OB II Unit 6 Fetal Abdomen 39- 58
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is Duodenal Atresia?
Double Bubble Sign
Blockage of duodenal lumen by membrane
Prohibits passage of swallowed fluid beoynd obstruction
Amniotic Fluid backs up into duodenum and stomach creating 2 echo-free structures in upper abdomen
Duodenal atresia may coexist with ______ ________ and 30% will have ________ ___
Annular pancreas
Trisomy 21
What will duodenal atresia have?
Elevated Amniotic AFP- inability to swallow
Poyhydramnios
What is duodenal atresia associated with?
Cardiovascular- leads to echo
Genitourinary
Imperforate anus
Esophageal atresia
Symmetric IUGR
What are the US findings of duodenal atresia?
Double Bubble sign
2 anechoic structures in upper abdomen, look for communication
Polyhydramnios
Symmetric IUGR commonly occurs
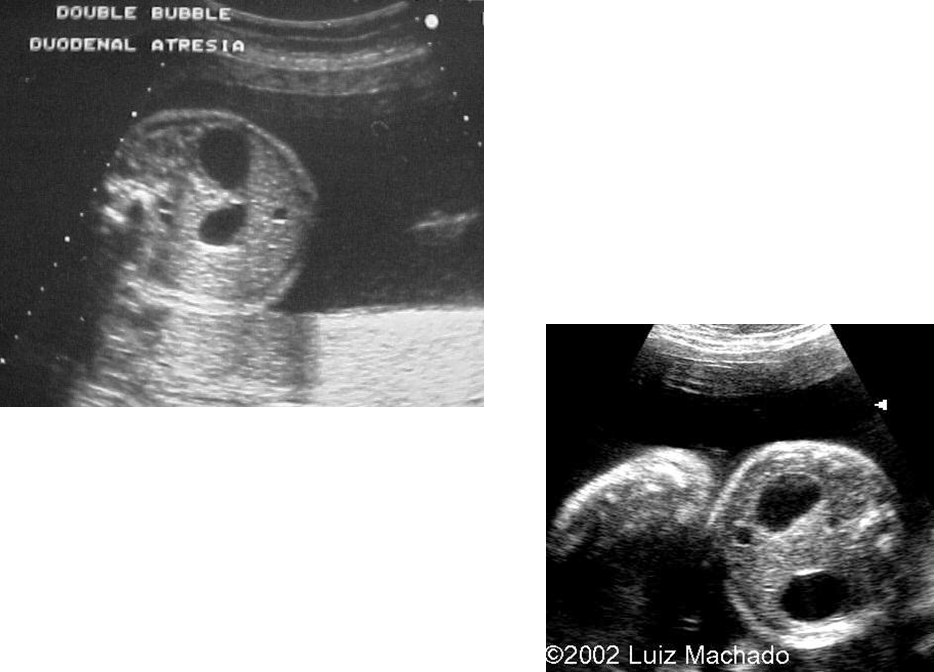
What are these images showing?
Duodenal Atresia
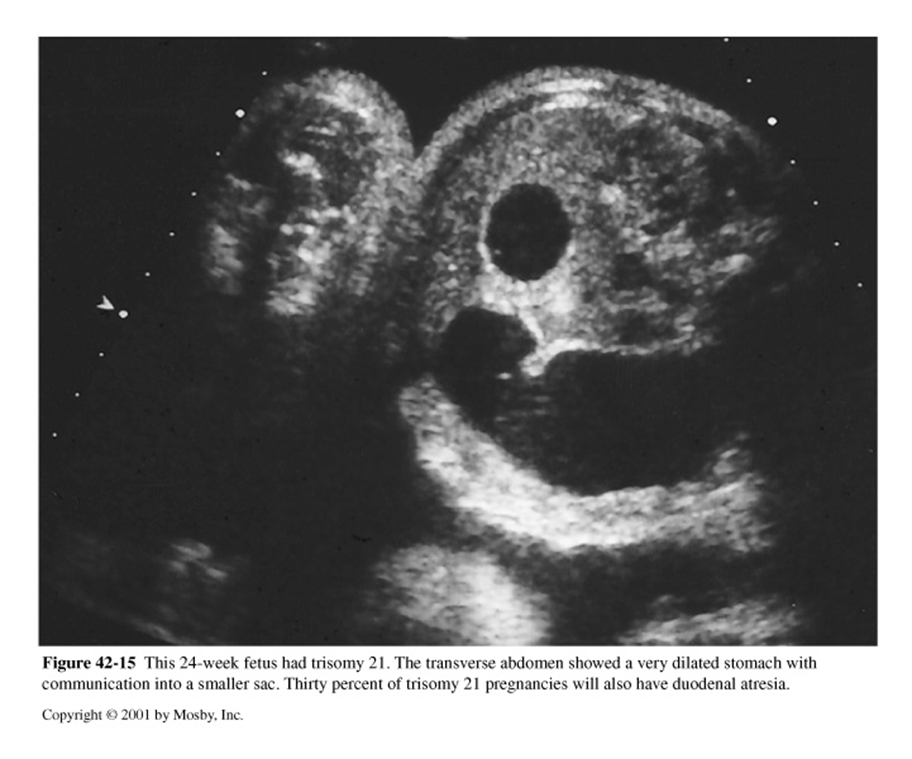
What is this image showing?
duodenal Atresia
What are causes of the double bubble sign?
Duodenal atresia
Duodenal stenosis
Annular Pancreas
Ladd’s bands- fibrous stalks of peritoneal tissue that connect secum to the retroperitoneal in the RLQ-leads to malrotation
Proximal jejunal atresia
Malrotation
Diaphragmatic hernia
What are VACTERL association?
A group of anomalies
•Vertebral defects
•Anal atresia
•Cardiac anomalies
• Tracheo-Esophageal fistula
•Renal anomalies
•Limb dysplasia
With Vacterl association, what are the requirements?
3 features must be identified
What is jejunoileal Atresia or Stenosis?
Vascular accident = secondary to volvulus, gastroschisis, or sporadic
What part of bowel is subject to obstruction?
Any of the bowel
When will normal bowel loops be identified?
In the 3rd trimester
When might you suspect a bowel obstruction?
If clear fluid loops of bowel are visualized
What are US finding for an obstructed bowel?
Multiple cystic structures, more than 2, proximal to site of atresia within abdomen discontinuous with stomach
Polyhydramnios is possible
What may an obstructed bowel be associated with?
Other anomalies
Ascites
Meconium Peritonitis
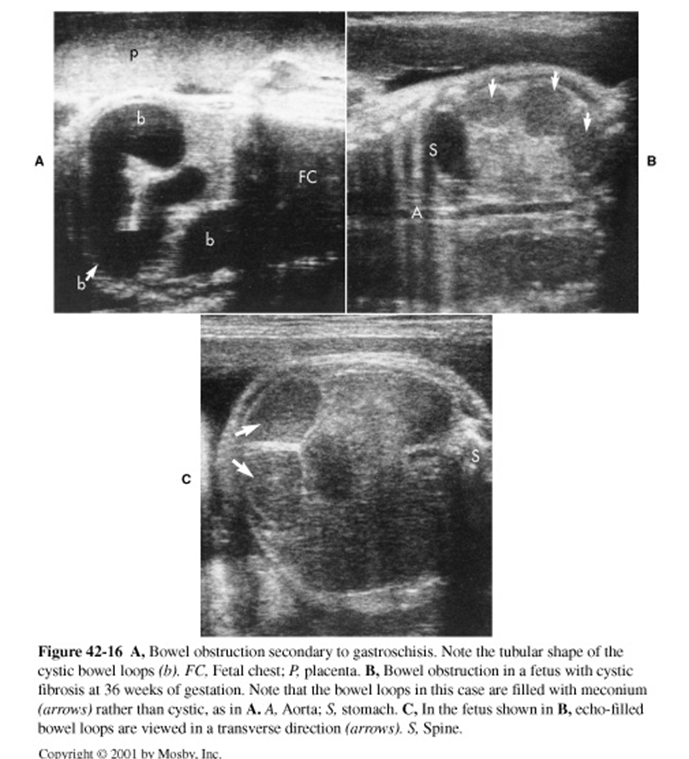
What are these images showing?
Bowel Obstruction
What is the most common malformation of the midgut?
Meckel’s Diverticulum
What is Meckel’s Diverticulum?
Remnant of proximal part of yolk stalk that fails to degenerate & disappear during early development
What does Meckel’s Diverticulum appear as?
Small fingerlike sac
5 cm in length
Projects from border of ileum in RLQ
What is this image showing?
Meckel’s Diverticulum
What is Meconium Ileus?
Thick meconium in distal ileus
Overproduction of meconium and mucus
What is meconium ileus seen with and its earliest manifestation?
Cystic Fibrosis
Autosomal recessive
Pancreatic disease
Respiratory problems (thick mucus)
What are the US findings for a meconium ileus?
Ileum dilates because of impacted meconium
Echogenic small bowel
Cystic Fibrosis
Cytomegalovirus
Trisomy 21
Polyhydramnios
Calcifications of peritoneal structures
Obstructed Bowel may perforate and = ____________ __________
Meconium Peritonitis
What is meconium peritonitis?
An inflammatory response from leakage of bowel contents, causing fibrosis of tissue & calcifications
Pseudocyst may develop because of chronic peritonitis
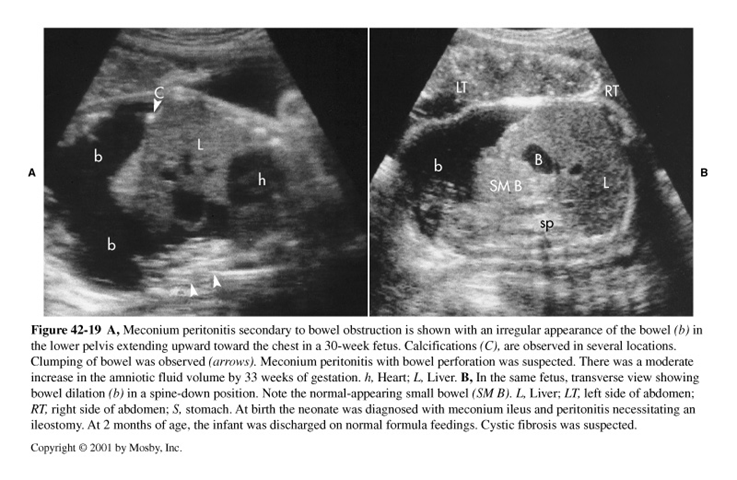
What is this image showing?
Meconium Peritonitis
what is Anorectal Atresia?
Complex disorder of bowel & genitourinary system
What is an imperforate anus?
membrane covering anus
What is anorectal atresia be associated with?
VACTERL association or caudal regression syndrome
Many assoc. anomalies
Incontinence of bowel & bladder is common in the infant
What are the US findings for Anorectal Atresia?
Dilated Colon
Calcified meconium
AFI is typically normal
Or decreased if assoc. renal problems
What is the prognosis of anorectal atresia?
Poor due to associated anomalies
What is Hirschsprung’s Disease?
Megacolon
Congenital disorder
Dilated bowel loops on US
With Hirschsprung’s Disease, it may be difficult to detect _________ but suspected with dilated bowel loops
prenatally
Hyperechoic bowel varies with what?
Location in SB or colon, gestational age, degree of echogenicity
How do you compare the echogenicity of bowel?
Compare with iliac wing of fetus
What are the 3 grades of degree of hyperechogenicity?
•1 = mildly echogenic & typically diffuse
•2 = moderately echogenic & typically focal
•3 = very echogenic, similar to bone structures
What is true Ascites?
Always an abnormal finding in fetal abdomen
What is true ascites caused by?
Nonimmune hydrops = poor prognosis
Bowel perforation
Urinary ascites from bladder rupture
What are the US findings of true ascites?
Fluid within abdominal cavity
To dependent side
Outlines falciform ligament & umbilical vein
Pleural effusions
Pericardial effusion
Integumentary edema
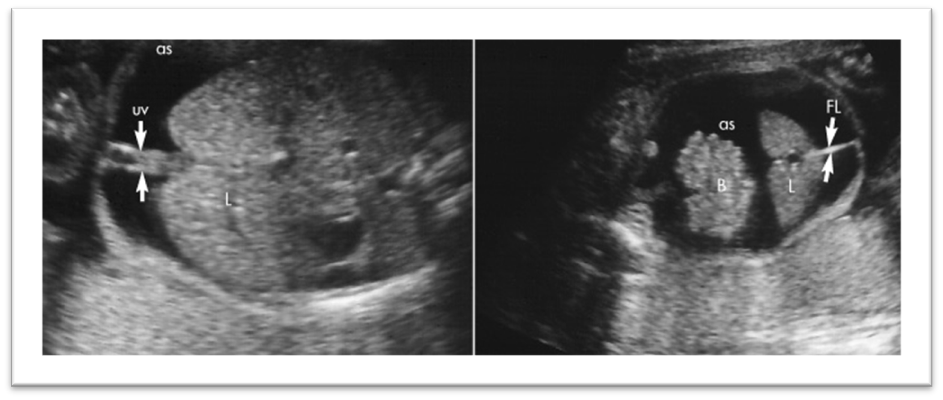
What is this image showing?
True Ascites
If finding a cystic mass, what should you determine?
Characteristics of mass
Precise location – origin if possible
Size of mass
? Compression of other organ systems
Evaluate all abdominal organ systems
Other possibilities
Ovarian – check gender – well circumscribed
Omentum – well circumscribed
Urachus – b/n umbilicus & bladder
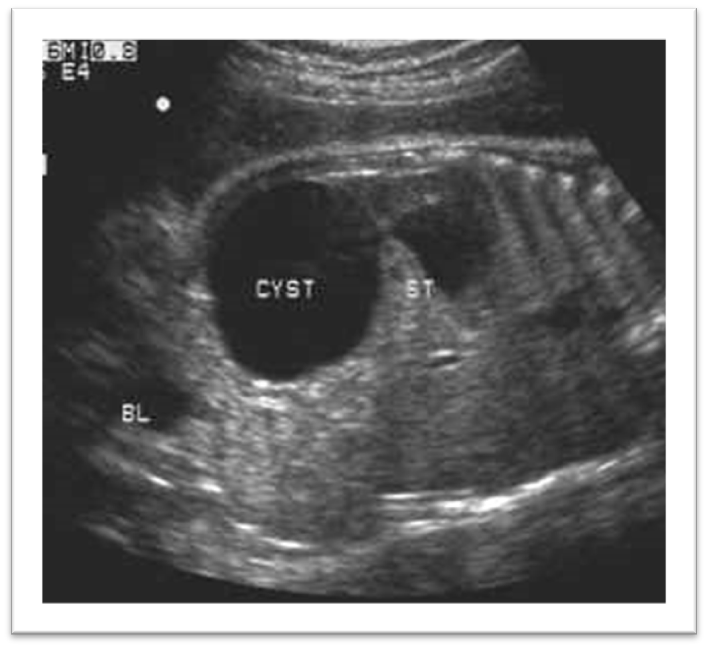
What is this image showing?
Ovarian cyst