AP Psychology Important Terms
1/452
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
453 Terms
Behavior
everything we do that can be directly observed
Behavioral Approach
an approach to psychology focusing on the scientific study of observable behavioral responses and their environmental determinants
Biological Approach
an approach to psychology focusing on the body, especially the brain and nervous system
Cognitive Approach
an approach to psychology focusing on the mental processes involved in knowing: how we direct our attention, perceive, remember, think, and solve problems
Evolutionary Approach
an approach to psychology focusing on evolutionary ideas such as adaptation, reproduction, and natural selection as the basis for explaining specific human behaviors
Functionalism
James's approach to mental processes, emphasizing the functions and purposes of the mind and behavior in the individual's adaptation to the environment
Humanistic Approach
an approach to psychology focusing on a person's positive qualities, the capacity for positive growth, and the freedom to choose one's destiny
Mental Processes
the thoughts, feelings, and motives that each of us experiences privately but that cannot be observed directly
Natural Selection
Darwin's principle of an evolutionary process in which organisms that are better adapted to their environment will survive and produce more offspring
Psychodynamic Approach
an approach to psychology focusing on unconscious thought, the conflict between biological drives (such as the drive for sex) and society's demands, and early childhood family experiences
Sociocultural Approach
an approach to psychology focusing on the ways in which social and cultural environments influence behavior
Structuralism
Wundt's approach to discovering the basic elements, or structures, of mental processes; so-called because of its focus on identifying the structures of the human mind
Case Study or Case History
an in-depth look at a single individual
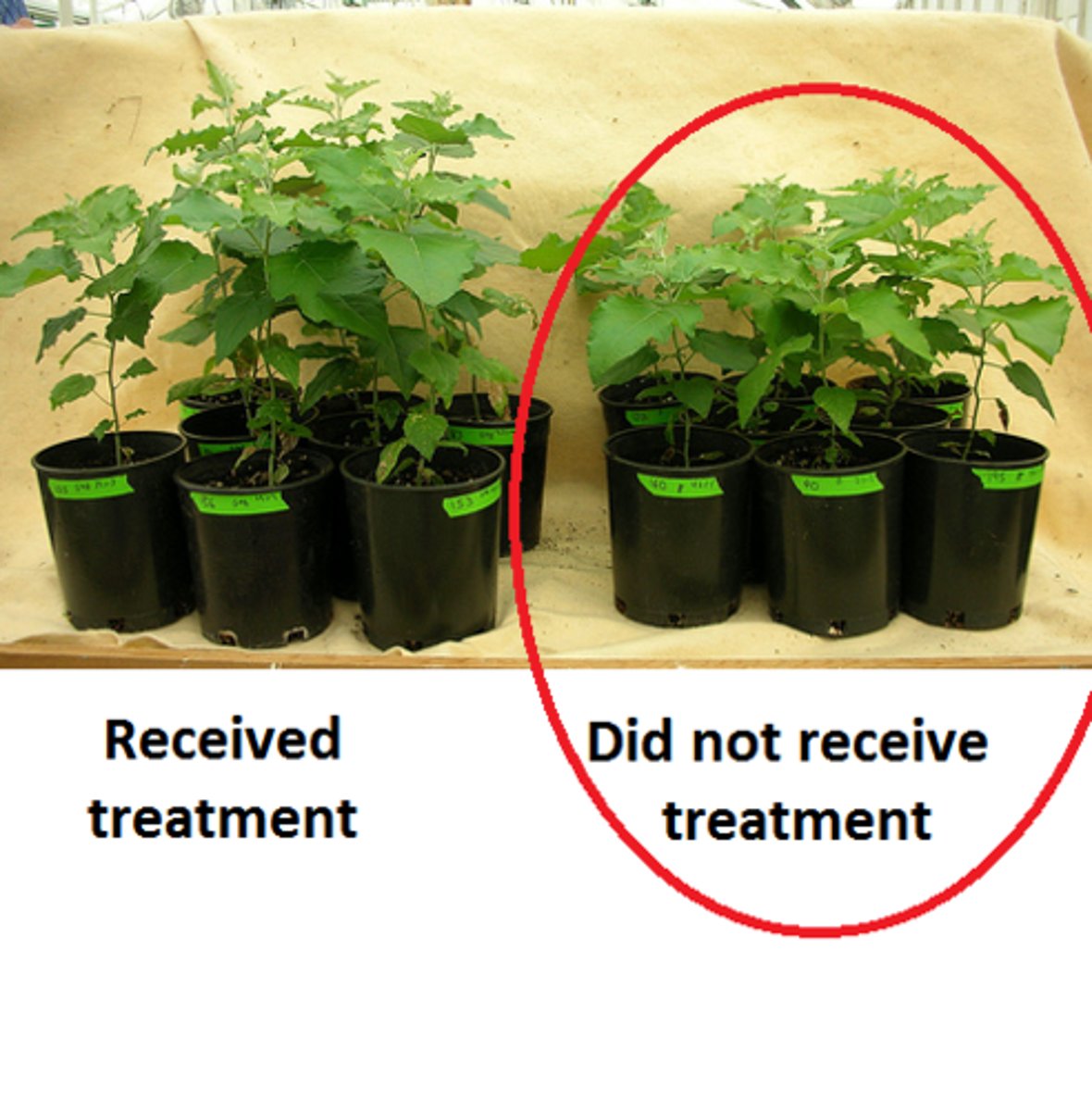
Control Group
the participants in an experiment who are as much like the experimental group as possible and who are treated in every way like the experimental group except for a manipulated factor, the independent variable

Correlational Research
research that examines the relationship between variables with the purpose of determining whether and how two variables change together
Demand Characteristics
any aspect of a study that communicates to the participants how the experimenter wants them to behave
Dependent Variable
the outcome; the variable that may change in an experiment in response to changes in the independent variable
Descriptive Research
research that determines the basic dimensions of a phenomenon—defining what it is, how often it occurs, and so on
Descriptive Statistics
mathematical procedures that are used to describe and summarize sets of data in a meaningful way
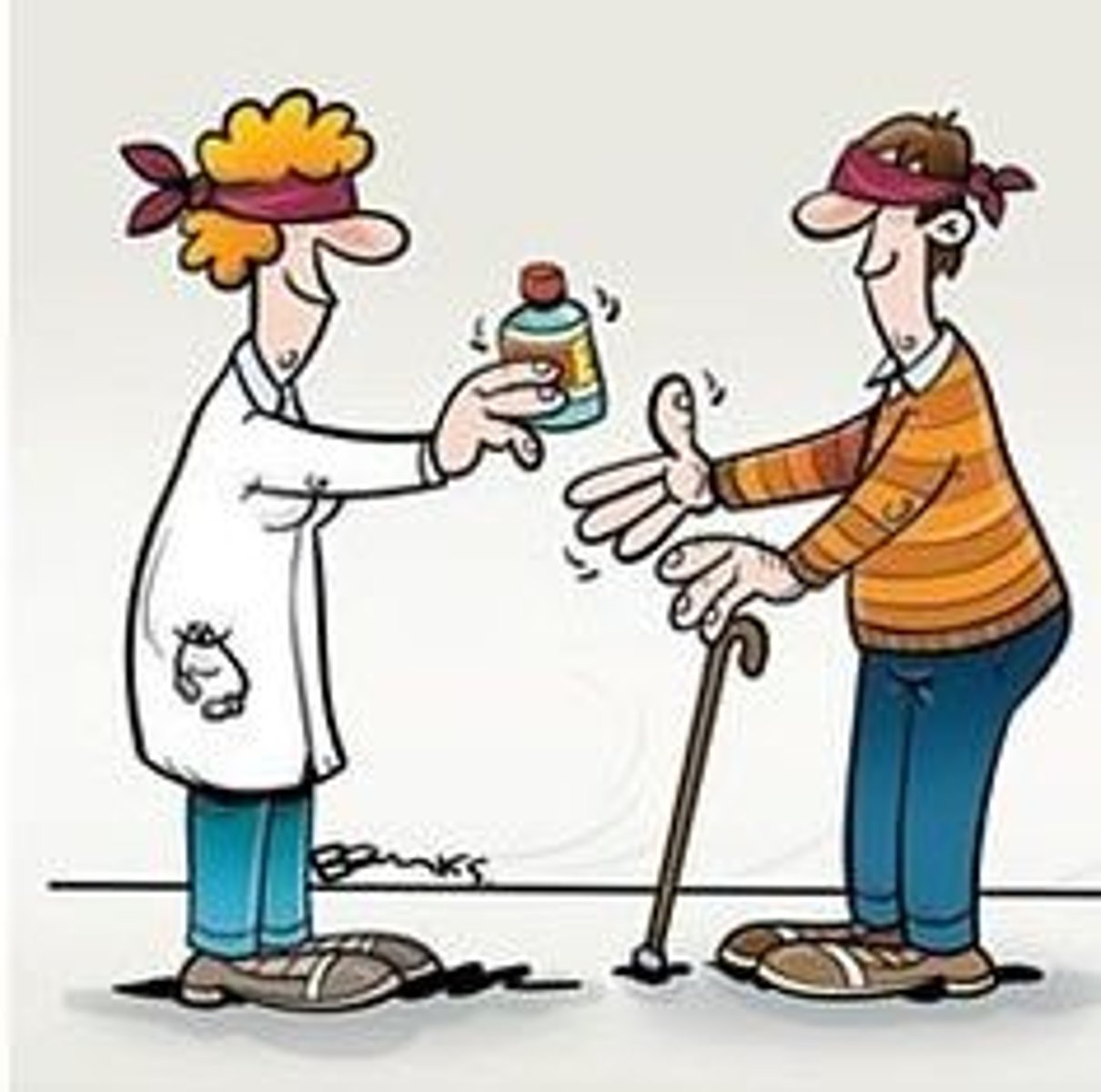
Double-Blind Experiment
an experimental design in which neither the experimenter nor the participants are aware of which participants are in the experimental group and which are in the control group until the results are calculated

Empirical Method
gaining knowledge through the observation of events, the collection of data, and logical reasoning
Experiment
a carefully regulated procedure in which the researcher manipulates one or more variables that is believed to influence some other variable
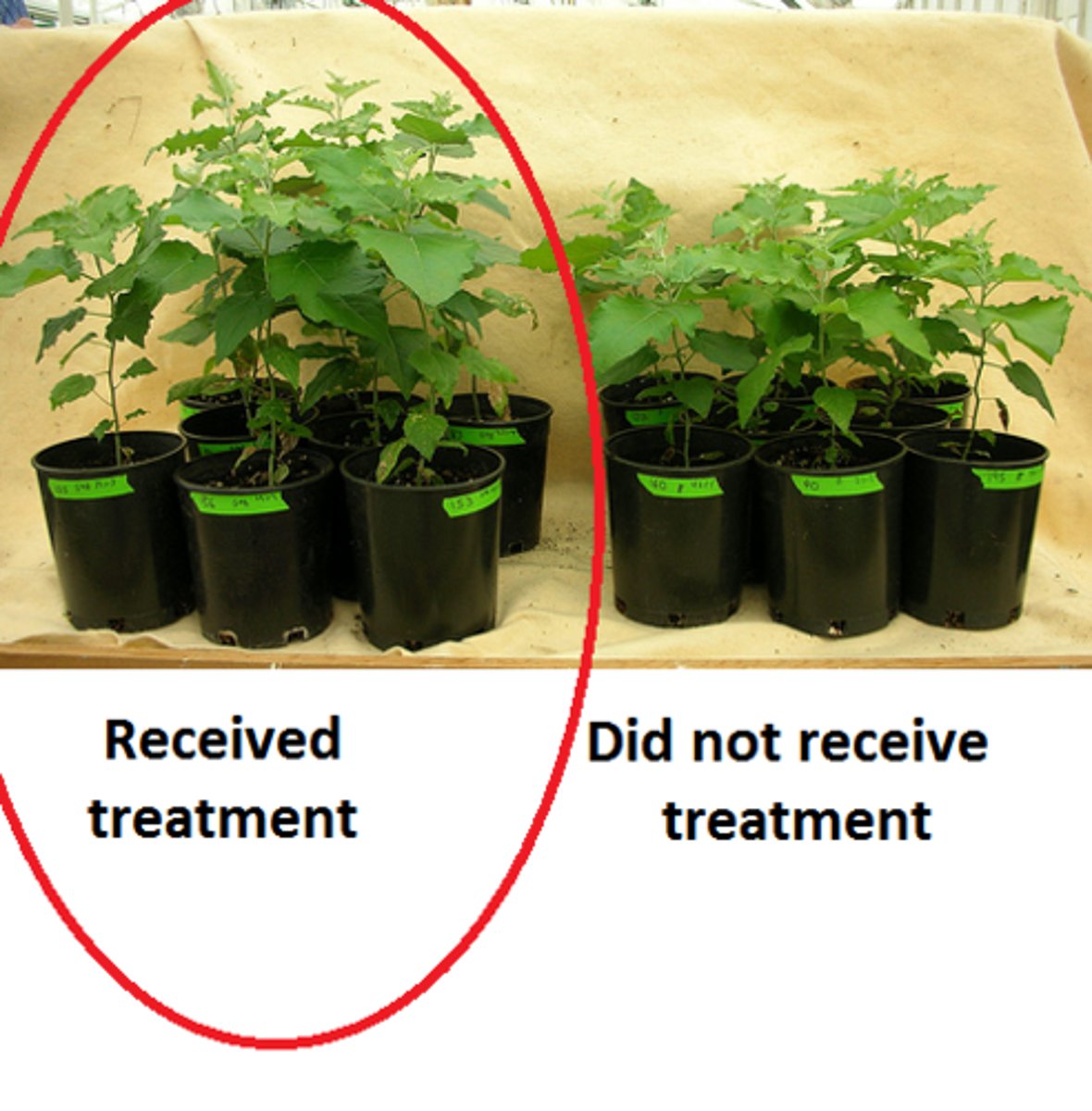
Experimental Group
the participants in an experiment who receive the drug or other treatment under study; those who are exposed to the change that the independent variable represents

Experimenter Bias
the influence of the experimenter's expectations on the outcome of the research
External Validity
the degree to which an experimental design actually reflects the real-world issues it is supposed to address
Hypothesis
an educated guess that derives logically from a theory; a prediction that can be tested
Independent Variable
a manipulated experimental factor; the variable that the experimenter changes to see what its effects are
Inferential Statistics
mathematical methods that are used to indicate whether the data sufficiently support a research hypothesis
Internal Validity
the degree to which changes in the dependent variable are due to the manipulation of the independent variable
Mean
a measure of central tendency that is the average for a sample
Median
a measure of central tendency that is the middle score in a sample
Mode
a measure of central tendency that is the most common score in a sample
Naturalistic Observation
the observation of behavior in a real-world setting
Operational Definition
a definition that provides an objective description of how a variable is going to be measured and observed in a particular study
Placebo
in a drug study, a harmless substance that has no physiological effect, given to participants in a control group so that they are treated identically to the experimental group except for the active agent
Placebo Effect
a phenomenon in which the expectation of the participants, rather than actual treatment, produces an outcome
Population
the entire group about which the investigator wants to draw conclusions
Random Assignment
the assignment of participants to experimental groups by chance, to reduce the likelihood that a study's results will be due to preexisting differences between groups
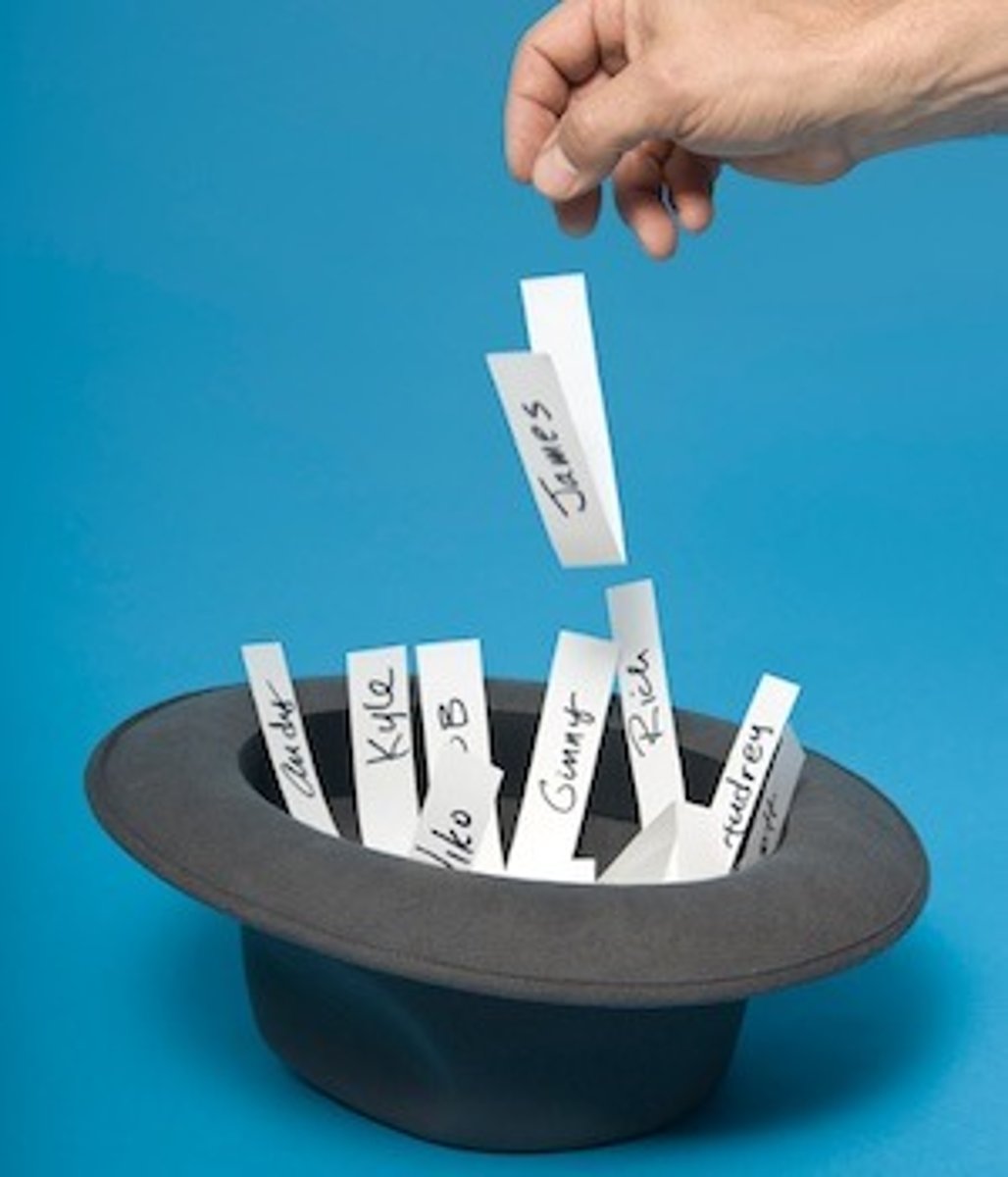

Random Sample
a sample that gives every member of the population an equal chance of being selected
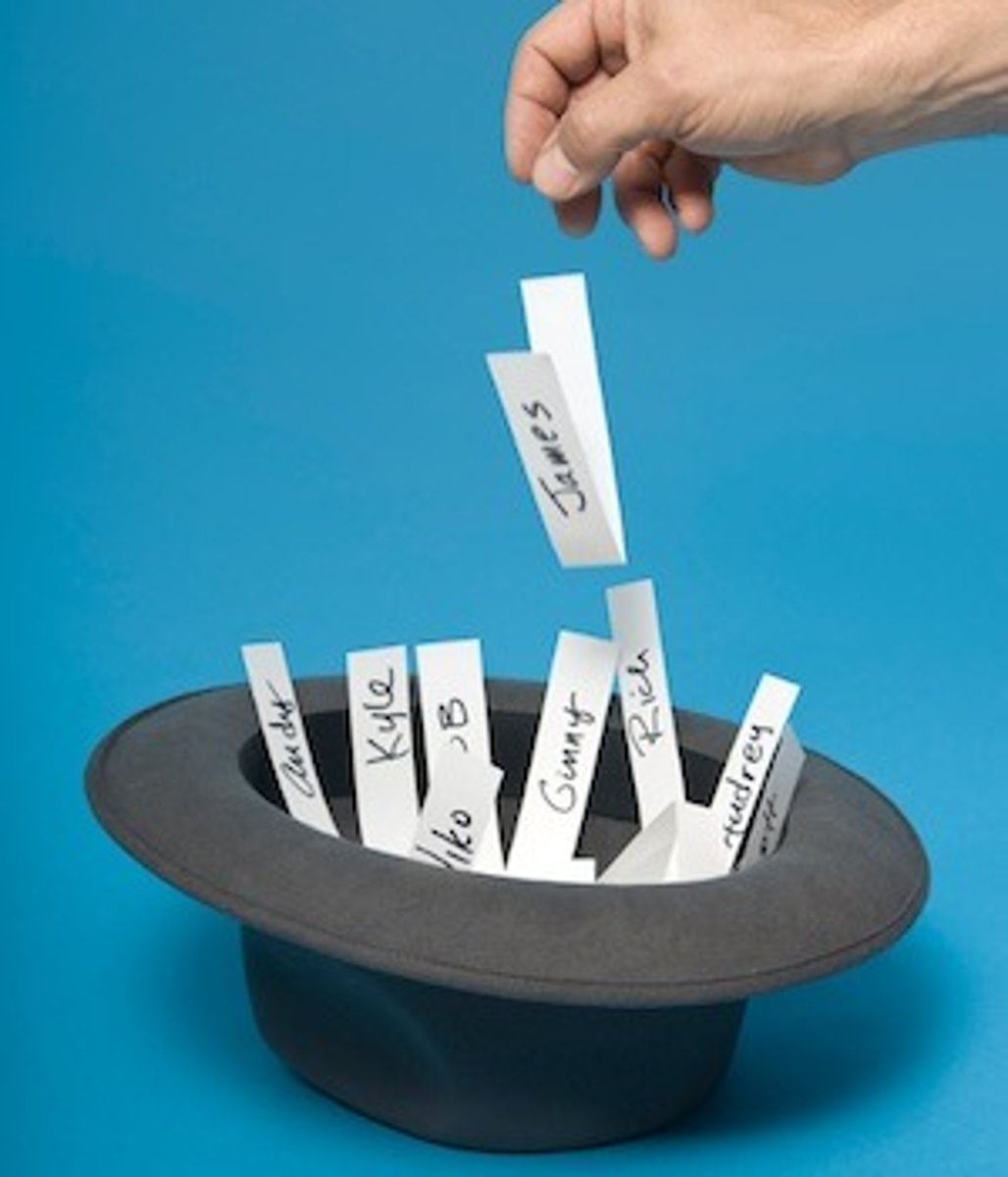

Range
a measure of dispersion that is the difference between the highest and lowest scores
Research Participant Bias
in an experiment, the influence of participants' expectations, and of their thoughts on how they should behave, on their behavior
Sample
the subset of the population chosen by the investigator for study
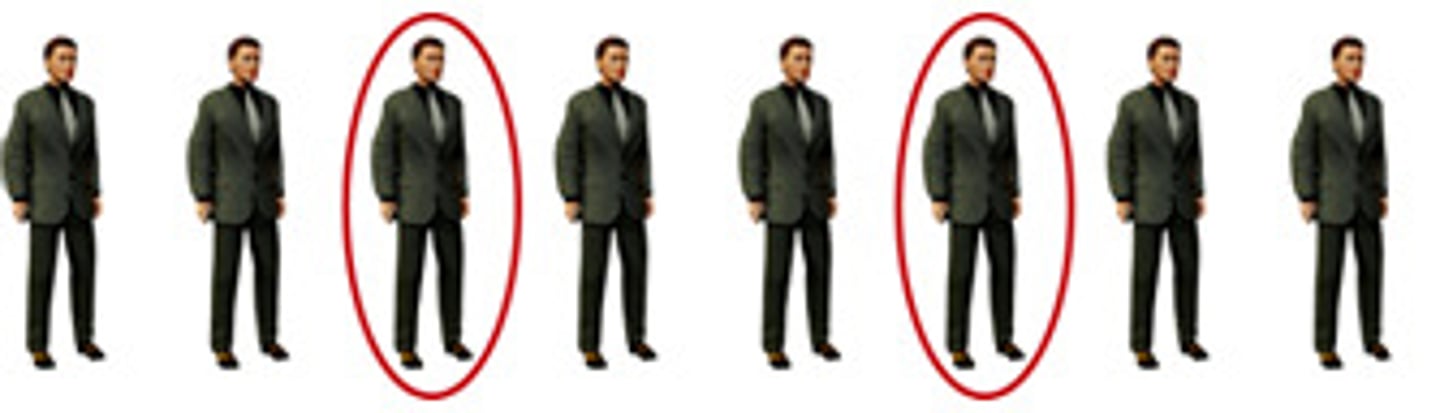

Standard Deviation
a measure of dispersion that indicates how much the scores in a sample differ from the mean in the sample
Theory
a broad idea or set of closely related ideas that attempts to explain observations and to make predictions about future observations
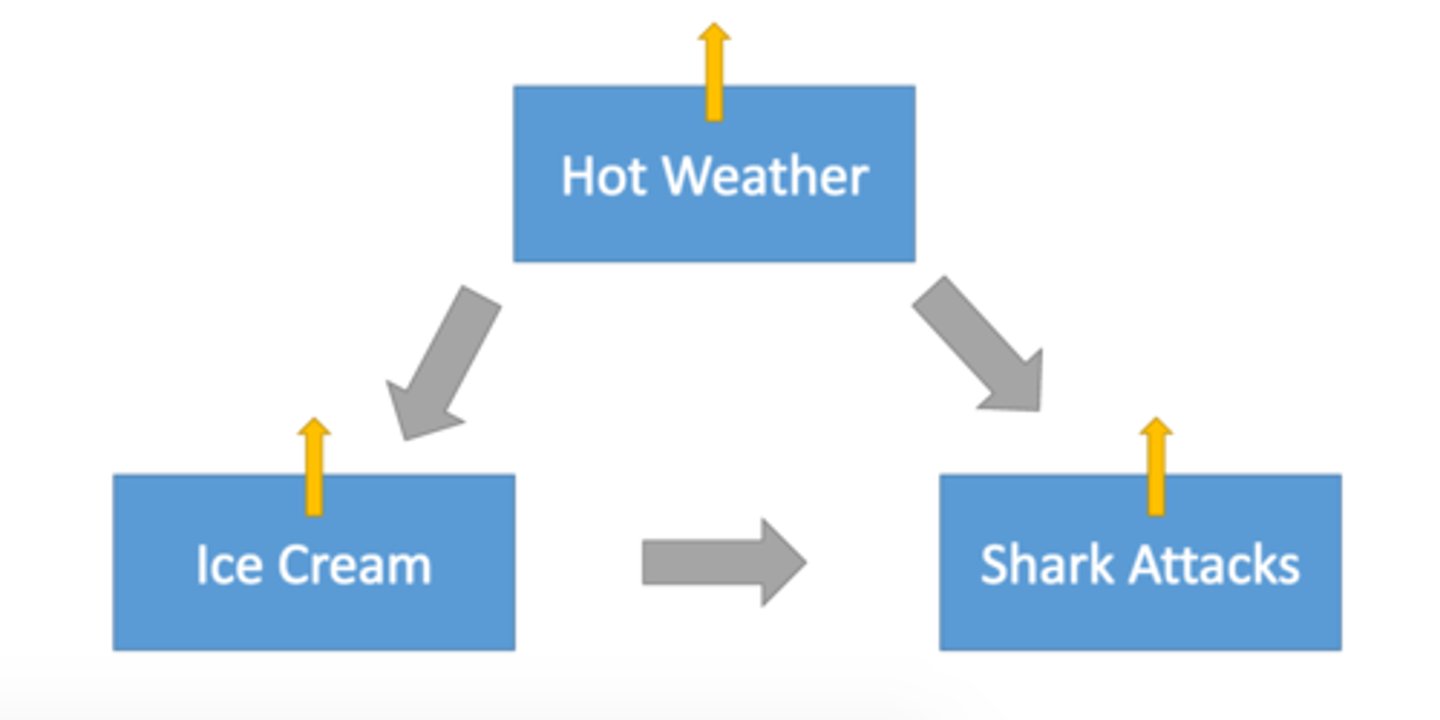
Third Variable Problem
the circumstance in which a variable that has not been measured accounts for the relationship between two other variables. third variables are also known as confounds
Variable
anything that can change.
Action Potential
the brief wave of positive electrical charge that sweeps down the axon
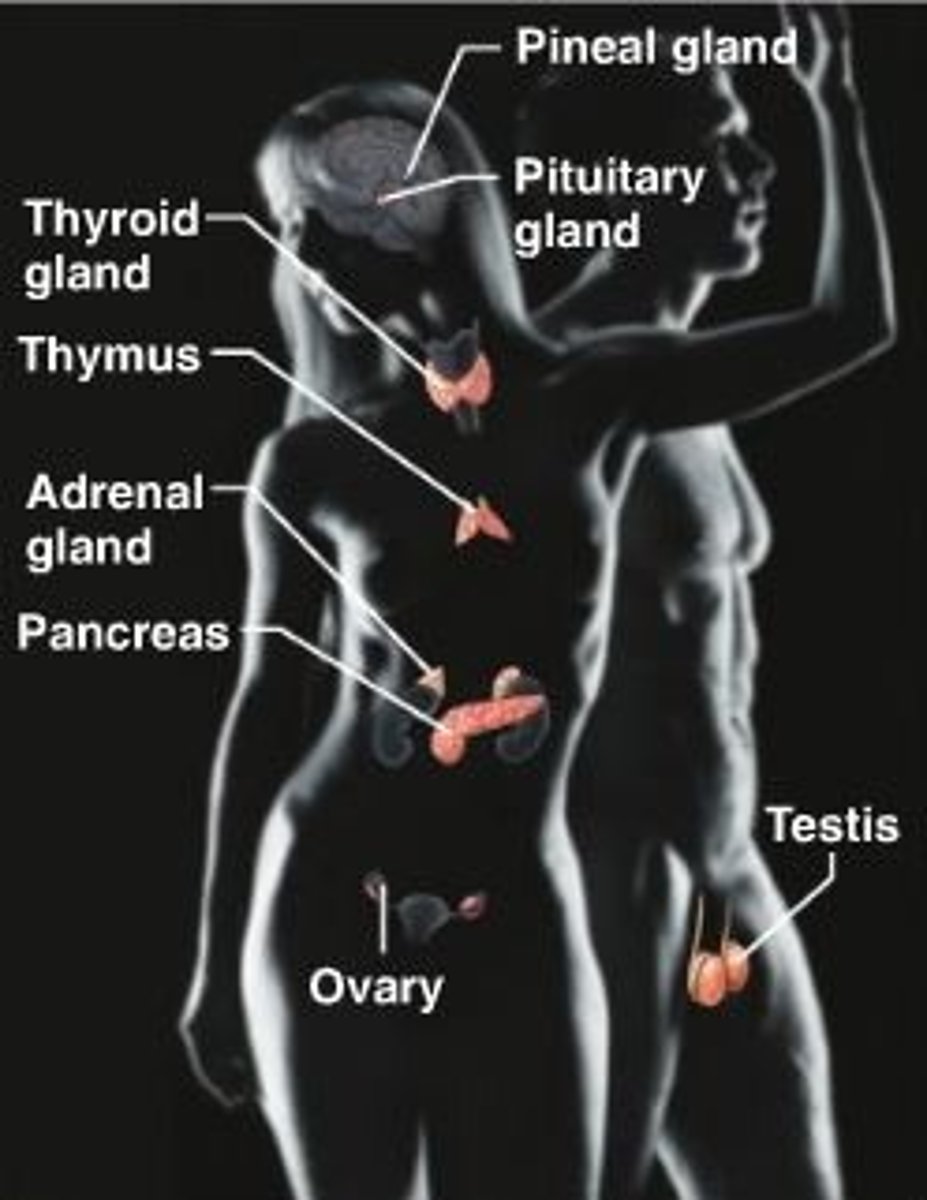
Adrenal Glands
glands at the top of each kidney that are responsible for regulating mood, energy level, and the ability to cope with stress
Afferent (Sensory) Nerves
nerves that carry information about the external environment to the brain and spinal cord via sensory receptors
All-or-Nothing Principle
the principle that once the electrical impulse reaches a certain level of intensity (its threshold), it fires and moves all the way down the axon without losing any intensity

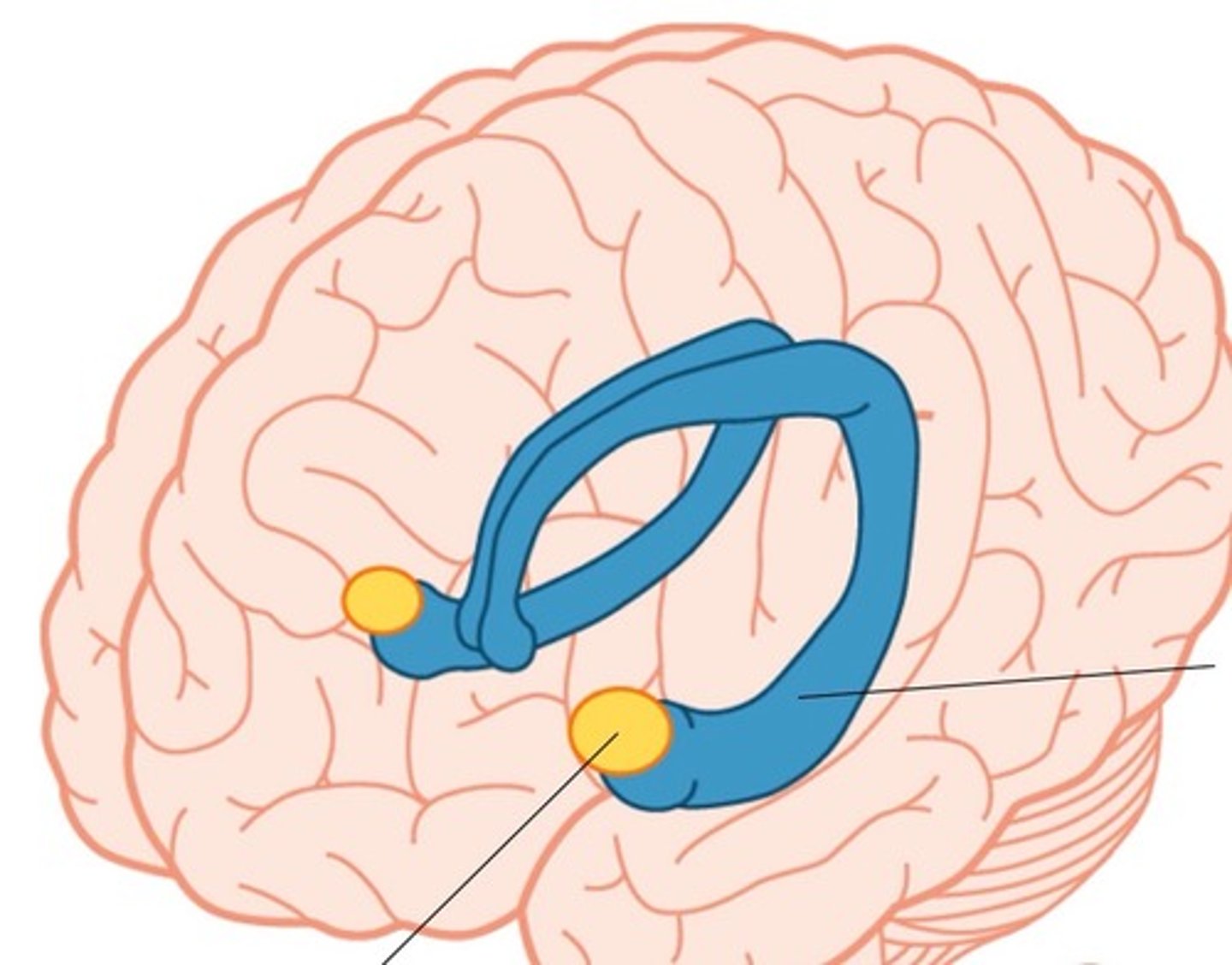
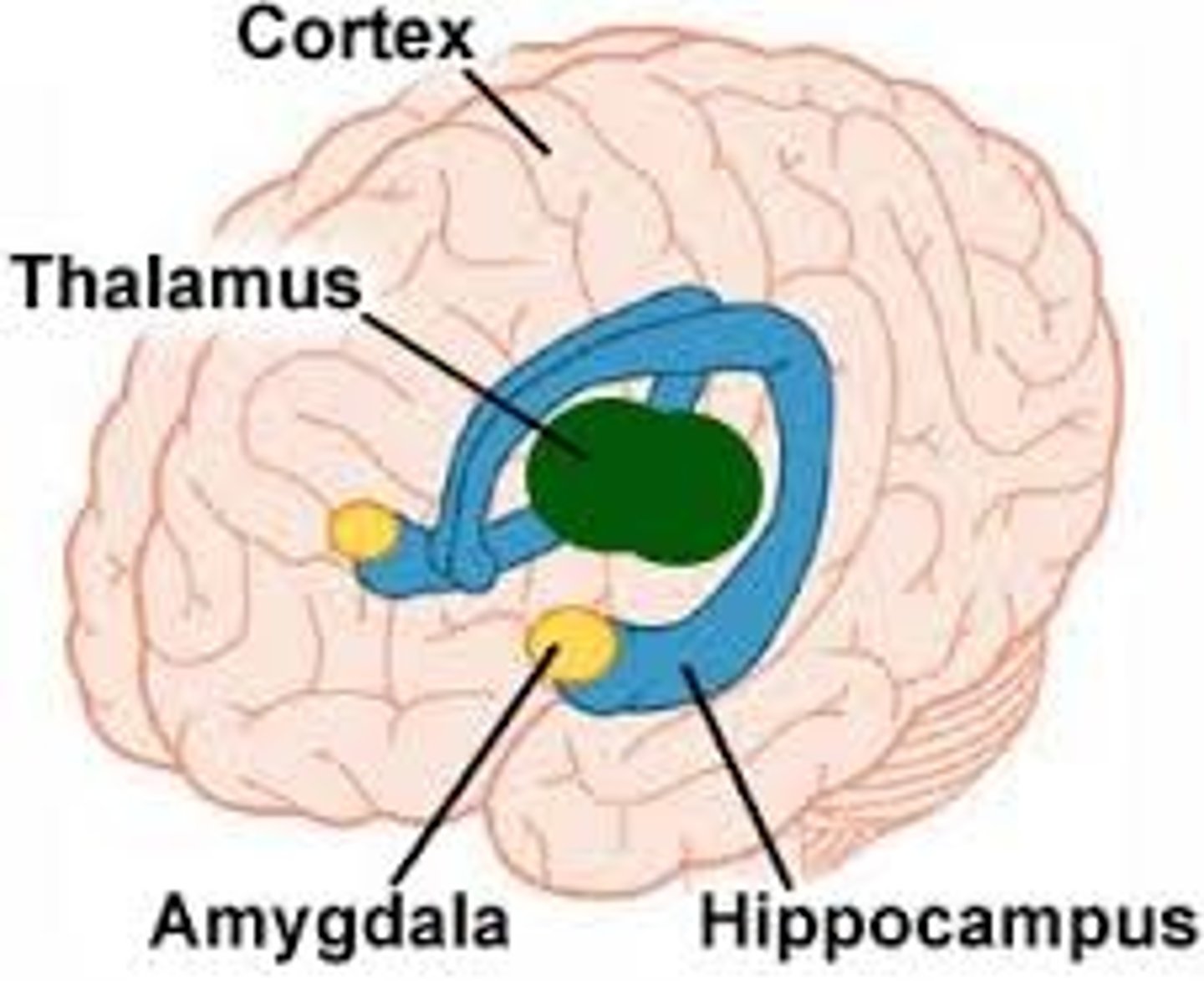
Amygdala
an almond-shaped structure within the base of the temporal lobe that is involved in the discrimination of objects that are necessary for the organism's survival, such as appropriate food, mates, and social rivals. there is one amygdala in each hemisphere of the brain
Association Cortex or Association Area
the region of the cerebral cortex that is the site of the highest intellectual functions, such as thinking and problem solving
Autonomic Nervous System
the body system that takes messages to and from the body's internal organs, monitoring such processes as breathing, heart rate, and digestion
Axon
the part of the neuron that carries information away from the cell body toward other cells
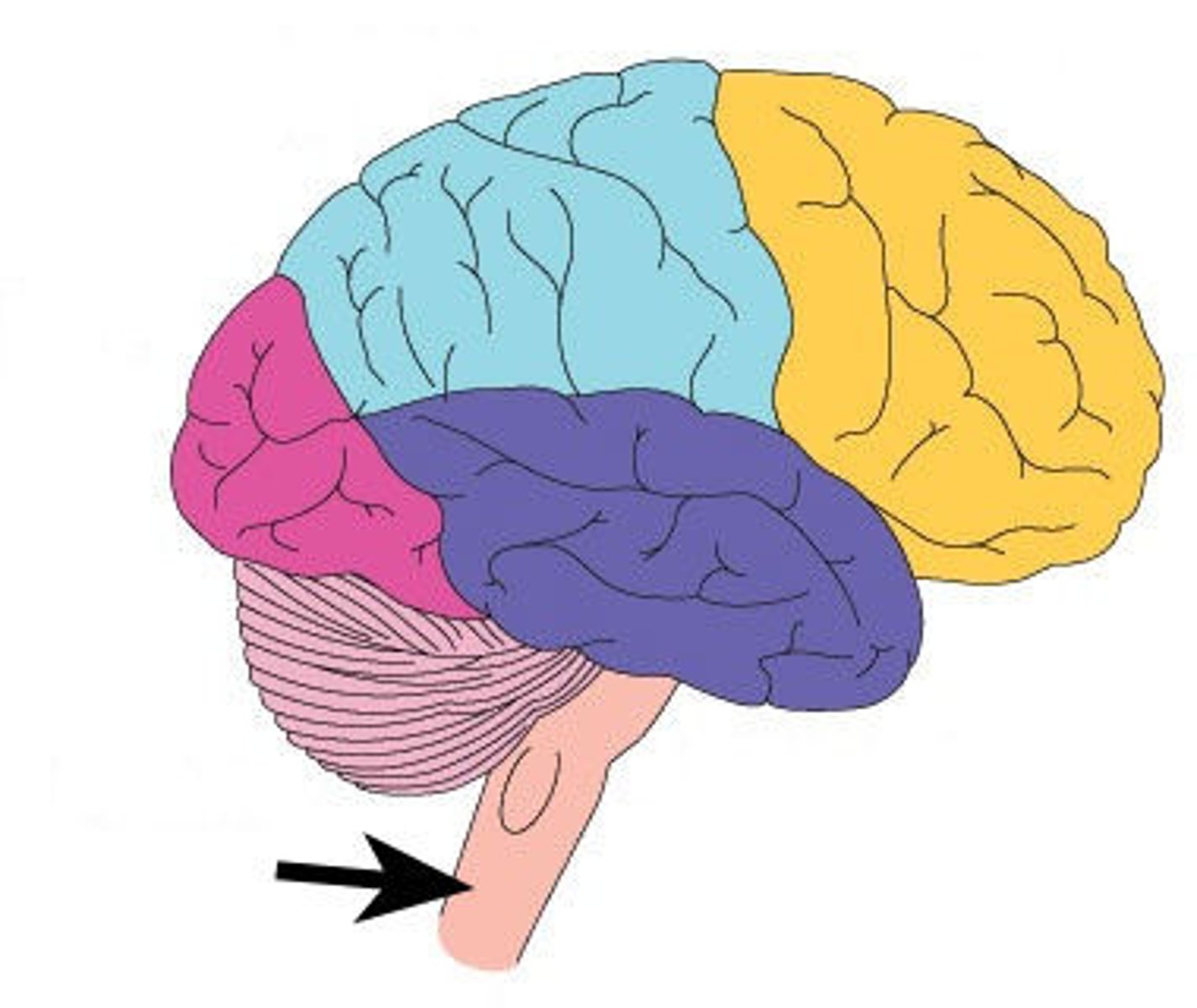
Brain Stem
the stemlike brain area that includes much of the hindbrain (excluding the cerebellum) and the midbrain; it connects with the spinal cord at its lower end and then extends upward to encase the reticular formation in the midbrain
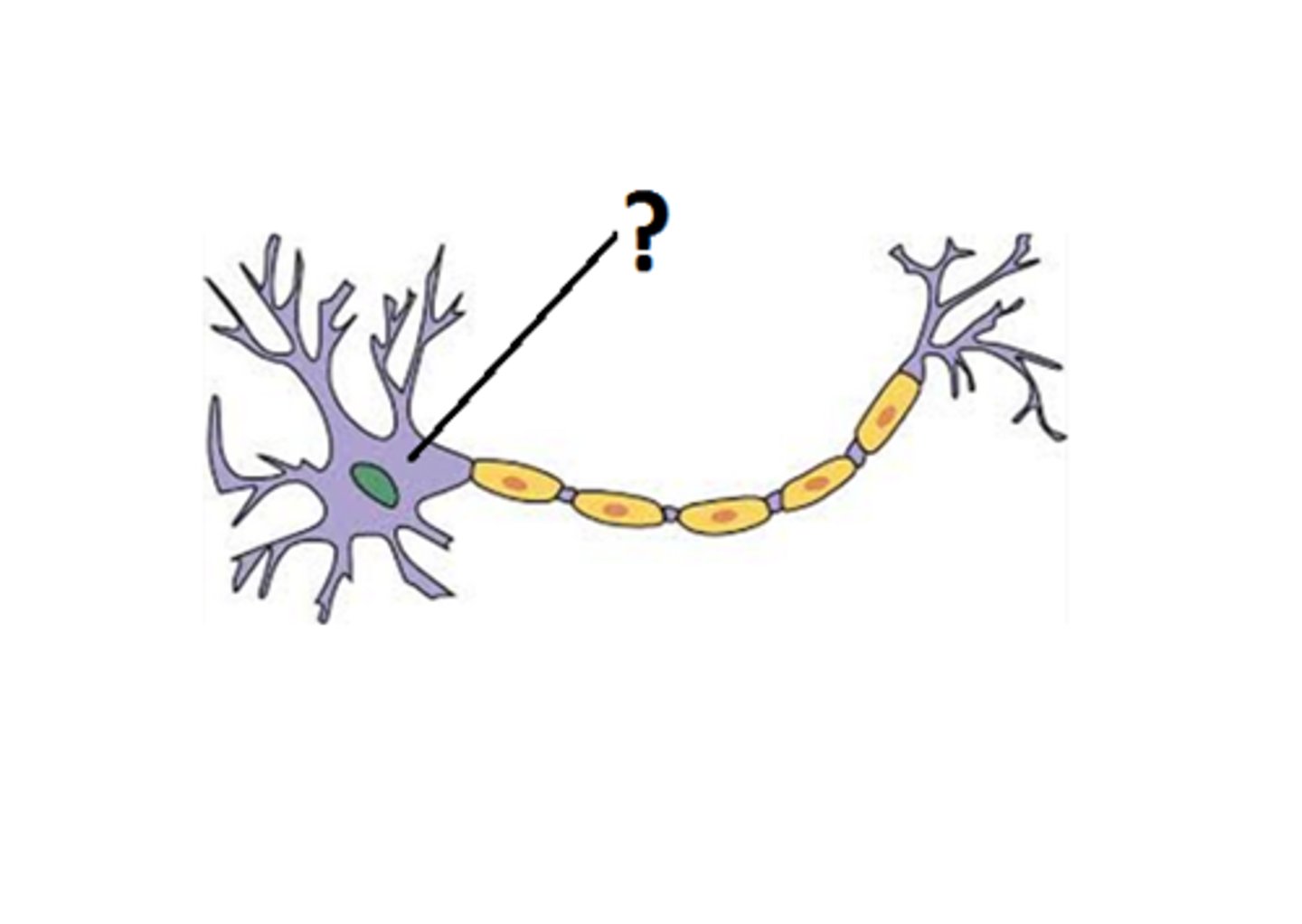
Cell Body (Soma)
the part of the neuron that contains the nucleus, which directs the manufacture of substances that the neuron needs for growth and maintenance
Central Nervous System (CNS)
the brain and spinal cord
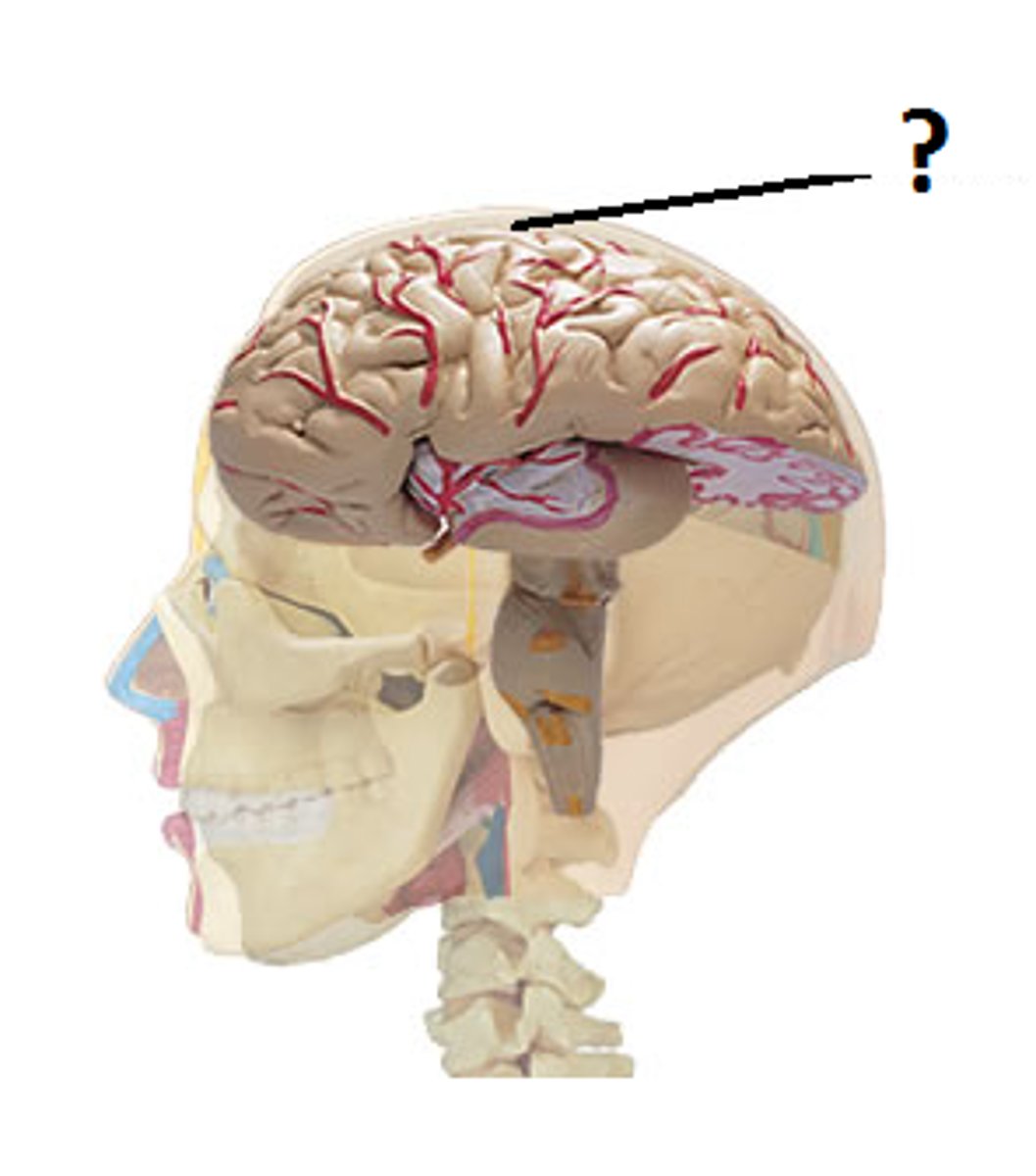
Cerebral Cortex
part of the forebrain, the outer layer of the brain, responsible for the most complex mental functions, such as thinking and planning
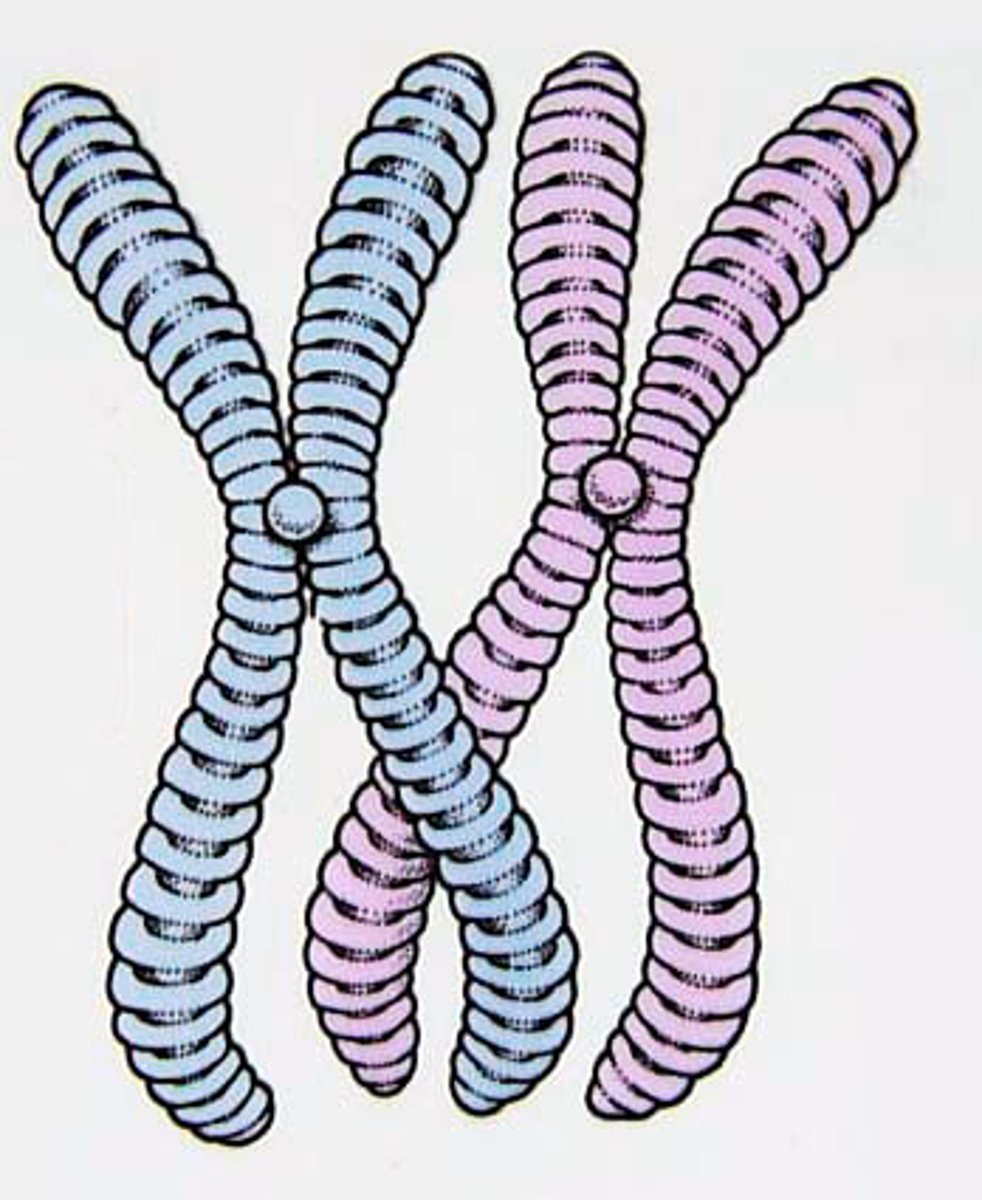
Chromosomes
in the human cell, threadlike structures that come in 23 pairs, one member of each pair originating from each parent, and that contain the remarkable substance DNA
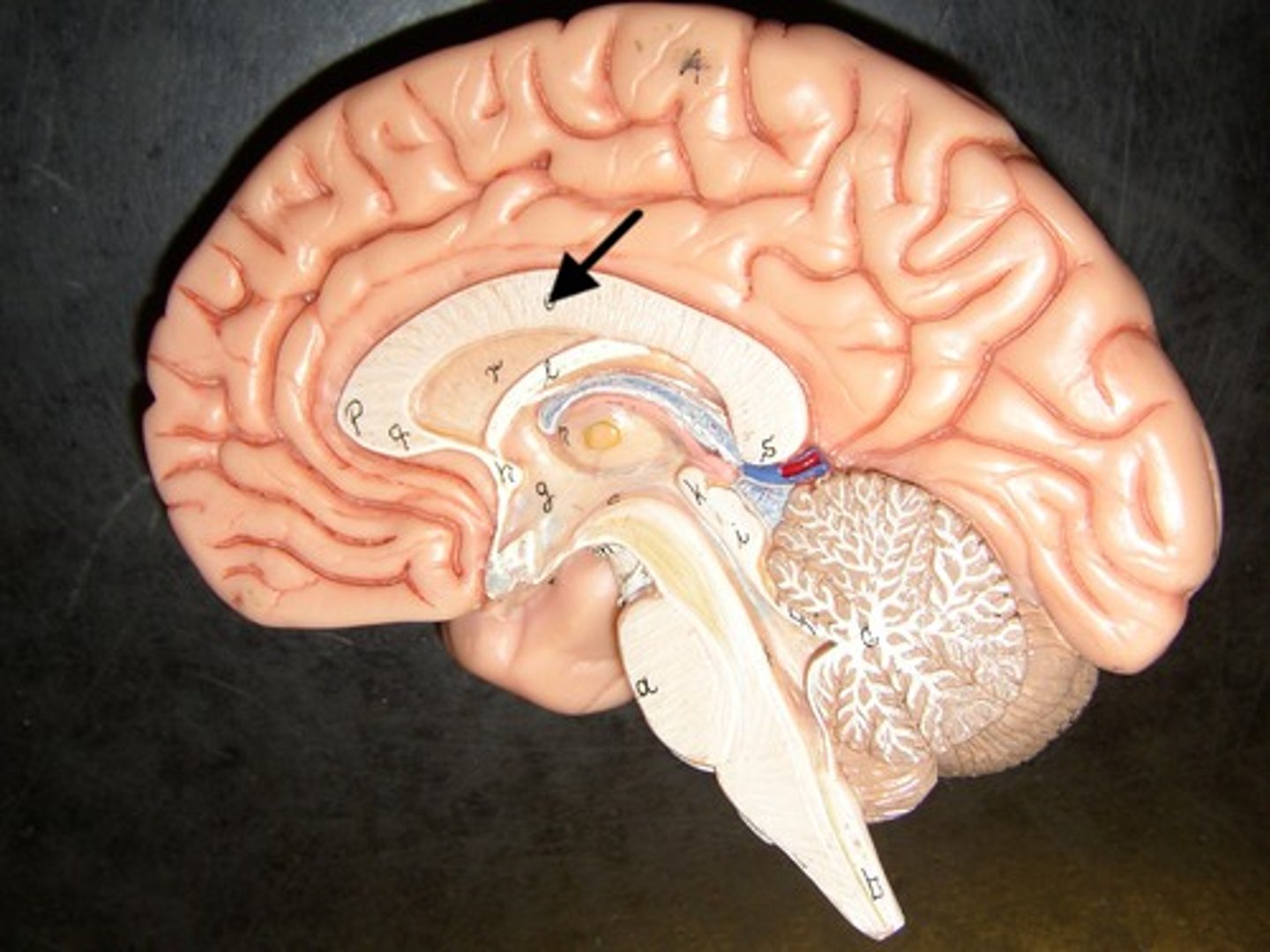
Corpus Callosum
the large bundle of axons that connects the brain's two hemispheres, responsible for relaying information between the two sides
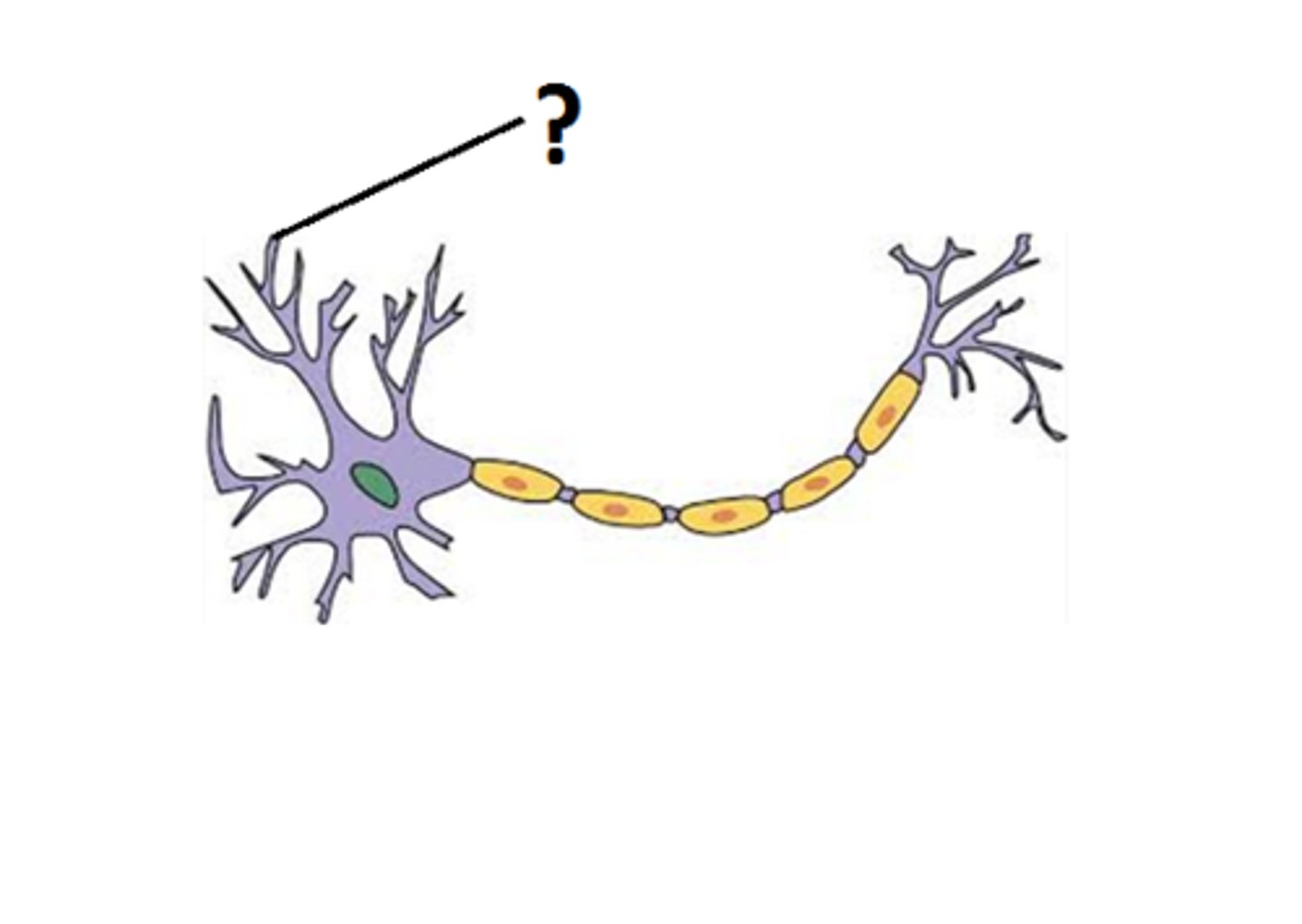
Dendrites
treelike fibers projecting from a neuron, which receive information and orient it toward the neuron's cell body
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
a complex molecule in the cell's chromosomes that carries genetic information

Dominant-Recessive Genes Principle
the principle that, if one gene of a pair is dominant and one is recessive, the dominant gene overrides the recessive gene. A recessive gene exerts its influence only if both genes of a pair are recessive
Efferent (Motor) Nerves
nerves that carry information out of the brain and spinal cord to other areas of the body
Endocrine System
the body system consisting of a set of glands that regulate the activities of certain organs by releasing their chemical products into the bloodstream
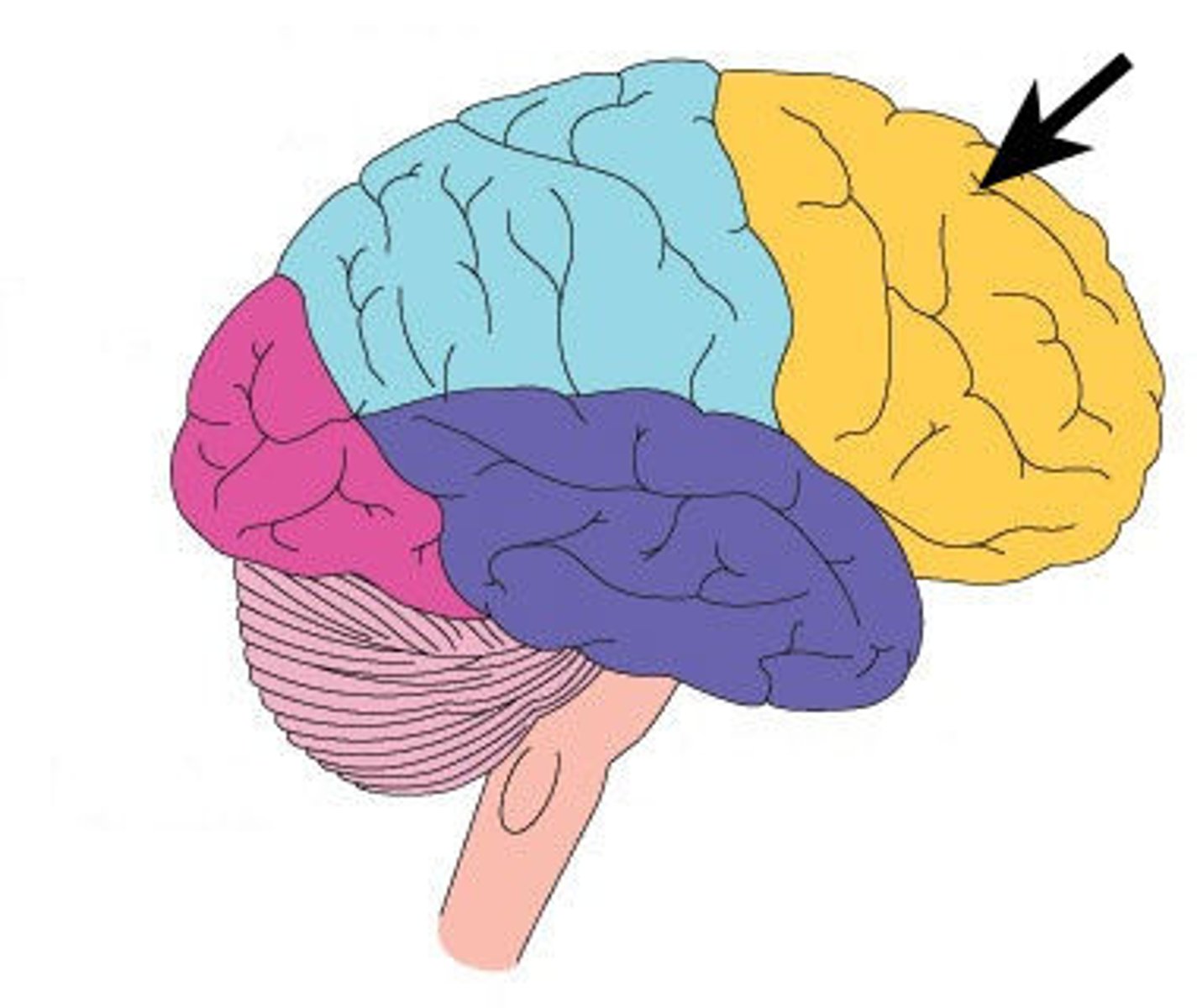
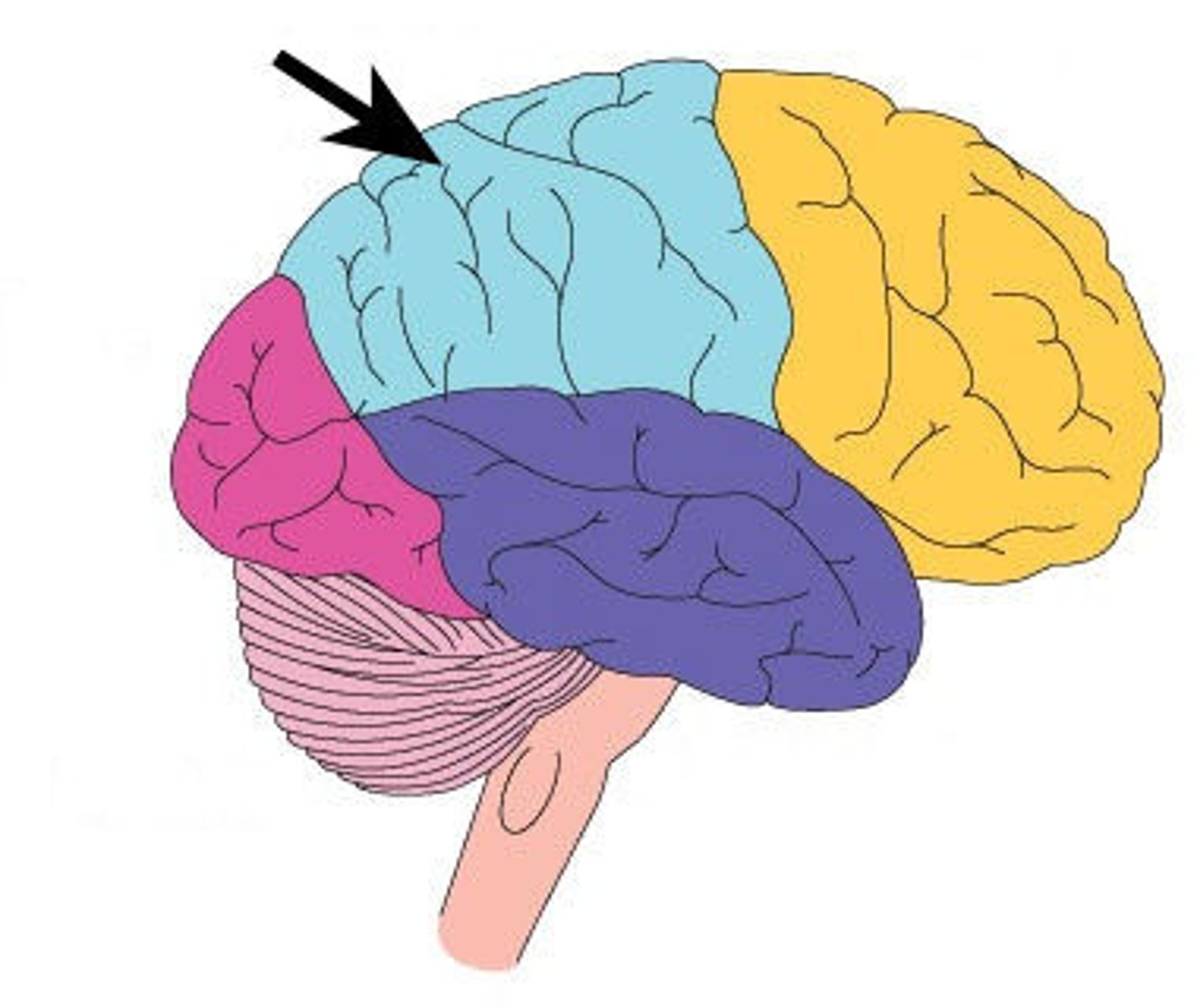
Frontal Lobe
the portions of the cerebral cortex behind the forehead that are involved in personality, intelligence, and the control of voluntary muscles
Genes
the units of hereditary information, consisting of short segments of chromosomes composed of DNA
Genotype
an individual's genetic heritage; one's actual genetic material
Glands
organs or tissues in the body that create chemicals that control many bodily functions
Glial Cells (Glia)
the second of two types of cells in the nervous system; glial cells provide support, nutritional benefits, and other functions and keep neurons running smoothly
Hippocampus
the structure in the limbic system that has a special role in the storage of memories
Hormones
chemical messengers that are produced by the endocrine glands and carried by the bloodstream to all parts of the body
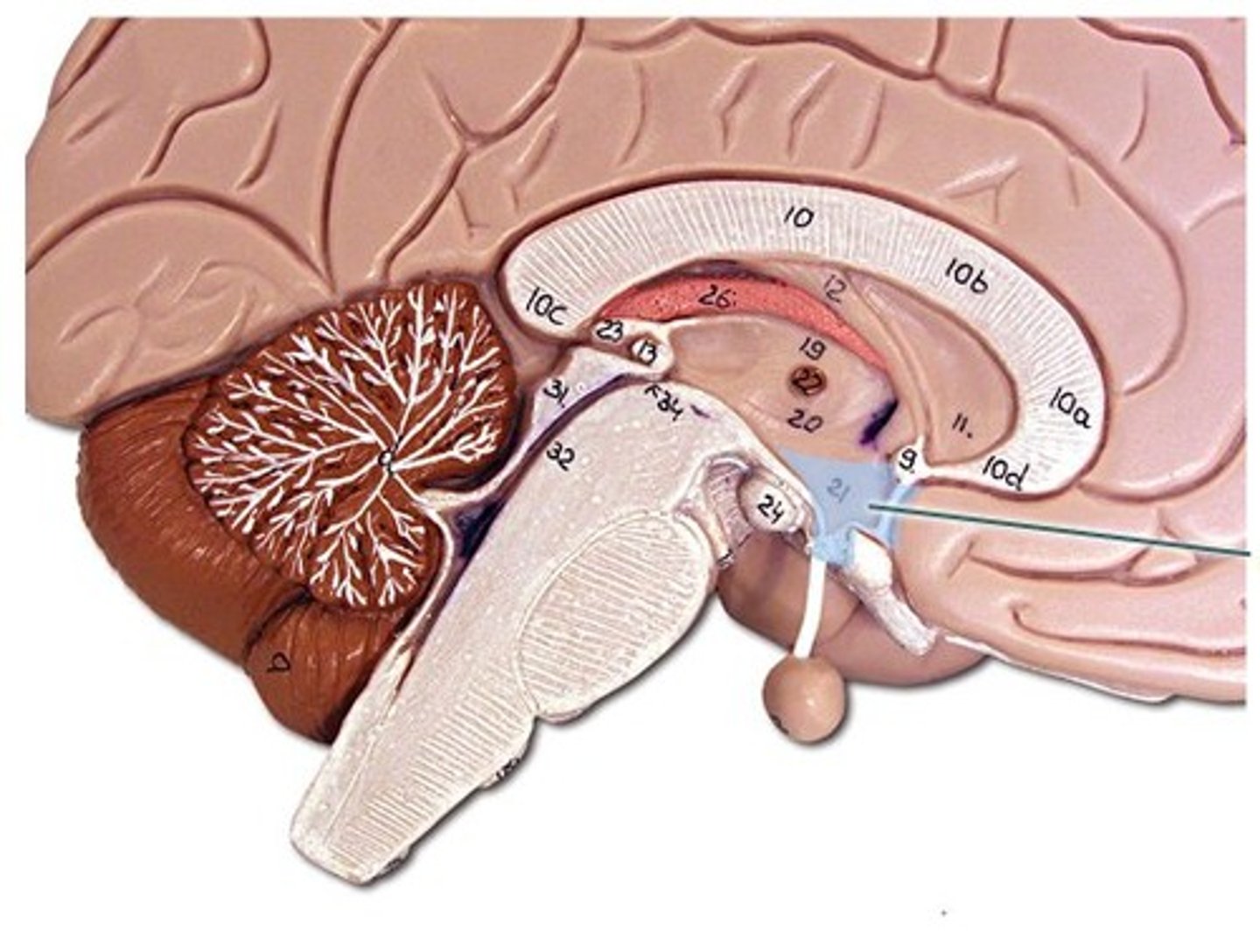
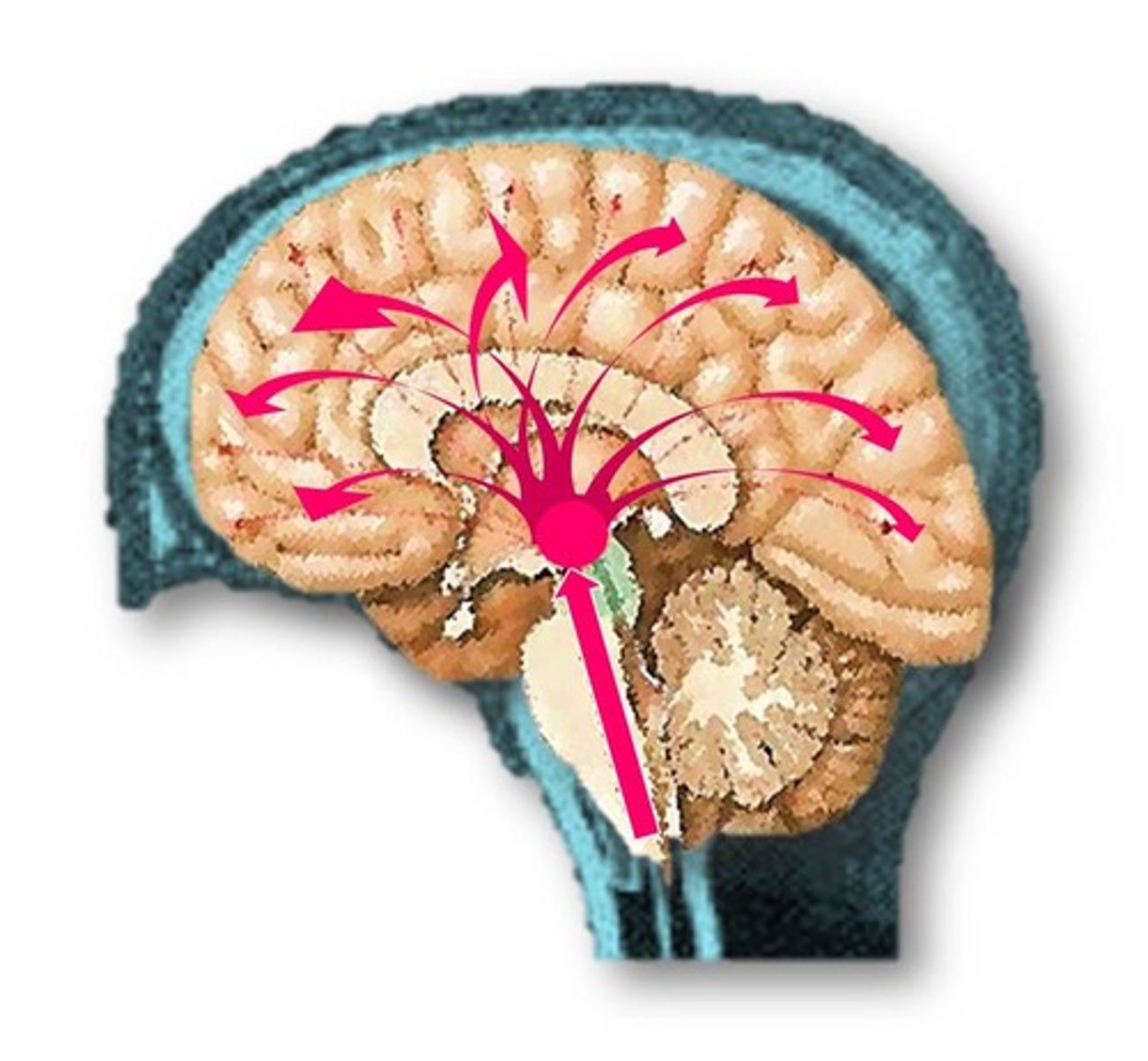
Hypothalamus
a small forebrain structure, located just below the thalamus, that monitors three pleasurable activities—eating, drinking, and sex—as well as emotion, stress, and reward
Limbic System
a loosely connected network of structures under the cerebral cortex, important in both memory and emotion. Its two principal structures are the amygdala and the hippocampus
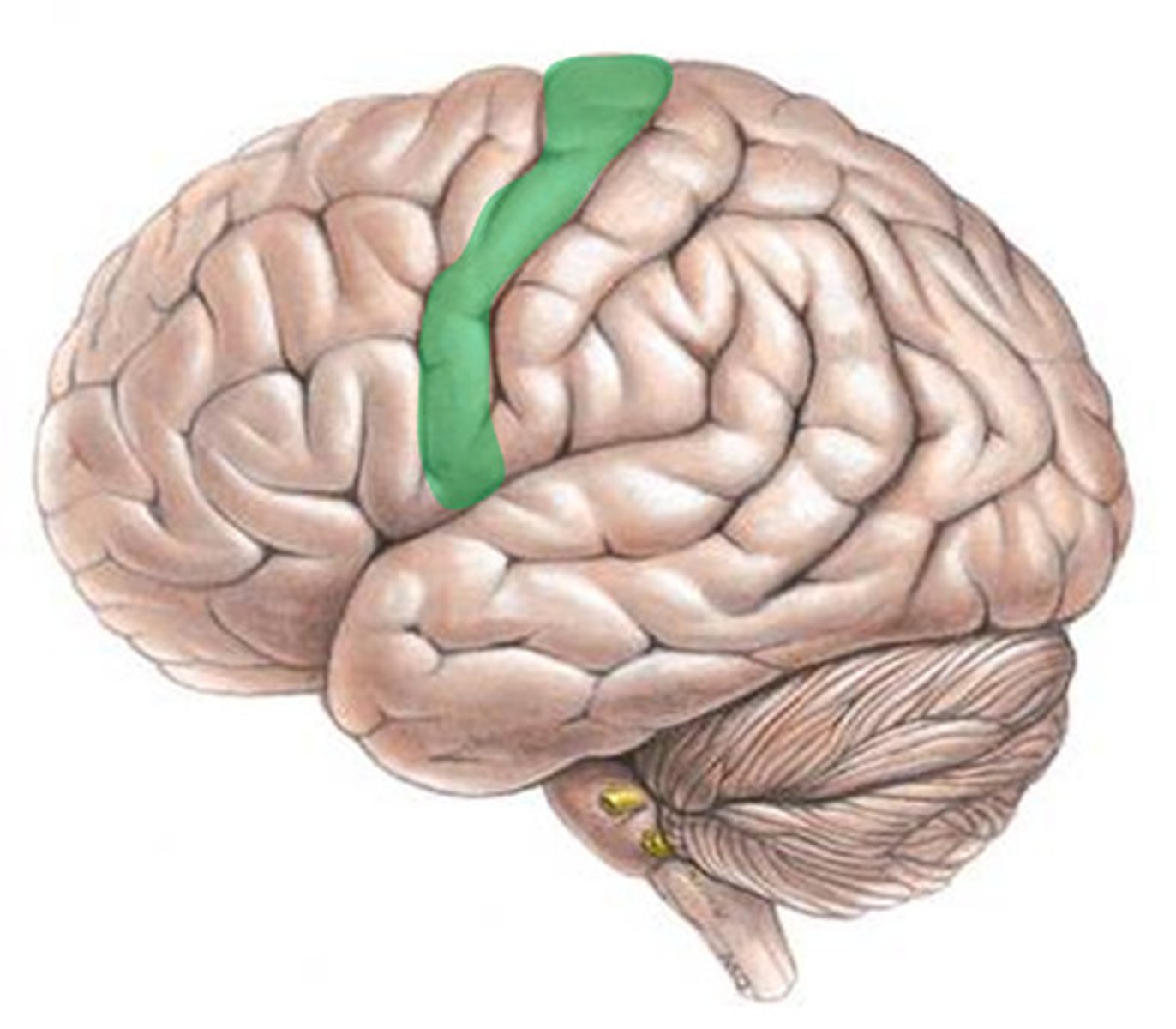
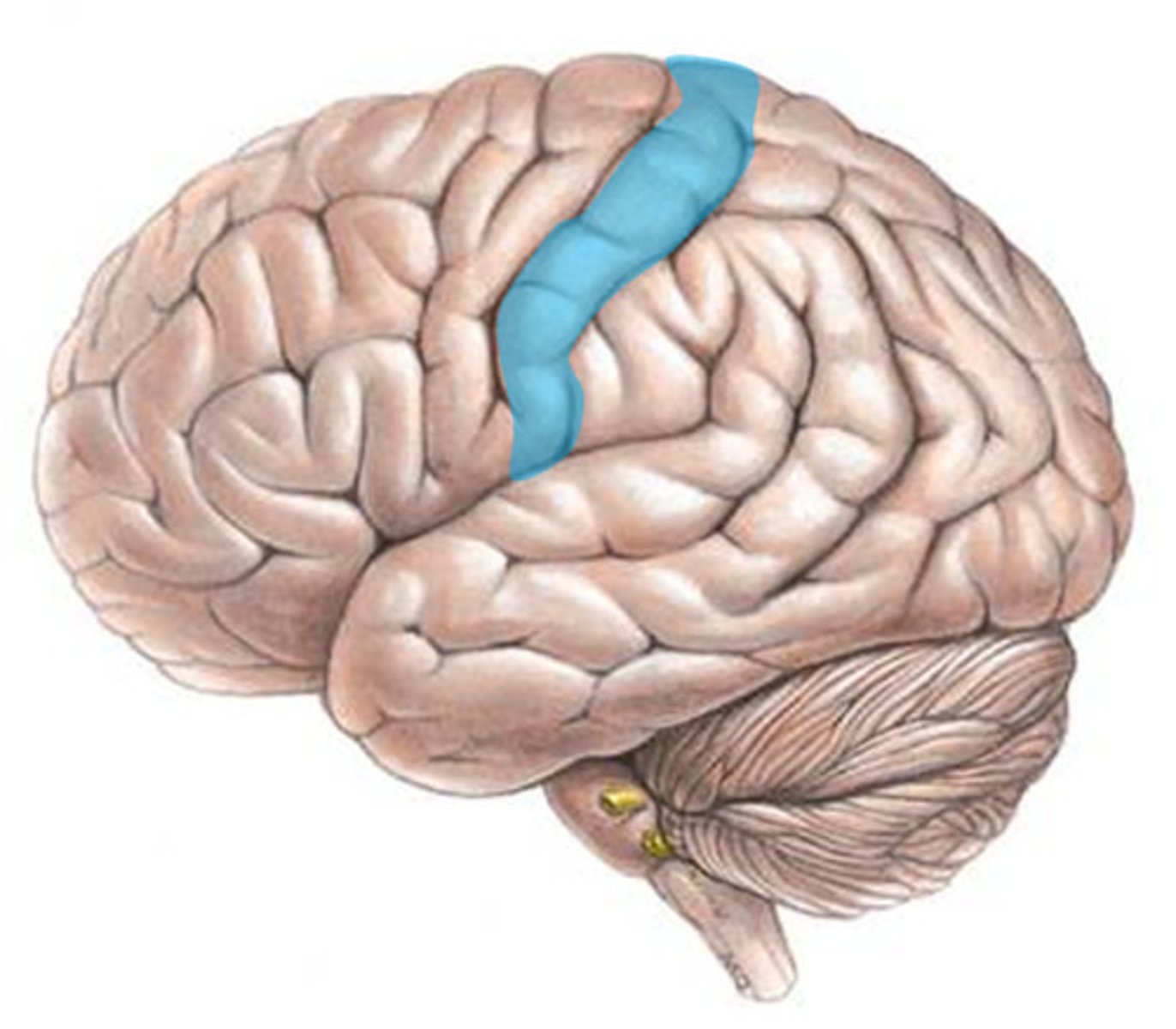
Motor Cortex
a region in the cerebral cortex that processes information about voluntary movement, located just behind the frontal lobes
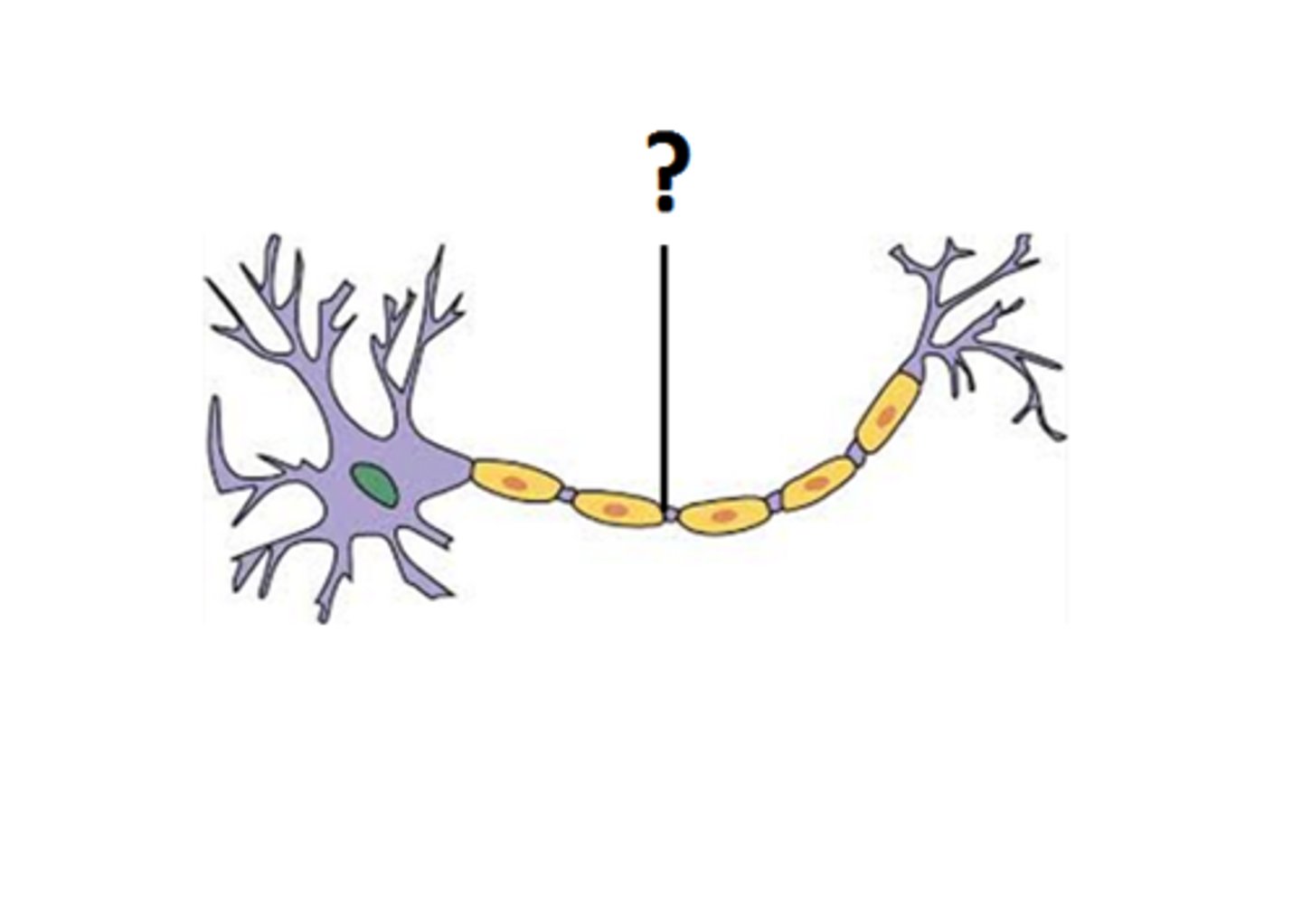
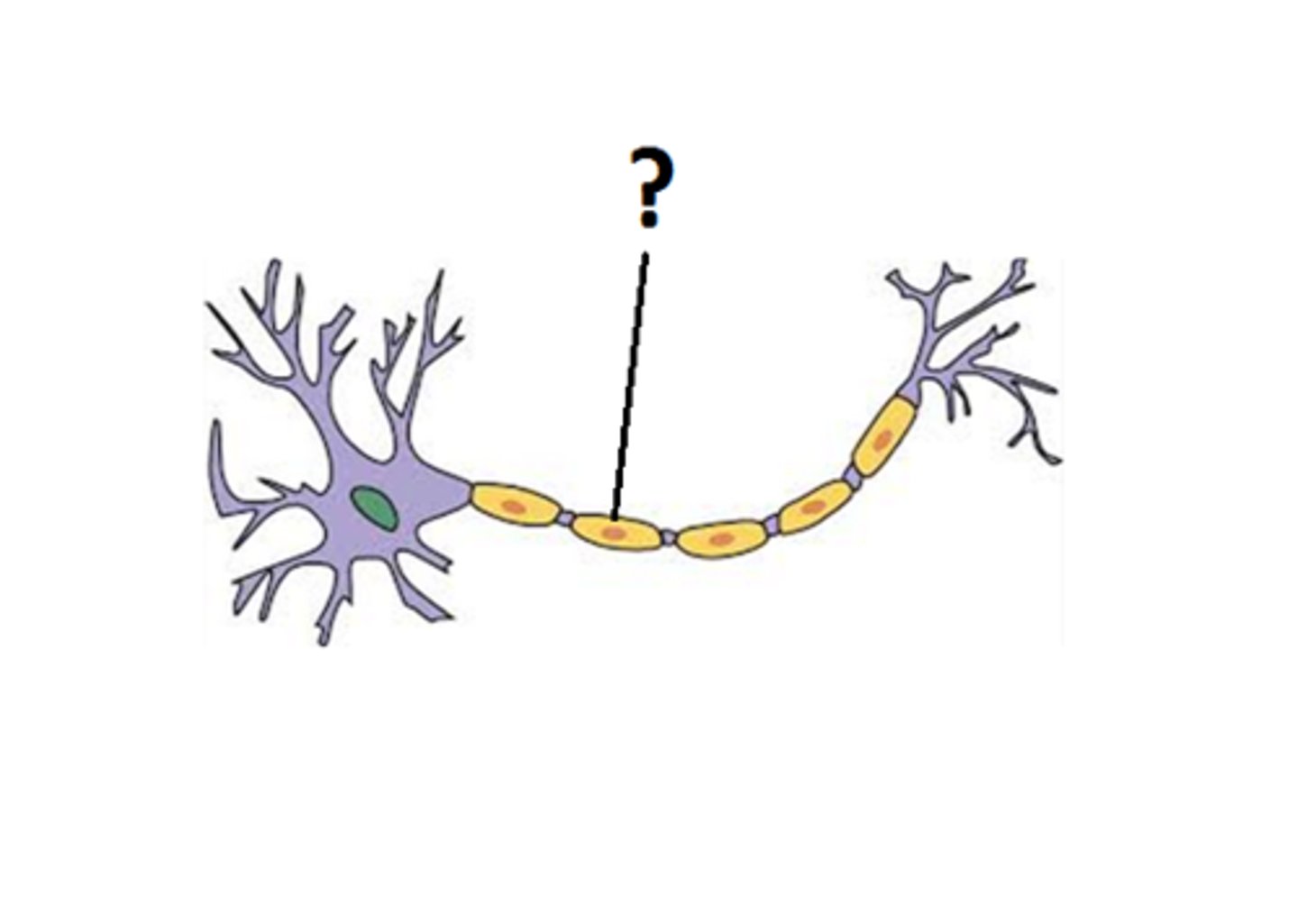
Myelin Sheath
a layer of fat cells that encases and insulates most axons
Nervous System
the body's electrochemical communication circuitry
Neural Networks
networks of nerve cells that integrate sensory input and motor output
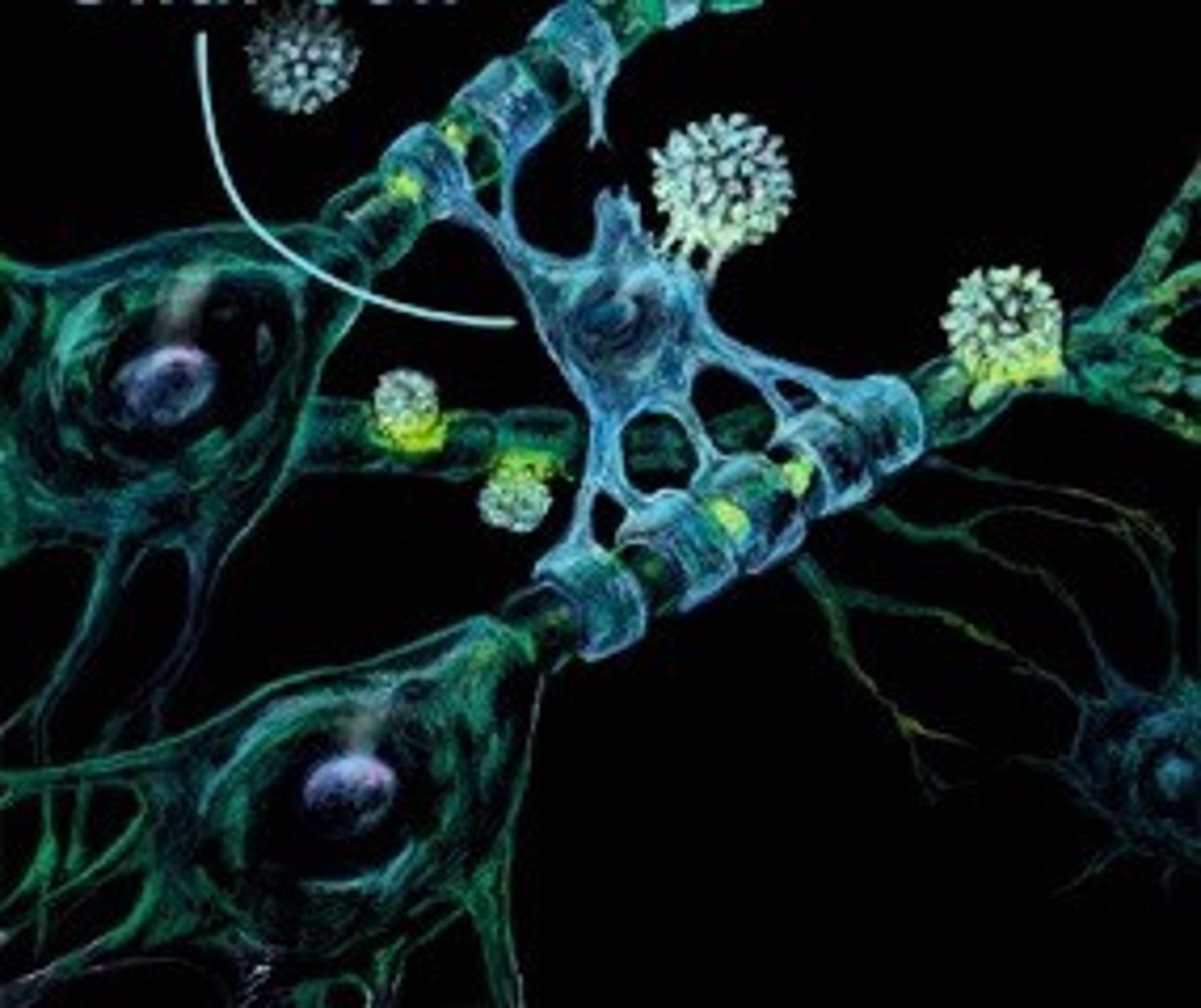
Neurons
one of two types of cells in the nervous system; neurons are the type of nerve cell that handles the information-processing function
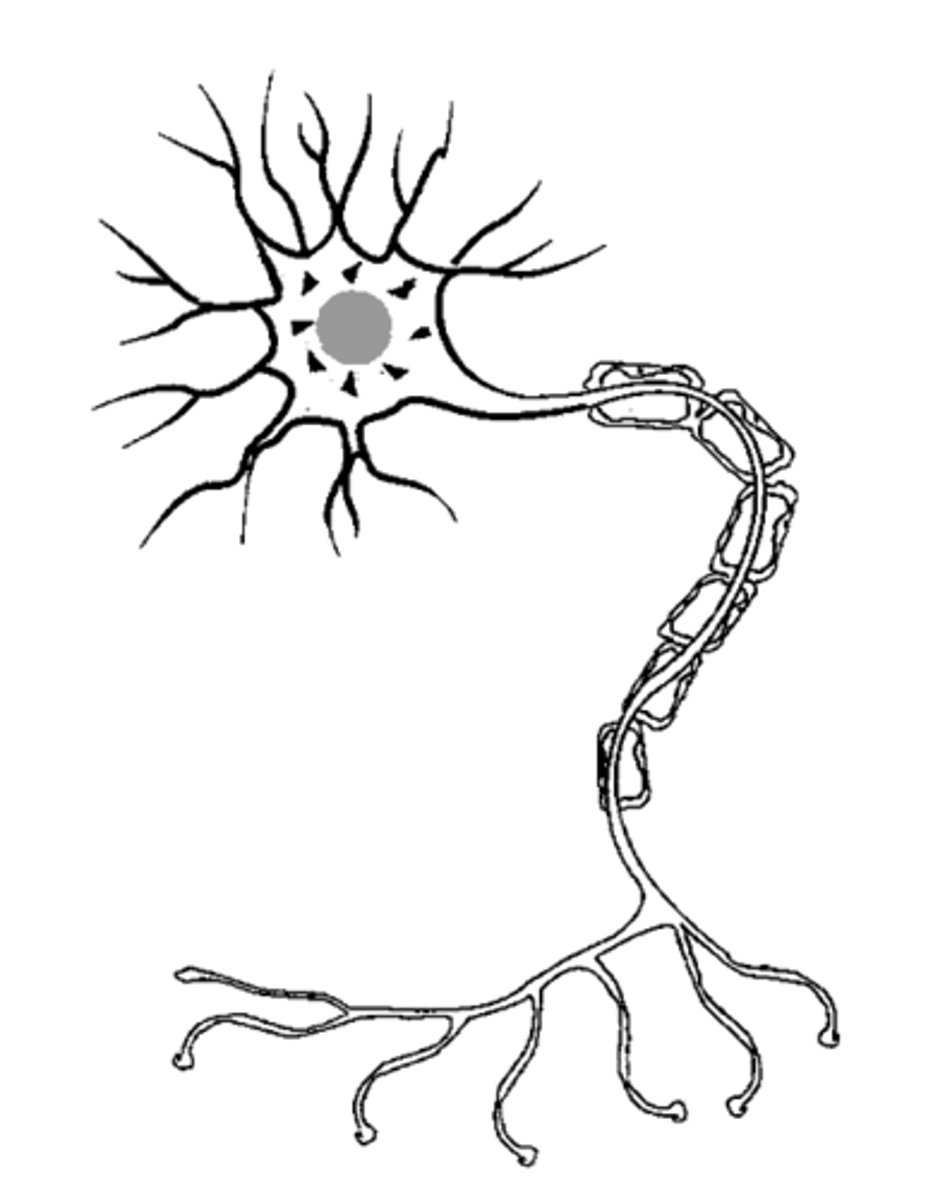
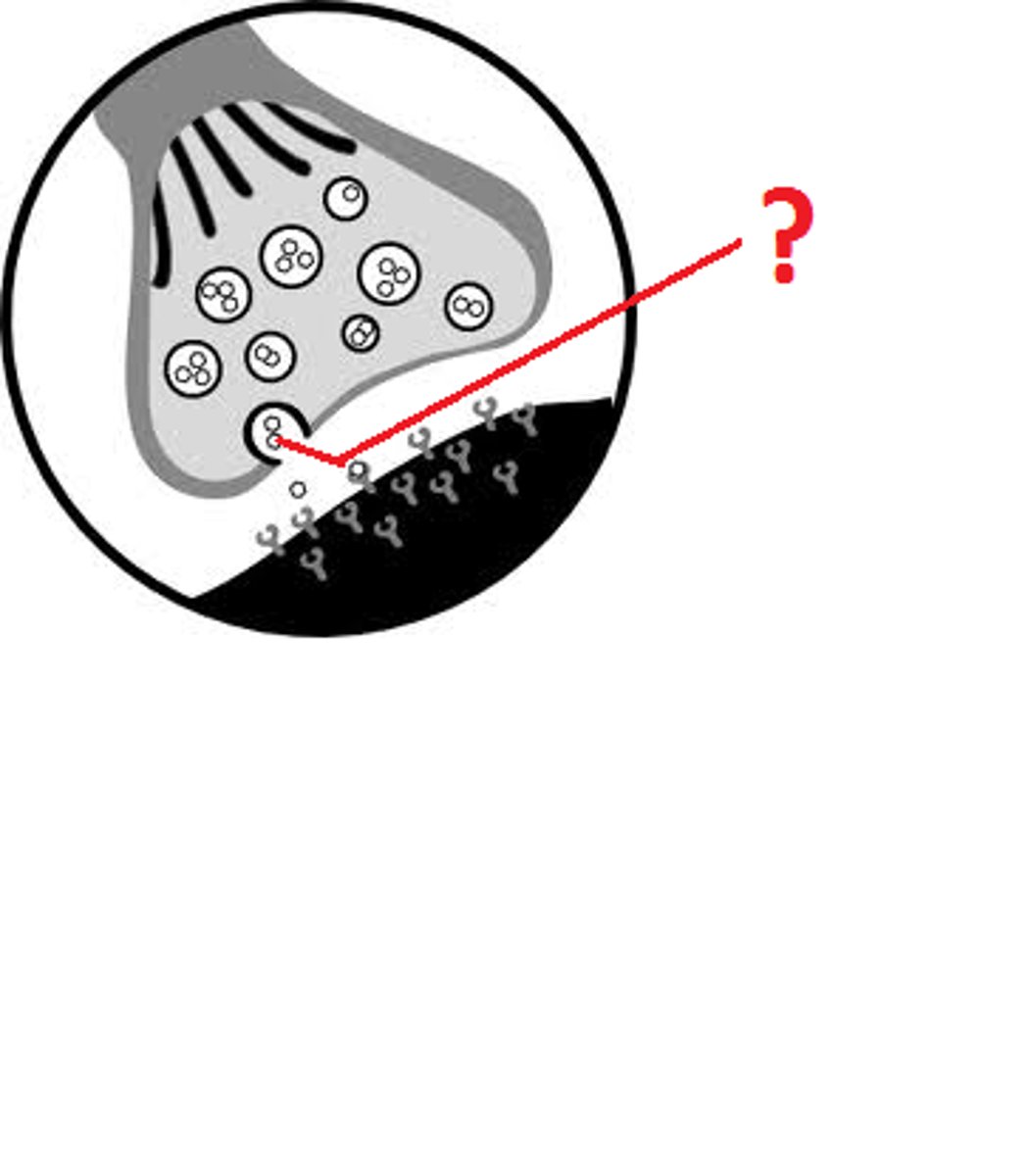
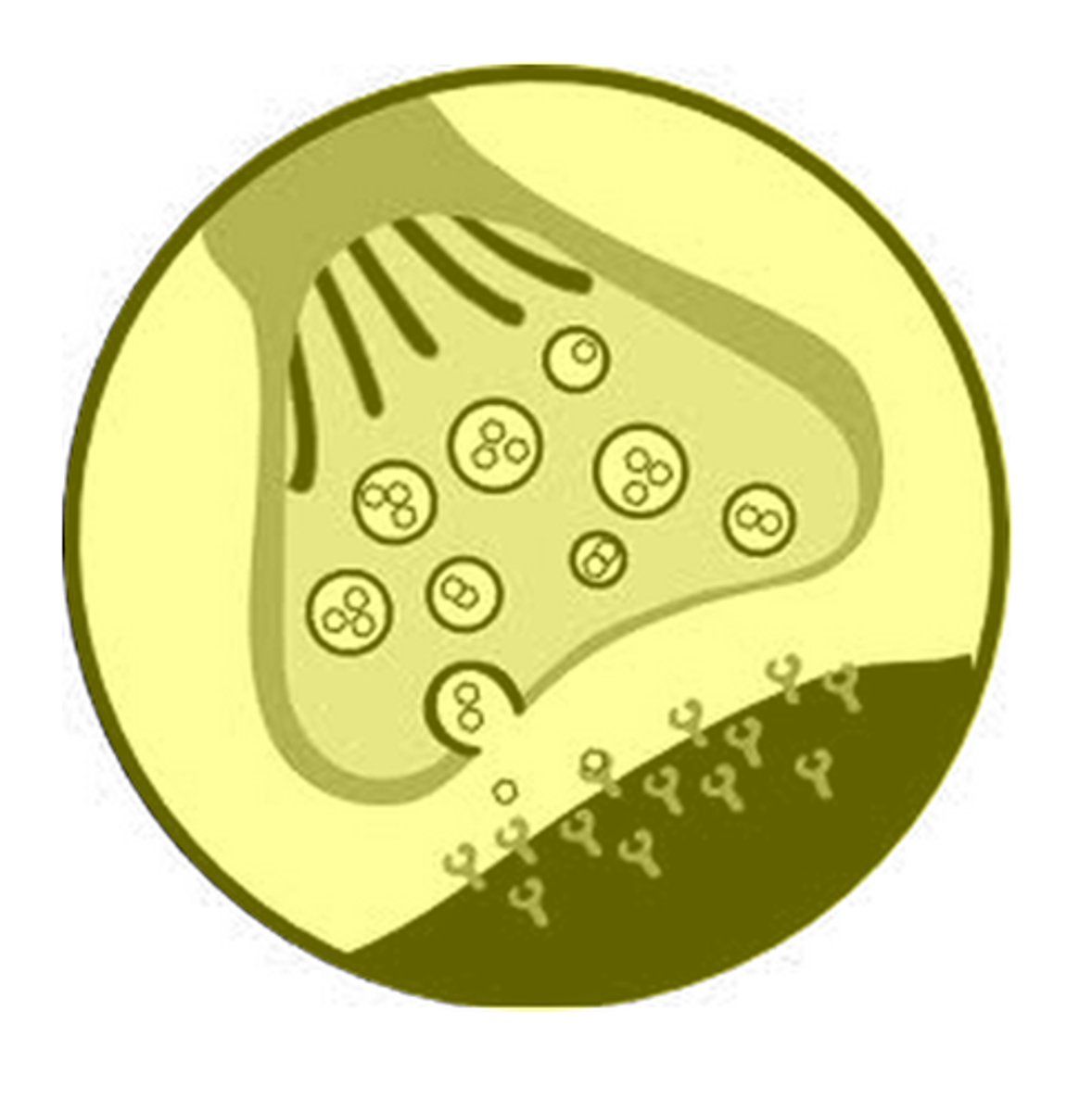
Neurotransmitters
chemical substances that are stored in very tiny sacs within the terminal buttons and involved in transmitting information across a synaptic gap to the next neuron
Occipital Lobe
structures located at the back of the head that respond to visual stimuli
Parasympathetic Nervous System
the part of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body
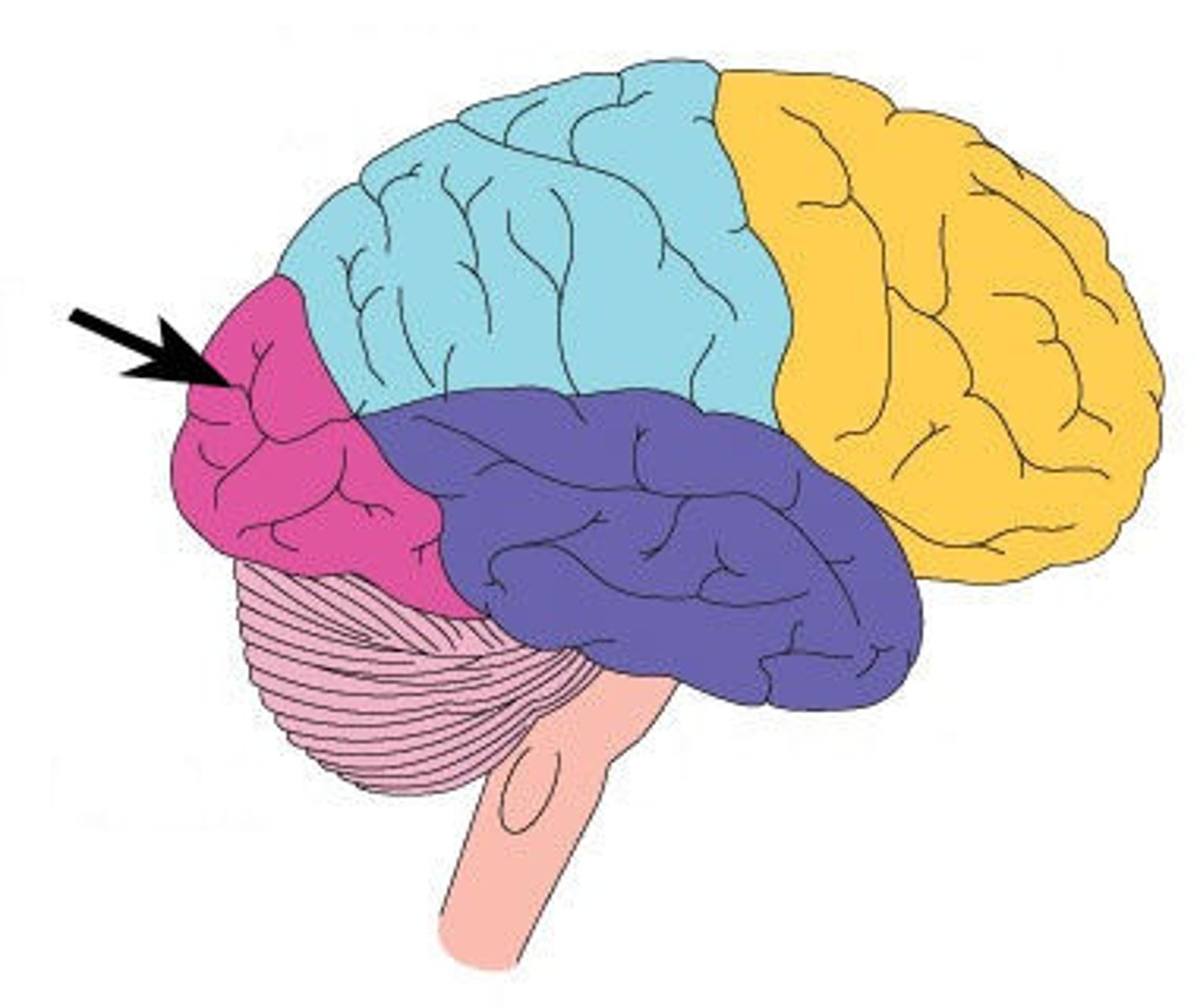
Parietal Lobe
structures at the top and toward the rear of the head that are involved in registering spatial location, attention, and motor control
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the network of nerves that connects the brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body
Phenotype
an individual's observable characteristics
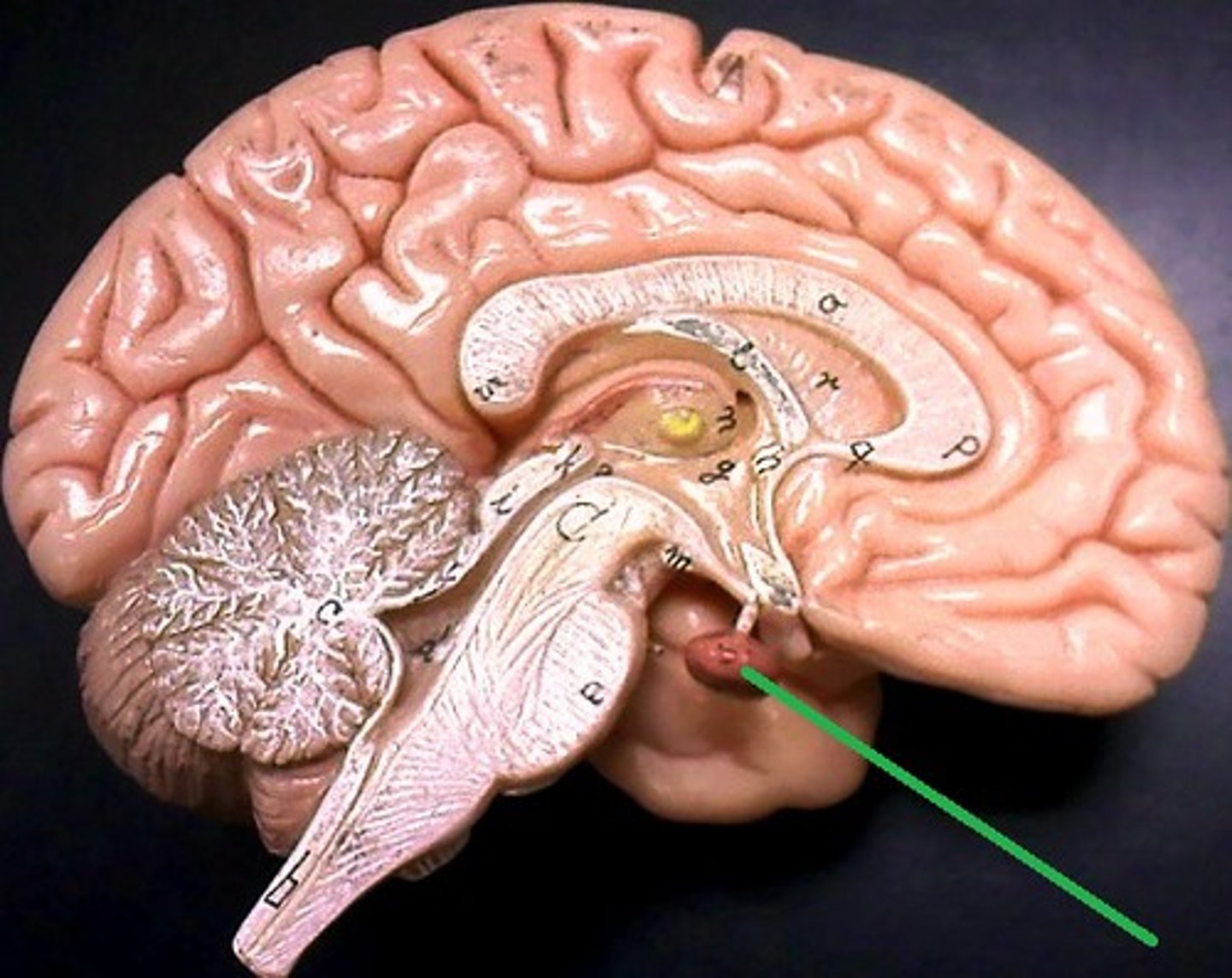
Pituitary Gland
a pea-sized gland just beneath the hypothalamus that controls growth and regulates other glands
Plasticity
the brain's special physical capacity for change
Resting Potential
the stable, negative charge of an inactive neuron
Reticular Formation
a system in the midbrain comprising a diffuse collection of neurons involved in stereotyped patterns of behavior such as walking, sleeping, and turning to attend to a sudden noise
Somatic Nervous System
the body system consisting of the sensory nerves, whose function is to convey information from the skin and muscles to the CNS about conditions such as pain and temperature, and the motor nerves, whose function is to tell muscles what to do
Somatosensory Cortex
a region in the cerebral cortex that processes information about body sensations, located at the front of the parietal lobes
Sympathetic Nervous System
the part of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body to mobilize it for action and thus is involved in the experience of stress
Synapses
tiny spaces between neurons; the gaps between neurons are referred to as synaptic gaps
Temporal Lobes
structures in the cerebral cortex that are located just above the ears and are involved in hearing, language processing, and memory
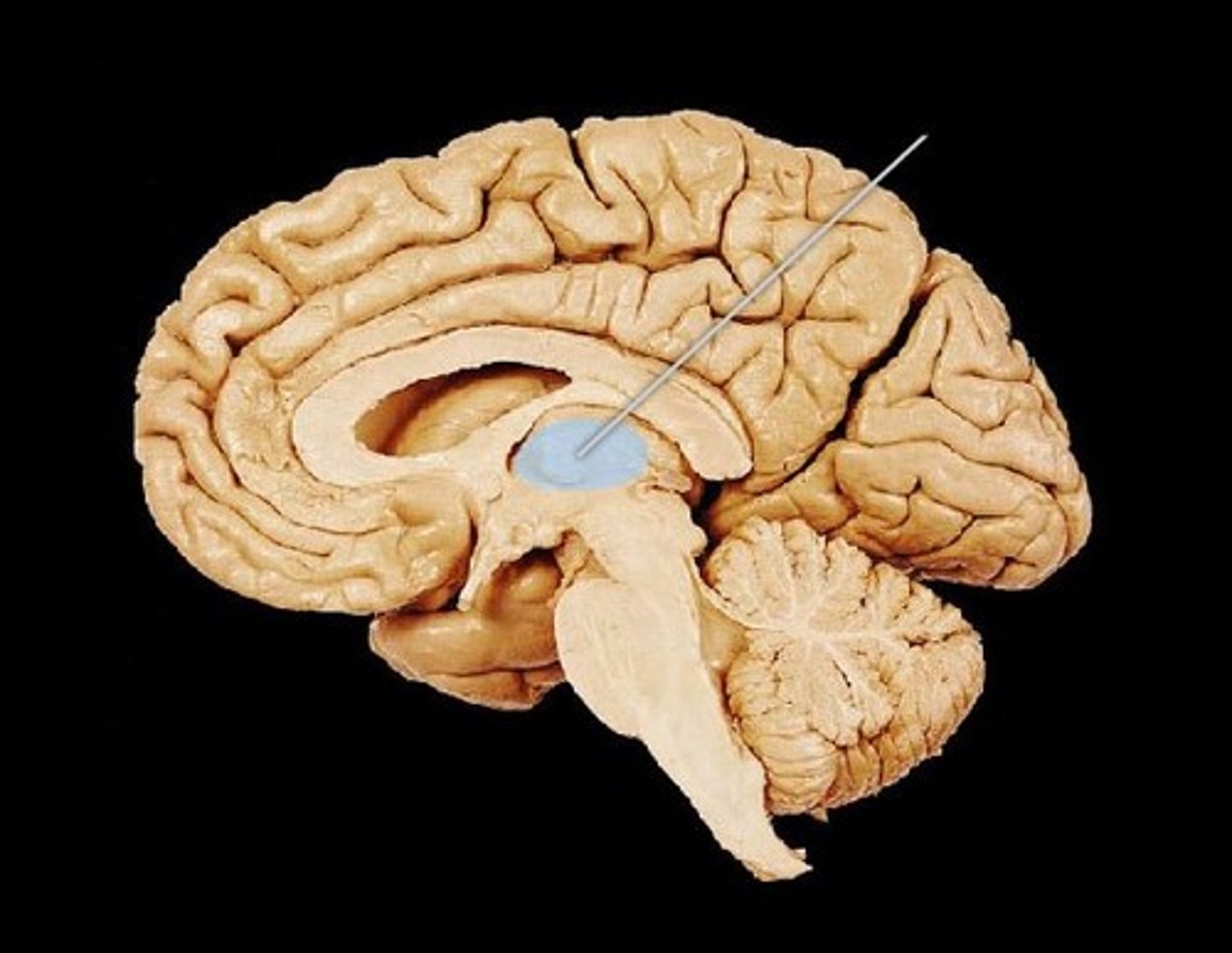
Thalamus
the forebrain structure that sits at the top of the brain stem in the brain's central core and serves as an important relay station
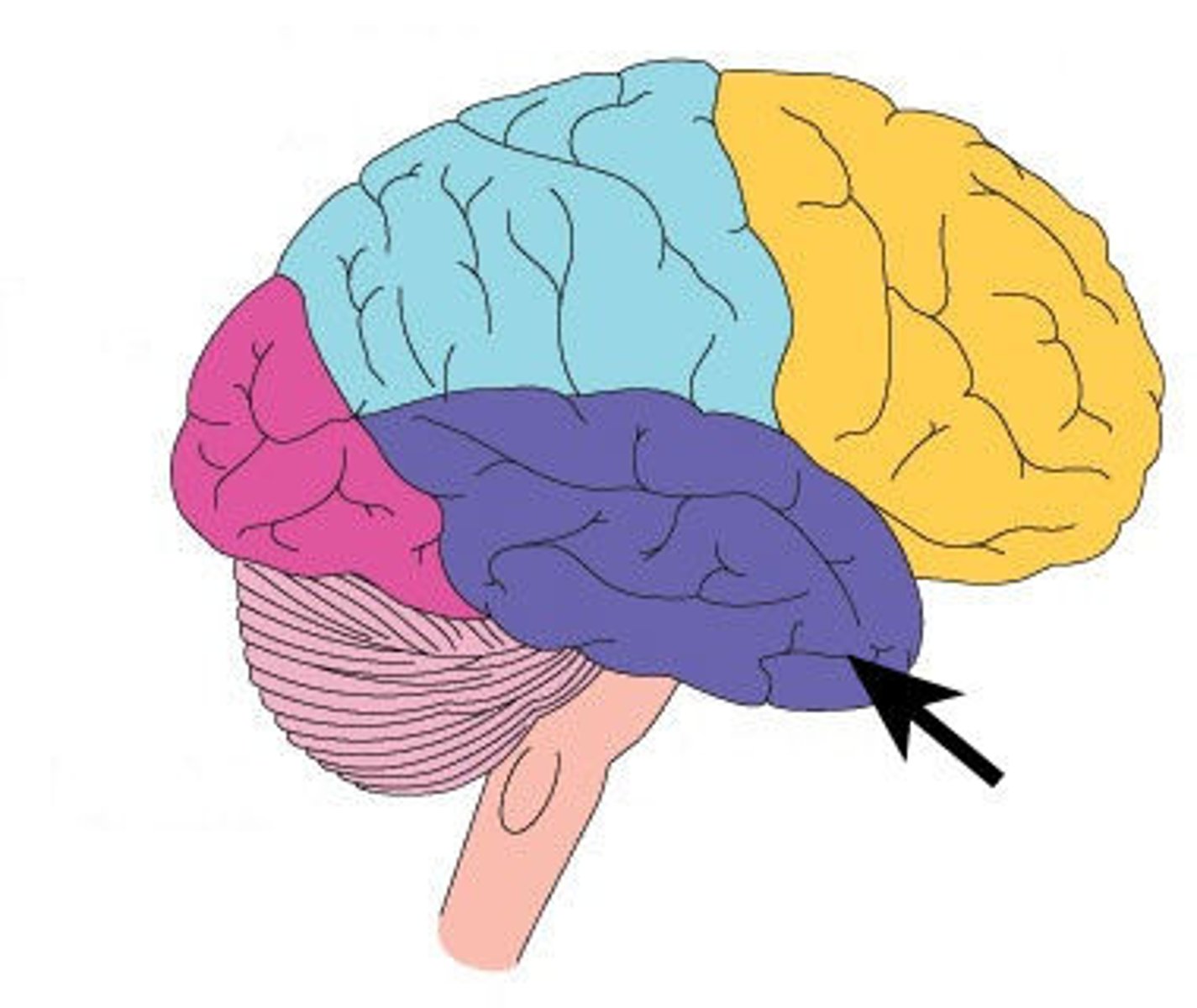
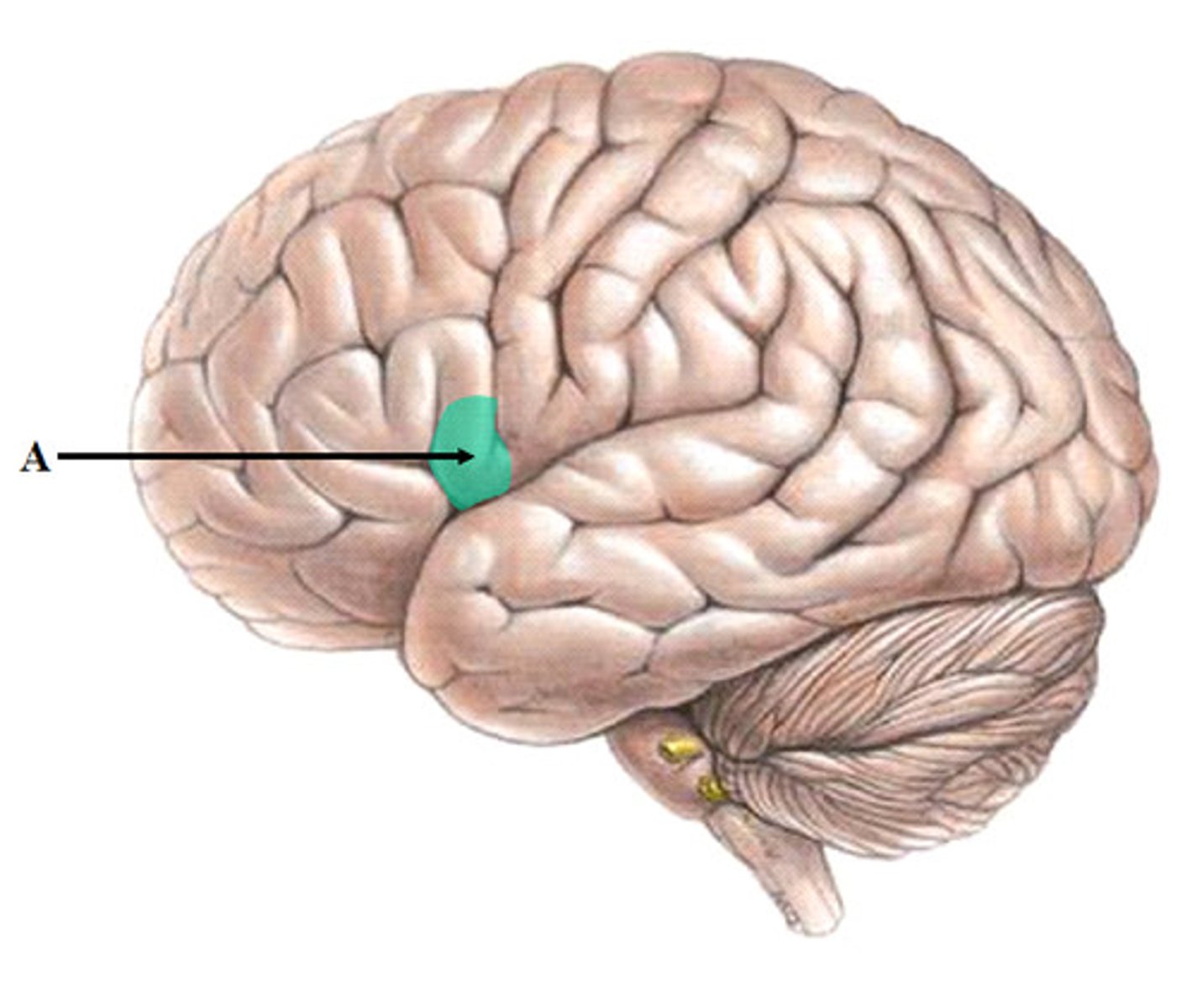
Broca's Area
controls language expression - an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech
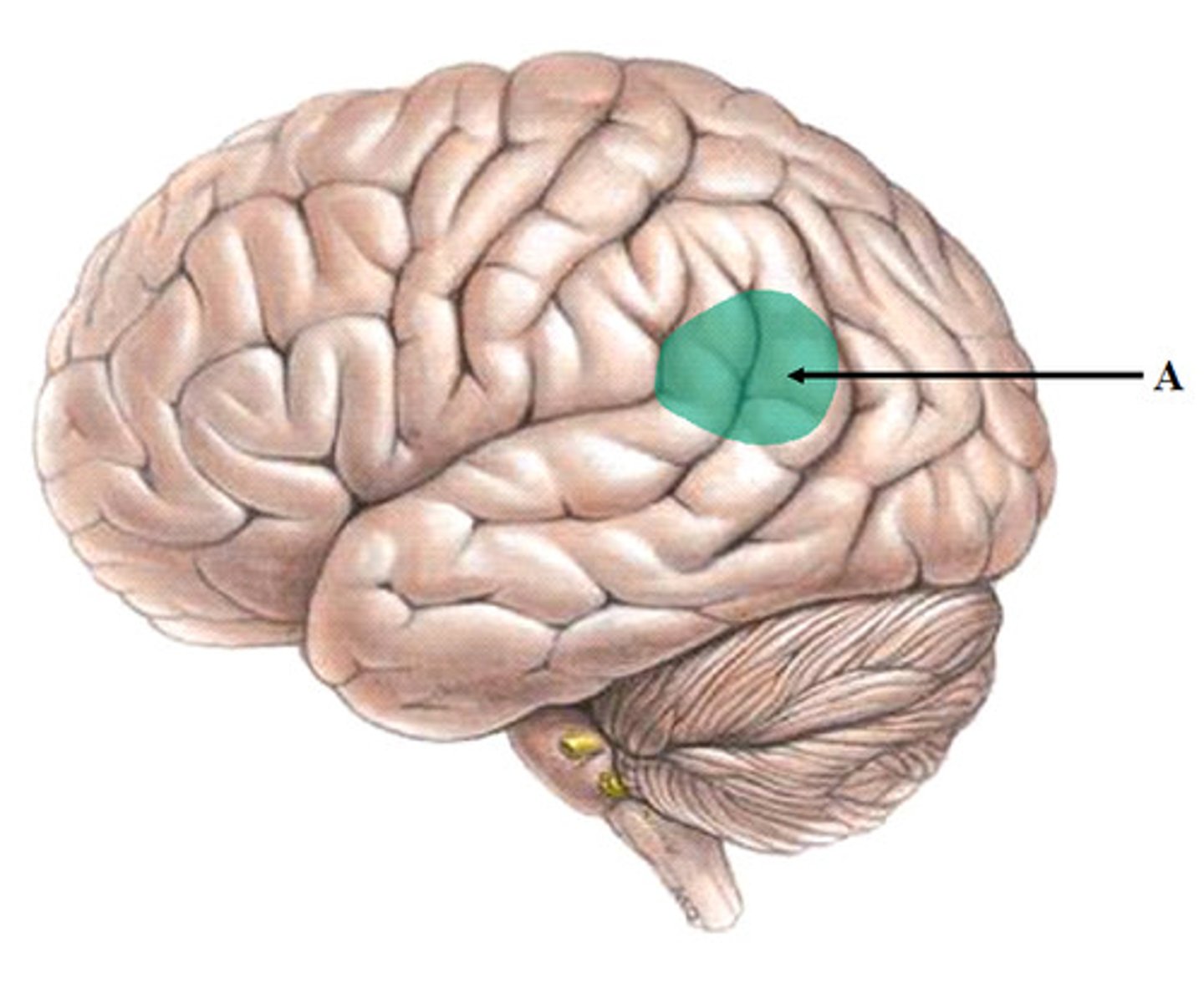
Wernicke's Area
controls language reception - a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe
Absolute Threshold
the minimum amount of stimulus energy that a person can detect
Apparent Movement
the perception that a stationary object is moving
Attention
the process of focusing awareness on a narrow aspect of the environment