PBSI 107 Bernard: Chapter 11, 12, 13, 14, 15
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
health psychology
a field that integrates research on health and on psychology
Well-being
a positive state that includes striving for optimal health and life satisfaction
Biopsychosocial model
integrates effects of biological, behavioral, & social factors on health &illness
Body mass index (BMI)
a ratio of body weight to height, used to measure obesity
Anorexia nervosa
characterized by excessive fear of becoming fat and thus restricting energy intake to obtain a significantly low body weight
Bulimia nervosa
characterized by the alternation of dieting, binge eating, and purging (self-induced vomiting)
Binge-eating disorder
characterized by binge eating that causes significant distress
Stress
a type of response that typically involves an unpleasant state, such as anxiety or tension
Stressor
something in the environment that's perceived as threatening/demanding that produces stress
Coping response
any attempt made to avoid, escape from, or minimize a stressor
Eustress
the stress of positive events
Distress
the stress of negative events
2 categories of stressors
major life stressors and daily hassles
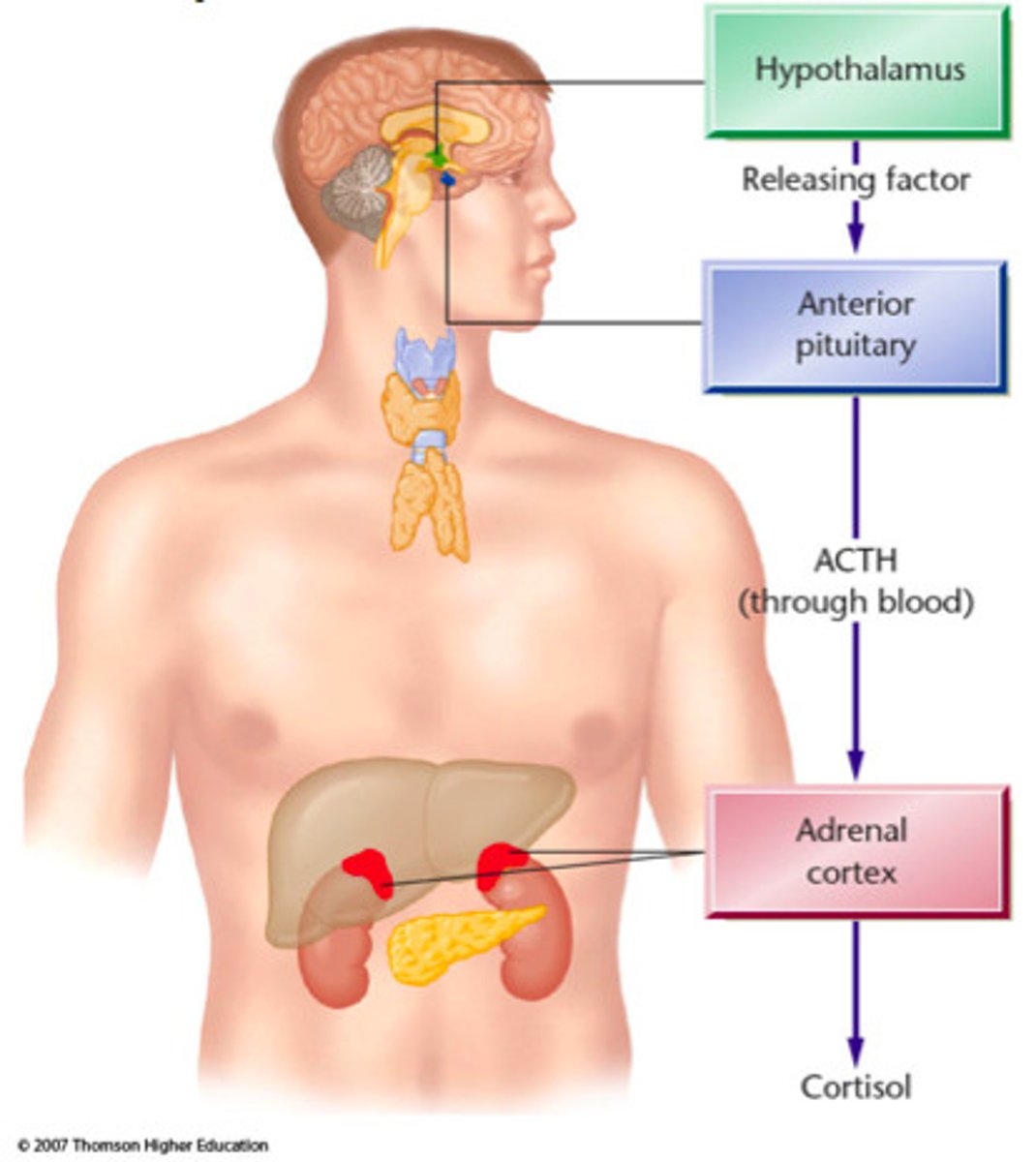
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
a body system involved in stress responses
Fight-or-flight response
the physiological preparedness of animals to deal with danger by either fighting or fleeing
Tend-and-befriend response
females' tendency to protect and care for their offspring and form social alliances rather than fight or flee in response to threat
Oxytocin
a hormone that is important for mothers in bonding to newborns and may encourage affiliation during social stress
Immune system
the body's mechanism for dealing with invading microorganisms
Psychoneuroimmunology
field in which the response of the body's immune system to psychological variables is studied
Lymphocytes
specialized white blood cells that make up the immune system (B cells- remember some invaders, T cells- attack invaders directly, natural killer cells-kill viruses and tumors)
Type A behavior pattern
characterized by competitiveness, achievement orientation, aggressiveness, hostility, restlessness, impatience with others, and inability to relax (at an increased risks for disease and early death)
Type B behavior pattern
characterized by noncompetitive, relaxed, easygoing, and accommodating behavior
Being stressed or feeling negative emotions can cause heart problems in three ways
1. People often cope with these states through behaviors that are bad for health.
2. Some personality traits have negative effects on people's social networks and on any support they may provide against stress.
3. Negative personality traits and stress can produce direct physiological effects on the heart.
High Chronic stress can lead to
overstimulation of the sympathetic nervous system higher blood pressure, constriction of blood vessels, elevated cortisol, increased release of fatty acids into the bloodstream, and greater buildup arterial plaque• Each of these conditions leads to heart disease.
Lazarus' two-part cognitive appraisal process
Primary appraisals: making decisions about whether a stimulus is stressful, benign, or irrelevant Secondary appraisals: people evaluate their response options and choose coping behaviors
The two general coping categories
Emotion-focused coping: people try to prevent having an emotional response to a stressor
Problem-focused coping: people take direct steps to confront or minimize a stressor
Positive psychology
emphasizes the strengths and virtues that help people thrive; primary aim is understanding psychological well-being
happiness has three components
positive emotion and pleasure, engagement in life, a meaningful life
Social support helps people cope and maintain good health in two basic ways
People with social support experience less stress overall. Social support needs to imply that people care about the recipient of the support.
Buffering hypothesis
when others provide emotional support, the recipient is better able to cope with stressful events
Outgroup homogeneity effect
the tendency to view out group members as less varied than in group members
Social identity theory
the idea that in groups consist of individuals who perceive themselves to be members of the same social category and experience pride through their group membership
In group favoritism
the tendency for people to evaluate favorably and privilege members of the in group more than members of the out group
what part of the brain is especially important for thinking about other people?
medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC)
Deindividuation
a state of reduced individuality, reduced self-awareness, and reduced attention to personal standards; may occur when people are part of a group
Conformity
altering one's behaviors and opinions to match those of other people or to match other people's expectations
Why do we conform?
Normative influence: conforming to fit in with the group
Informational influence: conforming when assuming the behavior of others is the correct way to respond
Social norms
expected standards of conduct, which influence behavior
Obedience
when a person follows the orders of a person of authority
Milgram's experiments
Milgram's experiments required a participant to shock someone for giving an incorrect answer. His research demonstrated that ordinary people may do horrible things when ordered to do so by an authority. Individuals who are concerned about others' perceptions of them are more likely to be obedient.
Obedience decreases with greater distance from the authority.
Aggression
any behavior that involves the intention to harm another.
MAOA gene is connected to aggression.
Physical aggression is common among young children. Adults' aggressive acts more often involve words
Prosocial behaviors
actions that tend to benefit others, such as doing favors or helping
Why are humans prosocial?
motivated by empathy, selfish motives (to relieve one's negative mood), inborn tendency to help others
Altruism
providing help when it is needed, without any apparent reward for doing so
Inclusive fitness
an explanation for altruism that focuses on the adaptive benefit of transmitting genes, such as through kin selection, rather than focusing on individual survival
Bystander intervention effect
the failure to offer help by those who observe someone in need when other people are present
reciprocal helping
an evolutionary principle stating that people expect that anyone helping another will have that favor returned at some future time, also known as reciprocal altruism
Attitudes
people's evaluations of objects, of events, or of ideas
Mere exposure effect
the idea that greater exposure to a stimulus leads to greater liking for it
Attitude accessibility
the ease or difficulty that a person has in retrieving an attitude from memory
Explicit attitudes
those that a person can report
Implicit attitudes
influence a person's feelings and behavior at an unconscious level
Cognitive dissonance
an uncomfortable mental state resulting from a contradiction between two attitudes or between an attitude and a behavior
Ex: when they smoke even though they know that smoking might kill them or choosing between colleges
Post-decisional dissonance
a person focuses on chosen things positive aspects and the others negative aspects (usually happens unconsciously)
Stereotypes
cognitive schemas that help us organize information about people on the basis of their membership in certain groups. Can lead to prejudice and discrimination
Why do stereotypes lead to prejudice and discrimination?
People treat others as scapegoats to relieve the tensions of daily living. People discriminate against others to protect their own self-esteem. People tend to favor their own groups and stigmatize those who pose threats to their groups.
Modern racism
subtle forms of prejudice that coexist with the rejection of racist beliefs
relationships
connections with friends and romantic partners. People similar in attitudes, values, interests, backgrounds, and personalities tend to like each other. Proximity plays a big role in relationships.
Matching principle
the most successful romantic couples also tend to be the most physically similar
Passionate love
a state of intense longing and desire
Companionate love
a strong commitment based on friendship, trust, respect, and intimacy
Personality
a person's characteristic thoughts, emotional responses, and behaviors
Personality trait
a pattern of thought, emotion, and behavior that is relatively consistent over time and across situations. (most have a genetic component, 40-60%)
Temperaments
biologically based tendencies to feel or act in certain ways (Classification at age 3 predicted personality structure and behaviors in early adulthood)
what 3 personality characteristics can be considered temperaments?
Activity level: overall amount of energy Emotionality: intensity of emotional reactions
Sociability: general tendency to affiliate with others
Psychodynamic theory
the Freudian theory that unconscious forces determine behavior (ego, id, and superego)
what are the Psychodynamic theory's 3 components?
Id: the component of personality that is completely submerged in the unconscious, operates according to the pleasure principle
Superego: the internalization of societal and parental standards of conduct
Ego: tries to satisfy the wishes of the id while being responsive to the dictates of the superego
Rotter's expectancy-value approach
Internal/external locus of control
Locus of control: personal beliefs about how much control people have over outcomes in their lives-Internal locus of control is a belief they bring about their own rewards.
External locus of control is a belief rewards result from forces beyond their control.
What are Bandura's 3 factors influence how a person acts?
1. the person's environment
2. multiple person factors, which include the person's characteristics, self-confidence, and expectations
3. behavior
Reciprocal determinism
how personality is expressed can be explained by the interaction of environment, person factors, and behavior itself
Humanistic approaches
approaches to studying personality that emphasize how people seek to fulfill their potential through greater self-understanding
Self-actualization
people seek to fulfill their potential for personal growth through greater self-understanding
Trait approach
an approach to studying personality that focuses on how individuals differ in personality dispositions
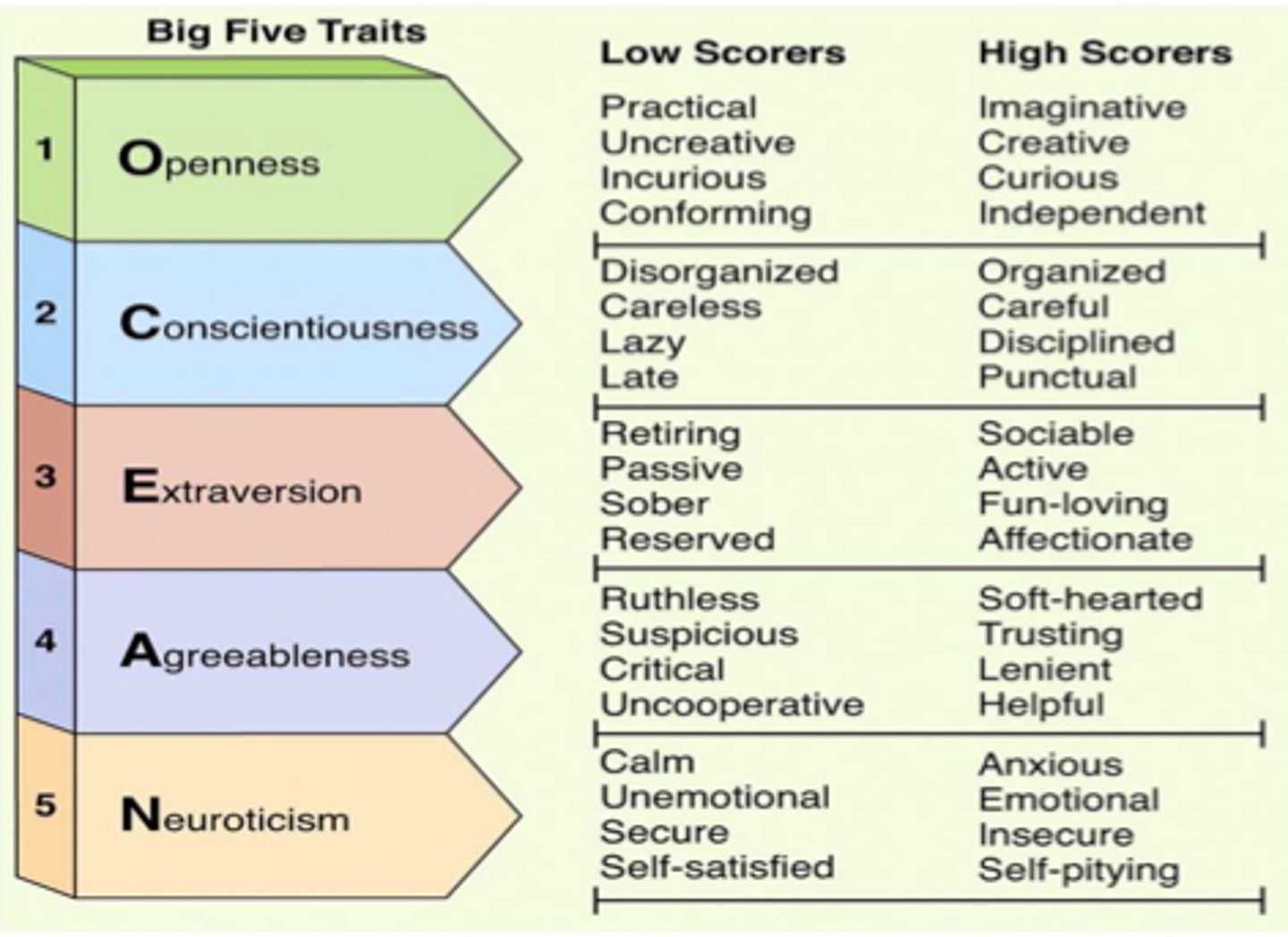
Five-factor theory
personality can be described using five factors
What are the Big Five?
openness to experience,
conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness,
and neuroticism
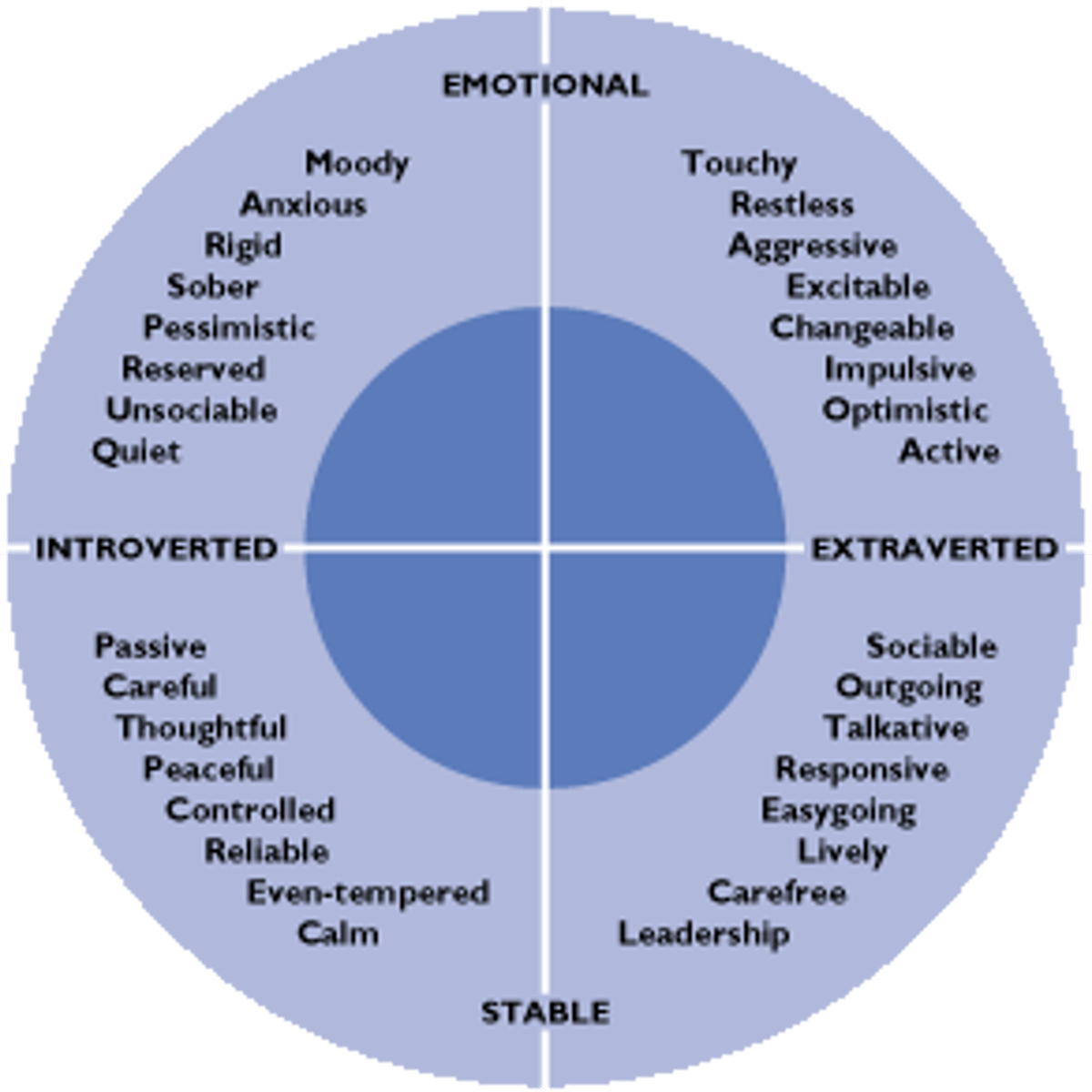
What two major dimensions did Eysenck propose that personality traits had?
introversion/extraversion and emotional stability
What did Eysenck believe?
believed differences in arousal produce the behavioral differences between extraverts (low arousal) and introverts (high arousal).
Gray believed personality is rooted in what 2 motivational functions?
Behavioral approach system (BAS): brain system involved in the pursuit of incentives or rewards; "go" system (linked to extraversion)
Behavioral inhibition system (BIS): brain system sensitive to punishment and inhibits behavior that might lead to danger or pain; "stop" system (linked to neuroticisms)
Situationism
the theory that behavior is determined more by situations than by personality traits
Interactionism
theory that behavior is determined jointly by situations and underlying dispositions
What happens to personality with age?
people become less neurotic, less extraverted, and less open to new experiences; they also tend to become more agreeable and more conscientious
Idiographic approaches
focus is on individual lives and how various characteristics are integrated into unique persons
Central traits: important for defining one's self
Secondary traits: less personally descriptive or not applicable
Nomothetic approaches
focus on how common characteristics vary from person to person
The five-factor theory looks at how all people vary on five basic personality traits
Projective measures
examine unconscious processes by having people interpret ambiguous stimuli
Rorschach inkblot test
a person looks at an apparently meaningless inkblot and describes what it appears to be
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
A person is shown an ambiguous picture and is asked to tell a story about it
what is the sense of self involve?
one's mental representations of personal experiences (memories and perceptions), one's thought processes, a sense of one's physical body, a conscious awareness of being separate from others and unique
self-concept
s everything you know and believe about yourself ( often gender, age, status)
self-schema
the cognitive aspect of the self-concept;
a network of interconnected knowledge about the self (related to middle of the frontal lobes)
Self-esteem
the evaluative aspect of the self-concept in which people feel worthy or unworthy
(high self-esteem is associated with narcissism)
Reflected appraisal
self-esteem is based on how we believe others perceive us
Sociometer
an internal monitor of social acceptance or rejection
low probability of rejection = high self-esteem
imminent possibility of rejection = low self-esteem
What are the three personality traits that make up a dark triad?
1. narcissism
2. psychopathy
3. machiavellianism
Psychopathology
sickness or disorder of the mind; psychological disorder (often defined in terms of maladaptiveness)
Etiology
factors that contribute to the development of a disorder
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5)
disorders are described in terms of observable symptoms
Comorbidity
Many psychological disorders occur together even though the DSM-5 treats them as separate disorders
Research Domain Criteria (RDoC)
defines basic aspects of functioning, considers them across multiple levels of analysis
Assessment
examination of a person's cognitive, behavioral, or emotional functioning to diagnose possible psychological disorders
Diathesis-stress model
a disorder may develop when an underlying vulnerability is coupled with a precipitating event