6- Liquids and Solids
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
small repeating units that make up crystalline solids stacked over and over
unit cell
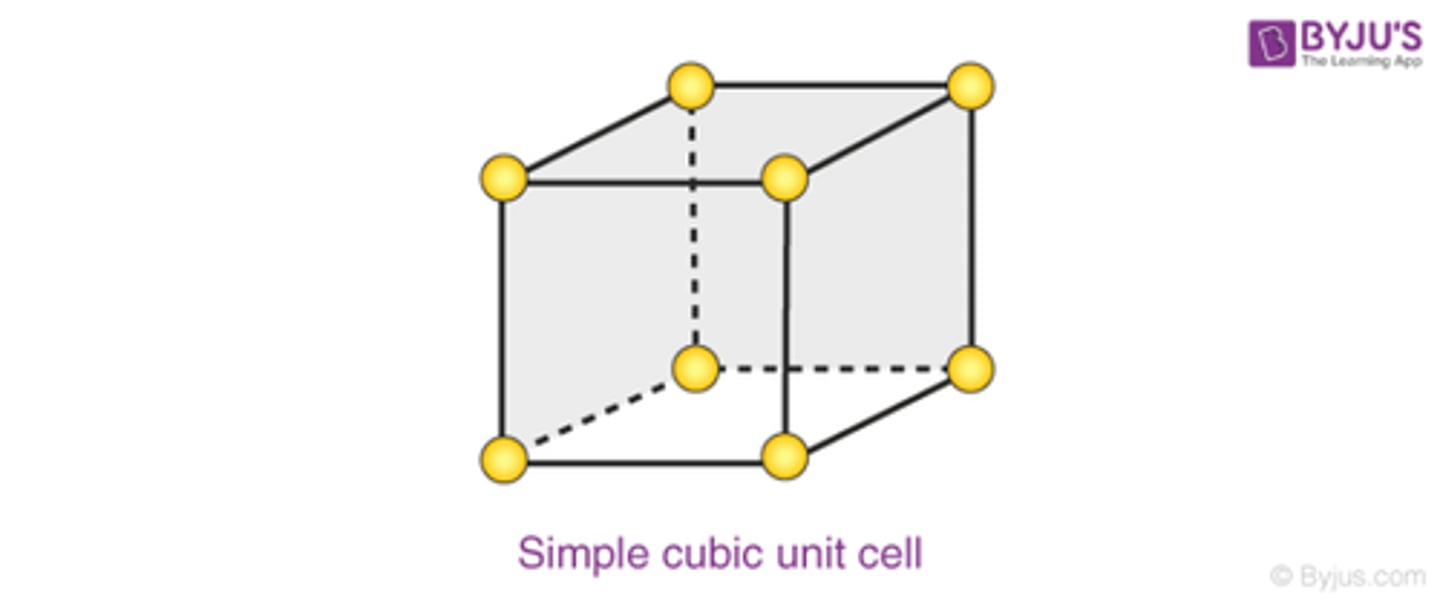
How many atoms are in a simple cubic unit cell?
1
-atoms at corners of the unit cell comprise 1 whole atom
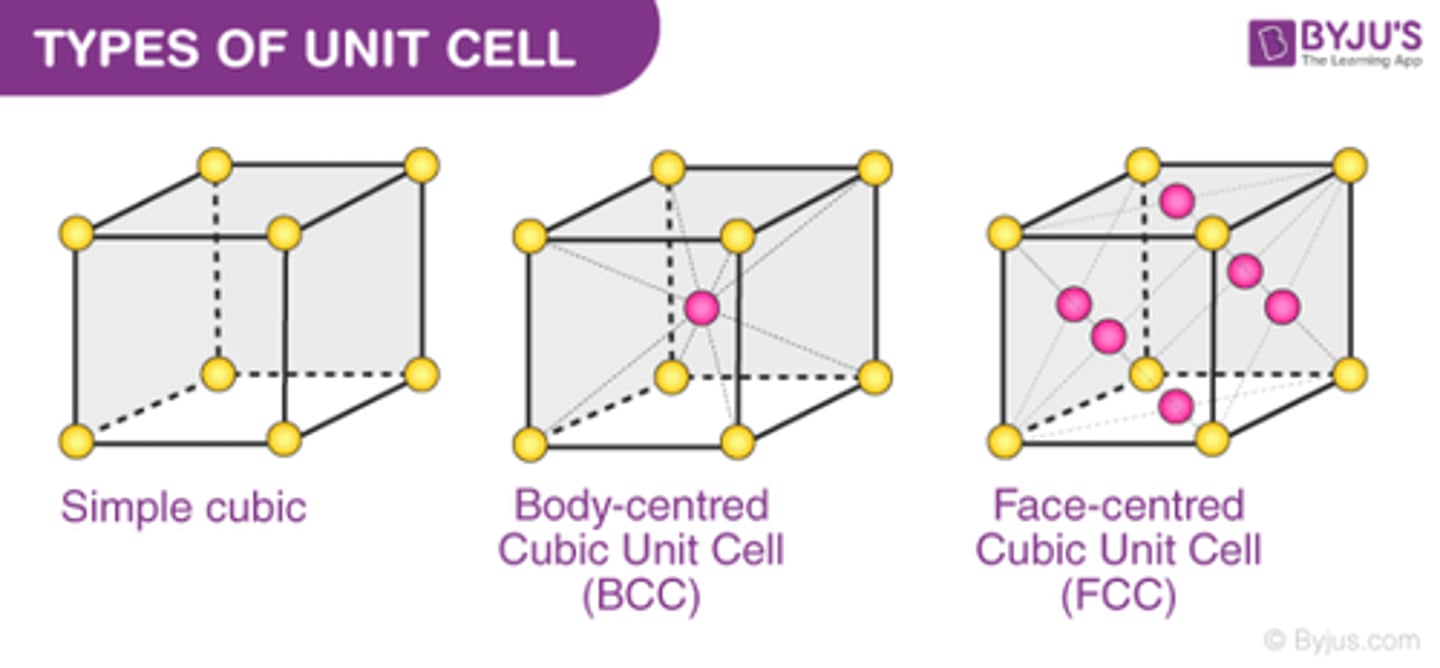
How many atoms are in a body-centered cubic unit cell?
2
-atoms at the corners of the unit cell comprise 1 whole atom, plus the whole atom in the middle of the unit cell
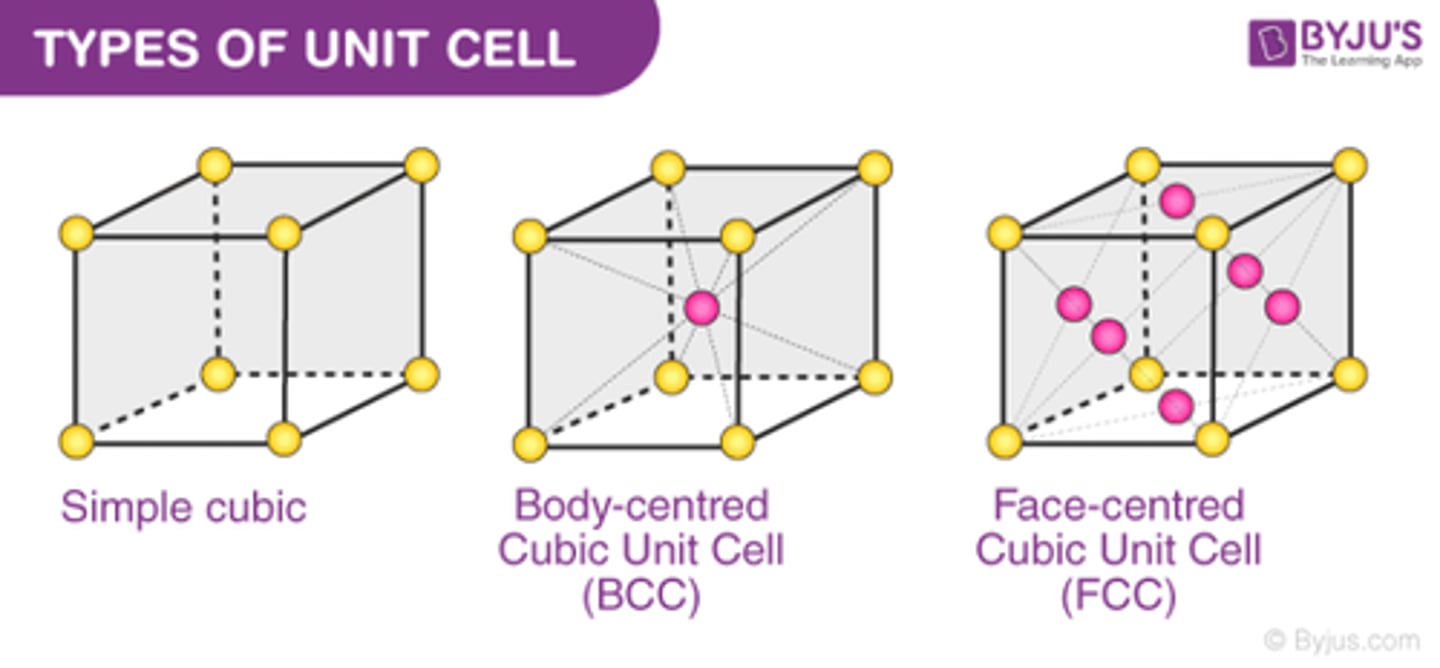
How many atoms are in a face-centered cubic unit cell?
4
-atoms at the corners of the unit cell comprise 1 whole atom, plus the 6 atoms that exist halfway on each face comprise 3 whole atoms
liquid to gas
vaporization
gas to liquid
condensation
liquid to solid
cystallization
solid to liquid
fusion (melting)
solid to gas
sublimation
gas to solid
deposition
what are the endothermic phase changes?
endothermic (consume heat)
endothermic = +delta H (enthalpy)
endothermic = +delta S (entropy; more disorder)
sublimation, fusion (melting), or vaporization (boiling)
what are the exothermic phase changes?
exothermic (release heat)
exothermic = -delta H (enthalpy)
exothermic = -delta S (entropy, less disorder)
condensation, deposition, crystallization
when vapor pressure = external/atmospheric pressure
boiling point
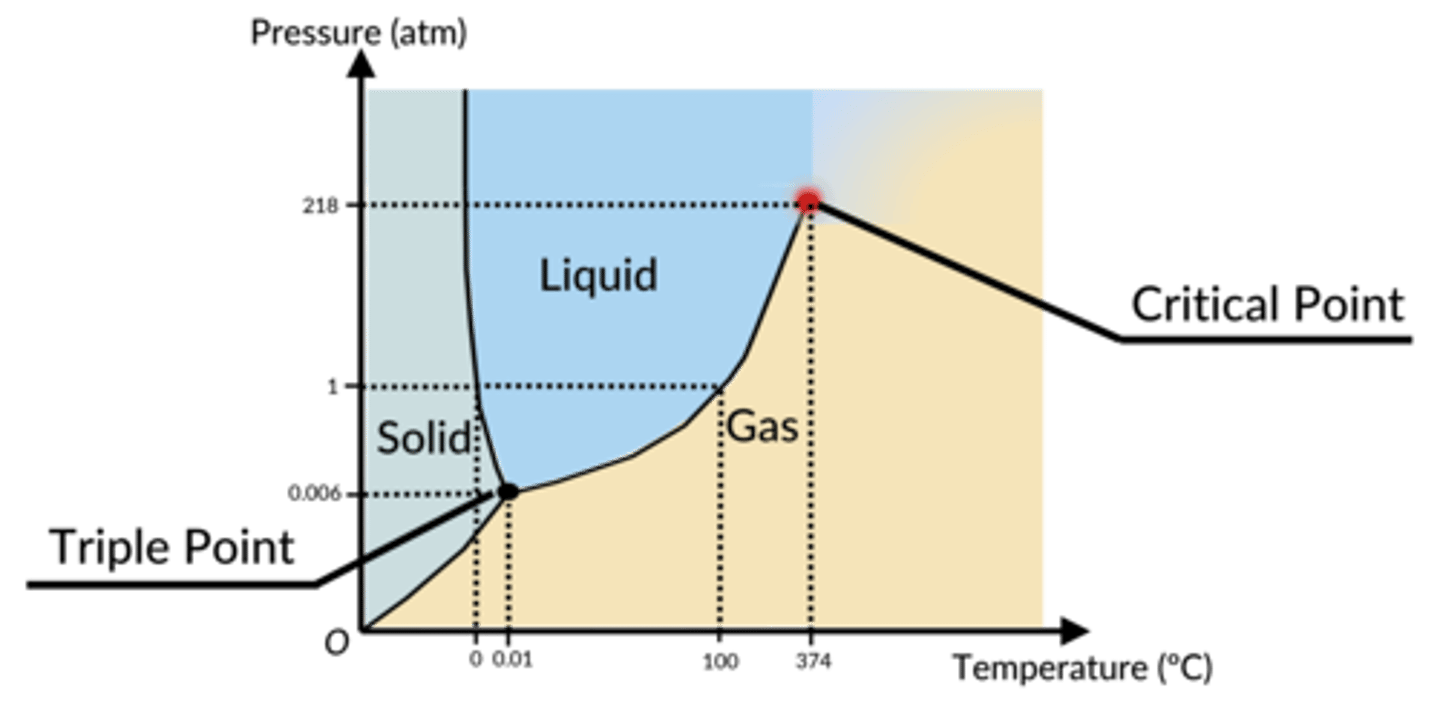
a graphical way to show the pressures and temperatures at which a substance will exist as a solid, a liquid, or a gas, or in some kind of equilibrium in between two or more of these states
phase diagram (looks like a butt)
-outside of butt: gas
-left cheek: solid
-right cheek: liquid
triple point is where all these lines converge and it's the pressure/temperature combination at which all three phases exist at the same time, in equilibrium with each other
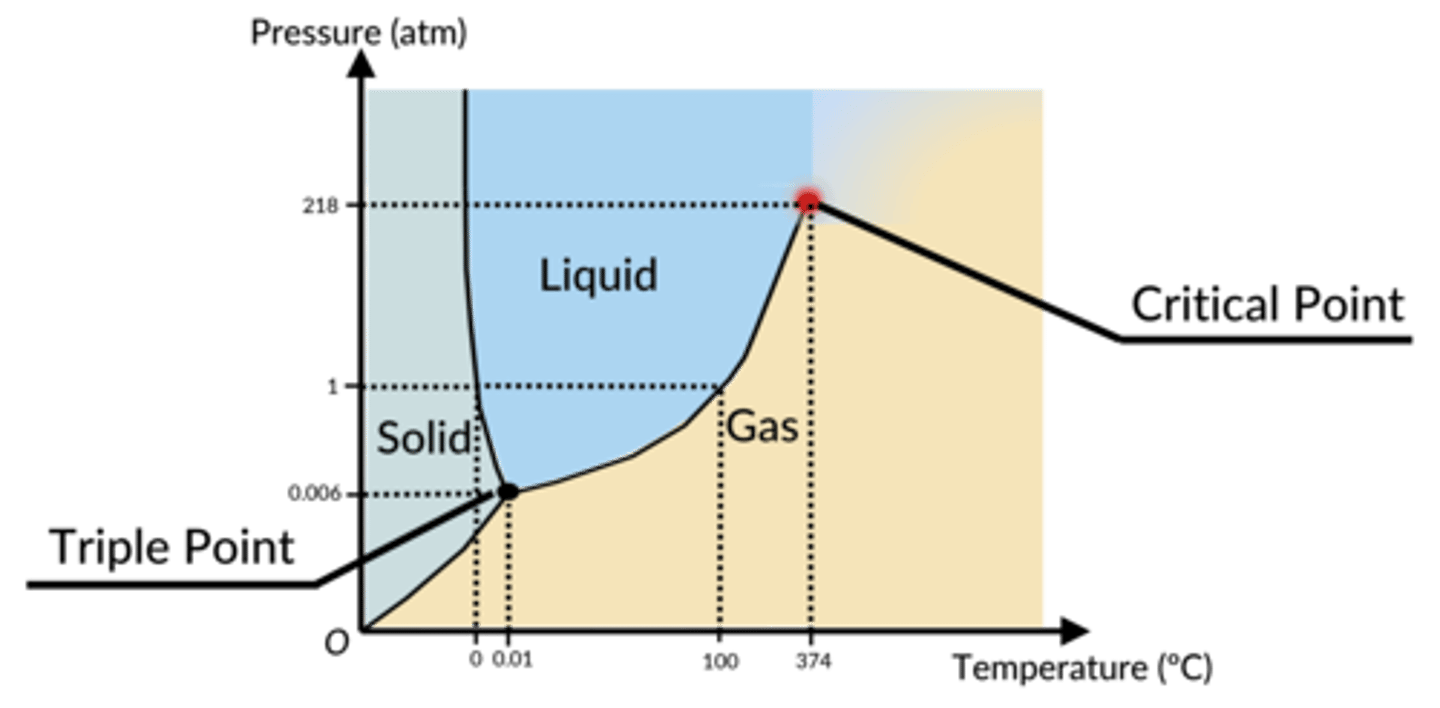
what do the axes in a phase diagram represent?
x axis: temperature
y axis: pressure
what is a critical point in a phase diagram?
the pressure/temperature combination at which liquids and gases are indistinguishable
(the liquid-gas line no longer exists here)