistic
ECRB rerouted around 2nd MCP and attached to AP
restores key pinch
Brachioradialis to AP
Ulnar nerve transfer for low ulnar nerve injury
restores key pinch
BR rerouted around 2nd MCP and attached to AP
Littler Transfer
Ulnar nerve transfer for low ulnar nerve injury
LF FDS to AP
restores key pinch
FDP Side-to-Side
ulnar nerve transfer for high ulnar nerve injury
FDP side to side
all 4 FDP tendons are lassoed together
for DIP flexion to RF, SF
Brachial Plexus Injury Transfers
loss of suprascapular nerves: loss of supraspinatus and infraspinatus
Signs:
loss of strength in ER and first 30 deg abd, coordination and stability
+ sulcus sign
Increased joint mobility
Musculocutaneous nerve: loss of brachialis, coracobrachialis, and biceps brachii resulting in loss of elbow flexion
MMT of each of these; all must present with limitations to indicate nerve injury
L’Episcopo Transfer
Lattissimus Dorsi & Teres Major to Rotator Cuff
restores external rotation and GH stability, due to suprascapular loss
Orthotic: shoulder sling for 6 weeks, 30-40 deg abduction and in ER - wedge needed for this position
6 weeks p/o: light short arc ; grade I joint mobs; avoid fatigue during exercise
no weight bearing or resistance until 12 weeks post
Lats, Pec Major, or Triceps to Biceps
restores bicep flexion, due to musculocutaneous loss
these muscles are re-routed to bicep
proximal muscle group transfers less successful that distal: lats and pec major
triceps more successful but still tricky as its not a synergistic muscle
Orthotic: Immobilize at 110-120 degrees of elbow flexion
hinged elbow ideal to begin slow progression of ext block weekly at 6 weeks
Proximal muscle group: extend 15 degrees weekly for pec or lat transfer
Week 6: AROM to block of hinge or splint; no PROM
Week 8: PROM appropriate; let gravity help at this point
D/C orthotic when able to demo 90 degrees of flexion against gravity
Steindler Transfer
Common flexor tendon transferred more proximally to distal humerus
restores elbow flexion after musculocutaneous loss
“when you close, now you’re elbow flexes” - synergistic
Orthotic: Immobilize at 110-120 degrees of elbow flexion
hinged elbow ideal to begin slow progression of ext block weekly at 6 weeks
Steindler: progress 30 degrees per week
Week 6: AROM to block of hinge or splint; no PROM
Week 8: PROM appropriate; let gravity help at this point
D/C orthotic when able to demo 90 degrees of flexion against gravity
5lb max lifting restriction for life
Lats, Bicep, or Deltoid to Triceps
restores elbow extension after loss of radial nerve
Mannerfelt Syndrome Transfer
RA rupture transfer
loss of FPL of TH or IF FDP - frays and ruptures over osteophytes over scaphoid
Assess FDP of LF to rule out AIN paralysis
FDS RF or LF to FPL or IF FDP
restores TH or IF IP flex
Orthotic: FA based dorsal blocking TH spica in wrist flex for FPL
If FDP, DBS for digits
4 weeks p/o: early mobilization
6 weeks p/o neuromuscular reeducation
8 weeks p/o strengthening
12 weeks p/o return to activity
Vaughn Jackson Transfer
RA rupture transfer
EDC ruptures over styloid resulting in loss of ext in RF, SF
EIP to EDC of SF, RF
they may also use FDS if more than SF, RF EDC lost
restores RF and SF extension
Orthotic: Volar resting orthotic with MCPs in ext and IPs free
4 weeks p/o: early mobilization
6 weeks p/o neuromuscular reeducation
8 weeks p/o strengthening
12 weeks p/o return to activity
EIP to EPL Transfer
RA rupture transfer
EPL rupture over lister’s tubercle
APB can extend IP slightly in some cases but retropulsion fully lost
synergistic movement
restores TH extension
Orthotic: full ext of TH, volar FA based TH spica orthotic
delay mobility to 4 weeks p/o
4 weeks p/o: early mobilization
6 weeks p/o neuromuscular reeducation
8 weeks p/o strengthening
12 weeks p/o return to activity
Nerve regeneration timeline
and sequence of return
Apparent 6-8 weeks after nerve repair
Sequence of return
deep pressure and pin prick
moving touch
static touch
discriminative touch
Successful Tx for Intrinsic Minus Hand
Dorsal MCP jt. blocking orthosis
FDS to A1 pulley
FDS to lateral bands
A patient sustained a wrist laceration from punching glass. The patient lacerated his median and ulnar nerve, developing a claw hand. The patient underwent a Zancolli lasso procedure 3 weeks ago. You are advising the patient to activate the transfer. What would you tell the patient to do?
To flex and extend the MCPs within a small range (20-30 degrees)
With the Zancolii lasso procedure, the flexor digitorium superficialis is detached from its insertion and wrapped around the second annular ligament near the volar aspect of the MCP joint, where it acts as a pulley.
This limit the extensor digitorum communis of the EDC at the MCP joint by preventing hyperextension