Shaffer’s stages of attachments (Caregiver-infant interactions)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:25 PM on 5/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
1
New cards
**Shaffer & Emerson study**
**Aim:** investigate **formation of early attachments**: ages they develop, emotional intensity, who they attach to.
__**procedure:**__
* 60 babies, WC, Glasgow
* longitudinal study: 18 months, monthly intervals at home (natural obv).
* interactions observed, CG’s interviews.
* **separation anxiety:** mother asked about child’s behaviour during everyday separation
* **stranger anxiety:** mother asked about child’s anxiety response to strangers.
__**Findings & conclusions:**__
* attachments occurred in clear stages.
* 8 months: 50 infants, multiple attachments
* 25-32 weeks: 50%, separation anxiety towards a particular adult (primary attachment, mother).
* quality of care influences attachments: primary=most sensitive responsiveness.
\
__**procedure:**__
* 60 babies, WC, Glasgow
* longitudinal study: 18 months, monthly intervals at home (natural obv).
* interactions observed, CG’s interviews.
* **separation anxiety:** mother asked about child’s behaviour during everyday separation
* **stranger anxiety:** mother asked about child’s anxiety response to strangers.
__**Findings & conclusions:**__
* attachments occurred in clear stages.
* 8 months: 50 infants, multiple attachments
* 25-32 weeks: 50%, separation anxiety towards a particular adult (primary attachment, mother).
* quality of care influences attachments: primary=most sensitive responsiveness.
\
2
New cards
**Evaluate Schaffer & Emerson’s study: method = longitudinal study**
**Longitudinal studies = good method of observing attachments**
* Ensures same infants measured over full period of research
**Strength,** eliminates CV of individual differences between Ps.
* Alt would be cross-sectional research, just looks at different age groups of infants - problem: different groups might vary in terms of individual differences.
* S & E’s study therefore has good internal validity, studies same group over time.
* Ensures same infants measured over full period of research
**Strength,** eliminates CV of individual differences between Ps.
* Alt would be cross-sectional research, just looks at different age groups of infants - problem: different groups might vary in terms of individual differences.
* S & E’s study therefore has good internal validity, studies same group over time.
3
New cards
**Evaluate Schaffer & Emerson’s study: high in ecological validity**
**Naturalistic observation = high in ecological validity**
* most observations were made by parents at home during ordinary activities and reported to the researchers.
* behaviour unlikely to be affected by the presence of observers.
**Strength,** highly likely Ps behaved naturally while being observed, **increases ecological validity of data**
* most observations were made by parents at home during ordinary activities and reported to the researchers.
* behaviour unlikely to be affected by the presence of observers.
**Strength,** highly likely Ps behaved naturally while being observed, **increases ecological validity of data**
4
New cards
**Evaluate Schaffer & Emerson’s study: lacks cultural/population validity**
**Might be criticised for being culturally biassed, favouring Scottish, WC families.**
* Child bearing practices vary significantly across other countries \* cultures and classes, may influence attachments in infants.
**Weakness,** unrepresentative, results can’t be generalised across diff social & cultural contexts, lacks population validity.
* Child bearing practices vary significantly across other countries \* cultures and classes, may influence attachments in infants.
**Weakness,** unrepresentative, results can’t be generalised across diff social & cultural contexts, lacks population validity.
5
New cards
**Outline the stages of attachments in Schaffer & Emmerson’s theory**
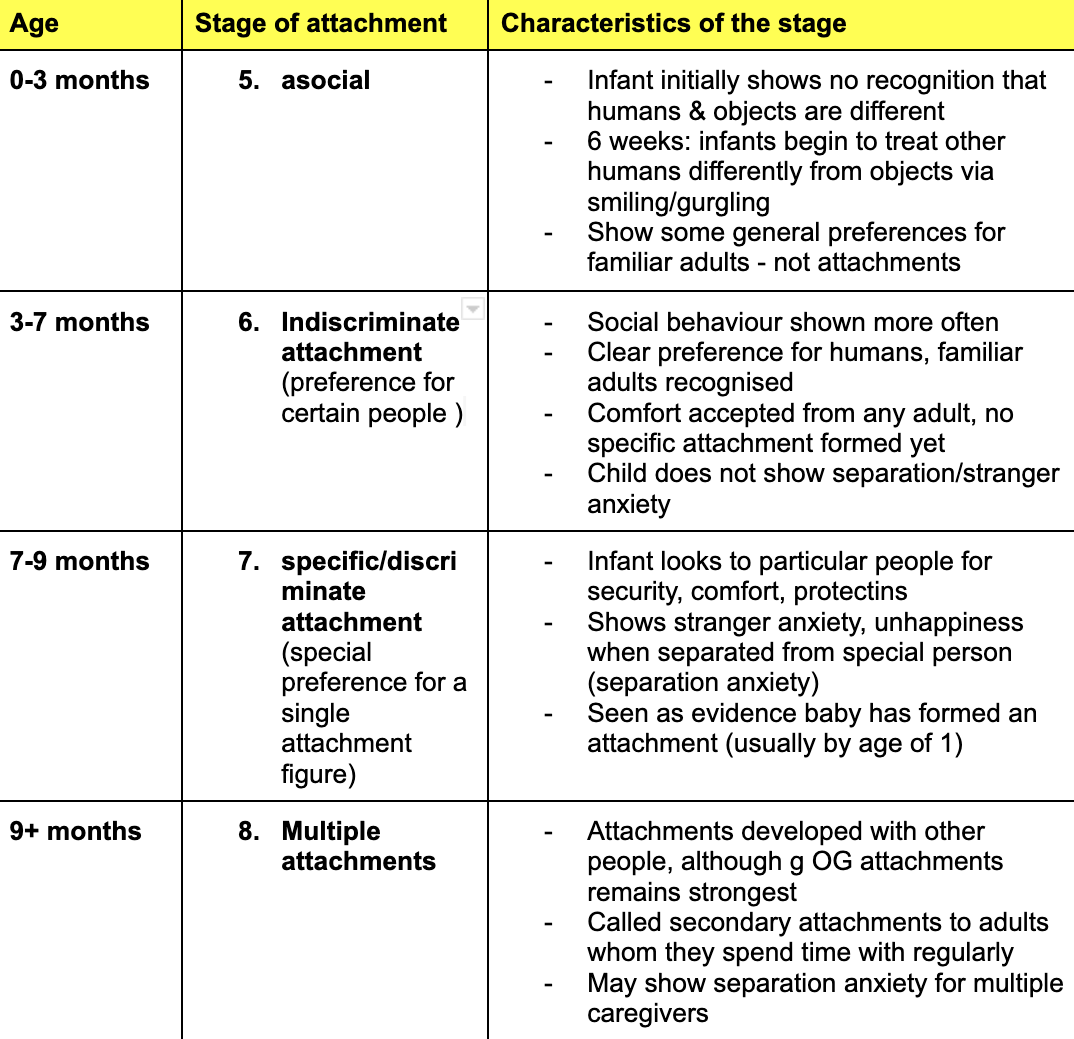
6
New cards
**Evaluate stages of attachment theory: culturally biassed findings**
**Model based on individualistic culture, might not reflect formation of attachment collectivists cultures, thus it is culturally biassed.**
* E.g **Sagi et al 1994** compared attachment formation in both cultures, found collectivist infants can form multiple attachments before they form single attachments
* Suggest rigid ordering of S & E’s stages of attachment are not universal.
**Weakness,** stage theory may not be adequate explanation of development of attachment in other cultures.
* E.g **Sagi et al 1994** compared attachment formation in both cultures, found collectivist infants can form multiple attachments before they form single attachments
* Suggest rigid ordering of S & E’s stages of attachment are not universal.
**Weakness,** stage theory may not be adequate explanation of development of attachment in other cultures.
7
New cards
**Evaluate stages of attachment theory: measuring asocial stage (0-3)**
**Due to very young age, very difficult to measure where they are up to with attachment formation**
* Infant eyesight, motor coordination, mobility so underdeveloped - judgement of behaviour are really guesses
* Brains may be highly social but behavioural evidence cant conclusively show this.
\
**Weakness,** can’t rely on evidence: infant’s actions may just have been random occurrence - measure for asocial stage may not be valid.
* Infant eyesight, motor coordination, mobility so underdeveloped - judgement of behaviour are really guesses
* Brains may be highly social but behavioural evidence cant conclusively show this.
\
**Weakness,** can’t rely on evidence: infant’s actions may just have been random occurrence - measure for asocial stage may not be valid.
8
New cards
**Evaluate stages of attachment theory: measuring multiple attachments**
**Could be issues in how multiple attachments are measured**
* Baby distressed after individual leaves room does not signify ‘true’ attachment type
* **Bowlby pointed out children have playmates, may get distressed when they leave - doesn’t signify attachment**
**Weakness,** difficult to measure if MA have been formed.
* Baby distressed after individual leaves room does not signify ‘true’ attachment type
* **Bowlby pointed out children have playmates, may get distressed when they leave - doesn’t signify attachment**
**Weakness,** difficult to measure if MA have been formed.
9
New cards
**Evaluate stages of attachment theory: particle applications**
**Theory can be used to find out if child is developing normally/making attachments**
* If child gets to certain age and not formed specific attachments then intervention strategies can be followed to ensure child developing on more normal route.
**Strength, can be used irl to help parents**, procedures can be put into place to aid child’s development.
* If child gets to certain age and not formed specific attachments then intervention strategies can be followed to ensure child developing on more normal route.
**Strength, can be used irl to help parents**, procedures can be put into place to aid child’s development.