Immunology & Serology - Lecture - 8 - Immunochemistry & Immunoassays - Part 1 - Until ELISA only - Complete
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
Immunoassays
Are those in which an antigen-antibody interactions form the basis for serological testing
Precipitation or agglutination of antigen-antibody complexes
It is the endpoint for detection in immunoassays
Labelling
This makes quantitation in immunoassays possible if this are done on either the antigen or antibody with a molecule that is detected using instrumentation
Analyte
This refers to the substance to be measured (e.g., bacterial antigens, hormones, drugs, tumor markers, specific immunoglobulins, and among others)
Labelled immunoassays
Other name for immunoassays because they use labels
Radioisotope, enzyme, fluorescent, chemiluminescent
What are the different types of labels in immunoassays?
Remain attached throughout the test, Must not alter reactivity of the molecule to which it is attached, Retain its activity throughout the shelf life of the reagent, Measurable by several methods including visual inpsection
What properties should immunoassays label have?
Homogenous, Heterogenous, Non-competitive, Competitive
Different forms of labelled immunoassays
Homogenous immunoassay
What type of immunoassay does not require washing steps or separation before analysis?
Homogenous immunoassay
What type of immunoassay has competitive formats?
Homogenous immunoassay
What type of immunoassay are generally less sensitive than heterogenous assays
Homogenous immunoassay
What type of immunoassay are more rapid, simple to perform, and easier to automate than heterogenous assays?
Separation immunoassay
Other name for heterogenous immunaossays
Heterogenous immunoassay
What type of immunoassay is a multistep assay that requires washing steps for separation of analyte-antibody complexes prior to analysis.
Heterogenous immunoassay
What type of immunoassay can have a competitive or noncompetitive format?
Non-competitive immunoassay
What type of immunoassay uses excess labeled antibody to bind with analyte?
Non-competitive immunoassay
What type of immunoassay have reagent antibodies that are specific for the analyte are immobilized and adsorbed on the surface of a solid phase?
Non-competitive immunoassay
What type of immunoassay?
The patient sample containing the antigen (analyte) is bound to the immobilized antibodies.
After washing, excess labeled antibodies are added which will attach to any patient antigens that have been captured.
Any excess antibodies that was not able to bind to the analyte will be removed via washing.
Directly proportional
What is the relationship of the amount of label measured to the amount of patient antigen (analyte) present in the sample in non-competitive immunoassays?
Competitive immunoassay
What type of immunoassay has the analyte (unlabeled antigen) compete with the labeled antigen for limited number of binding sites on a high-affinity antibody?
Labeled, unlabeled
What are the two possible antigen-antibody complexes formed in competitive immunoassays?
Labeled antigen
What is the 1st reagent in competitive immunoassays?
Labeled antigen
It is the same kind of substance to be detected in the patient's sample in competitive immunoassays
CRP molecule
For example, in competitive immunoassays, what is the labeled antigen for the detection of C-Reactive Protein?
Labeled antigen
What antigen in competitive immunoassays are labeled with a radioisotope, enzyme, fluorochrome, or chemiluminescent label?
High affinity antibody
It is the 2nd reagent in competitive immunoassays
High affinity antibody
In competitive immunoassays, this is specific against the analyte.
Unlabeled antigen
Analyte or substance of interest in a patient sample in competitive immunoassays
Labels
In competitive immunoassays, components of the reaction can only be measured if they have _____
Directly proportional
In competitive immunoassays, what is the relationship of amount unbound labeled antigen to amount of unlabeled antigen?
Greater
In competitive immunoassays, the more unbound (Free) labeled detected, the (greater/lesser) amount of analyte present in the patient sample.
Inversely proportional
In competitive immunoassays, what is the relationship of amount bound labeled antigen to amount of unlabeled antigen?
Lesser
In competitive immunoassays, the more bound labeled antigen detected, the (greater/lesser) amount of analyte present in the patient sample.
Affinity
It is the strength of the primary interaction between a single antibody combining site and an antigenic determinant (epitope)
Competitive binding assay
In what type of assay is there random interaction between individual antigen and antibody molecules?
Larger
The higher the affinity of antibody for antigen, the (smaller/larger) amount of antigen bound to antibody, and the more accurately specific binding can be measured.
High Affinity Antibody
What component of immunoassays refers to where the antibody used should also be very specific for the antigen involved in the reaction?
High Affinity Antibody
What component of immunoassays refers to where the ultimate sensitivity of the immunoassay depends largely on the magnitude of affinity?
Monoclonal antibodies
The discovery of these antibodies has made available a constant source of highly specific antibodies that has increased the ability to detect small amounts of analytes with great accuracy.
Separation method through a solid phase
What component of immunoassays refers to where once reactions between antigens and antibodies have taken place, there must be a partitioning step or a way to separate reacted from unreacted analytes?
Separation method through a solid phase
What component of immunoassays refers to where the efficiency of the separation is critical to the accuracy of the results?
Polystyrene test tubes, Microtiter plates, Glass or polystyrene beads, Magnetic beads, Cellulose membranes
Most immunoassays use solid-phase vehicles for separation and the materials used are:
Physical adsorption
In separation methods through a solid phase, the antigen or antibody is attached to the solid phase by this process.
attached
In the illustration, the antibody is attached to the solid phase. Once antigen is added and specific binding takes place, the complexes formed remain _________ to the solid phase —providing a simple way to separate bound and free reactants

Labeled analyte
What is detected in the last step common to all immunoassays?
Radioimmunoassay
This type of immunoassay involves a system for counting radioactivity.
Enzyme, Fluorescence, Chemiluminescence
What type of immunoassays have this where a change in absorbance in a substrate is measured by spectrophotometry?
Detection method
What component of immunoassays refers to where all systems must use stringent quality controls?
Yalow, Berson
They developed the Radioimmunoassay in 1959.
Radioisotopes
What do radioimmunoassays use to detect antigens or antibodies?
Radioimmunoassay
What type of immunoassay uses radioisotopes to detect antigens or antibodies?
Radioisotopes
Is an atom of an element possessing an increasing number of neutrons in the nucleus, creating an unstable nucleus called radionucleotide, that will spontaneously transform into a more stable nuclear specie with the emission of radiation.
Iodine 125, Iodine 131, Tritiated hydrogen
What radioactive labels are used in the radioimmunoassay?
Iodine 125
It is the most frequently used radioactive label in radioimmunoassays.
Radioimmunoassay
RIA meaning
Competitive Radioimmunoassay
What type of radioimmunoassay have high-affinity antibodies specific for the analyte are adsorbed or covalently-bound to the solid phase?
Radiolabeled antigen
What is added together with the patient sample, which contains the analyte, in competitive radioimmunoassays?
Competitive Radioimmunoassay
What type of radioimmunoassay have radiolabeled antigens competing with the analyte for a limited number of binding sites on the high-affinity antibody?
Competitive Radioimmunoassay
What type of radioimmunoassay has the concentration of the labeled radioactive antigens in excess so all binding sites on antibody will be occupied?
Competitive Radioimmunoassay
What type of radioimmunoassay is it if the patient antigen is present, then some of the binding sites will be filled with the unlabeled analyte, thus decreasing the amount of bound radioactive label?
Inversely proportional
In competitive radioimmunoassays, when bound and free radiolabeled antigens are separated and a washing step is done, the amount of radiolabeled antigen in the bound phase is (what relationship) to the amount of analyte or patient antigen present?
Increase
In this case in competitive radioimmunoassay, very little patient antigen is present, and the radiolabeled antigen was able to bind to most of the binding sites making solid-phase (increase/decrease) in radioactivity.
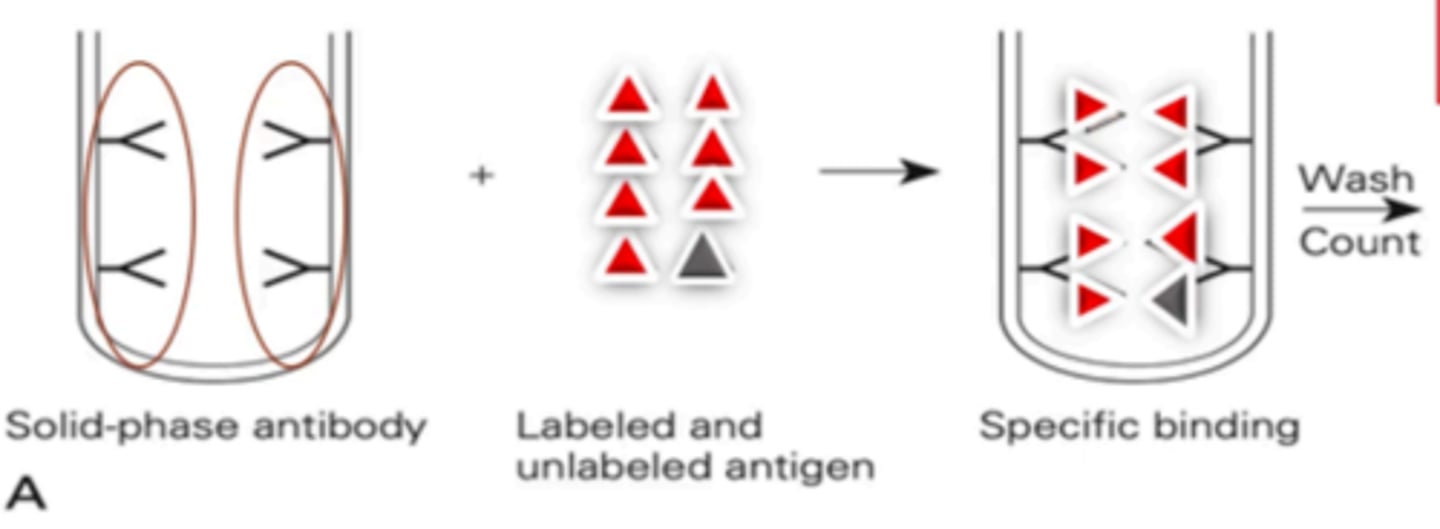
Decreased
In this case in competitive radioimmunoassay, as the amount of analyte increases, more binding sites are occupied by unlabeled antigen and fewer binding sites will be occupied by the radiolabeled antigen, thus radioactivity of the solid phase is (increased/decreased) in proportion to the amount of analyte or patient antigen bound
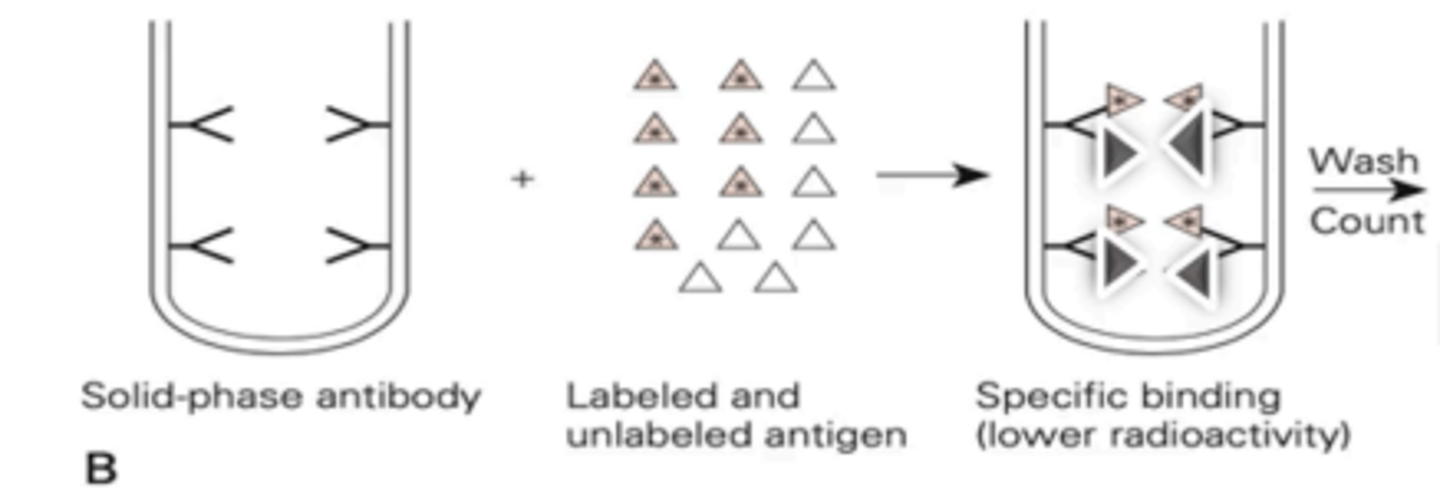
Scintillation counter
Instrument used for measuring ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation
What is measured by a Scintillation counter?
Scintillation counter
What instrument is involved if radioactive materials emit radiation, causing scintillation materials to emit flashes of light when it absorbs the radiation?
Scintillations
These are the brief flashes of light given off which strikes a photo-sensitive surface.
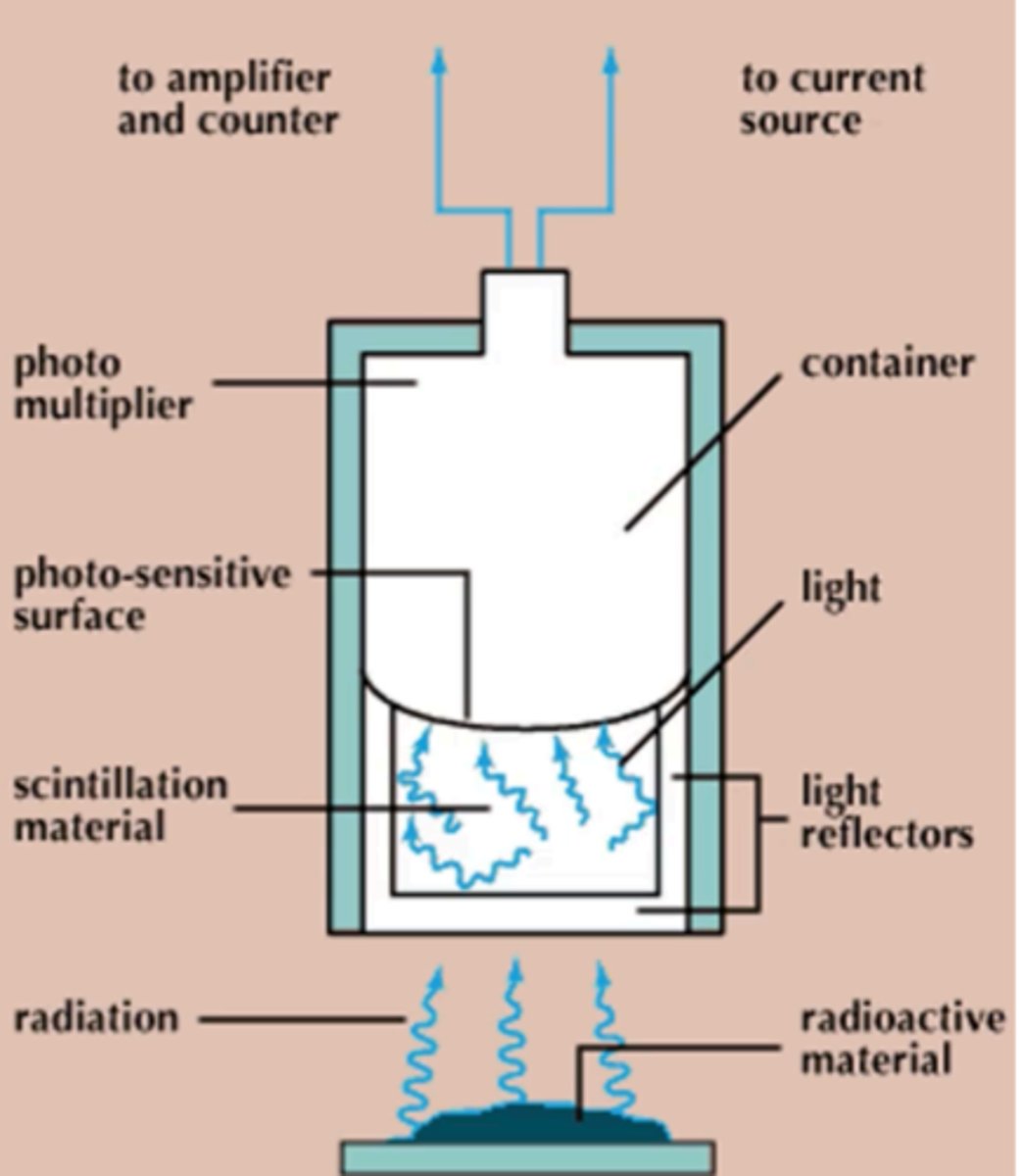
Photomultiplier
This component of a scintillation counter measures the light signals, converting them to an electrical signal that can be amplified and counted.
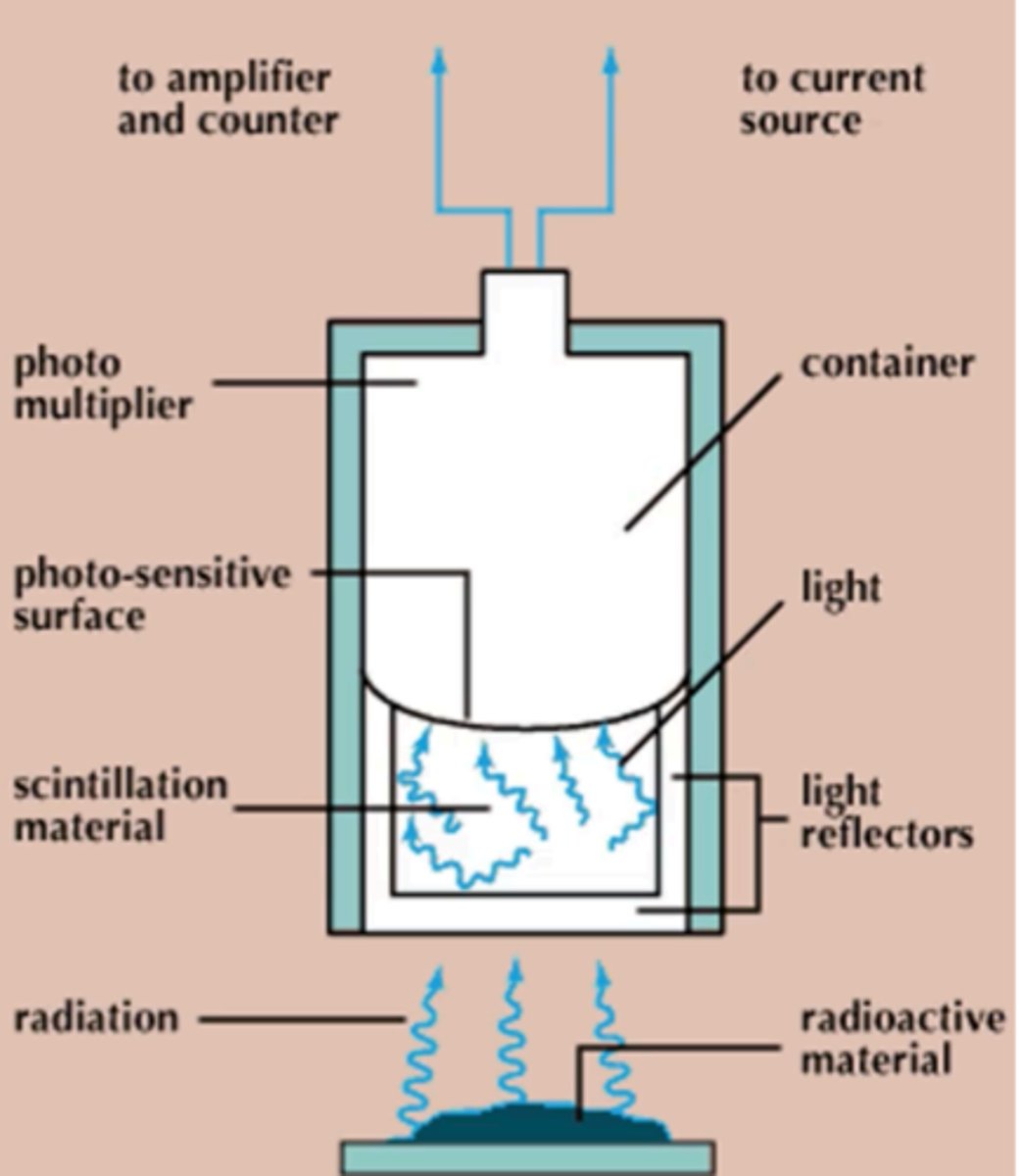
Gamma emissions
In the scintillation counter, by selecting the size of the pulse to be counted, it is possible to count these types of emissions from one type of atom and exclude others.
Counts per minute
A scintillation counter read-out is displayed in what unit?
Advantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Competitive Radioimmunoassay:
Very sensitive with the use of Iodine-125
Advantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Competitive Radioimmunoassay:
Easily automated and practical if large batches
Disadvantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Competitive Radioimmunoassay:
Inconvenient to dispose or store.
Disadvantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Competitive Radioimmunoassay:
Radioisotope labels have a short half-life of 1-2 months.
Advantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Competitive Radioimmunoassay:
Precise technique for determining trace amounts of analytes that are small in size.
Disadvantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Competitive Radioimmunoassay:
Health hazard
Immunoradiometric assay
It is a noncompetitive sandwich immunoassay in which the analyte to be measured is sandwiched between 2 antibodies.
Capture antibody
Which antibody in the
immunoradiometric assay is immobilized on the solid phase?
Capture antibody
Which antibody in the
immunoradiometric assay is specific for a unique antigenic determinant on the antigen of interest (analyte)?
2nd antibody
Which antibody in the
immunoradiometric assay is radiolabeled with Iodine-125?
2nd antibody
Which antibody in the
immunoradiometric assay recognizes a second unique antigenic determinant on the same molecule?
Sandwich
This is the term used in immunoradiometric assay because the analyte is bound between two antibodies?
Immunoradiometric assay
This type of immunoassay is used to detect high molecular mass antigens with at least two antigenic determinants.
Directly proportional
In the Immunoradiometric assay, what is the relationship between the amount of patient analyte and the amount of radioactivity?
Disadvantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Immunoradiometric assay:
Health Hazard
Advantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Immunoradiometric assay:
Faster and more sensitive than RIA
Disadvantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Immunoradiometric assay:
Radioisotope labels have short half life of 1-2 months
Advantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Immunoradiometric assay:
The use of radiolabeled antibody eliminates the need to isolate the antigen, which is often present in low quantities
Disadvantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Immunoradiometric assay:
Inconvenient to dispose or store
Advantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Immunoradiometric assay:
Decrease the problems of labeling structurally dissimilar antigens.
Advantage
Determine if it an advantage or disadvantage of Immunoradiometric assay:
Provide reagents that are more stable
Radioimmunosorbent test
RIST meaning
Radioimmunosorbent test
It is a competitive immunoassay that measure total serum IgE level
Anti-human IgE
What is adsorbed on a solid phase in the Radioimmunosorbent test?
Radioimmunosorbent test
What immunoassay has the patient serum added and any IgE present in the serum will bind to the anti-human IgE?
Radioimmunosorbent test
What immunoassay has known amounts of radiolabeled IgE added, which will compete with the patient IgE for binding?
Inversely proportional
What is the relationship of the total serum IgE level to the amount of radioactivity in the Radioimmunosorbent test?
Less
In the Radioimmunosorbent test, the more the patient IgE present in the serum, the (more/less) IgE is able to bind = less radioactivity is measured.
Radioallergosorbent test
RAST meaning
Allergen-specific IgE
What is measured in the Radioallergosorbent test?