CBA 300 Exam 2 ch 6-10, Dr. Craig D. Macaulay, CSULB
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
International investment. Two ways.
Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI). Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI)
Holding securities of firms in other countries but without a controlling interest.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Investing equity stake of 10% or more in a foreign based enterprise.
Types of FDI
Horizontal FDI, Vertical FDI, Upstream Vertical FDI, Downstream Vertical FDI.
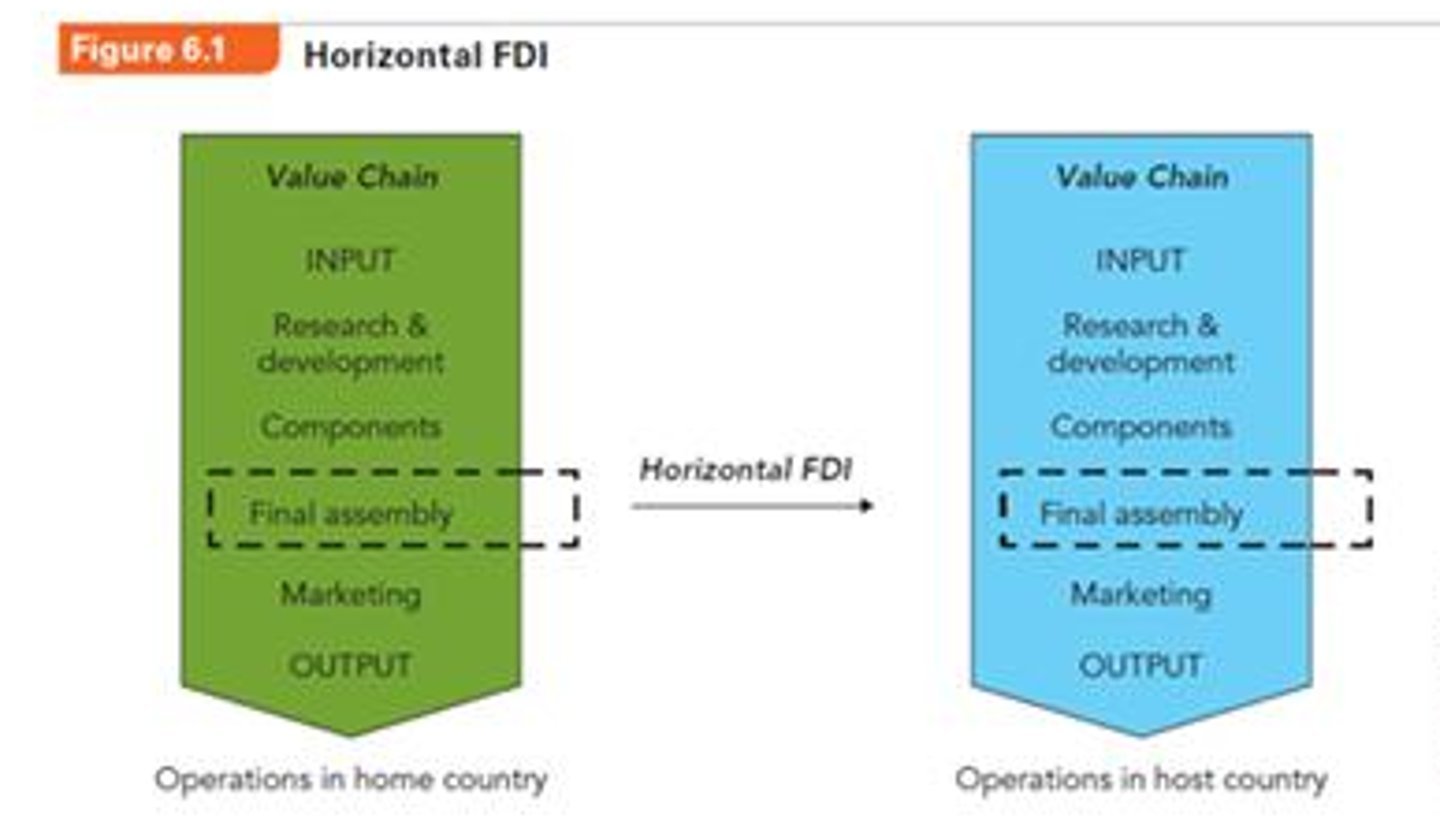
Horizontal FDI
Firms produce same products or offers the same services in a host country as at home.
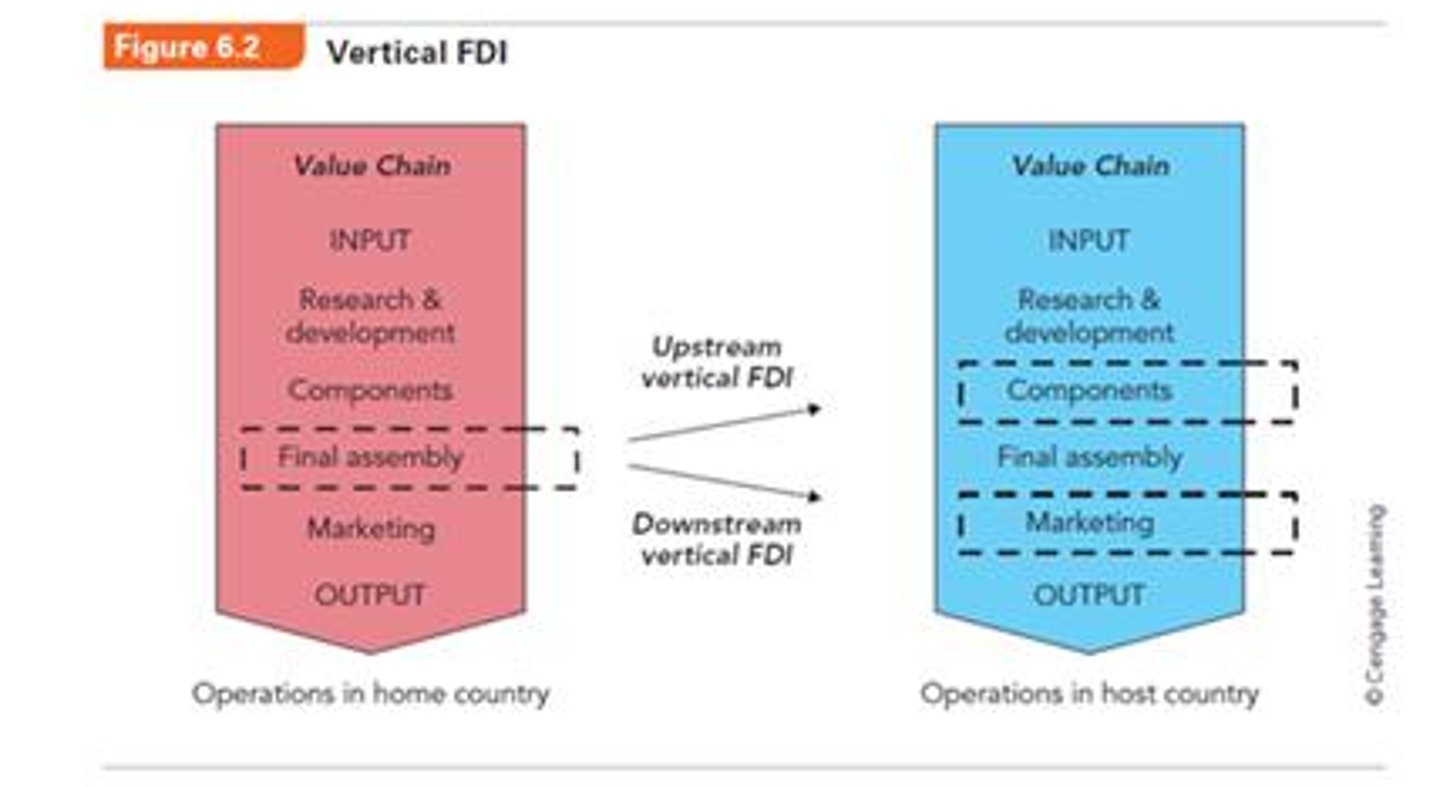
Vertical FDI
Firm moves upstream or downstream in a different value chain stages in a host country.
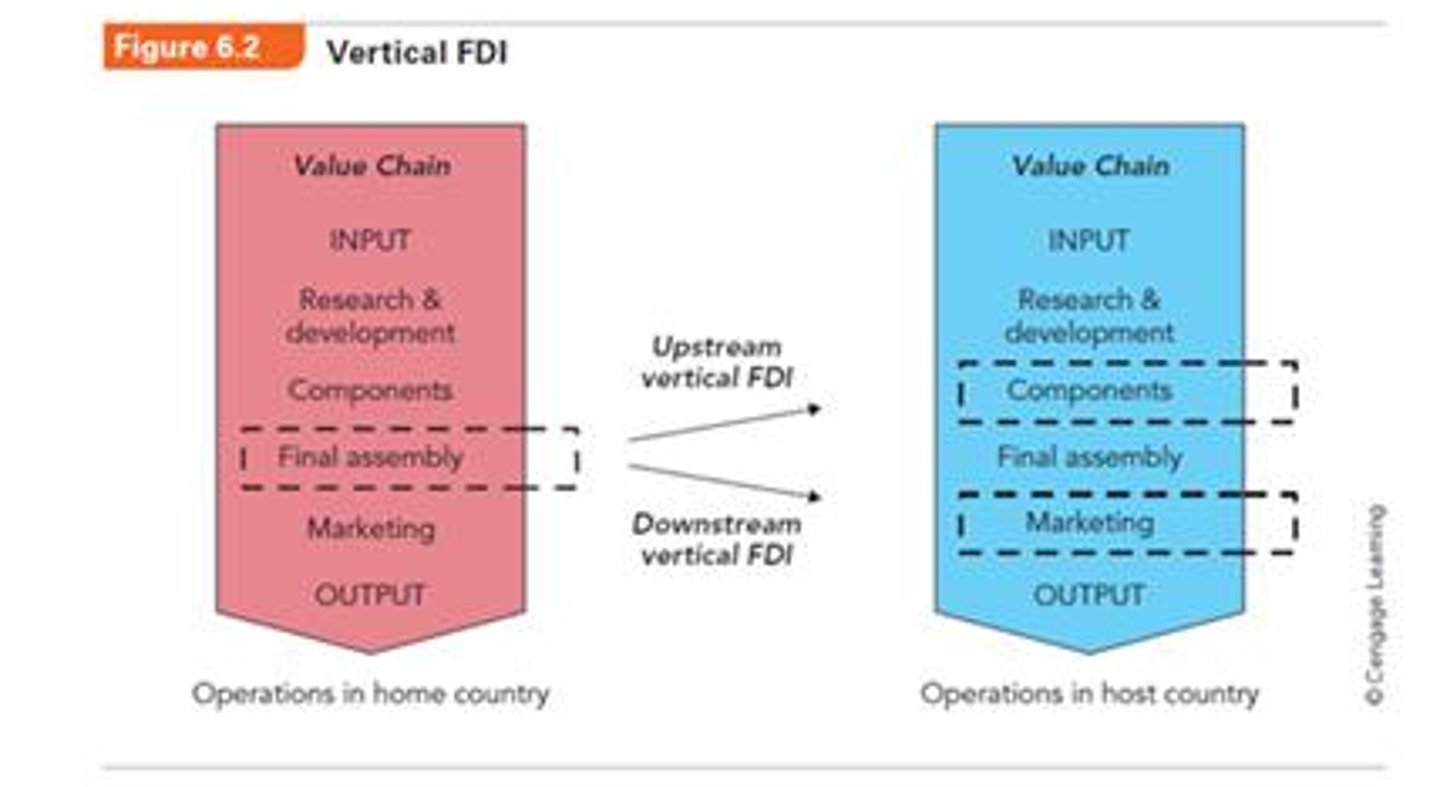
Upstream Vertical FDI
Firm engages in an upstream stage of the value chain
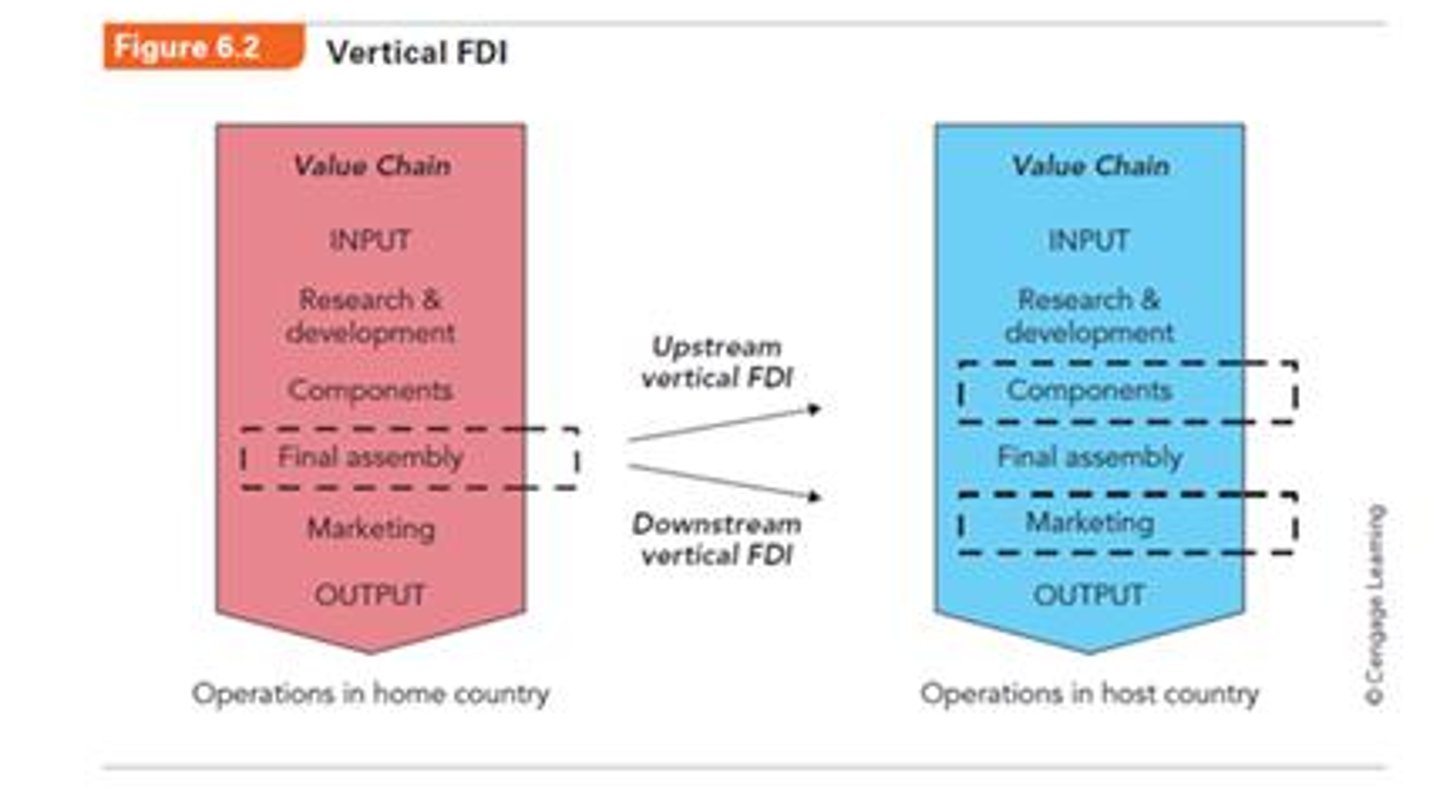
Downstream Vertical FDI
Firm engages in a downstream stage of the value chain
FDI Flow
Amount of FDI in a given period in a certain direction
FDI Inflow
FDI moving into a country in a year
FDI outflow
FDI moving out of a country in a year
FDI stock
Total accumulation of inbound FDI in a country or outbound FDI of a country across a given period of time (usually many years)
MNE
Firm that engages in FDI when doing business abroad.
Non-MNE
Firm that does business abroad by exporting and importing, licensing and franchising, outsourcing, or engaging in FPI
Reasons firms engage in FDI
- Ownership advantages
- Location advantages
- Internalization advantages
Benefits of Direct Ownership
- Combination of equity ownership rights and management control rights
- Ownership rights provide the management control rights
- FDI facilitates firm-specific resources and capabilities abroad to overcome foreign liabilities
Why firms prefer FDI to licensing
- FDI reduces dissemination risks
- FDI provides tight control over foreign operations
- FDI facilitates the transfer of tacit knowledge through "learning by doing"
Agglomeration
clustering of economic activities in certain locations
advantages of agglomeration
- Diffusion of knowledge from one firm to others among closely located firms
- Industry demand that creates a skilled labor force
- Industry demand that facilitates a pool of specialized suppliers and buyers in a region
Location Advantages
Obtained by a firm when operating in a location owing to its firm specific capabilities
Acquiring and Neutralizing Location Advantages
- Rivals hope to acquire or neutralize location advantages
- Mostly followed by oligopolistic industries
Advantages of Internalization
- Domestic transaction costs are cheaper than international transaction costs
- Combats market failure by replacing the external market with in-house links
Political views on FDI
Radical View.
Free Market View.
Pragmatic Nationalism.
Radical View
FDI is an instrument of imperialism and vehicle for foreign exploitation
(govt. nationalizes MNE assets or bans inbound MNE)
Free market view
When FDI is unrestricted by government intervention, it enables countries to tap into their absolute and comparative advantages (by specializing in the production of goods and services)
Pragmatic Nationalism
FDI is approved only when its benefits outweigh its costs
Foreign exchange rate
Price in one currency in terms of another
Appreciation
Increase in currency value
Depreciation
Loss in currency value
Determinants of foreign exchange rates
- Relative price differences and PPP
- Interest rates and money supply
- productivity and balance of payments
- Exchange rate policies
- Investor psychology
Supply and demand of foreign exchange
- Commodity's price is fundamentally determined by its supply and demand
- Strong demand will lead to price hikes
- Oversupply will result in price drops
Relative price difference
- purchasing power parity (PPP)
- determines equivalent amount of goods and services different currencies can purchase
- captures differences in cost of living between countries
- argues that exchange rates should move towards levels that would equalize the prices of an identical basket of goods in any two countries in the long run
Interest rates and money supply
- high-interest rates enhance exchange values
- exchange rate is influenced by:
- rate of inflation
- money supply
Productivity and balance of payments
Increase in productivity:
- improves a countries competitive position in international trade
- increases the value of home currency
- changes balances of trade
Affects Balance of Payments (BOP):
- currency account surplus leads to currency appreciation
Floating exchange rate policy
Willingness of a government to let demand and supply conditions determine exchange rates
-clean float
-dirty float
Clean float
pure market solution to determine exchange rates
Dirty float
uses selective government intervention to determine exchange rates
Fixed rate policy
Setting exchange rate of a currency relative to other currencies
Pegging
Setting exchange rate of a domestic currency in terms of another currency
- stabilizes import and export prices
- restrains domestic inflation when pegged to a country with relatively no inflation
Investor psychology
predicts short-run movements of exchange rates
Bandwagon effect
Effect of investors moving in the same direction at the same time, like a herd
capital flight
phenomenon in which a large number of individuals and companies exchange domestic currencies for a foreign currency
The gold standard (1870 - 1914)
Value of major currencies was maintained by fixing their prices in terms of gold
-Global peg system
-less volatile
-highly predictable and stable
The Bretton woods system (1944 - 1973)
All currencies were pegged at a fixed rate to the U.S. dollar
- reflected the higher U.S. productivity level
- rising productivity in the world and U.S. inflationary policies led to its demise
The post-Bretton woods system (1973 - present)
- System of flexible exchange rate regimes
- No official common denominator
- Characterized by the diversity of exchange rates
Drawbacks:
- Turbulence and uncertainty
International monetary fund (IMF)
International organization
- Established to promote international monetary cooperation, exchange stability, and orderly exchange arrangements
Core responsibility: lending
- collects fund from member countries
Strategic responses of financial companies
Primary strategic goal is to profit from the foreign exchange market
Foreign exchange market
The market where individuals, firms, governments, and banks buy and sell currencies of other countries
Functions:
- to service the needs of trade and investments
- to trade in its own commodity
Types of foreign exchange transactions
spot transaction, forward transaction, currency hedging, forward discount, forward premium, currency swap
Spot transaction
classic single shot exchange of one currency for another
Forward transaction
participants buy and sell currencies now for future delivery
Currency hedging
Protects traders and investors from exposure to the fluctuations of the spot rate
Forward discount
Forward rate of one currency relative to another currency is higher than the spot rate
Forward premium
Forward rate of one currency relative to another currency is lower than the spot rate
Currency swap
conversion of one currency into another at time one.
- Includes an agreement to report it to the original currency at a specified time two in the future
Spread
difference between offer rate and bid rate
Offer rate
Price at which a bank is willing to sell a currency
Bid rate
price at which bank is willing to buy a currency
Outcome of integrated nature of the foreign exchange market
- Razor thin spread
- Quick decisions on buying and selling
- Ever-increasing volume in order to make more profits
Strategic responses of nonfinancial companies
companies cope with currency risks by:
- Invoicing their own currency
- currency hedging
- strategic hedging
Strategic hedging
Spreading out activities across different currency zones to offset currency losses in one region through gains in other countries
Regional Economic Integration
efforts to reduce trade and investment barriers within one region
Global economic integration
efforts to reduce trade and investment barriers around the globe
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
Multilateral agreement governing the international trade of goods
- became the world trade organization (WTO) in 1995
- economic integration in Europe led to the European Union EU
Benefits of global integration
Political:
- Promotes peace with trade as investment
- builds confidence in multilateral trading system
Economic:
- Disputes handled constructively
- Rules make life easier and discrimination impossible for participating countries
- Free trade and investment raise incomes and stimulate economic growth
GATT
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
- Reduced level of tariffs through multilateral negotiations
Areas of concern:
- Did not cover trade in services and intellectual property
- Loopholes in merchandise trade require reforming
- Global recessions led to governments to invoke nontariff barriers (NTBs)
World Trade Organization (WTO) (1955 - Present)
GATT's successor
Features:
- General agreement on trade in services (GATs)
- Trade related aspects of intellectual property rights(TRIPS)
-Trade dispute settlement mechanisms
- Trade policy reviews
The Doha round
Round of WTO negotiations to:
- reduce agricultural subsidies in developed countries
- slash tariffs
- free up trade in services
- strengthen intellectual property protection
Pros of regional economic integration
- promotes peace
- free trade and investment raise incomes and stimulate economic growth
- enables constructive handling of disputes
- consistent rules prevent discrimination
Cons of regional economic integration
- discrimination against firms outside of region
- loss of sovereignty
Types of regional economic integration
- political union
- economic union
- common market
- customs union
- free trade area
Political origin of the EU
- Countries integrated to end the cycle of hatred and violence
- Signed the European coal and steel community (ECSC) treaty in 1951
- Signed by Belgium, France, West Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands
Treaty of Rome 1957
Launched the European Economic Community (EEC)
Maastricht Treaty 1993
Established a single Economic Union
Lisbon Treaty 2009
Amended the Maastricht treaty that served as a constitutional basis for the EU
European Union (EU)
Has 28 member countries, 500 million citizens, $18 trillion GDP
- Contributes about 26% of the worlds GDP
- Worlds largest economy
- Largest exporter and importer of goods and services
- Does not have internal trade barriers
- Built a single market in aviation
- EU and its predecessors gave more than 60 years of peace and prosperity
Euro
Currency used in 19 countries
Benefits of Adopting the Euro
1. Reduce currency conversion costs
2. Facilitate direct price comparison
3. Impose monetary discipline on governments
Costs of Adopting the Euro
1. Unable to implement independent monetary policy
2. Limit the flexibility in fiscal policy (in areas such as deficit spending)
Challenges faced by the EU
- Internal divisions
- Enlargement concerns
- Existential crisis
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
FTA among Canada, Mexico, and the United States
Benefits of NAFTA
- Trilateral merchandise trade increased to $1.1 Trillion in 2016
- Increase in U.S. exports to Canada and Mexico
Costs of NAFTA
- Loss of jobs
- Many multinationals shifted work to china
Andean Community and Mercosur
- Customs unions formed in 1969 and 1991, respectively
- Not very effective as the majority of its members' trade is outside the region
Union of South American Nations (USAN)
- Formed in 2008 by integrating Andean community and Mercosur
- Modeled after EU
United States - Dominican Republic - Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA)
- Formed in 2005
- Modeled after NAFTA
- Six CAFTA countries collectively represent the second largest U.S. export market in Latin America
- Central American Countries, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua
Australia-New Zealand Closer Economic Relations Trade Agreement (ANZCERTA or CER)
- Removed tariffs and NTBs
- Allowed citizens of one country to freely work and live in the other country
Association of Southeast Asia Nations (ASEAN)
- Established ASEAN free trade market
- Main trade partners are outside the region
- Launched ASEAN - China free trade agreement (ACFTA) 2010
Asia - Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
Includes ASEAN, CER, NAFTA, Japan, Chile, Peru, Russia
- contributes 46% of world trade
- contributes 54% of world GDP
Trans - Pacific partnership (TPP)
Multilateral free trade agreement being negotiated by 12 Asia Pacific Countries
Management methods for Global and regional economic integration
Focus on regional than global levels
- Most countries within a region share some cultural, economic, and geographical similarities
- Can lower the liability of foreignness when moving within the region
Small and medium-sized enterprise (SME)
Firms with:
- Fewer than 500 employees in the U.S.
- Fewer than 250 employees in the EU
Entreoreneurship
Identification and exploitation of previously unexplored opportunities
Entrepreneurs
Founders and owners of new businesses or managers of existing firms
International Entrepreneurship
Innovative, proactive, and risk-seeking behavior that crosses national borders
- Intended to create wealth in organizations
Institutions and entrepreneurship
Development of entrepreneurship within a country us based on its entrepreneur friendly institutional framework
Informal institutions
Individualistic and low uncertainty avoidance societies encourage entrepreneurship
Resources and entrepreneurship
Value (V), Rarity(R), Imitability(I), Organizational(O)
Characteristics of a growing entrepreneurial firm
growth, innovation, financing, internationalization
Born global firm
Start-up company that attempts to do business abroad from inception
- International transaction costs are high
Reasons:
- Numerous differences in formal institutions and informal institutions
- high potential opportunism